🏊 DB Connection Pool (DBCP)
🏊
DB Connection Poolis aresource management techniquethat creates multipledatabase connectionsin advance, and anapplicationacquires aconnectionwhenever necessary and returns it after use.
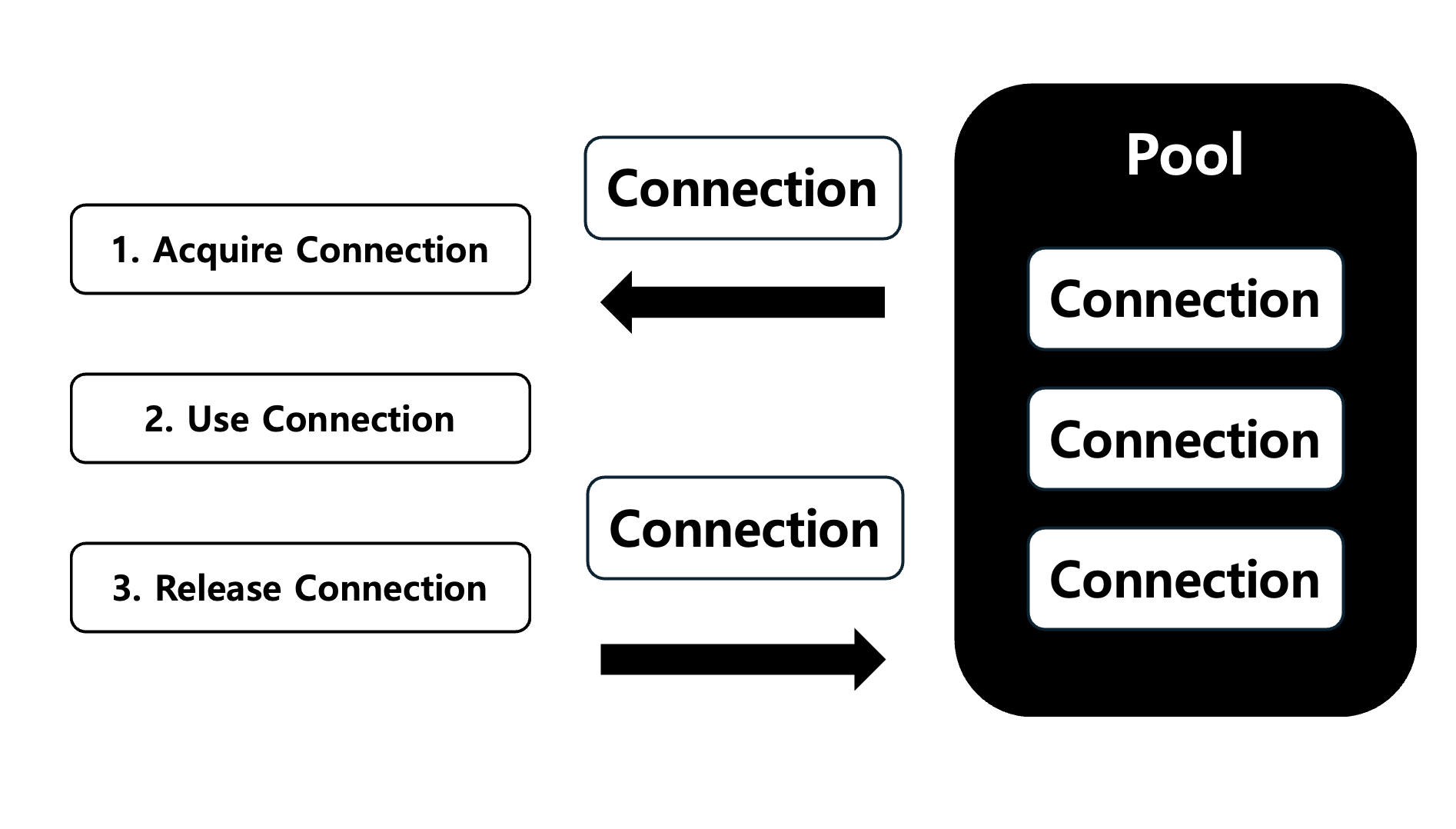
DB Connection Pool was introduced followed by innate inefficiencies directly leading to lower performance in database connection in which given the code like below, the database connection has to be acquired to execute an SQL every single time.
