Stack(스택)
LIFO(Last-In-First-Out, 후입선출)구조
- 뒤에 들어온 것이 가장 먼저 나가는 구조
Stack(스택)의 개념과 원리
- 맨 위의 원소만 접근이 가능하다.
- 스택의 맨 위 원소를 스택 탑(Top) 또는 탑 원소라고 한다.
- 새 원소를 삽입하는 경우 스택 탑 바로 윗자리에 원소를 저장한 후 새 원소가 새 스택 탑이 되게 한다.
- 원소를 삭제하는 경우 무조건 탑에 있는 원소를 삭제한 후 바로 아래 원소가 새 스택 탑이 되게 한다.
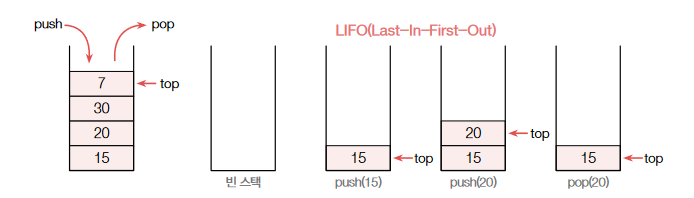
[그림 1] 스택의 개념과 원리
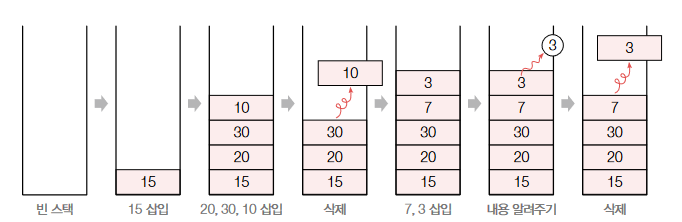
[그림 2] 스택에서 행하는 작업의 예
활용
-> 완료되지 않은 함수가 다른 함수를 호출할때 정보를 저장하는 스택 가상 메모리의 영역
배열을 이용한 스택
stack[] <- 스택의 원소들이 저장되는 배열
topIndex <- 스택 탑 원소 자리의 인덱스
push(x) <- 스택의 맨위에 있는 원소x를 삽입한다.
pop() <- 스택의 맨위에 있는 원소를 알려주고 삭제한다.
top() <- 스택의 맨위에 있는 원소를 알려준다.
isEmpty() <- 스택이 비었는지 알려준다.
popAll() <- 스택을 정리한다.스택에 원소를 삽입하는 경우
topIndex++ //-> 탑 원소 자리의 인덱스를 늘려준다.
stack[topIndex] = x //스택의 topIndex자리에 새 원소를 저장하는 것원소를 삽입하는 코드의 핵심은 먼저 topIndex를 1 증가시킨 다음 그 자리에 새 원소를 저장한다.
만약 topIndex = stack.length-1인 경우 배열이 꽉 차있어서 더 이상 들어갈 공간이 없다.
알고리즘은 다음과 같다.
push(x):
if(isFull()) //만약 꽉 차있다면?
// 에러처리
else // 꽉 차있지 않다면?
topIndex++
stack[topIndex] = x원소를 삭제하는 경우
topItem = stack[topIndex]
topIndex--
retrun topItem원소를 삭제하는 코드의 핵심은 먼저 topIndex의 원소를 리턴하면서 topIndex를 1 감소시키는 것이다.
만약 topIndex가 -1인 경우 스택이 비어있는 상태이다.
스택에서 원소를 삭제하는 알고리즘은 다음과 같다.
pop():
if(isEmpty()) //만약 비어있다면?
// 에러처리
else // 비어있지 않다면?
topItem = stack[topIndex]
topIndex--
retrun topItem탑 원소를 알려주는 함수 top()
top():
if(isEmpty()) // 만약 비어있다면?
// 에러처리
else
return stack[topIndex] //topIndex의 내용을 반환한다.스택이 꽉 차있는지 확인하는 isFull()
isFull():
//topIndex가 stack의 길이-1만큼 있는 경우 (배열은 0부터 인덱스가 시작한다.)
if(topIndex = stack.length-1)
return true //꽉 차있다.
