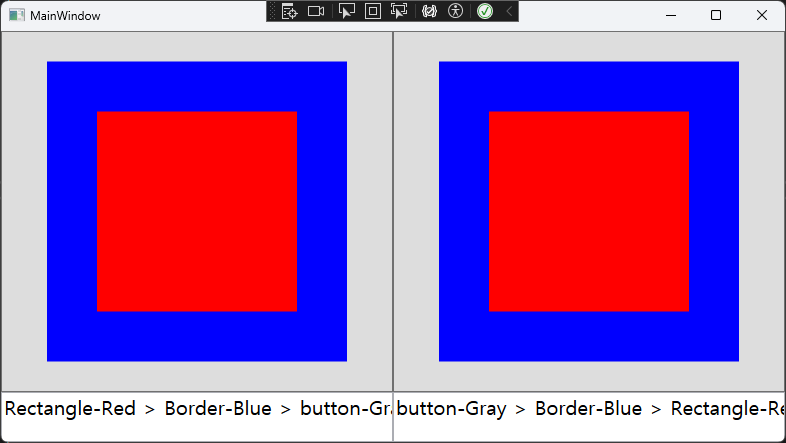
WPF에서 버블링(Bubbling)과 터널링(Tunneling)은 라우트된 이벤트(Routed Event)의 두 가지 중요한 동작 방식이다. 이들은 UI 요소 계층을 따라 이벤트가 전달되는 방식을 정의한다.
1. 버블링 (Bubbling)
정의
이벤트가 발생한 자식 요소에서 부모 요소 방향으로 전파되는 방식이다.
특징
- 일반적으로 가장 많이 사용되는 이벤트 전달 방식.
- 버튼 클릭이나 마우스 동작 같은 이벤트가 자식 요소에서 발생한 후, 부모 요소로 전달된다.
- 이벤트의 소스(Source)는 이벤트가 발생한 자식 요소이다.
ex)
<StackPanel MouseDown="Parent_MouseDown"> <Button Content="Click Me" MouseDown="Button_MouseDown"/> </StackPanel>사용자가 버튼을 클릭하면
Button_MouseDown이벤트가 먼저 호출된다(자식 요소).- 이후
Parent_MouseDown이벤트가 호출된다(부모 요소).적용된 이벤트 이름
이벤트 이름이 단순히
MouseDown,Click처럼 정의된다.2. 터널링 (Tunneling)
정의
이벤트가 발생하기 전에 부모 요소에서 자식 요소 방향으로 전파되는 방식이다.
특징
- 이벤트가 발생하기 전, 부모가 이벤트를 먼저 처리할 기회를 가진다.
- 주로 부모가 자식 이벤트를 가로채거나 미리 준비할 필요가 있을 때 사용된다.
- WPF에서는 터널링 이벤트 이름이 "Preview"로 시작한다.
ex)
<StackPanel PreviewMouseDown="Parent_PreviewMouseDown"> <Button Content="Click Me" PreviewMouseDown="Button_PreviewMouseDown"/> </StackPanel>사용자가 버튼을 클릭하면
Parent_PreviewMouseDown이벤트가 먼저 호출된다 (부모 요소).- 이후
Button_PreviewMouseDown이벤트가 호출된다 (자식 요소).적용된 이벤트 이름
이벤트 이름이
PreviewMouseDown,PreviewTextInput처럼 정의된다.3. 버블링과 터널링의 차이점
특성 버블링 (Bubbling) 터널링 (Tunneling) 방향 자식 요소 → 부모 요소 부모 요소 → 자식 요소 이벤트 이름 일반 이름 ( MouseDown,Click)Preview로 시작 (PreviewMouseDown)용도 기본 이벤트 처리 이벤트를 가로채거나 미리 처리 호출 순서 자식이 먼저 호출됨 부모가 먼저 호출됨 4. 이벤트 처리 흐름
WPF에서는 일반적으로 터널링 → 버블링 순서로 이벤트가 발생한다.
1. 터널링 이벤트: 부모 → 자식 방향으로 내려간다.
2. 실제 이벤트 발생: 이벤트 소스에서 발생한다.
3. 버블링 이벤트: 자식 → 부모 방향으로 올라간다.5. 실습 예제
아래 코드는 두 이벤트의 흐름을 확인하는 간단한 예제이다.
<Window x:Class="EventTest.MainWindow" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" Title="Event Test" Height="200" Width="400"> <StackPanel PreviewMouseDown="OnPreviewMouseDown" MouseDown="OnMouseDown"> <Button Content="Click Me" PreviewMouseDown="OnButtonPreviewMouseDown" MouseDown="OnButtonMouseDown"/> </StackPanel> </Window>public partial class MainWindow : Window { public MainWindow() { InitializeComponent(); } private void OnPreviewMouseDown(object sender, MouseButtonEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("StackPanel PreviewMouseDown (Tunneling)"); } private void OnMouseDown(object sender, MouseButtonEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("StackPanel MouseDown (Bubbling)"); } private void OnButtonPreviewMouseDown(object sender, MouseButtonEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("Button PreviewMouseDown (Tunneling)"); } private void OnButtonMouseDown(object sender, MouseButtonEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("Button MouseDown (Bubbling)"); } }실행 흐름:
StackPanel의PreviewMouseDown→ (부모)Button의PreviewMouseDown→ (자식)Button의MouseDown→ (자식)StackPanel의MouseDown→ (부모)6. 결론
- 터널링은 이벤트를 부모에서 자식으로 전달하며, 부모가 이벤트를 미리 가로채거나 처리할 기회를 제공한다.
- 버블링은 이벤트를 자식에서 부모로 전달하며, 자식이 처리하지 않은 이벤트를 부모가 처리할 수 있도록 한다.
- 두 방식은 WPF의 라우트된 이벤트 모델의 핵심이며, 유연한 이벤트 처리를 가능하게 한다.
ex)