Example
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
sql = "SELECT * FROM T_BOARD"
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASSWORD);
pstmt = conn.createStatement();
rs = pstmt.executeQuery(sql);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
conn.close();
pstmt.close();
rs.close();
}
}
the above approach implies that there is an overhead in resources and time as database connection involves TCP/IP protocols at the transport layer level further implying that TCP 3 way handshake should run for every single attempt to connect to databases.
Reusing connections from the DB connection pool saves the time required to establish new connections, enhancing the application's performance as it reduces database performance bottlenecks in web applications that need to handle a large number of simultaneous requests.
Good example of DBCPs are Apache Commons DBCP, Tomcat-JDBC pool and Hikari CP, where the Hikari CP is the default connection pool for Spring Boot after 2.0.
🧬 Properties (Hikari CP)
Common properties that configure the DB Connection Pool (Hikari CP) are:
Connection Behavior Properties
-
✅
autoCommit(Default:true)
Controls whetherconnectionsare set toauto-commitby default when returned from thepool. -
🔤
connectionTestQuery(Default:none)
Aqueryused to validateconnectionsforlegacy JDBC driversthat don’t support theisValid() API. If not needed, leave it unset.
Timeout Properties
-
⏳
connectionTimeout(Default:30000 msor30 seconds)
Maximum time aclientwaits for aconnectionfrom thepoolbefore aSQLExceptionis thrown. Minimum value is 250 ms. -
⏳
idleTimeout(Default:600000 msor10 minutes)
Maximum time anidle connectionstays in thepoolbefore being removed, provided thepool sizeis aboveminimumIdle. Minimum allowed value is 10 seconds; 0 disablesidle connectionremoval. -
⏳
keepaliveTime(Default:0,disabled)
Interval to"ping" idle connectionsto keep them alive, where theconnectionis shortly removed then returned after the"ping". It must be shorter thanmaxLifetimeand ideally set in minutes to avoid excessive checks. Minimum allowed value is 30 seconds. -
⏳
maxLifetime(Default:1800000 msor30 minutes)
Maximum time anyconnectioncan exist in thepoolbefore it’s replaced, helping to avoid stale connections. Should be slightly shorter than anydatabase connection limits. Minimum allowed value is 30 seconds.
Pool Sizing Properties
-
🔢
minimumIdle(Default:maximumPoolSize)
