🐛 Spring AOP
🐛 Spring AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming)is a complementary feature toOOPby providingmodularitiesinaspectsthan aclass.
AOP strictly refers to the repetitively executing logics (cross cutting concerns) across multiple types of objects and codes, and enables these logics to become modularised individually by implementing simple annotations.
AOP enables:
- 🔺 enhanced
code-readability - 🔺 easier maintainance on
cross cutting concerns
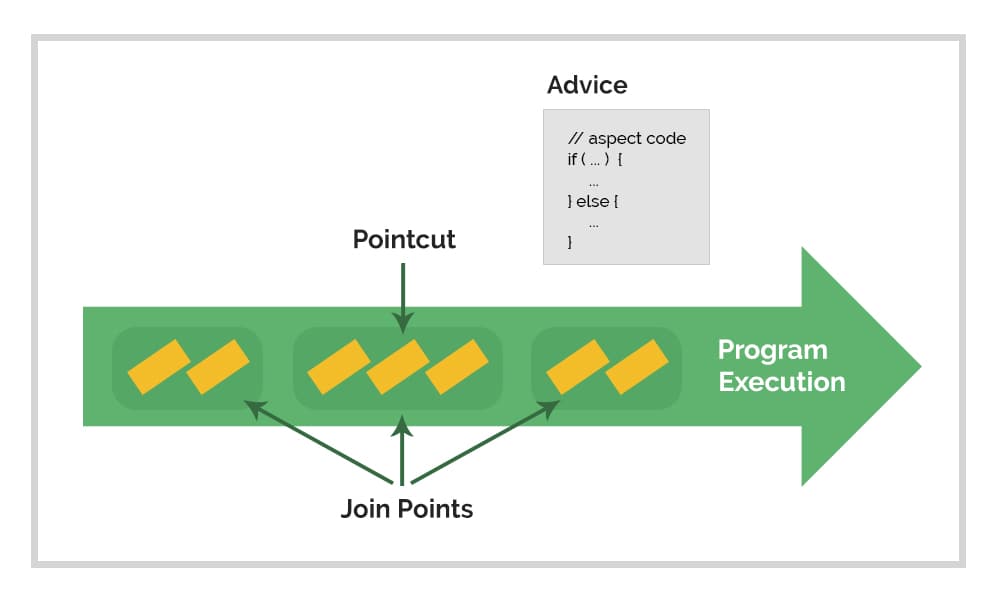
Geeks for Geeks Available at here
🦉 AOP Concepts
Foundational AOP concepts forming AOP are:
-
@Aspectmodularisationof acrosscutting concerns- declared with
@Aspecteither combined with@Componentor@EnableAspectJAutoProxyfrom@AspectJ support
-
JoinPoint- a point during the execution of a
programme, such as the execution of amethodor the handling of anexception. InSpring AOP, aJoinPointalways represents amethod execution.
- a point during the execution of a
-
Advice- an action taken by an
aspectat a particularJoinPoint
- an action taken by an
-
Pointcut- a
predicatethat matchesJoinPoints - an
adviceis associated with apointcut expressionand runs at anyJoinPointmatched by thepointcut(for example, the execution of amethodwith a certain name)
- a
-
AOP Proxy- a
proxy instancecreated byAOP frameworkto implement theaspect contracts(advice method executionsand so on) - In the
Spring Framework, anAOP proxyis aJDK dynamic proxyor aCGLIB proxy.
- a
-
@Before- an
advicethat runs before aJoinPoint - has no control over the
JoinPoint proceedings
- an
-
@After- an
advicethat runs after the execution of aJoinPoint
(if aJoinPointran successfully).
- an
-
@Around- an
advicethat surrounds aJoinPoint. - can implement customised behaviours
before&afteraJoinPoint.
- an
🧾 Pointcut Expression
Supported Pointcut designators for the Pointcut expressions are:
-
execution- a primary
pointcut designatorforSpring AOP - matches
method executionjoin pointswithregex
- a primary
-
within- limits matching to
join pointswithin certain types
- limits matching to
-
this- limits matching to
join pointswhere thebean referenceis aninstanceof the giventype
- limits matching to
-
target- limits matching to
join pointswhere thetarget objectis aninstanceof the giventype
- limits matching to
-
args- limits matching to
join pointswhere theargumentsareinstancesof the given types
- limits matching to
-
@target- limits matching to
join pointswhere theclassof the executingobjecthas anannotationof the giventype.
