문제풀이
함수
1번
- 산술연산 계산기를 함수를 이용해서 만들어보자.
def add(n1, n2):
return n1 + n2
def sub(n1, n2):
return n1 - n2
def mul(n1, n2):
return n1 * n2
def div(n1, n2):
return n1 / n2
def mod(n1, n2):
return n1 % n2
def flo(n1, n2):
return n1 // n2
def exp(n1, n2):
return n1 ** n2
while True:
print('-'*60)
selectNum = int(input('1. 덧셈, 2. 뺄셈, 3. 곱셈, 4. 나눗셈, 5. 나머지, 6. 몫, 7. 제곱승, 8. 종료 : '))
if selectNum == 8:
print('Bye~')
break
num1 = float(input('첫 번째 숫자 입력 : '))
num2 = float(input('두 번째 숫자 입력 : '))
if selectNum == 1:
print(f'{num1} + {num2} = {add(num1, num2)}')
elif selectNum == 2:
print(f'{num1} - {num2} = {sub(num1, num2)}')
elif selectNum == 3:
print(f'{num1} * {num2} = {mul(num1, num2)}')
elif selectNum == 4:
print(f'{num1} / {num2} = {div(num1, num2)}')
elif selectNum == 5:
print(f'{num1} % {num2} = {mod(num1, num2)}')
elif selectNum == 6:
print(f'{num1} // {num2} = {flo(num1, num2)}')
elif selectNum == 7:
print(f'{num1} ** {num2} = {exp(num1, num2)}')
else:
print('잘못 입력했습니다. 다시 입력하세요.')
print('-' * 60)- 출력 결과
-
덧셈, 2. 뺄셈, 3. 곱셈, 4. 나눗셈, 5. 나머지, 6. 몫, 7. 제곱승, 8. 종료 : 1
첫 번째 숫자 입력 : 10
두 번째 숫자 입력 : 3.14
10.0 + 3.14 = 13.14 -
덧셈, 2. 뺄셈, 3. 곱셈, 4. 나눗셈, 5. 나머지, 6. 몫, 7. 제곱승, 8. 종료 : 2
첫 번째 숫자 입력 : 3.14
두 번째 숫자 입력 : 0.12
3.14 - 0.12 = 3.02 -
덧셈, 2. 뺄셈, 3. 곱셈, 4. 나눗셈, 5. 나머지, 6. 몫, 7. 제곱승, 8. 종료 : 3
첫 번째 숫자 입력 : 3
두 번째 숫자 입력 : 7
3.0 * 7.0 = 21.0 -
덧셈, 2. 뺄셈, 3. 곱셈, 4. 나눗셈, 5. 나머지, 6. 몫, 7. 제곱승, 8. 종료 : 4
첫 번째 숫자 입력 : 10
두 번째 숫자 입력 : 3
10.0 / 3.0 = 3.3333333333333335 -
덧셈, 2. 뺄셈, 3. 곱셈, 4. 나눗셈, 5. 나머지, 6. 몫, 7. 제곱승, 8. 종료 : 5
첫 번째 숫자 입력 : 10
두 번째 숫자 입력 : 3
10.0 % 3.0 = 1.0 -
덧셈, 2. 뺄셈, 3. 곱셈, 4. 나눗셈, 5. 나머지, 6. 몫, 7. 제곱승, 8. 종료 : 6
첫 번째 숫자 입력 : 10
두 번째 숫자 입력 : 3
10.0 // 3.0 = 3.0 -
덧셈, 2. 뺄셈, 3. 곱셈, 4. 나눗셈, 5. 나머지, 6. 몫, 7. 제곱승, 8. 종료 : 7
첫 번째 숫자 입력 : 10
두 번째 숫자 입력 : 3
10.0 ** 3.0 = 1000.0 -
덧셈, 2. 뺄셈, 3. 곱셈, 4. 나눗셈, 5. 나머지, 6. 몫, 7. 제곱승, 8. 종료 : 8
Bye~
2번
- 이동거리와 이동시간을 반환하는 함수를 만들어 보자.
# 거리(km) = 속도(km/h) * 시간(h)
def getDistance(speed, hour, minute):
Distance = speed * (hour + minute / 60)
return Distance
# 시간 100:75 = 60:x --> x = 75 * 60 / 100
def getTime(speed, distance):
time = distance / speed
h = int(time)
m = int((time - h) * 100 * 60 / 100)
return [h, m]
print('-'*60)
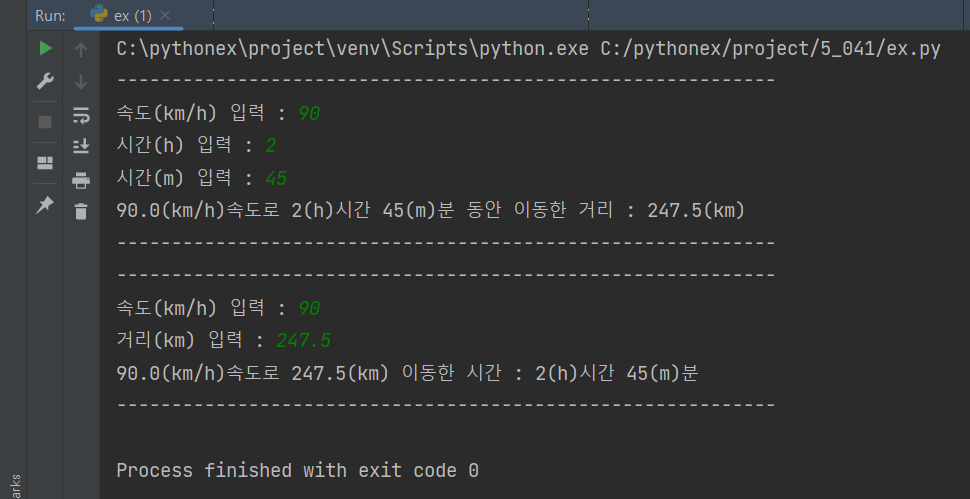
s = float(input('속도(km/h) 입력 : '))
h = float(input('시간(h) 입력 : '))
m = float(input('시간(m) 입력 : '))
d = getDistance(s, h, m)
print(f'{s}(km/h)속도로 {int(h)}(h)시간 {int(m)}(m)분 동안 이동한 거리 : {d}(km) ')
print('-'*60)
print('-'*60)
s = float(input('속도(km/h) 입력 : '))
d = float(input('거리(km) 입력 : '))
t = getTime(s, d)
print(f'{s}(km/h)속도로 {d}(km) 이동한 시간 : {t[0]}(h)시간 {t[1]}(m)분 ')
print('-'*60)- 출력결과
3번
- 비행기 티켓 영수증 출력 함수를 만들어 보자.
childPrice = 18000
infantPrice = 25000
adultPrice = 50000
specialDC = 50
def formetedNumber(n):
return format(n, ',')
def printAirPlaneReceipt(c1, c2, i1, i2, a1, a2):
cp = c1 * childPrice
cp_dc = int(c2 * childPrice * 0.5)
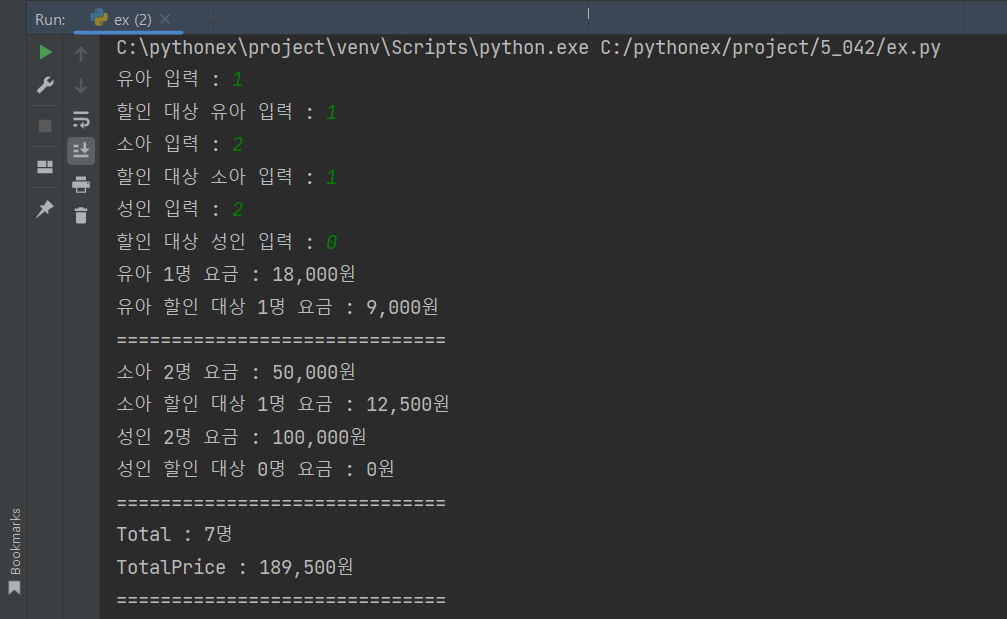
print(f'유아 {c1}명 요금 : {formetedNumber(cp)}원')
print(f'유아 할인 대상 {c2}명 요금 : {formetedNumber(cp_dc)}원')
ip = i1 * infantPrice
ip_dc = int(i2 * infantPrice * 0.5)
print('=' * 30)
print(f'소아 {i1}명 요금 : {formetedNumber(ip)}원')
print(f'소아 할인 대상 {i2}명 요금 : {formetedNumber(ip_dc)}원')
ap = a1 * adultPrice
ap_dc = int(a2 * adultPrice * 0.5)
print(f'성인 {a1}명 요금 : {formetedNumber(ap)}원')
print(f'성인 할인 대상 {a2}명 요금 : {formetedNumber(ap_dc)}원')
print('=' * 30)
print(f'Total : {c1 + c2 + i1 + i2 + a1 + a2}명')
print(f'TotalPrice : {formetedNumber(cp + cp_dc + ip + ip_dc + ap + ap_dc)}원')
print('=' * 30)
childCnt = int(input('유아 입력 : '))
specialDCChildCnt = int(input('할인 대상 유아 입력 : '))
infantCnt = int(input('소아 입력 : '))
specialDCInfantCnt = int(input('할인 대상 소아 입력 : '))
adultCnt = int(input('성인 입력 : '))
specialDCAdultCnt = int(input('할인 대상 성인 입력 : '))
printAirPlaneReceipt(childCnt, specialDCChildCnt, infantCnt,
specialDCInfantCnt, adultCnt, specialDCAdultCnt)
4번
- 재귀함수를 이용해서 팩토리얼 함수를 만들어보자.
def fNumber(n):
return format(n, ',')
def recursionFun(n):
if n == 1:
return n
return n * recursionFun(n-1)
inputnumber = int(input('input Number : '))
print(fNumber(recursionFun(inputnumber)))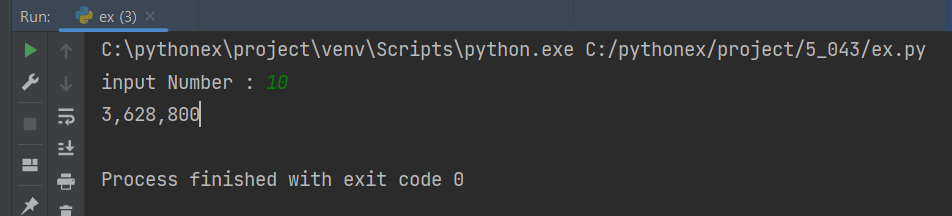
4-1번
- 단리/월복리 계산기 함수를 만들어보자.
