🍑 REST API
🍑
REST APIis aninterfacebased on the principles of theREST.
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architecture that was specifically designed to better employ the HTTP protocol.
Representational refers to the server-side resources represented in URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) combined with HTTP methods representing CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) and its status codes. While State Transfer refers to the communication of resource states between the client and the server.
Hence, REST standardises the representation and transfer of resources through URIs, HTTP methods, and stateless interactions, making it highly scalable and easy to integrate across different platforms.
REST has the following characteristics or principles:
-
🍞
Uniform Interface-
an
architectural stylewhere the operations on resources specified by aURIare performed in astandardisedandlimited interface. -
implies that all
API requestsfor thesame resourceshould yield an identical outcome.
-
-
💻
Client - Server Architecture-
same
Client - Server modelfrom theHTTP protocol. -
the
clientconcerns theUIand theserverconcerns thedata processing,security, andetc.
-
-
💨
Stateless-
identical
statelessfrom theHTTP protocol. -
a
serverdoes not maintain a state information leadingREST APIto be scalable.
-
-
📦
Cacheable-
identical
cacheablefeature in theHTTP protocol. -
contributes to the
high performancesfromcaching.
-
-
🎨
Self-Descriptive- allows
REST API messagesto be easily understood just by reading it.
- allows
-
🌊
Layered system-
extra hierarchical layers can be implemented
-
a
Load Balanceror aproxy serverare good examples.
-
🧱 REST API Design Guide
Designing a REST API can be largely summarised into two key elements:
-
℁ An
URIshould represent the available informationalresources. -
✊ An
actionuponresourcesshould be represented in theHTTP methods(GET,POST,PUT/PATCH,DELETE)
where the key principles combined with collections that underlie the layered URI architecture can be represented as underneath:
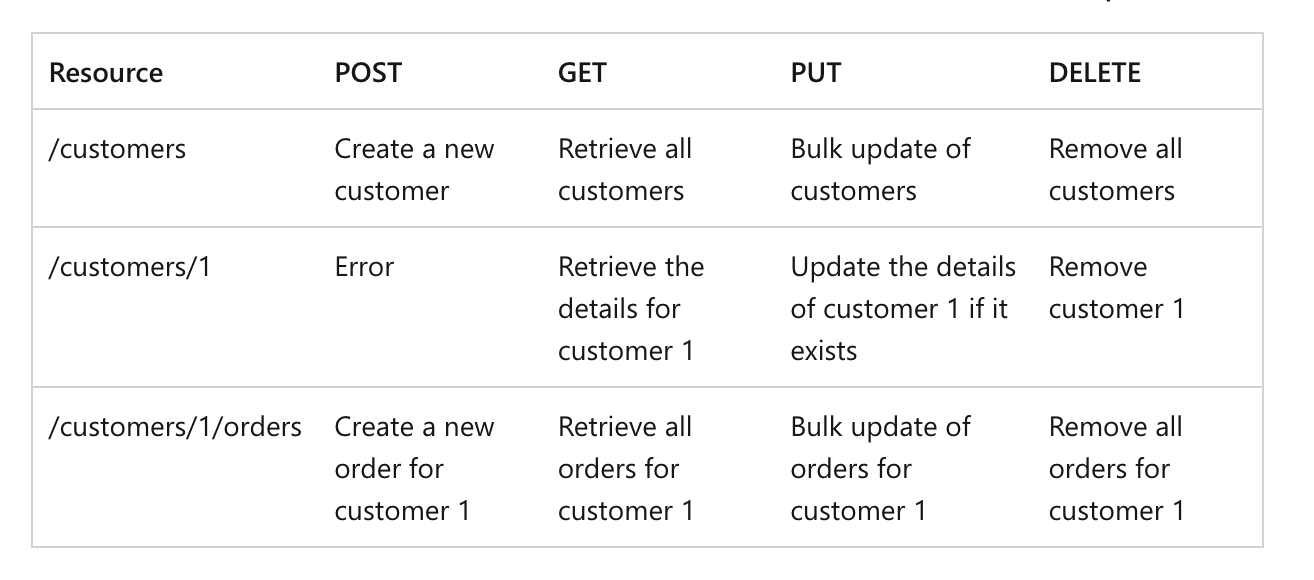 Microsoft Available at here
Microsoft Available at here
Hence, a request based on the REST API is advised not to contain any actions on the URI where the actions should be represented with the HTTP methods.
The below GET /members/delete/1 therefore can be replaced by DELETE /members/1.
REST API Request 1
GET /members/delete/1 -> DELETE /members/1In practice, however, the above REST API rule can be hardly maintained once the represented resources over the URI become too complicated and vast in volume. This happens to be an exceptional cases where the URI may contain any action words:
REST API Request 2
GET : /users/{userid}/likes/devices 🍓 RESTful API
🍓
RESTfulcontains all attributes fromRESTand contains further containsHATEOAS (Hypermedia as the engine of application state ).
HATEOAS means that when a client receives a response from the server, the response includes information about the next possible actions the client can take.
HATEOAS allows the client to understand what actions to take based solely on the server's response. It makes the communication between the client and the server more flexible.
This characteristic of RESTful services significantly improves the scalability and maintainability of web services. This is because the client and server can evolve independently.
Underneath could be a mock RESTful response where it contains HATEOAS as a part of its response:
RESTful API Response (JSON)
{
"id": 123,
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john.doe@example.com",
"status": "active",
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "/api/v1/users/123"
},
"update": {
"href": "/api/v1/users/123",
"method": "PUT"
},
"delete": {
"href": "/api/v1/users/123",
"method": "DELETE"
},
"orders": {
"href": "/api/v1/users/123/orders",
"method": "GET"
}
}
}