🐇 Object Oriented Programming (OOP)
🐇 Object Oriented Programming
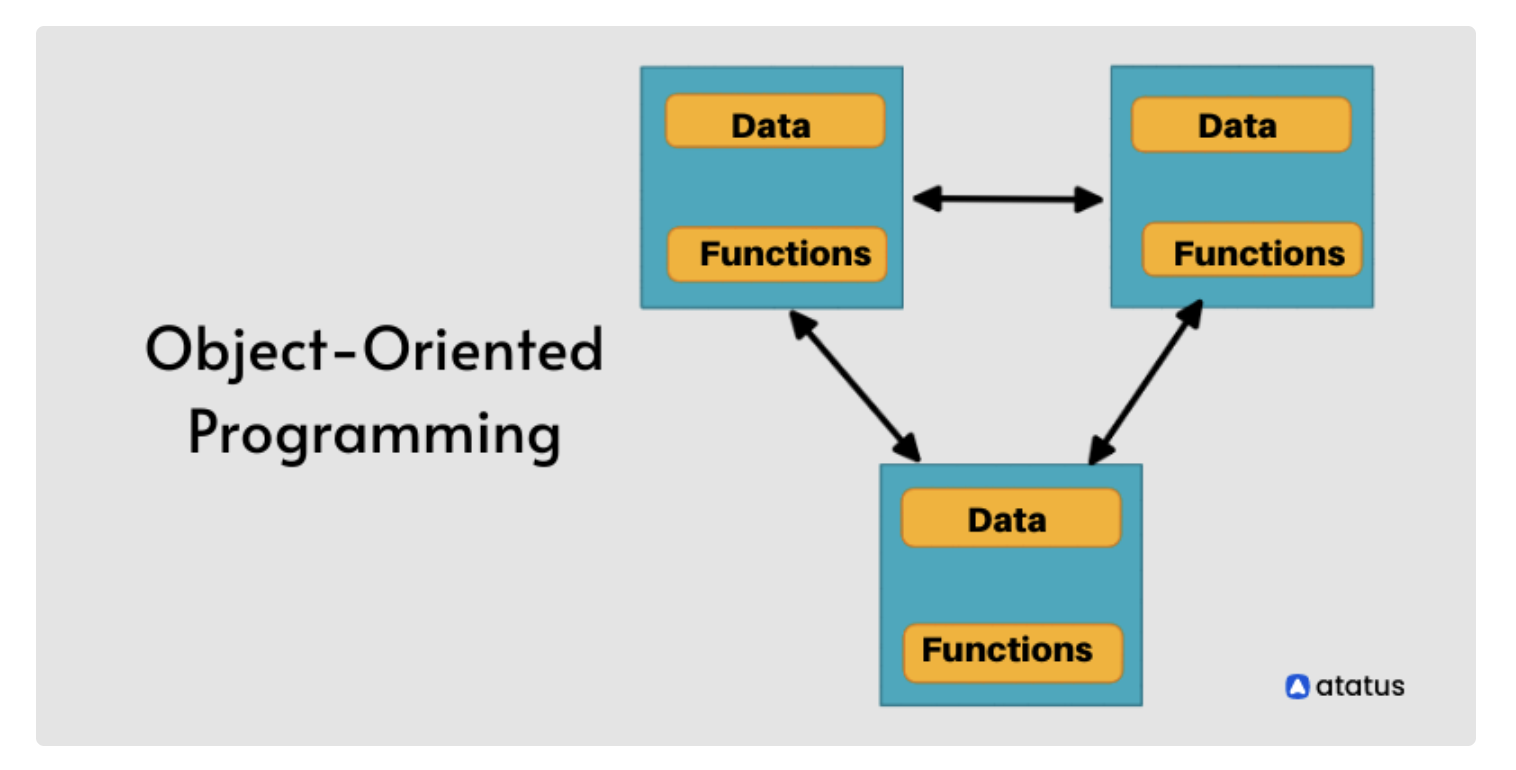
Object Oriented Programming, shortly OOP, is a programming paradigm that sets object as its base unit and develops a system in which these independent objects interactively communicate with each other.
object is a human-defined abstract concept that can be implemented from a class and has its state, behaviour, and its unique identity.
OOP is widely considered to partly reflect the real world. Specifically, each object can be designed to reflect an entity from the real world and hence allows developers to better understand the overall system architecture and its innate interactions.
Programming Languages devised to well serve OOP are notably C++, JAVA, Python, and etc.
💡 Programming Paradigm
An approach or a method for solving a problem
🐢 Other Programming Paradigms
🦖 Procedural Programming Paradigm
Procedural Programming Paradigm is a programming paradigm that splits the programme into small modular functions and implements these functions into a series of steps, procedures.
Procedural Programming Paradigm is well suitable for small projects due to its intuitively easy implementation. Programming Languages devised to well serve Procedural Programming Paradigm are notably C, JavaScript, and etc.
🐗 Functional Programming
Functional Programming is a representative programming paradigm from a Declarative Programming Paradigm that constructs a programme with pure functions in other words mathematical functions.
pure functionsare functions that does not cause anyside effects(no outside changes in variables outside a function body) and where an identicaloutputis derived followed after identicalinput.
it enbales good maintainability and testability and due to the presence of pure functions, it is suitable for parrarel programming and concurrencies.
Programming Languages devised to well serve Functional Programming are notably Haskell, OCaml and etc.
🤷♀️ Comparisons (OOP vs Procedural vs Functional)
OOP followed by its key principles Abstraction, Encapsulation, Inheritance, and Polymorphism enables the codes to have increased reusability and maintainability further leading to good scalability and flexibility upon the code updates. Object capability to partly reflect the real-world phenomenon thereby enabling intuitive software development is also a reason why OOP is preferred.
OOP, however, compared to procedural and functional programming paradigms may have difficulties in implementing parallel programming and concurrencies as states (properties) in OOP constantly changes via behaviours (methods). Additionally, the above advantages of OOP comes at the expanse of performances where the performance level of OOP often appears to be poor comapred to that of functional and procedural programming. This strictly follows the OOP's interactions across objects where individual states has to be addressed indirectly via getters and setters.