def fNumber(n):
return format(n, ',')
# 단리
def singleRateCalculator(m, t, r):
totalMoney = 0
totalRateMoney = 0
for i in range(t):
totalRateMoney += m * (r * 0.01)
totalMoney = m + totalRateMoney
return fNumber(int(totalMoney))
# 월복리
def multiRateCalculator(m, t, r):
t = t * 12
rpm = (r / 12) * 0.01
totalMoney = m
for i in range(t):
totalMoney += totalMoney * rpm
return fNumber(int(totalMoney))
money = int(input('예치금(원) : '))
term = int(input('기간(년) : '))
rate = int(input('연 이율(%) : '))
print('-'*30)
print('[단리 계산기]')
print(f'{term}년 후 총 수령액 : {singleRateCalculator(money, term, rate)}')
print('-'*30)
print('[월복리 계산기]')
print(f'{term}년 후 총 수령액 : {multiRateCalculator(money, term, rate)}')
print('-'*30)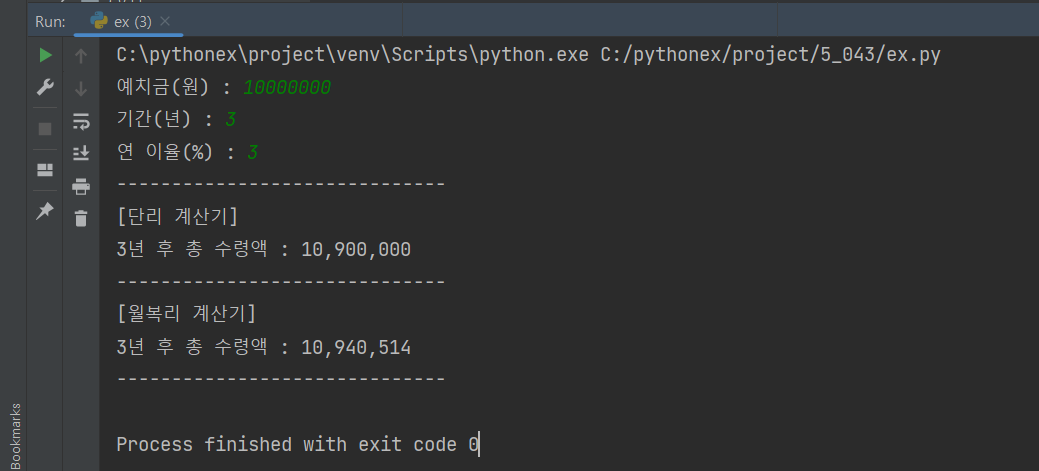
5번
- 등차 수열의 n번째 값과 합을 출력하는 함수를 만들어보자.
# 등차 수열 공식 : an = a1 + (n-1) * d
# 등차 수열 합 공식 : sn = n * (a1 + an) / 2
def sequenceCal(n1, d, n):
valueN = 0; sumN = 0;
i = 1
while i <= n:
if i == 1:
valueN = n1
sumN += valueN
print(f'{i}번째 항의 값 : {valueN}')
print(f'{i}번째 항까지의 합 : {sumN}')
i += 1
continue
valueN += d
sumN += valueN
print(f'{i}번째 항의 값 : {valueN}')
print(f'{i}번째 항까지의 합 : {sumN}')
i += 1
inputN1 = int(input('a1 입력 : '))
inputD = int(input('공차 입력 : '))
inputN = int(input('n 입력 : '))
sequenceCal(inputN1, inputD, inputN)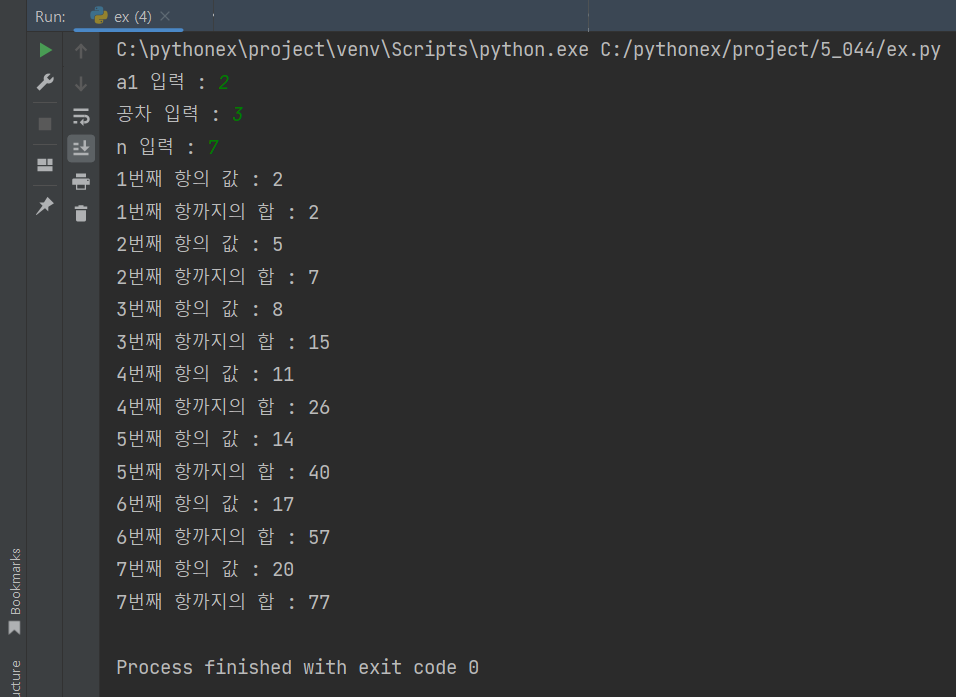
6번
- 등비 수열의 n번째 값과 합을 출력하는 함수를 만들어보자.
# 등비 수열(일반항) 공식 : an = a1 * r^(n-1)
# 등비 수열(합) 공식 : an = a1 * (1-r^n) / (1-r)
def sequenceCal(n1, r, n):
valueN = 0; sumN = 0;
i = 1
while i <= n:
if i == 1:
valueN = n1
sumN = valueN
print(f'{i}번째 항의 값 : {valueN}')
print(f'{i}번째 항까지의 합 : {sumN}')
i += 1
continue
valueN *= r
sumN += valueN
print(f'{i}번째 항의 값 : {valueN}')
print(f'{i}번째 항까지의 합 : {sumN}')
i += 1
inputN1 = int(input('a1 입력 : '))
inputR = int(input('공비 입력 : '))
inputN = int(input('n 입력 : '))
sequenceCal(inputN1, inputR, inputN)
모듈
7번
- 과목별 점수를 입력하면 합격 여부를 출력하는 모듈을 만들어보자.
# 출력하는 모듈 생성
def exampleResult(s1, s2, s3, s4, s5):
passAvgScore = 60; limitScore = 40;
def getTotal():
totalScore = s1 + s2 + s3 + s4 + s5
print(f'총점 : {totalScore}')
return totalScore
def getAverage():
avg = getTotal() / 5
print(f'평균 : {avg}')
return avg
def printPassOrFail():
# for num in s:
print(f'{s1}: Pass') if s1 >= limitScore else print(f'{s1}: Fail')
print(f'{s2}: Pass') if s2 >= limitScore else print(f'{s2}: Fail')
print(f'{s3}: Pass') if s3 >= limitScore else print(f'{s3}: Fail')
print(f'{s4}: Pass') if s4 >= limitScore else print(f'{s4}: Fail')
print(f'{s5}: Pass') if s5 >= limitScore else print(f'{s5}: Fail')
def printFinalPassOrFail():
if getAverage() >= passAvgScore:
if s1 >= limitScore and s2 >= limitScore and s3 >= limitScore and s4 >= limitScore and s5 >= limitScore:
print('Final Pass!!')
else:
print('Final Fail!!')
else:
print('Final Fail!!')
getAverage()
printPassOrFail()
printFinalPassOrFail()# 생성된 모듈을 사용하는 코드
import passOrFail as pf
if __name__ == '__main__':
sub1 = int(input('과목1 점수 입력 : '))
sub2 = int(input('과목2 점수 입력 : '))
sub3 = int(input('과목3 점수 입력 : '))
sub4 = int(input('과목4 점수 입력 : '))
sub5 = int(input('과목5 점수 입력 : '))
pf.exampleResult(sub1, sub2, sub3, sub4, sub5)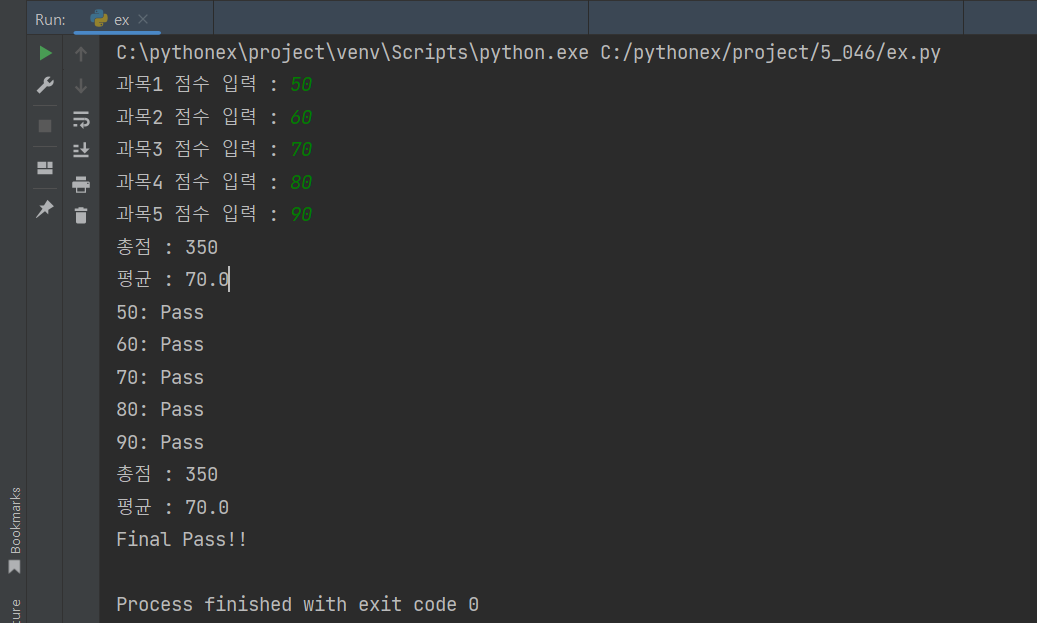
8번
- 상품 구매 개수에 따라 할인율이 결정되는 모듈을 만들고, 다음과 같이 계산 결과가 출력되는 프로그램을 만들어보자.