The minimum number ofidle connectionsHikariCPmaintains. If the number ofidle connectionsdrops below this, new connections are created as long as thepool sizeremains belowmaximumPoolSize. -
🔢
maximumPoolSize(Default:10)
The maximum number oftotal connections(idle and in-use) in thepool. When thepoolreaches this limit, newconnectionrequestswill wait up toconnectionTimeoutbefore timing out.
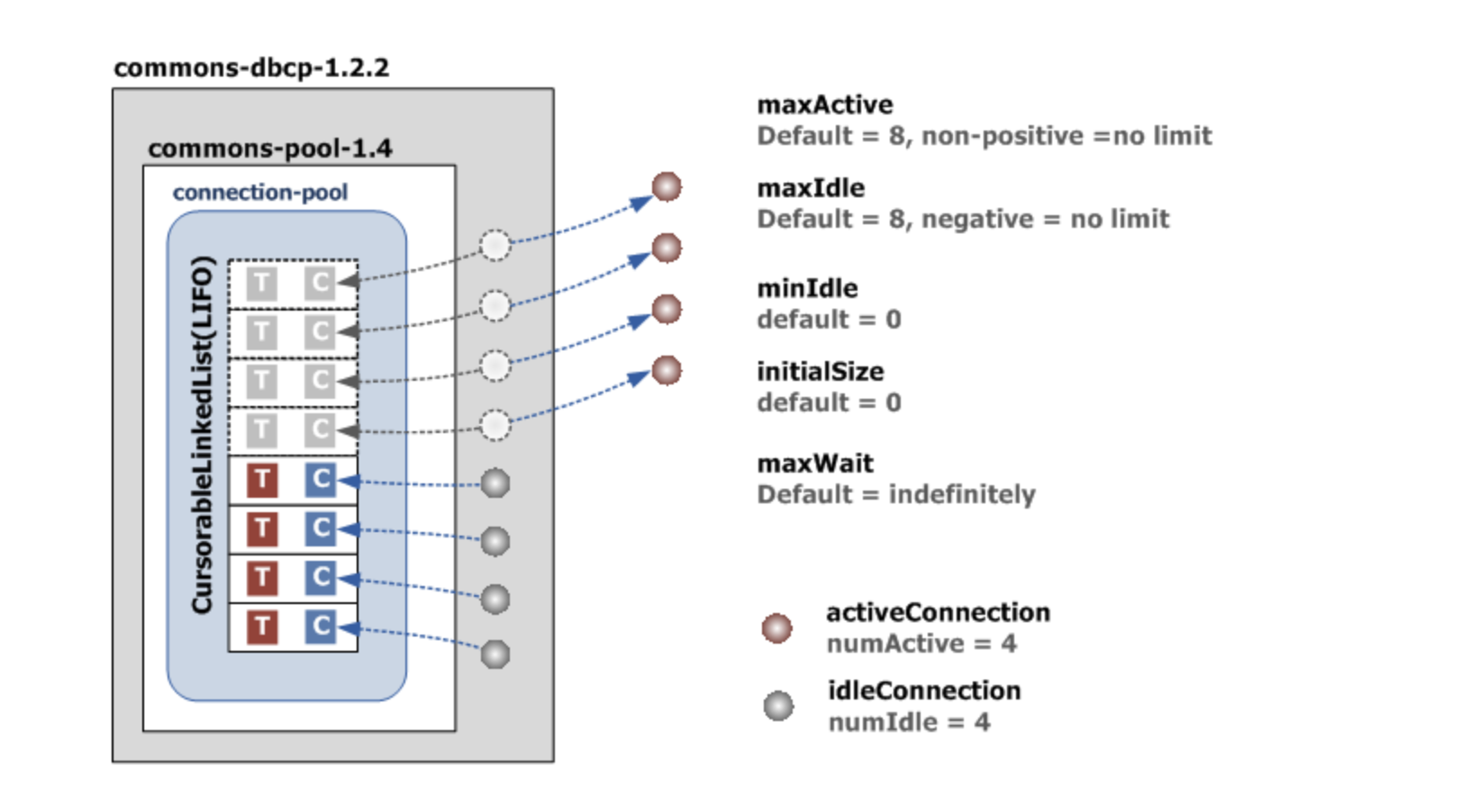
Commons DBCP Available at here
🔬 DBCP Internal Mechanism
HikariCP is available from JDBC via DataSource or DataSourceUtils classes:
Example
// given
private final DataSource dataSource;
datasource.getConnection();
// or
DataSourceUtils.getConnection(datasource);DataSourceUtils class, however, internally uses the datasource.getConnection() method and hence, database connection is managed via the datasource.getConnection() method where the DataSource class is the class that holds the Connection Pool.
💡 Instantiating the
DataSource classfalls toSpring.
💡 By default,HikariDataSource classwill be instantiated.
Below is the code snippet that contains the logic strictly related to the database connection. It is clear that from the HikariDataSource class, the HikariPool instance is responsible for database connection where HikariPool specifically uses ConcurrentBag that is implemented via blocking queue data-structure to handle the database connection complemented with ThreadLocals and shared connection lists implemented via CopyOnWriteArrayList.
HikariDataSource Class
public class HikariDataSource extends HikariConfig implements DataSource, Closeable
{
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HikariDataSource.class);
private final AtomicBoolean isShutdown = new AtomicBoolean();
private final HikariPool fastPathPool;
private volatile HikariPool pool;
...
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (isClosed()) {
throw new SQLException("HikariDataSource " + this + " has been closed.");
}
if (fastPathPool != null) {
return fastPathPool.getConnection();
}
// See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Double-checked_locking#Usage_in_Java
HikariPool result = pool;
if (result == null) {
synchronized (this) {
result = pool;
if (result == null) {
validate();
LOGGER.info("{} - Starting...", getPoolName());
try {
pool = result = new HikariPool(this);
this.seal();
}
catch (PoolInitializationException pie) {
if (pie.getCause() instanceof SQLException) {
throw (SQLException) pie.getCause();
}
else {
throw pie;
}
}
LOGGER.info("{} - Start completed.", getPoolName());
}
}
}
return result.getConnection();
}
...
