row cache lock
- dictionary cache(row cache)는 oracle dictionary 정보에 대한 cache 메모리
- 유저,테이블, 인덱스, 시퀀스, 컬럼, 함수, 프로시저, 패키지, 트리거....
- DDL, DCL 작업을 수행하면 dictionary 정보가 입력, 수정, 삭제 작업을 수행한다.
- SQL문 수행시에 semantic, 권한 체크할때 dictionary 정보를 이용한다.
- row cache lock은 dictionary object를 보호하는 시스템 lock이다.
-
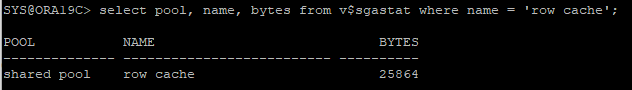
row cache 확인
select pool, name, bytes from v$sgastat where name = 'row cache';
-
row cache 안의 정보 확인
select cache#, type, parameter from v$rowcache;- 대부분의 row cache의 경합은 sequence객체 때문에 발생된다.
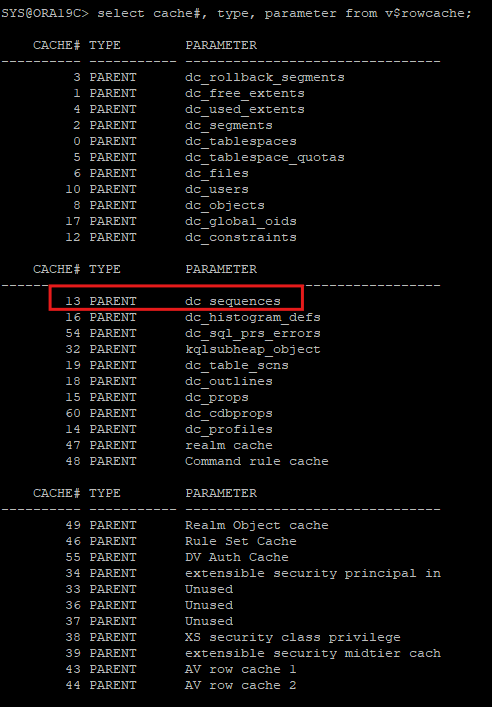
- 대부분의 row cache의 경합은 sequence객체 때문에 발생된다.
- 시퀀스 객체 생성
NOCACHE옵션은값을 캐시하지 않고, 필요할 때마다 매번 값을 생성한다.
create sequence hr.seq_1 nocache;
- 시퀀스 정보 확인
- 해당 정보는 row cache안에 있는 정보를 조회하는거다.
select * from dba_sequences where sequence_owner='HR' and sequence_name='SEQ_1';

- 실제 시퀀스정보는 system 테이블스페이스안에 있다.
select* from seq$;
실습
<<session 1>>
execute dbms_application_info.set_client_info('sess_1');
declare
v_value number;
begin
for i in 1..100000 loop
select hr.seq_1.nextval into v_value from dual;
end loop;
end;
/<<session 2>>
execute dbms_application_info.set_client_info('sess_2');
declare
v_value number;
begin
for i in 1..100000 loop
select hr.seq_1.nextval into v_value from dual;
end loop;
end;
/<<session 3>>
select client_info, sid from v$session where client_info in ('sess_1','sess_2');select sid, event, total_waits, time_waited/100
from v$session_event
where sid in (39,282);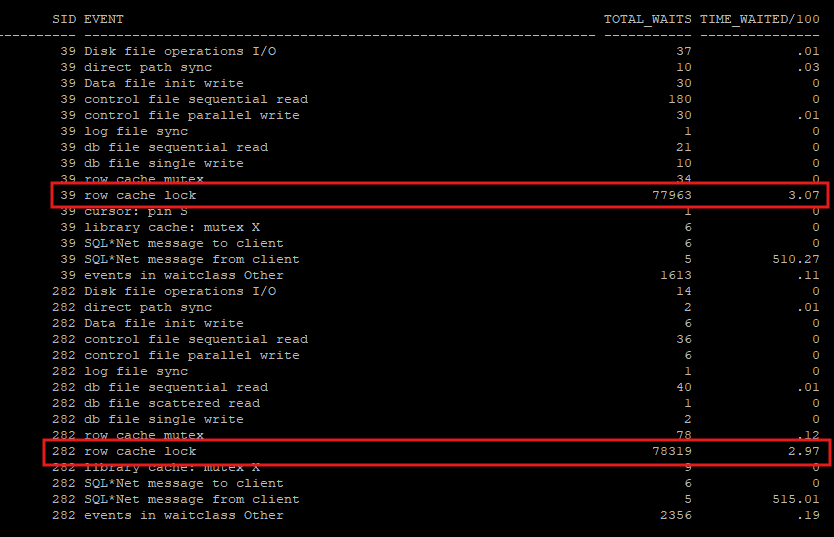
- sequence를 생성할때 nocache 옵션으로 설정하였기 때문에 필요할때마다 생성해서 채번해야 하는데 생성 후 last number를 다음 값으로 update 한다. update를 할때 row cache lock이 걸리기 때문에 다른 세션에서 sequence dictionary를 참조하려고 할때 row cache lock waite event가 발생한다.