# 모듈
def fNumber(n):
return format(n, ',')
def calculatorTotalPrice(gs):
if len(gs) <= 0:
print('구매 상품이 없습니다.')
return
rate = 25
totalPrice = 0
rates = {1:5, 2:10, 3:15, 4:20}
if len(gs) in rates:
rate = rates[len(gs)]
# 매개변수로 들어온 리스트의 길이를 확인할수 있는 len함수를 이용하여 횟수를
# 구하고 그횟수에 맞는 할인률을 딕셔너리로 대조해여 출력하는 방법
for g in gs:
totalPrice += g * (1 - rate * 0.01)
return [rate, fNumber(int(totalPrice))]# 사용 코드
import discount as dc
if __name__ == '__main__':
gs = []
while True:
selectNumber = int(input('1. 구매, 2. 종료 : '))
if selectNumber == 1:
goods_price = int(input('상품 가격 입력 : '))
gs.append(goods_price)
elif selectNumber == 2:
result = dc.calculatorTotalPrice(gs)
break
print(f'할인율 : {result[0]}%')
print(f'합계 : {result[1]}원')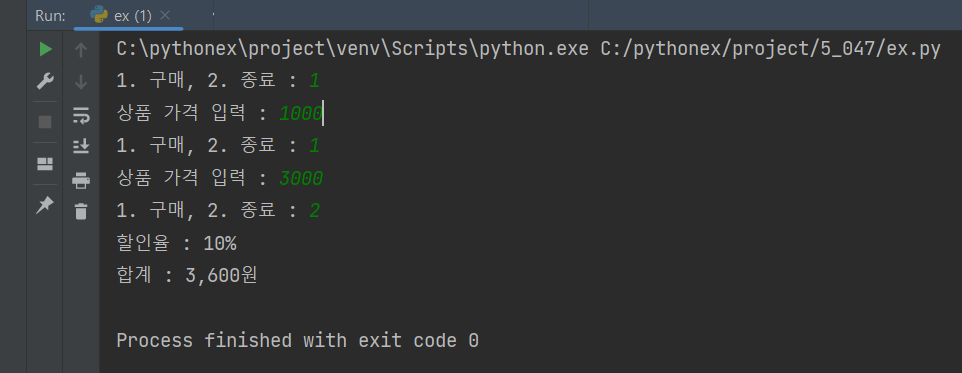
9번
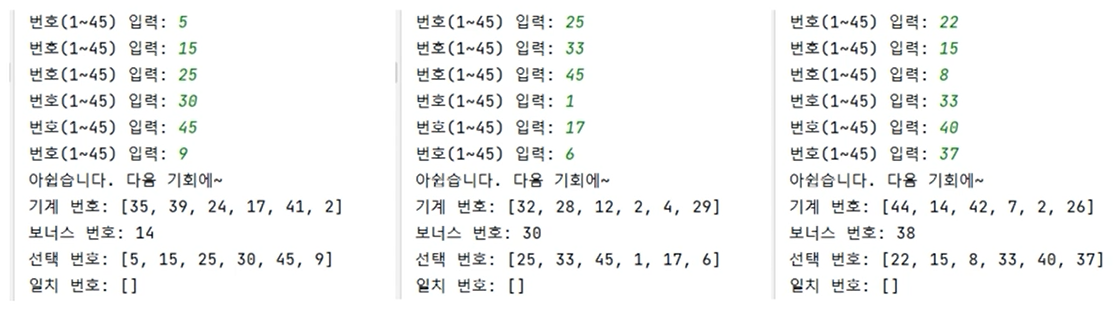
- 로또 모듈을 만들고 다음과 같이 로또 결과가 출력될 수 있도록 프로그램을 만들어보자.
# 모듈
import random
userNums = []; randNums = []; collNums = [];
randBonuNum = 0
def setUserNums(ns):
global userNums
userNums = ns
def getUserNums():
return userNums
def setRandNums():
global randNums
randNums = random.sample(range(1,46), 6)
def getRandNums():
return randNums
def setBonuNums():
global randBonuNum
while True:
randBonuNum = random.randint(1, 45)
if randBonuNum not in randNums:
break
def getBonuNums():
return randBonuNum
def lottoResult():
global userNums
global randNums
global collNums
collNums = []
for un in userNums:
if un in randNums:
collNums.append(un)
if len(collNums) == 6:
print('1등 당첨!!')
print(f'번호 : {collNums}')
elif (len(collNums) == 5) and (randBonuNum in userNums):
print('2등 당첨!!')
print(f'번호 : {collNums}, 보너스 번호 : {randBonuNum}')
elif len(collNums) == 5:
print('3등 당첨!!')
print(f'번호 : {collNums}')
elif len(collNums) == 4:
print('4등 당첨!!')
print(f'번호 : {collNums}')
elif len(collNums) == 3:
print('5등 당첨!!')
print(f'번호 : {collNums}')
else:
print('아쉽습니다. 다음 기회에~')
print(f'기계 번호 : {randNums}')
print(f'보너스 번호 : {randBonuNum}')
print(f'선택 번호 : {userNums}')
print(f'일치 번호 : {collNums}')
def startLottol():
n1 = int(input('번호(1~45) 입력 : '))
n2 = int(input('번호(1~45) 입력 : '))
n3 = int(input('번호(1~45) 입력 : '))
n4 = int(input('번호(1~45) 입력 : '))
n5 = int(input('번호(1~45) 입력 : '))
n6 = int(input('번호(1~45) 입력 : '))
selectNums = [n1, n2, n3, n4, n5, n6]
setUserNums(selectNums)
setRandNums()
setBonuNums()
lottoResult()# 위에서 만들었던 모듈을 실행하여 로또 마춰보기
import lotto as lt
lt.startLottol()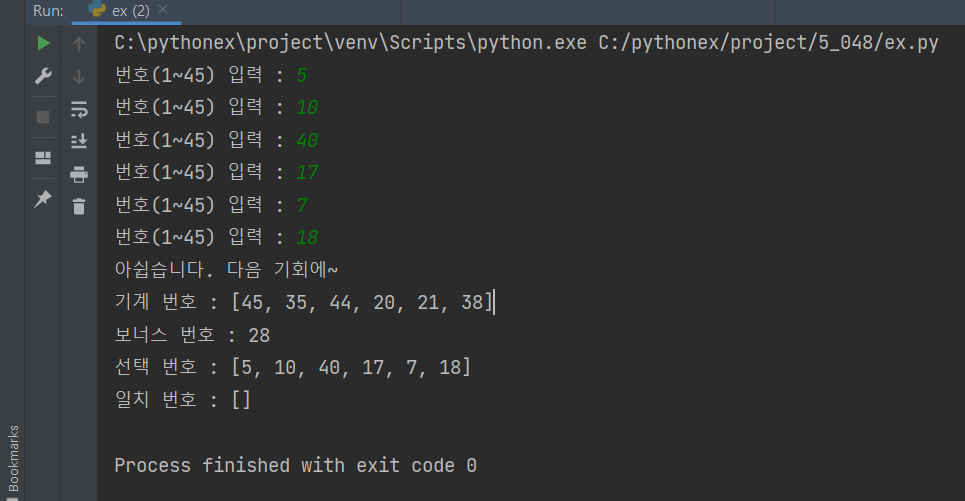 역시 일치 숫자는 없다.
역시 일치 숫자는 없다.
10번
- 순열 계산 모듈을 만들고 다음 순열 계산결과를 출력해 보자.

def getParmutationCnt(n, r):
result = 1
for n in range(n, (n-r), -1):
result = result * n
return result
from itertools import permutations
def getPermutations(ns, r):
pList = list(permutations(ns,r))
print(f'{len(ns)}P{r} 개수 : {len(pList)}')
for n in permutations(ns, r):
print(n, end='')import permutation as pt
listVar = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
rVar = 3
pt.getPermutations(listVar, rVar)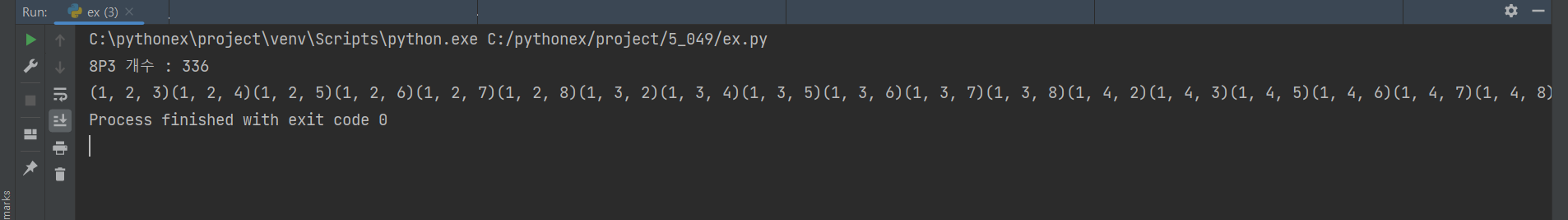
11번
- 조합 계산 모듈을 만들고 다음 조합 계산 결과를 출력해 보자.

def getCombinationCnt(n, r, logPrint = True):
# 로그를 보고싶다면 getCombinationCnt(n, r, logPrint = True)
# 인수에 logPrint = True를 추가하면된다.
resultP = 1
resultR = 1
resultC = 1
for n in range(n, (n-r), -1):
resultP = resultP * n
if logPrint : print(f'resultP : {resultP}') # logPrint로 로그데이터 출력할경우
for n in range(r, 0, -1):
resultR = resultR * n
if logPrint: print(f'resultR : {resultR}') # logPrint로 로그데이터 출력할경우
resultC = int(resultP / resultR)
if logPrint: print(f'resultC : {resultC}') # logPrint로 로그데이터 출력할경우
return resultCimport combination as ct
numN = int(input('numN 입력 : '))
numR = int(input('numR 입력 : '))
print(f'{numN}C{numR} : {ct.getCombinationCnt(numN, numR)} ')
# 로그데이터 출력을 하고싶지않다면 getCombinationCnt(numN, numR, logPrint = False)
# 매개변수 항목에 logPrint = False로 입력해주면 된다.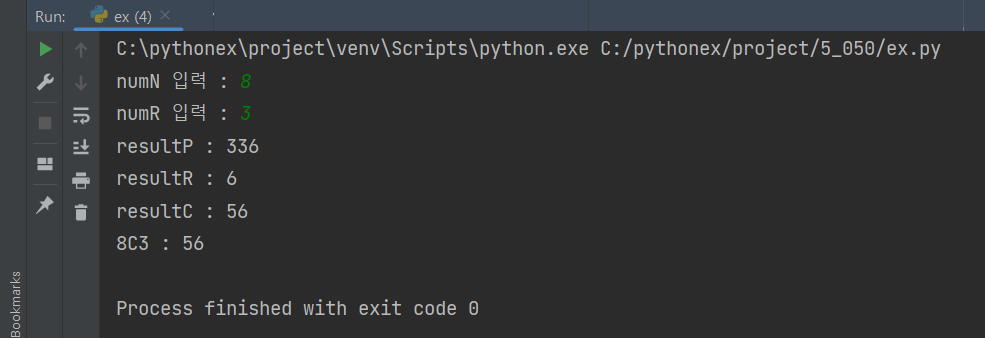
lohPrint = True로 출력을 하여서 데이터가 출력된걸 확인할 수 있다.
