for - each
: '향상된 for문'이라고도 하며 for - each문이라고도 한다.
: 주로 ArrayList와 Array 같은 데이터를 순회할 때 사용한다.
사용방법
- 순회할 요소
: ArrayList<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<>();
: int[] intList = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; - for('순회할 요소의 자료타입' '순회요소를 담을 참조변수' : '순회할 요소의 변수명'){};
for문과 for - each문 차이점
: Array에 적용한다면
- for문 : 인덱스 번호를 활용하여 인덱스 번호에 맞는 값을 꺼내온다.
- for - each문 : Array에 있는 값을 순회할 요소를 담은 참조변수에 넣고 변수에 넣어진 값을 활용하여 출력된다.
예시
public class ForEach {
public static void main(String[] arge){
// 순환할 요소
int[] intList = {1,2,3,4,5};
// for문 인덱스 사용
for(int i = 0; i < intList.lenght; i++){
System.out.print(intList[i]);
}
// 12345
// for - each으로 Array에 있는 요소들 출력해보기
for(int num : intList){
System.out.print(num);
}
// 12345
}
}
객체가 담긴 ArrayList에 활용해보자
이전
public class Id{
public static void main(String[] arge){
// 객체를 담는 ArrayLIst 생성
ArrayList<Post> postList = new ArrayList<>();
// 객체에 고유번호로 담을 변수
int postId = 1;
// 1~100까지 for문으로 객체를 만들어서 ArrayList에 담았다.
for(int i = 0; i <= 100; i++){
Post post = new Post(1,"제목","내용");
postList.add(post);
// 객체에 담기는 숫자는 매번 달라저야 하므로 증가식을 써서
// 들어가는 고유번호가 달라지게 만들어준다.
postId++;
}
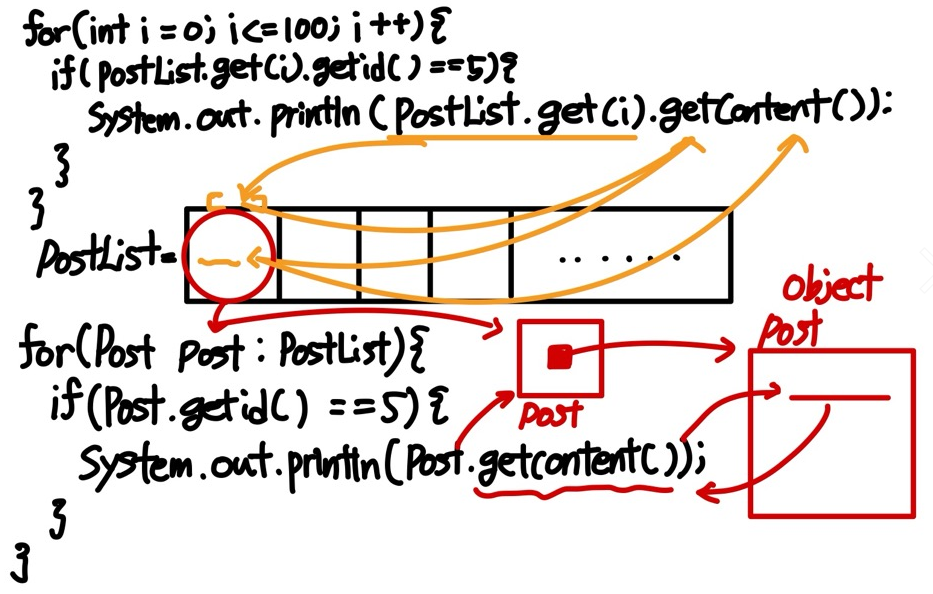
// 예를들어 5번을 담고 있는 객체를 내용을 출력하고 싶을때
for(int i = 0; i <= 100; i++){
if(postList.get(i).getid() == 5){
System.out.printnl(postList.get(i).getContent());
}
}
// 인덱스로 찾으면 인덱스 찾기+아이디 / 인덱스 찾기 + 내용으로
// 좀더 코드가 길다.
}
}
class Post{
private int id;
private String title;
private String body
public Post(int id, String title, String body){
// 생성자를 이용하여 매개변수로 받아 객체 id 변수에 담음
this.id = id ;
this.title = title;
this.body = body;
}
}for-each
public class Id{
public static void main(String[] arge){
// 객체를 담는 ArrayLIst 생성
ArrayList<Post> postList = new ArrayList<>();
// 객체에 고유번호로 담을 변수
int postId = 1;
// 1~100까지 for문으로 객체를 만들어서 ArrayList에 담았다.
for(int i = 0; i <= 100; i++){
Post post = new Post(1,"제목","내용");
postList.add(post);
// 객체에 담기는 숫자는 매번 달라저야 하므로 증가식을 써서
// 들어가는 고유번호가 달라지게 만들어준다.
postId++;
}
// 만약 for - each를 사용한다면
for(Post post : postList){
if(post.getid() == 5){
System.out.printnl(post.getContent());
}
}
// post에 직접적으로 content으로 연결하여 쓸 수 있어서 코드가 더 간결해진다.
}
}
class Post{
private int id;
private String title;
private String body
public Post(int id, String title, String body){
// 생성자를 이용하여 매개변수로 받아 객체 id 변수에 담음
this.id = id ;
this.title = title;
this.body = body;
}
}
결론
인덱스를 다루지 않아도 될 때는
for-each를 활용해 변수에 담아 객체안으로 접근하는 것이 더 간결하다.
하지만 특정 인덱스를 다루어야 한다면 for문을 활용하는 것이 더 좋다.