- 어떤 세션에서 문제가 되었는지 경합발생중에 확인(경합이 끝난이후에는 조회되지 않는다)
select h.address, h.saddr, s.sid, h.lock_mode
from v$rowcache_parent h, v$rowcache_parent w, v$session s
where h.address = w.address
and w.saddr=(select saddr from v$session where event='row cache lock' and rownum=1)
and h.saddr = s.saddr
and h.lock_mode > 0;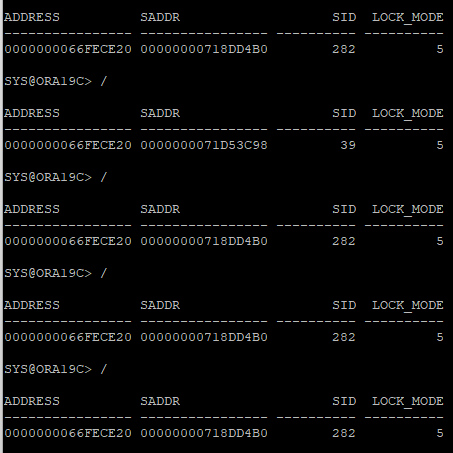
- 문제를 유발한 세션이 이전에 사용한 sql 쿼리문을 조회
select prev_sql_addr from v$session where sid = 282;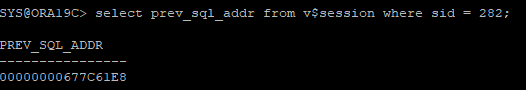
- 문제가 된 특정 sql address를 조건으로 sql 쿼리문을 확인하면 문제가 되는 시퀀스 객체를 확인할 수 있다.
select sql_text
from v$sql
where address=(select prev_sql_addr from v$session where sid = 282);
- 문제가 되는 시퀀스를 찾아서 조회를 해보니 CACHE_SIZE가 0으로 되어있어 채번할때마다 새롭게 생성해서 문제가 되는걸 확인할 수 있다.
select * from dba_sequences where sequence_owner='HR' and sequence_name='SEQ_1';
row cache lock이 발생하는 경우
- sequence를 nextval 수행할 때 마다 data dictionary 정보를 변경하기 위해서 SSX(Shared Sub Exclusive), SRX(Shared Row Exclusive) lock mode(5)를 획득해야할때 row cache lock wait event가 발생한다.
해결방법
- cache 속성을 수정
- nocahe -> cache 20 (20개의 번호를 미리 메모리에 올려놓음)
실습 (sequence에 캐시기능을 설정)
drop sequence hr.seq_1;
create sequence hr.seq_1 cache 20;<<session 1>>
execute dbms_application_info.set_client_info('sess_1');
declare
v_value number;
begin
for i in 1..100000 loop
select hr.seq_1.nextval into v_value from dual;
end loop;
end;
/<<session 2>>
execute dbms_application_info.set_client_info('sess_2');
declare
v_value number;
begin
for i in 1..100000 loop
select hr.seq_1.nextval into v_value from dual;
end loop;
end;
/<<session 3>>
select client_info, sid from v$session where client_info in ('sess_1','sess_2');select sid, event, total_waits, time_waited/100
from v$session_event
where sid in (275,282);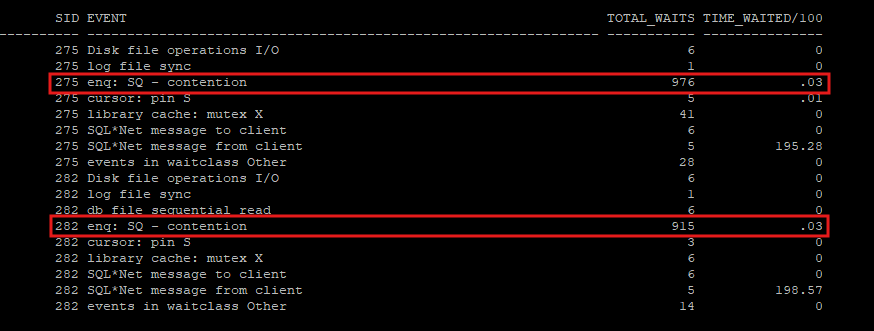
enq : SQ - contention wait event발생- cache 사이즈가 너무 작게 설정되었을 경우 발생
- 여러 세션이 동시에 같은 시퀀스 값을 요청할 때 발생
해결방법
- cache 크기를 적절하게 증가 시켜야 한다.