12번
- 수입과 공과금을 입력하면 공과금 총액과 수입 대비 공과금 비율을 계산하는 모듈을 만들어보자.
income = 0
waterPrice = 0; electicPrice = 0; gasPrice = 0;
# 각각 수도세, 전기세, 가스비
def setIncome(ic):
global income
income = ic
def getIncome():
return income
def setWaterPrice(wp):
global waterPrice
waterPrice = wp
def getWaterPrice():
return waterPrice
def setElecticPrice(ep):
global electicPrice
electicPrice = ep
def getElecticPrice():
return electicPrice
def setGasPrice(gp):
global gasPrice
gasPrice = gp
def getGasPrice():
return gasPrice
def getUtillityBill(): # 공과금의 합계
result = waterPrice + electicPrice + gasPrice
return result
def getUtillityBillRate(): # 수입 대비 비율
result = int(getUtillityBill()) / getIncome() * 100
return resultimport utillityBill as ub
def formetN(n):
return format(n, ',')
inputIncome = int(input('수입 입력 : '))
ub.setIncome(inputIncome)
inputWaterPrice = int(input('수도요금 입력 : '))
ub.setWaterPrice(inputWaterPrice)
inputElectricPrice = int(input('전기요금 입력 : '))
ub.setElecticPrice(inputElectricPrice)
inputGasPrice = int(input('가스요금 입력 : '))
ub.setGasPrice(inputGasPrice)
uub = ub.getUtillityBill()
uur = ub.getUtillityBillRate()
print(f'공과금 : {formetN(uub)}원')
print(f'수입 대비 공과금 비율 : {formetN(uur)}%')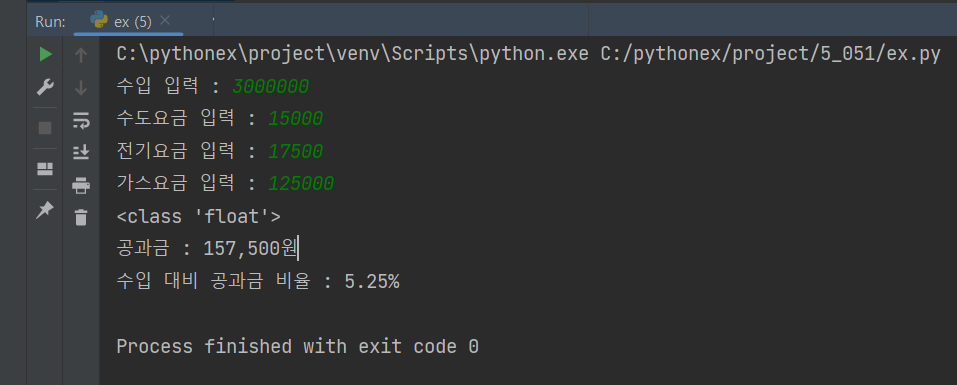
13번
- 다음과 같이 패키지와 모듈을 만들고 연산 결과를 출력해보자.
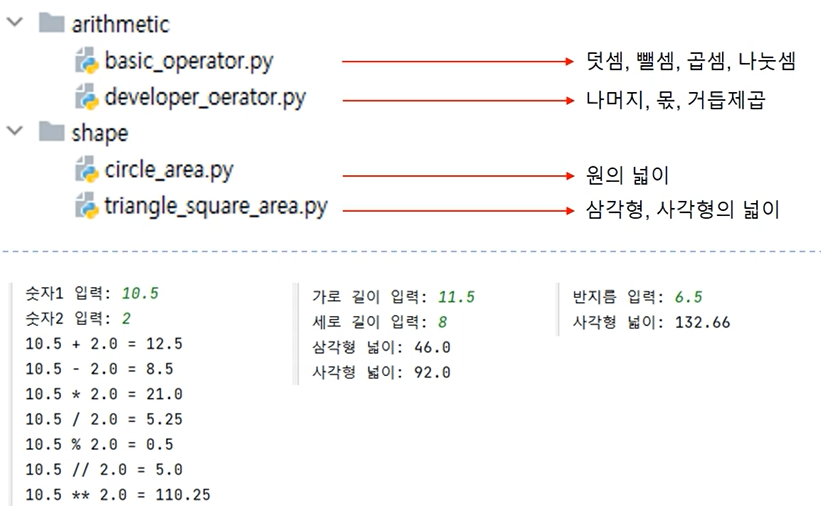
#덧셈, 뺄셈, 곱셈, 나눗셈 모듈
def add(n1, n2):
return round(n1 + n2, 2)
def sub(n1, n2):
return round(n1 - n2, 2)
def mul(n1, n2):
return round(n1 * n2, 2)
def div(n1, n2):
return round(n1 / n2, 2)
# 나머지, 몫, 거듭제곱 모듈
def mod(n1, n2):
return round(n1 % n2, 2)
def flo(n1, n2):
return round(n1 // n2, 2)
def exp(n1, n2):
return round(n1 ** n2, 2)
# 삼각형, 사각형의 넓이 모듈
def calTriangleArea(w, h):
return round(w * h / 2, 2)
def claSquareArea(w, h):
return round(w * h, 2)
# 원의 넓이 모듈
def calCircleArea(r):
return round(r ** 2 * 3.14, 2)# 모듈을 불러와서 출력하는 코드
from arithmetic import basic_operator as bo
from arithmetic import developer_operator as do
from shape import triangle_square_area as tsa
from shape import circle_area as ca
inputNumber1 = float(input('숫자1 입력 : '))
inputNumber2 = float(input('숫자2 입력 : '))
print(f'{inputNumber1} + {inputNumber2} = {bo.add(inputNumber1,inputNumber2)}')
print(f'{inputNumber1} - {inputNumber2} = {bo.sub(inputNumber1,inputNumber2)}')
print(f'{inputNumber1} * {inputNumber2} = {bo.mul(inputNumber1,inputNumber2)}')
print(f'{inputNumber1} / {inputNumber2} = {bo.div(inputNumber1,inputNumber2)}')
print(f'{inputNumber1} % {inputNumber2} = {do.mod(inputNumber1,inputNumber2)}')
print(f'{inputNumber1} // {inputNumber2} = {do.flo(inputNumber1,inputNumber2)}')
print(f'{inputNumber1} ** {inputNumber2} = {do.exp(inputNumber1,inputNumber2)}')
inputWidth = float(input('가로 입력 : '))
inputHeight = float(input('세로 입력 : '))
print(f'삼각형 넓이 : {tsa.calTriangleArea(inputWidth, inputHeight)}')
print(f'사각형 넓이 : {tsa.claSquareArea(inputWidth, inputHeight)}')
inputRadius = float(input('반지름 입력 : '))
print(f'원의 넓이 : {ca.calCircleArea(inputRadius)}')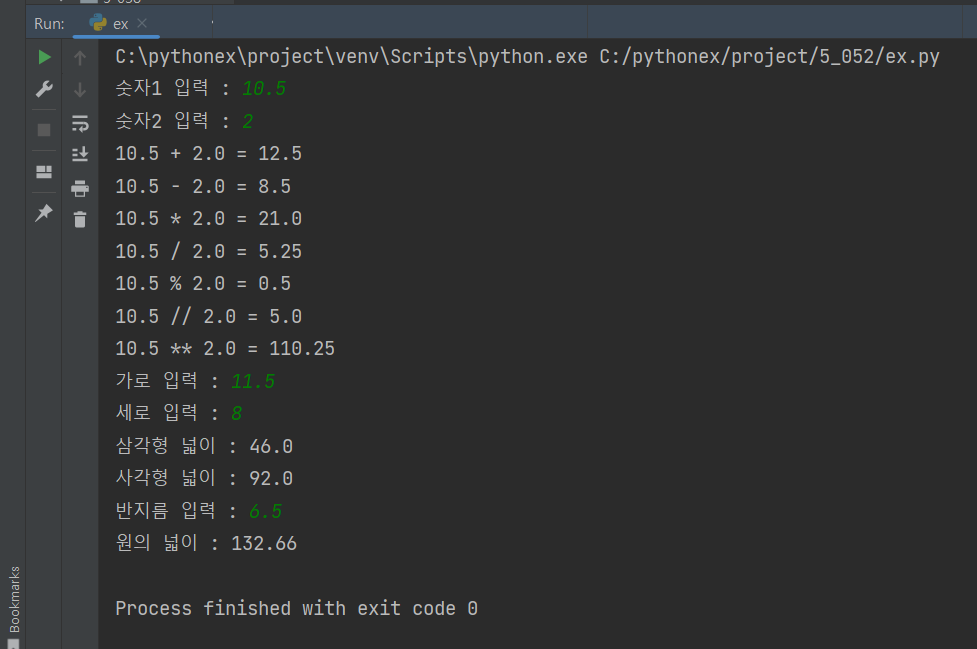
클래스
14번
- 회원가입 클래스와 회원정보를 관리하는 클래스를 만들고 회원가입 로그인 기능을 구현해 보자.
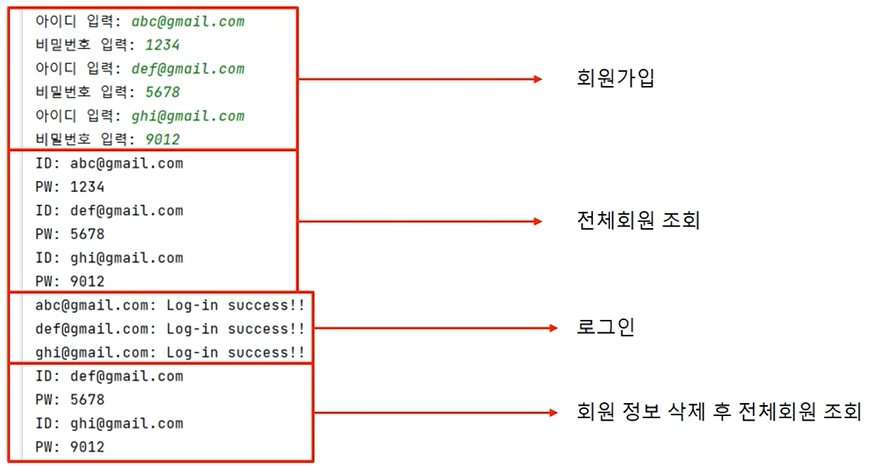
class Member:
def __init__(self, i, p):
self.id = i
self.pw = p
class MemberRestory:
def __init__(self):
self.members = {}
def addMember(self, m):
self.members[m.id] = m.pw
def loginMember(self, i, p):
isMember = i in self.members
if isMember and self.members[i] == p:
print(f'{i} : log-in success!!')
else:
print(f'{i} : log-in fail!!')
def removeMember(self, i, p):
del self.members[i]
def printMembers(self):
for mk in self.members.keys():
print(f'ID : {mk}')
print(f'PW : {self.members[mk]}')import member as mb
mems = mb.MemberRestory()
for i in range(3):
mId = input('아이디 입력 : ')
mPw = input('비밀번호 입력 : ')
mem = mb.Member(mId, mPw)
mems.addMember(mem)
mems.printMembers() # 로그인한 회원정보 출력
mems.loginMember('abc@gmail.com', '1234') # 회원정보 확인용
mems.loginMember('bed@gmail.com', '5678') # 회원정보 확인용
mems.loginMember('hifg@gmail.com', '9012') # 회원정보 확인용
mems.removeMember('abc@gmail.com', '1234') # 아이디 패스워드 정보 삭제
mems.printMembers() # 삭제된 정보를 제외하고 출력된걸 확인할수 있다.