}HikariPool is specifically responsible for instantiating the connection pool which followed by the configurations either customised or set by default, instantiates the pool via ConnectionBag instance.
HikariPool invokes the borrow() method to acquire the database connection or a Connection instance.
HikariPool Class
public final class HikariPool extends PoolBase implements HikariPoolMXBean, IBagStateListener
{
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HikariPool.class);
public static final int POOL_NORMAL = 0;
public static final int POOL_SUSPENDED = 1;
public static final int POOL_SHUTDOWN = 2;
public volatile int poolState;
private final long aliveBypassWindowMs = Long.getLong("com.zaxxer.hikari.aliveBypassWindowMs", MILLISECONDS.toMillis(500));
private final long housekeepingPeriodMs = Long.getLong("com.zaxxer.hikari.housekeeping.periodMs", SECONDS.toMillis(30));
private static final String EVICTED_CONNECTION_MESSAGE = "(connection was evicted)";
private static final String DEAD_CONNECTION_MESSAGE = "(connection is dead)";
private final PoolEntryCreator poolEntryCreator = new PoolEntryCreator();
private final PoolEntryCreator postFillPoolEntryCreator = new PoolEntryCreator("After adding ");
private final ThreadPoolExecutor addConnectionExecutor;
private final ThreadPoolExecutor closeConnectionExecutor;
private final ConcurrentBag<PoolEntry> connectionBag;
private final ProxyLeakTaskFactory leakTaskFactory;
private final SuspendResumeLock suspendResumeLock;
private final ScheduledExecutorService houseKeepingExecutorService;
private ScheduledFuture<?> houseKeeperTask;
/**
* Construct a HikariPool with the specified configuration.
*
* @param config a HikariConfig instance
*/
public HikariPool(final HikariConfig config)
{
super(config);
this.connectionBag = new ConcurrentBag<>(this);
this.suspendResumeLock = config.isAllowPoolSuspension() ? new SuspendResumeLock() : SuspendResumeLock.FAUX_LOCK;
this.houseKeepingExecutorService = initializeHouseKeepingExecutorService();
checkFailFast();
if (config.getMetricsTrackerFactory() != null) {
setMetricsTrackerFactory(config.getMetricsTrackerFactory());
}
else {
setMetricRegistry(config.getMetricRegistry());
}
setHealthCheckRegistry(config.getHealthCheckRegistry());
handleMBeans(this, true);
ThreadFactory threadFactory = config.getThreadFactory();
final int maxPoolSize = config.getMaximumPoolSize();
LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable> addConnectionQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(maxPoolSize);
this.addConnectionExecutor = createThreadPoolExecutor(addConnectionQueue, poolName + " connection adder", threadFactory, new CustomDiscardPolicy());
this.closeConnectionExecutor = createThreadPoolExecutor(maxPoolSize, poolName + " connection closer", threadFactory, new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
this.leakTaskFactory = new ProxyLeakTaskFactory(config.getLeakDetectionThreshold(), houseKeepingExecutorService);
this.houseKeeperTask = houseKeepingExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new HouseKeeper(), 100L, housekeepingPeriodMs, MILLISECONDS);
if (Boolean.getBoolean("com.zaxxer.hikari.blockUntilFilled") && config.getInitializationFailTimeout() > 1) {
addConnectionExecutor.setMaximumPoolSize(Math.min(16, Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()));
addConnectionExecutor.setCorePoolSize(Math.min(16, Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()));
final long startTime = currentTime();
while (elapsedMillis(startTime) < config.getInitializationFailTimeout() && getTotalConnections() < config.getMinimumIdle()) {
quietlySleep(MILLISECONDS.toMillis(100));
}
addConnectionExecutor.setCorePoolSize(1);
addConnectionExecutor.setMaximumPoolSize(1);
}
}
...