- limits matching to
-
@args- Limits matching to
join pointswhere theruntime typeof the actualargumentspassed haveannotationsof the giventypes.
- Limits matching to
-
@within- limits matching to
join pointswithintypesthat have the givenannotation
- limits matching to
-
@annotation- limits matching to
join pointswhere the subject of thejoin pointhas the givenannotation.
- limits matching to
Pointcut Expression Pattern
The format of an execution expression follows:
execution(modifiers-pattern?
ret-type-pattern
declaring-type-pattern?name-pattern(param-pattern)
throws-pattern?)where except ret-type pattern, name-pattern, and param-pattern, all other patterns are optional.
* wildcard is often used to represent any types and each pattern is emtpy space separated except for declaring-type-pattern?name-pattern(param-pattern) where the declaring-type-pattern and name-pattern has a . dot in between.
.. is often used as a wildcard at the declaring-type-pattern and (param-pattern) levels where:
com.xyz..a()- refers to a method
apresent incom.xyzpackageand itssubpackages
- refers to a method
(..)- any
parameters
- any
The following examples show some common pointcut expressions:
-
The execution of any
public method:execution(public * *(..)) -
The execution of any
methodwith a name that begins with set:execution(* set*(..)) -
The execution of any
methoddefined by the AccountServiceinterface:execution(* com.xyz.service.AccountService.*(..)) -
The execution of any
methoddefined in theservice package:execution(* com.xyz.service.*.*(..)) -
The execution of any
methoddefined in theservice packageor one of itssub-packages:execution(* com.xyz.service.*.*(..)) -
The execution of any
methodinclasseswhose names end with Service within thecom.myapp packageand all itssub-packages:execution(* com.myapp..*Service.*(..)) -
Any
join point(method executiononly inSpring AOP) within theservice package:within(com.xyz.service.*) -
Any
join point(method executiononly inSpring AOP) within theservice packageor one of itssub-packages:within(com.xyz.service..*) -
Any
join point(method executiononly inSpring AOP) where theproxyimplements theAccountService interface:this(com.xyz.service.AccountService) -
Any
join point(method executiononly inSpring AOP) where thetarget objectimplements theAccountService interface:target(com.xyz.service.AccountService) -
Any
join point(method executiononly inSpring AOP) that takes a singleparameterand where theargumentpassed atruntimeisSerializable:args(java.io.Serializable) -
Any
join point(method executiononly inSpring AOP) where thetarget objecthas a@Transactional annotation:@target(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional) -
Any
join point(method executiononly inSpring AOP) where the declaredtypeof thetarget objecthas an@Transactional annotation:@within(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional) -
Any
join point(method executiononly inSpring AOP) where the executingmethodhas an@Transactional annotation:@annotation(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional) -
Any
join point(method executiononly inSpring AOP) which takes a singleparameter, and where theruntime typeof theargumentpassed has the@Classified annotation:@args(com.xyz.security.Classified)
🧸 Example
Example introduces a Spring AOP that measures the start and end time of method execution defined in pointcut expressions.
Spring AOP in practice, can be implemented either via:
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy + @Aspect@Component + @Aspect
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy + @Aspect
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppConfig {
}
@Aspect
public class Aspect {
}@Component + @Aspect
@Aspect
@Component
public class Aspect {
}given the above @Aspect declarations, either the advices associated with @PointCut or advices with the specified JoinPoints can be further declared followed by the Pointcut expressions:
PointCuts
@Aspect
public class Aspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* transfer(..))") // the pointcut expression
private void anyOldTransfer() {} // the pointcut signature
}Advices
@Aspect
@Component
public class TimeTraceAop {
@Before("execution(* hello.hello_spring..*(..))")
public void beforeExecute() throws Throwable{
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("START TIME: " + start);
}
@After("execution(* hello.hello_spring..*(..))")
public void afterExecute() throws Throwable{
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("END TIME: " + end);
}
}@Aspect
@Component
public class TimeTraceAop {
@Around("execution(* hello.hello_spring..*(..))")
public Object execute(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("START: " + joinPoint.toString());
try {
return joinPoint.proceed();
} finally {
long finish = System.currentTimeMillis();
long timeMs = finish - start;
System.out.println("END: " + joinPoint.toString() + " " + timeMs + "ms");
}
}
}📚 References
스프링 입문을 위한 자바 객체 지향의 원리와 이해
스프링 핵심 원리 - 기본편 (김영한)
Spring DOC
Geeks for Geeks