15번
- TV클래스를 다음과 같은 상속 구조로 만들고 객체를 생성해 보자.
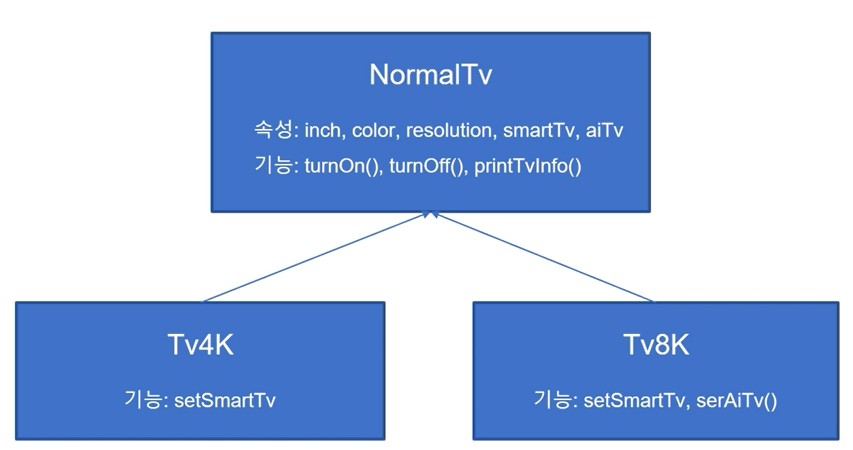
class NormalTv:
def __init__(self, i=32, c='black', r='full-HD'):
self.inch = i
self.color = c
self.resolution = r
self.smartTv = 'off'
self.aiTv = 'off'
def turnOn(self):
print('TV power on!!')
def turnOff(self):
print('TV power Off!!')
def printTvInfo(self):
print(f'inch : {self.inch}inch')
print(f'color : {self.color}')
print(f'resolution : {self.resolution}')
print(f'smartTv : {self.smartTv}')
print(f'aiTv : {self.aiTv}')
class Tv4k(NormalTv):
def __init__(self, i, c, r='4k'):
super().__init__(i,c,r)
def setSmartTv(self,s):
self.smartTv = s
class Tv8k(NormalTv):
def __init__(self, i, c, r='8k'):
super().__init__(i, c, r)
def setSmartTv(self, s):
self.smartTv = s
def setAiTv(self, a):
self.smartTv = aimport smartTV as st
# my4kTv = st.Tv4k('65', 'silver', '4k')
# my4kTv.setSmartTv('on')
# my4kTv.turnOn()
# my4kTv.printTvInfo()
# my4kTv.turnOff()
# print('-'*25)
# friend4kTv = st.Tv4k('55', 'white', '4k')
# friend4kTv.setSmartTv('off')
# friend4kTv.turnOn()
# friend4kTv.printTvInfo()
# friend4kTv.turnOff()
my8kTv = st.Tv8k('75', 'black', '8k')
my8kTv.setSmartTv('on')
my8kTv.setAiTv('on')
my8kTv.turnOn()
my8kTv.printTvInfo()
my8kTv.turnOff()
print('-'*25)
friend8kTv = st.Tv8k('86', 'red', '8k')
friend8kTv.setSmartTv('on')
friend8kTv.setAiTv('off')
friend8kTv.turnOn()
friend8kTv.printTvInfo()
friend8kTv.turnOff()
16번
- 다음 명세서를 참고해서 도서 관리 프로그램을 만들어보자.

class Book:
def __init__(self,name, price, isbn):
self.bName = name
self.bPrice = price
self.bIsbn = isbn
class BookRepository:
def __init__(self):
self.bDic = {}
def registBook(self, b): #bDic에 책을 저장해주기
self.bDic[b.bIsbn] = b
def removeBook(self, isbn): #bDic에서 책을 삭제해주기
del self.bDic[isbn]
def printBooksInfo(self): # 전체 도서를 출력하기
for isbn in self.bDic.keys():
b = self.bDic[isbn]
print(f'{b.bName}, {b.bPrice}, {b.bIsbn}')
def printBookInfo(self, isbn): # 도서 한권만 출력하기
if isbn in self.bDic:
b = self.bDic[isbn]
print(f'{b.bName}, {b.bPrice}, {b.bIsbn}')
else:
print('Lookup result does not exist.')import book as bk
myBRepository = bk.BookRepository()
myBRepository.registBook(bk.Book('python',20000, '1234567890'))
myBRepository.registBook(bk.Book('java',25000, '6543210987'))
myBRepository.registBook(bk.Book('c/c++',27000, '0987654321'))
myBRepository.printBooksInfo()
print('-'*25)
myBRepository.printBookInfo('6543210987')
myBRepository.printBookInfo('1234567890')
myBRepository.removeBook('1234567890')
print()
myBRepository.printBooksInfo()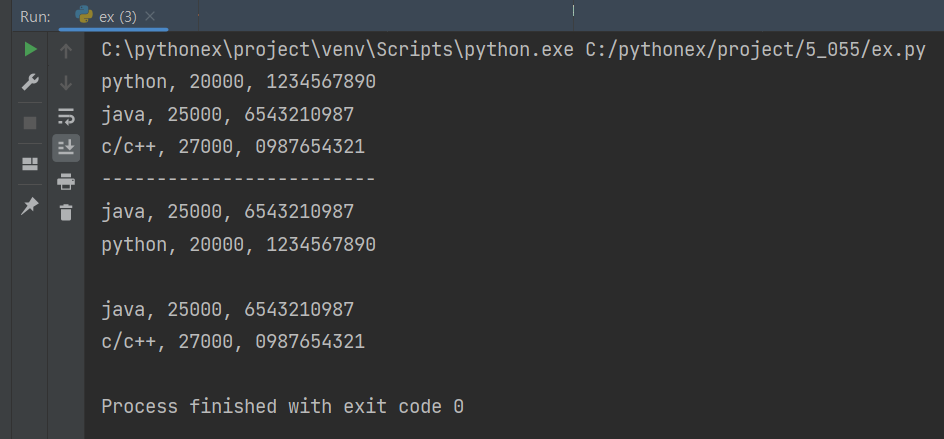
17번
- 다음 추상 클래스를 이용해서 한/영, 한/일 사전 클래스를 만들어보자.
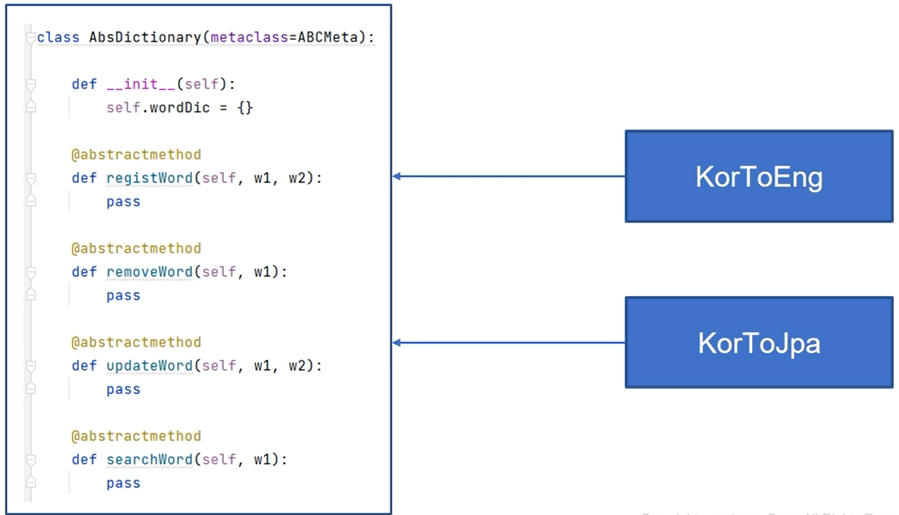
from abc import ABCMeta
from abc import abstractmethod
class AbsDictionar(metaclass=ABCMeta):
def __init__(self):
self.wordDic = {}
@abstractmethod
def registWord(self, w1, w2):
pass
@abstractmethod
def removeWord(self, w1):
pass
@abstractmethod
def updateWord(self, w1, w2):
pass
@abstractmethod
def searchWord(self, w1):
pass
class KorToEng(AbsDictionar):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def registWord(self, w1, w2):
print(f'[KorToEng] registWord() : {w1} to {w2}')
self.wordDic[w1] = w2
def removeWord(self, w1):
print(f'[KorToEng] removeWord() : {w1}')
del self.wordDic[w1]
def updateWord(self, w1, w2):
print(f'[KorToEng] updateWord() : {w1} to {w2}')
self.wordDic[w1] = w2
def searchWord(self, w1):
print(f'[KorToEng] searchWord() : {w1}')
return self.wordDic[w1]
def printWords(self):
for k in self.wordDic.keys():
print(f'{k} : {self.wordDic[k]}')
class KorToJpa(AbsDictionar):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def registWord(self, w1, w2):
print(f'[KorToJpa] registWord() : {w1} to {w2}')
self.wordDic[w1] = w2
def removeWord(self, w1):
print(f'[KorToJpa] removeWord() : {w1}')
del self.wordDic[w1]
def updateWord(self, w1, w2):
print(f'[KorToJpa] updateWord() : {w1} to {w2}')
self.wordDic[w1] = w2
def searchWord(self, w1):
print(f'[KorToJpa] searchWord() : {w1}')
return self.wordDic[w1]
def printWords(self):
for k in self.wordDic.keys():
print(f'{k} : {self.wordDic[k]}')import ADictionary as dic
kTe = dic.KorToEng()
kTe.registWord('책', 'bok')
kTe.registWord('나비', 'butterfly')
kTe.registWord('연필', 'pencil')
kTe.registWord('학생', 'student')
kTe.registWord('선생님', 'teacher')
kTe.printWords() # 전체 출력하기
kTe.updateWord('책', 'book') # 수정하기
kTe.printWords()
print(f'학생 : {kTe.searchWord("학생")}')
kTe.removeWord('책') # 삭제하기
kTe.printWords()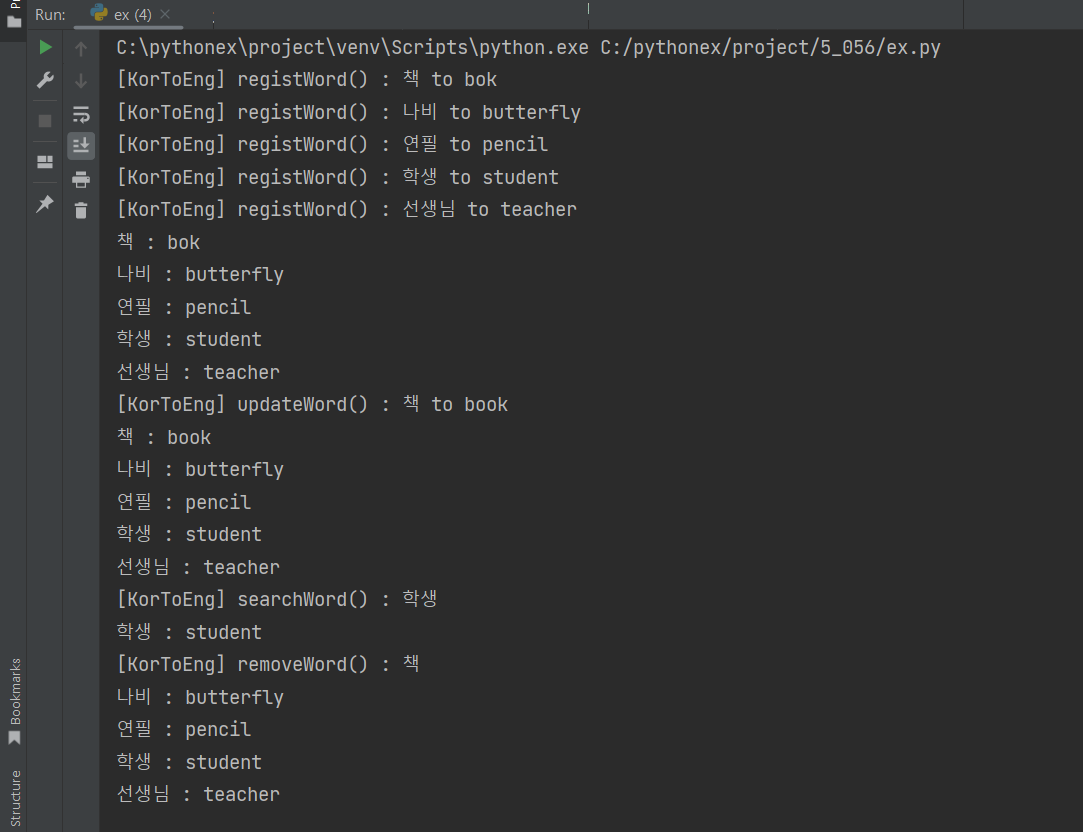
18번
- 주사위 게임 클래스를 만들고 컴퓨터와 사용자의 게임 결과를 출력해 보자.