else
return false //비어있다.스택이 비었는지 확인하는 isEmpty()
isEmpty():
if(topIndex = -1)
return true
else
return false스택을 완전히 비우는 경우 popAll()
popAll():
topindex = -1
stack = newObject[stack.length] //새로운 배열로 교체배열 스택의 구현
스택 인터페이스
// StackInterface.java
package stack
public interface StackInterface<E>{
public void push(E newItem);
public E pop();
public E top();
public boolean isEmpty();
public void popAll();
}클래스 구현
//ArrayStack.java
package stack;
public class ArrayStack<E> implements StackInterface<E> {
private E stack[];
private int topIndex; // 스택 탑 인덱스
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 64;
private final E ERROR = null; //임의의 에러 값
}
public ArrayStack() { //생성자 1
stack = (E()) new Object[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
topIndex = -1;
}
public ArrayStack(int n) { //생성자 2
stack = (E()) new Object[n];
topIndex = -1;
}
// 스택에 원소 x 삽입하기
public void push(E newItem) {
if(isFull()) {/* 에러 처리 */}
else stack[++topIndex] = newItem;
}
//스택에서 원소 삭제하기
public E pop() {
if(isEmpty()) return ERROR;
else return stack[topIndex]
}
// 스택 탑 원소 알려주기
public E top() {
if(isEmpty()) return ERROR;
else return stack[topIndex];
}
// 스택이 꽉 찼는지 확인하기
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (topIndex < 0);
}
// 스택이 비었는지 확인하기
public boolean isFull() {
return (topIndex == stack.length-1)
}
// 스택 비우기
public void popAll() {
stack = (E[]) new Object[stack.length];
topIndex = -1;
}사용 예
ArrayStack<Integer> s = new ArrayStack<>(10);
s.push(300);
s.push(150);
s.pop();여기서 ArrayStack 클래스의 생성자는 1번과 2번 총 2개이다.
1번의 경우는 배열의 크기가 주어지지 않은 경우
즉, 파라미터가 없이 호출되면 기본으로 주어진 상수 크기의 배열을 할당 받고,
위 사용 예의 경우 지정된 크기(10)만큼 배열을 할당 받는다.
위 클래스 구현에서는 popAll()에서 새로운 배열이 스택 역할을 하게 했다.
불필요할지 모르나 이건 후에 새로운 피드를 통해 따로 내용을 다루고자 한다.
연결 리스트를 이용한 스택
//LinkedStack.java
public class LinkedStack<E> implements StackInterface<E> {
private Node<E> topNode;
private final E ERROR = null; // 임의의 에러값
public LinkedStack() {
topNode = null;
}
// 스택에 원소 x 삽입하기
public void push(E newItem) {
topNode = new Node<>(newItem,topNode);
}
// 스택에서 원소 삭제하기
public E pop() {
if (isEmpty()) return ERROR;
else {
Node<E> temp = topNode;
topNode = topNode.next;
return temp.item;
}
}
// 스택에서 탑 원소 알려주기
public E top() {
if (isEmpty()) return ERROR;
else return topNode.item;
}
//스택이 비었는지 확인하기
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (topNode == null);
}
//스택 비우기
public void popAll() {
topNode = null;
}
}스택 응용
1. 문자열 뒤집기
package stack;
public class ReverseString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input = "Test Seq 12345";
String t = reverse(input);
System.out.println("Input string: " + input);
System.out.println("Reversed string: " + t);
}
private static String reverse(String s) {
ArrayStack<Character> st = new ArrayStack<>(s.length());
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
st.push(s.charAt(i););
String output = "";
while (!st.isEmpty())
output = output + st.pop();
return output;
}
}2. Postfix 계산
package stack;
public class PostfixEval {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String postfix = "700 3 47 + 6 * - 4 /";
System.out.println("Input string: " + postfix);
int answer = evaluate(postfix);
System.out.println("Answer: " + answer);
}
public static int evaluate(String postfix) {
int A,B
LinkedStack<Integer> s = new LinkedStack<>();
boolean digitPreviously = false;
for (int i = 0; i < postfix.length(); i++;) {
char ch = postfix.charAt(i)
if(Character.isDigit(ch)) {
if (digitPreviously = true;) {
int tmp = s.pop();
tmp = 10*tmp + (ch - '0');
s.push(tmp);
} else s.push(ch - '0')
digitPreviously = true;
} else if(isOperator(ch)) {
A = s.pop();
B = s.pop();
int val = operation(A,B,ch);
s.push(val)
digitPreviously = false;
} else digitPreviously = false;
}
return s.pop();
}
public static int operation(char ch, int a, int b) {
int val = 0;
switch (ch) {
case '*':
val = b*a;
break;
case '/':
val = b/a;
break;
case '+'
val = b+a;
break;
case '-':
val = b-a;
break;
}
}
public static boolean isOperator(char ch) {
return ch == '+' || ch == '-' || ch == '*' || ch == '/';
}
}
그림 1, 2는 쉽게 배우는 자료구조 with 자바에서 참조했습니다.