public Connection getConnection(final long hardTimeout) throws SQLException
{
suspendResumeLock.acquire();
final var startTime = currentTime();
try {
var timeout = hardTimeout;
do {
var poolEntry = connectionBag.borrow(timeout, MILLISECONDS);
if (poolEntry == null) {
break; // We timed out... break and throw exception
}
final var now = currentTime();
if (poolEntry.isMarkedEvicted() || (elapsedMillis(poolEntry.lastAccessed, now) > aliveBypassWindowMs && isConnectionDead(poolEntry.connection))) {
closeConnection(poolEntry, poolEntry.isMarkedEvicted() ? EVICTED_CONNECTION_MESSAGE : DEAD_CONNECTION_MESSAGE);
timeout = hardTimeout - elapsedMillis(startTime);
}
else {
metricsTracker.recordBorrowStats(poolEntry, startTime);
return poolEntry.createProxyConnection(leakTaskFactory.schedule(poolEntry));
}
} while (timeout > 0L);
metricsTracker.recordBorrowTimeoutStats(startTime);
throw createTimeoutException(startTime);
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new SQLException(poolName + " - Interrupted during connection acquisition", e);
}
finally {
suspendResumeLock.release();
}
}
...
}A ConcurrentBag instance then followed by its logics where it:
1. checks the available Connection in ThreadLocal.
2. checks the available Connection in sharedList (CopyOnWriteArrayList).
3. wait for the available Connection in BlockingQueue.
finds a PoolEntry instance that holds Connection instance and returns it.
After its execution the connection is then returned:
1. to the other threads requiring the connection instance.
2. to the ThreadLocal.
the sharedList always holds the physical connection instances and will know their logical availabilities via their state properties as in STATE_NOT_IN_USE, STATE_IN_USE and etc.
ConcurrentBag Class
public class ConcurrentBag<T extends IConcurrentBagEntry> implements AutoCloseable
{
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ConcurrentBag.class);
private final CopyOnWriteArrayList<T> sharedList;
private final boolean weakThreadLocals;
private final ThreadLocal<List<Object>> threadList;
private final IBagStateListener listener;
private final AtomicInteger waiters;
private volatile boolean closed;
private final SynchronousQueue<T> handoffQueue;
....
public T borrow(long timeout, final TimeUnit timeUnit) throws InterruptedException
{
// Try the thread-local list first
final var list = threadList.get();
for (int i = list.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final var entry = list.remove(i);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final T bagEntry = weakThreadLocals ? ((WeakReference<T>) entry).get() : (T) entry;
if (bagEntry != null && bagEntry.compareAndSet(STATE_NOT_IN_USE, STATE_IN_USE)) {
return bagEntry;
}
}
// Otherwise, scan the shared list ... then poll the handoff queue
final int waiting = waiters.incrementAndGet();
try {
for (T bagEntry : sharedList) {
if (bagEntry.compareAndSet(STATE_NOT_IN_USE, STATE_IN_USE)) {
// If we may have stolen another waiter's connection, request another bag add.
if (waiting > 1) {
listener.addBagItem(waiting - 1);
}
return bagEntry;
}
}
listener.addBagItem(waiting);
timeout = timeUnit.toNanos(timeout);
do {
final var start = currentTime();
final T bagEntry = handoffQueue.poll(timeout, NANOSECONDS);
if (bagEntry == null || bagEntry.compareAndSet(STATE_NOT_IN_USE, STATE_IN_USE)) {
return bagEntry;
}
timeout -= elapsedNanos(start);
} while (timeout > 10_000);
return null;
}
finally {
waiters.decrementAndGet();
}
}
public void requite(final T bagEntry)
{
bagEntry.setState(STATE_NOT_IN_USE);
for (var i = 0; waiters.get() > 0; i++) {
if (bagEntry.getState() != STATE_NOT_IN_USE || handoffQueue.offer(bagEntry)) {
return;
}
else if ((i & 0xff) == 0xff) {
parkNanos(MICROSECONDS.toNanos(10));
}
else {
Thread.yield();
}
}
final var threadLocalList = threadList.get();
if (threadLocalList.size() < 50) {
threadLocalList.add(weakThreadLocals ? new WeakReference<>(bagEntry) : bagEntry);
}
}
...
}Pool Entry Class
final class PoolEntry implements IConcurrentBagEntry
{
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PoolEntry.class);
private static final AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<PoolEntry> stateUpdater;
Connection connection;
long lastAccessed;
long lastBorrowed;
...
}