import random as rd
class Dice:
def __init__(self):
self.cNum = 0
self.uNum = 0
def setCnum(self):
print('[Dice] setCnum()')
self.cNum = rd.randint(1, 6)
def setUnum(self):
print('[Dice] setUnum()')
self.uNum = rd.randint(1, 6)
def startGame(self):
print('[Dice] startGame()')
self.setCnum()
self.setUnum()
def printResult(self):
print('[Dice] printResult()')
if self.cNum == 0 or self.uNum == 0:
print('주사위 숫자 설정 전 입니다.')
else:
if self.cNum > self.uNum:
print(f'컴퓨터 vs 유저 : {self.cNum} vs {self.uNum} >> 컴퓨터 승!!')
elif self.cNum < self.uNum:
print(f'컴퓨터 vs 유저 : {self.cNum} vs {self.uNum} >> 유저 승!!')
elif self.cNum == self.uNum:
print(f'컴퓨터 vs 유저 : {self.cNum} vs {self.uNum} >> 무승부!!')import dice
dc = dice.Dice()
dc.startGame()
dc.printResult()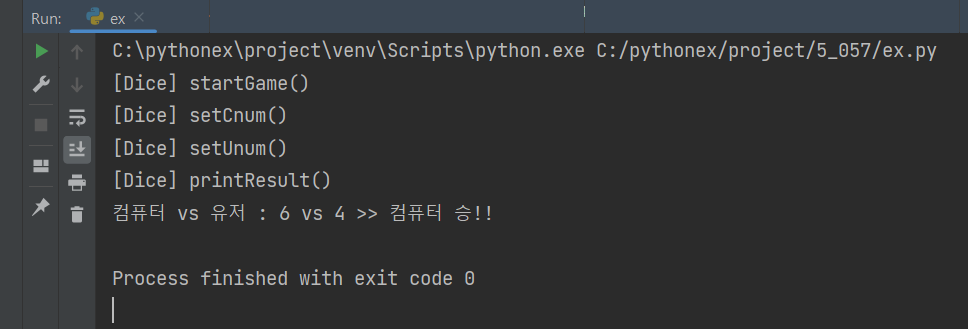
19번
- 자동차 경주 게임 클래스를 만들어 보자. 자동차는 랜덤하게 이동하며, 편의상 10초 동안 주행한다고 할 때 가장 멀리 이동한 자동차가 우승하는 게임이다.
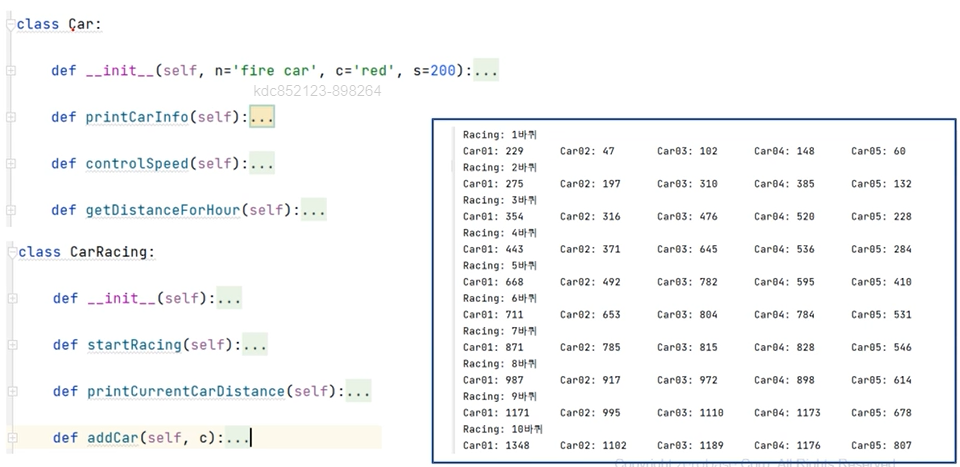
# car 모듈
import random
class Car:
def __init__(self, n='fire car', c='red', s=200):
self.name = n
self.color = c
self.max_speed = s
self.distance = 0
def printCarInfo(self):
print(f'name : {self.name}, color : {self.color}, max_speed : {self.max_speed}')
def controlSpeed(self):
return random.randint(0, self.max_speed)
def getDistanceForHour(self):
return self.controlSpeed() * 1
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# racing모듈
from time import sleep
class CarRacing:
def __init__(self):
self.cars = []
self.rankings = []
def startRacing(self):
for i in range(10):
print(f'Racing : {i+ 1}바퀴')
for car in self.cars:
car.distance += car.getDistanceForHour()
sleep(1)
self.printCurrentCarDistance()
def printCurrentCarDistance(self):
for car in self.cars:
print(f'{car.name} : {car.distance} \t\t', end='')
print()
def addCar(self, c):
self.cars.append(c)# 모듈의 실행
from car_game import racing as rc
from car_game import car
myCarGame = rc.CarRacing()
Car01 = car.Car('Car01', 'White', 250)
Car02 = car.Car('Car02', 'Black', 200)
Car03 = car.Car('Car03', 'Yellow', 220)
Car04 = car.Car('Car04', 'Red', 280)
Car05 = car.Car('Car05', 'Blue', 150)
myCarGame.addCar(Car01)
myCarGame.addCar(Car02)
myCarGame.addCar(Car03)
myCarGame.addCar(Car04)
myCarGame.addCar(Car05)
myCarGame.startRacing()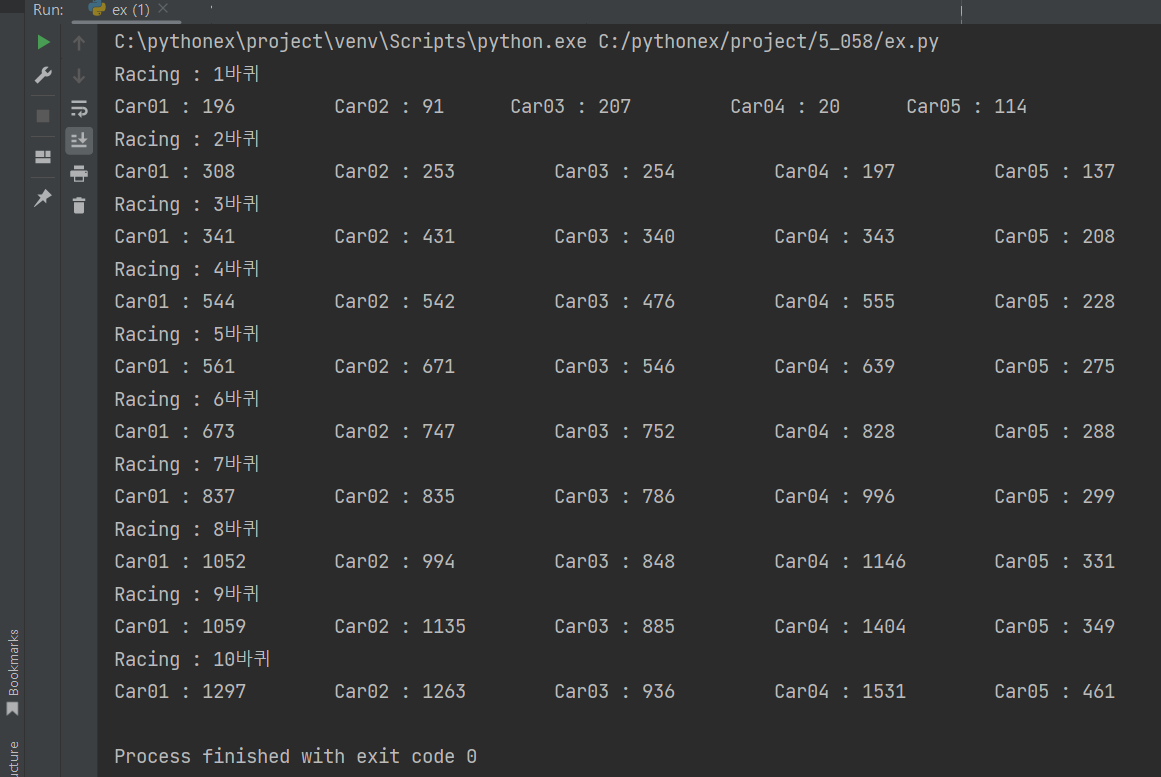
20번
- 다음과 같이 mp3 플레이어 클래스를 만들고 노래 등록 후 재생해보자.