alter sequence hr.seq_1 cache 100;
과도한 hard parsing 문제점
- 실행계획 생성시에 과도한 CPU, 메모리 사용량 증가
- library cache chain의 확장으로 인한 검색시간이 증가(soft parsing), latch(mutex)점유 시간이 길어진다.
- shared pool fragmentation(단편화)가 많이 발생한다. 작은 chunk 크기로 메모리 조각이 증가된다.
- hard parsing 시 필요한 필요한 chunk를 찾지 못해서
ORA-4031가 발생할 확률이 높아진다.
Shared Reserved Pool
-
shared pool의 일부영역을 예비해 두었다가 메모리 부족으로 ORA-4031 오류 발생하는것을 방지할 목적
-
shared pool 크기의 5%를 reserved pool로 사용한다.
-
shared pool에서 필요한 chunk크기를 찾지 못하고 그 크기가 4400byte 이상이면 reserved pool를 사용할 수 있다.
-
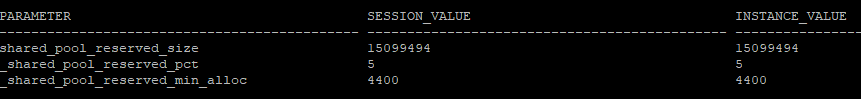
shared reserved pool 히든파라미터 확인
select a.ksppinm as parameter,b.ksppstvl as session_value, c.ksppstvl as instance_value
from x$ksppi a, x$ksppcv b, x$ksppsv c
where a.indx = b.indx
and a.indx = c.indx
and a.ksppinm in ('shared_pool_reserved_size','_shared_pool_reserved_pct','_shared_pool_reserved_min_alloc');shared_pool_reserved_size = _shared_pool_reserved_pct(5%) * shared_pool_size
_shared_pool_reserved_min_alloc : reserved pool를 사용할 수 있는 최소 크기 기준
shared pool에 library cache에 객체를 고정시키는 작업(keep)
-
객체 keep 설정
execute dbms_shared_pool.keep('comm_pkg'); -
keep한 객체 조회
- keep한 객체는 flush를 해도 shared pool 메모리를 유지하고 있다.
select name, namespace, type
from v$db_object_cache
where kept='YES'
and type in ('PACKAGE','PROCEDURE','FUNCTION');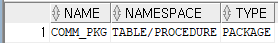
- shared pool에 library cache에 객체를 keep 해지작업
execute dbms_shared_pool.unkeep('comm_pkg');
패키지, 프로시저, 함수 를 create 해서 compile 하면 pl/sql 쿼리문이 parse 되면서 디스크 딕셔너리에 저장하게 된다. pl/sql 쿼리문안에 sql문이 static sql문이면 parse 단계에서 실행계획도 만들어져서 p-code or machine code에 같이 녹여져서 만들어 진다. 하지만 해당 실행계획은 유저딴에서는 확인할 수 없다(p-code에 녹여져 있기 때문에). 그렇게 만들어진 패키지 or 프로시저 or 함수를 execute 하면 shared pool의 library cache의 pl/sql area에 해당 pl/sql 쿼리문의 (handel, lco)가 있는지 확인한 뒤 없으면 할당하고 내부 sql문의 실행계획은 p-code에서 가져와 sql area의 lco안에 복사해 넣어놓는다.