from time import sleep
import random
class Song:
def __init__(self, t, s, pt):
self.title = t
self.singer = s
self.play_time = pt
def printSongInfo(self): # 음악 정보 불러오기
print(f'Title : {self.title}, Singer : {self.singer}, Play_time : {self.play_time}')
class Player:
def __init__(self):
self.songList = []
self.isLoop = False
def addSong(self,s): # 목록에 음악을 추가해주는 함수
self.songList.append(s)
def play(self): # 음악 목록 대로 반복재생 시켜주는 함수
if self.isLoop:
while self.isLoop:
for s in self.songList:
print(f'Title : {s.title}, Singer : {s.singer}, Play_time : {s.play_time}sec')
sleep(s.play_time)
else:
for s in self.songList:
print(f'Title : {s.title}, Singer : {s.singer}, Play_time : {s.play_time}sec')
sleep(s.play_time)
def suffle(self): # 음악 목록을 섞어주는 함수
random.shuffle(self.songList)
def setIsLoop(self, flag):
self.isLoop = flagimport mp3player as mp3
s1 = mp3.Song('신호등', '이무진', 3)
s2 = mp3.Song('Permission', '방탄소년단', 4)
s3 = mp3.Song('Butter', '방탄소년단', 2)
s4 = mp3.Song('Weekend', 'TAEYON', 5)
s5 = mp3.Song('좋아좋아', '조정석', 4)
player = mp3.Player()
player.addSong(s1)
player.addSong(s2)
player.addSong(s3)
player.addSong(s4)
player.addSong(s5)
player.setIsLoop(False) # True 로 바꿔주면 무한 반복에 빠진다.
player.suffle()
player.play()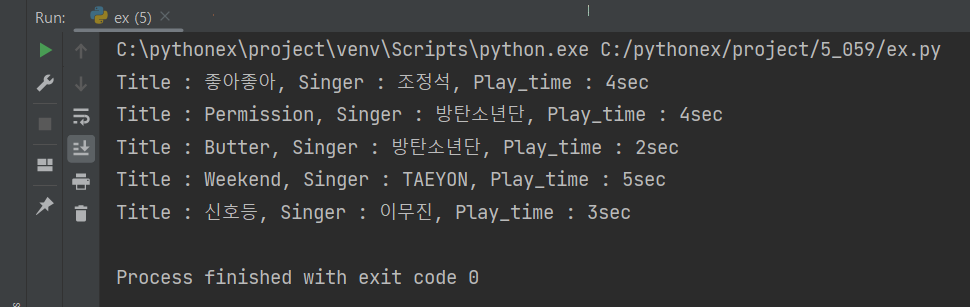
예외처리
21번
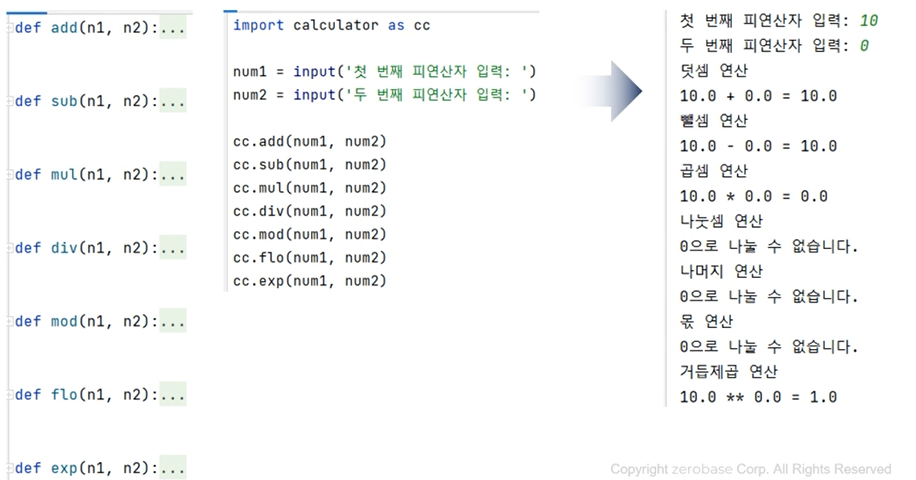
- 사용자가 입력한 숫자를 이용해서 산술연산 결과를 출력하는 모듈을 만들되, 예상하는 예외에 대한 예외처리 코드를 작성해 보자.
def add(n1, n2):
print('덧셈 연산')
try:
n1 = float(n1)
except:
print('첫 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.')
return
try:
n2 = float(n2)
except:
print('두 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.')
return
print(f'{n1} + {n2} = {n1 + n2}')
def sub(n1, n2):
print('뺄셈 연산')
try:
n1 = float(n1)
except:
print('첫 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.')
return
try:
n2 = float(n2)
except:
print('두 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.')
return
print(f'{n1} - {n2} = {n1 - n2}')
def mul(n1, n2):
print('곱셈 연산')
try:
n1 = float(n1)
except:
print('첫 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.')
return
try:
n2 = float(n2)
except:
print('두 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.')
return
print(f'{n1} * {n2} = {n1 * n2}')
def div(n1, n2):
print('나눗셈 연산')
try:
n1 = float(n1)
except:
print('첫 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.')
return
try:
n2 = float(n2)
except:
print('두 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.')
return
# if n2 == 0:
# print('0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.')
# return
try:
print(f'{n1} / {n2} = {n1 / n2}')
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
print(e)
print('0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.')
print(f'{n1} / {n2} = {n1 / n2}')
def mod(n1, n2):
print('나머지 연산')
try:
n1 = float(n1)
except:
print('첫 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.')
return
try:
n2 = float(n2)
except:
print('두 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.')
return
if n2 == 0:
print('0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.')
return
print(f'{n1} % {n2} = {n1 % n2}')
def flo(n1, n2):
print('몫 연산')
try:
n1 = float(n1)
except:
print('첫 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.')
return
try:
n2 = float(n2)
except:
print('두 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.')
return
if n2 == 0:
print('0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.')
return
print(f'{n1} // {n2} = {n1 // n2}')
def exp(n1, n2):
print('제곱근 연산')
try:
n1 = float(n1)
except:
print('첫 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.')
return
try:
n2 = float(n2)
except:
print('두 번째 피연산자는 숫자가 아닙니다.')
return
print(f'{n1} ** {n2} = {n1 ** n2}')import calculator as cc
num1 = input('첫 번째 피연산자 입력 : ')
num2 = input('두 번째 피연산자 입력 : ')
cc.add(num1, num2)
cc.sub(num1, num2)
cc.mul(num1, num2)
cc.div(num1, num2)
cc.mod(num1, num2)
cc.flo(num1, num2)
cc.exp(num1, num2)
22번
- 상품 구매에 따른'총 구매 금액을 출력하되, 다음과 같이 개수가 잘 못 입력된 경우 별도로 출력하도록 프로그램을 만들어보자.

g1Price = 1200; g2Price = 1000; g3Price = 800; g4Price = 2000; g5Price = 900;
def calculator(*gcs):
gcsDic = {}
againCntInput = {}
for idx, gc in enumerate(gcs):
try:
gcsDic[f'g{idx+1}'] = int(gc) # 상품 구매의 순서대로 갯수를 입력한다.
except Exception as e:
againCntInput[f'g{idx+1}'] = gc
print(e)
totalPrice = 0
for g in gcsDic.keys():
totalPrice += globals()[f'{g}Price'] * gcsDic[g] # globals()는 [f'{g}Price']를 하나의 변수명으로 찾아서 들어가는방법이다.
print('----------------------------------------')
print(f'총 구매 금액 : {totalPrice}원')
print('------------- 미결재 금액 ------------')
for g in againCntInput.keys():
print(f'삼품 : {g}, \t 구매 개수 : {againCntInput[g]}')
print('----------------------------------------')import calculatorPurchase as cp
g1Cnt = input('goods1 구매 개수 : ')
g2Cnt = input('goods2 구매 개수 : ')
g3Cnt = input('goods3 구매 개수 : ')
g4Cnt = input('goods4 구매 개수 : ')
g5Cnt = input('goods5 구매 개수 : ')
cp.calculator(g1Cnt, g2Cnt, g3Cnt, g4Cnt, g5Cnt)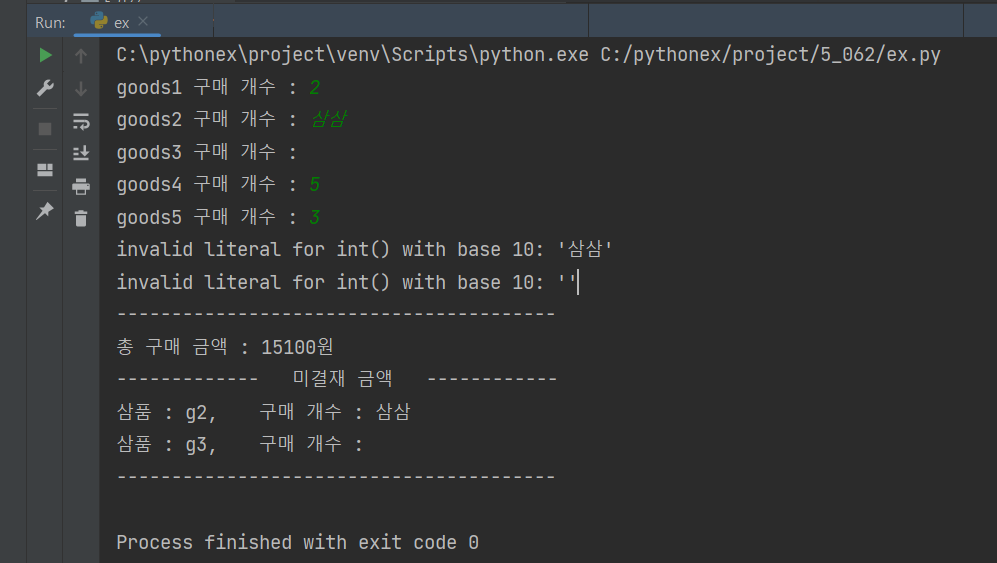 format()함수를 이용해서 3자릿수씩 끊어서 표기할수도있다.
format()함수를 이용해서 3자릿수씩 끊어서 표기할수도있다.
23번
- 회원가임 프로그램을 만들되 입력하지 않은 항목이 있는 경우 에러 메시지를 출력하는 프로그램을 만들어보자.

class EmptyDataException(Exception): # 예외처리할떄 불러주기 위한 클래스 생성
def __init__(self, i):
super().__init__(f'{i} is empty!')
def checkInputData(n, m, p, a, ph):
if n =='':
raise EmptyDataException('name') # raise는 공란이 발생했을때 예외처리를 호출하기위해 사용
elif m =='':
raise EmptyDataException('mail')
elif p =='':
raise EmptyDataException('password')
elif a =='':
raise EmptyDataException('address')
elif ph =='':
raise EmptyDataException('phone')
class RegistMember():
def __init__(self, n, m, p, a, ph):
self.m_name = n
self.m_mail = m
self.m_pw = p
self.m_addr = a
self.m_phone = ph
print('Membership complete!!')
def printMemberInfo(self):
print(f'm_name = {self.m_name}')
print(f'm_mail = {self.m_mail}')
print(f'm_pw = {self.m_pw}')
print(f'm_addr = {self.m_addr}')
print(f'm_phone = {self.m_phone}')import mem
m_name = input('이름 입력 : ')
m_mail = input('메일 주소 입력 : ')
m_pw = input('비밀번호 입력 : ')
m_addr = input('주소 입력 : ')
m_phone = input('연락처 입력 : ')
try:
mem.checkInputData(m_name, m_mail, m_pw, m_addr, m_phone)
newMember = mem.RegistMember(m_name, m_mail, m_pw, m_addr, m_phone)
newMember.printMemberInfo()
except mem.EmptyDataException as e:
print(e)
24번
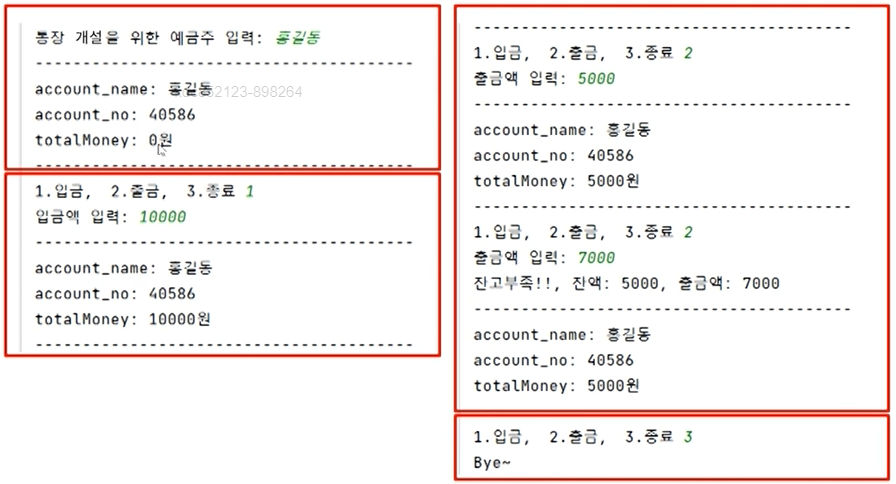
- 다음과 같은 은행 계좌 개설 및 입/출금 프로그램을 만들어보자.
import random
def formatn(n):
return format(n, ',')
class PrivateBank:
def __init__(self, bank, account_name):
self.bank = bank
self.account_name = account_name
while True:
newAccountNo = random.randint(10000, 99999)
if bank.isAccount(newAccountNo):
continue
else:
self.account_no = newAccountNo
break
self.totalMoney = 0
bank.addAccount(self)
def printBankInfo(self):
print('-' * 40)
print(f'account_name: {self.account_name}')
print(f'account_no: {self.account_no}')
print(f'totalMoney: {formatn(self.totalMoney)}원')
print('-' * 40)
class Bank:
def __init__(self): # 계좌번호 관리
self.accounts = {}
def addAccount(self, privateBank): # accounts에 계좌를 생성하는 함수
self.accounts[privateBank.account_no] = privateBank
def isAccount(self, ano): # accounts에 ano가 있는지 없는지 여부 확인하는 함수
return ano in self.accounts
def doDeposit(self,ano, m): # ano계좌번호에 m을 입금하는 함수
pb = self.accounts[ano]
pb.totalMoney = pb.totalMoney + m
def doWithdraw(self, ano, m): # ano계좌번호에 m을 출금하는 함수
pb = self.accounts[ano]
if pb.totalMoney - m < 0:
raise LackException(pb.totalMoney, m)
pb.totalMoney = pb.totalMoney - m
class LackException(Exception):
def __init__(self, m1, m2):
super().__init__(f'잔고 부족!!, 잔액 : {m1}, 출금액 : {m2}원')import bank
koreaBank = bank.Bank()
new_account_name = input('통장 개설을 위한 예금주 입력 : ')
myAccount = bank.PrivateBank(koreaBank,new_account_name)
myAccount.printBankInfo()
while True:
selectNumber = int(input('1. 입금, 2. 출금, 3. 종료 : '))
if selectNumber == 1:
m = int(input('입금액 입력 : '))
koreaBank.doDeposit(myAccount.account_no, m)
myAccount.printBankInfo()
elif selectNumber == 2:
m = int(input('출금액 입력 : '))
try:
koreaBank.doWithdraw(myAccount.account_no, m)
except bank.LackException as e:
print(e)
finally:
myAccount.printBankInfo()
elif selectNumber == 3:
print('Bye~')
break
else:
print('잘못 입력했습니다. 다시 선택하세요.')
continue
텍스트파일
25번
- 회원 계정별 텍스트 파일을 생성한 후 회원 본인 파일에 '한 줄 일기'를 쓰고 읽는 프로그램을 만들어보자.

import time
def writeDiary(u, f, d):
lt = time.localtime()
timeStr = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %I:%M:%S %p',lt)
filePath = u + f
with open(filePath ,'a') as f:
f.write(f'[{timeStr}] {d}\n')
def readDiary(u, f):
filePath = u + f
datas = []
with open(filePath ,'r') as f:
datas = f.readline()
return datasimport diary
members = {}
uri = 'C:/PythonTxt/'
def printMembers():
for m in members.keys():
print(f'ID:{m} \t PW: {members[m]}')
while True:
selectNum = int(input('1. 회원가입, 2. 한줄일기쓰기, 3. 일기보기, 4. 종료 : '))
if selectNum == 1:
mId = input('input ID : ')
mPw = input('input PW : ')
members[mId] = mPw
printMembers()
elif selectNum == 2:
mId = input('input ID : ')
mPw = input('input PW : ')
if mId in members and members[mId] == mPw:
print(f'login success!!')
fileName = 'myDiary_' + mId + '.txt'
data = input('오늘 하루 인상 깊은 일을 기록하세요.')
diary.writeDiary(uri, fileName, data)
else:
print('login fail!!')
printMembers()
elif selectNum == 3:
mId = input('input ID : ')
mPw = input('input PW : ')
if mId in members and members[mId] == mPw:
print(f'login success!!')
fileName = 'myDiary_' + mId + '.txt'
datas = diary.readDiary(uri, fileName)
for d in datas:
print(d, end='')
else:
print('login fail!!')
printMembers()
elif selectNum == 4:
print('Bay~')
break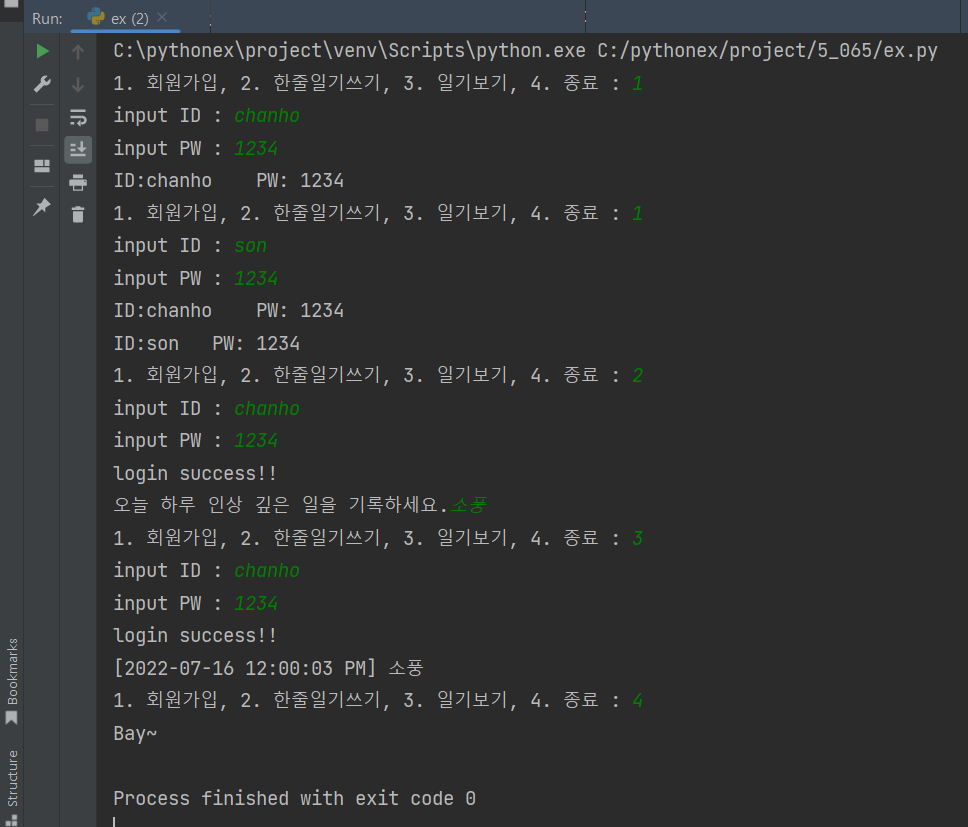
26번
- 텍스트 파일에 수입과 지출을 기록하는 가계부를 만들어보자.

import time
def formatN(n):
return format(n, ',')
def getTime():
lt = time.localtime()
st = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %I:%M:%S %p ', lt)
return st
while True:
selectNumber = int(input('1. 입금, \t 2. 출금, \t 3. 종료 : '))
if selectNumber == 1:
money = int(input('입금액 입력 : '))
with open('C:/PythonTxt/bank/money.txt', 'r') as f:
m = f.read()
with open('C:/PythonTxt/bank/money.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write(str(int(m) + money))
memo = input('입금 내역 입력 : ')
with open('C:/PythonTxt/bank/poketMoneyRegister.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write('---------------------------------------- \n')
f.write(f'{getTime()} \n')
f.write(f'[입금]{memo} : {str(formatN(money))}원 \n')
f.write(f'[잔액] : {str(formatN(int(m) + money))}원 \n')
print('입금 완료!!')
print(f'기존 잔액 : {formatN(m)}원')
print(f'입금 후 잔액 : {formatN(int(m) + money)}원')
elif selectNumber == 2:
money = int(input('출금액 입력 : '))
with open('C:/PythonTxt/bank/money.txt', 'r') as f:
m = f.read()
with open('C:/PythonTxt/bank/money.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write(str(int(m) - money))
memo = input('출금 내역 입력 : ')
with open('C:/PythonTxt/bank/poketMoneyRegister.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write('---------------------------------------- \n')
f.write(f'{getTime()} \n')
f.write(f'[출금]{memo} : {str(formatN(money))}원 \n')
f.write(f'[잔액] : {str(formatN(int(m) - money))}원 \n')
print('출금 완료!!')
print(f'기존 잔액 : {m}원')
print(f'출금 후 잔액 : {formatN(int(m) - money)}원')
elif selectNumber == 3:
print('Bay~')
break
else:
print('다시 입력하세요!!')
continue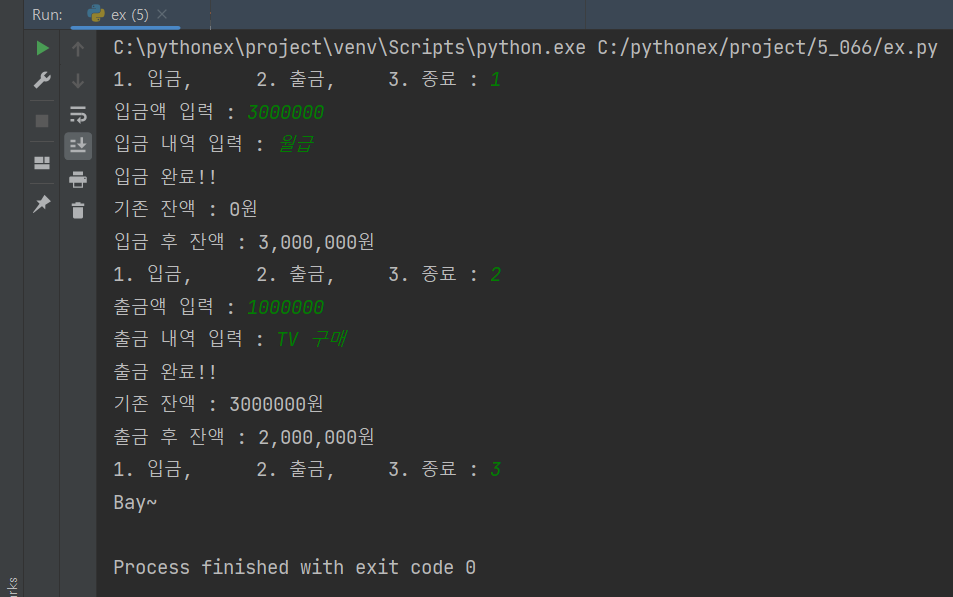
27번
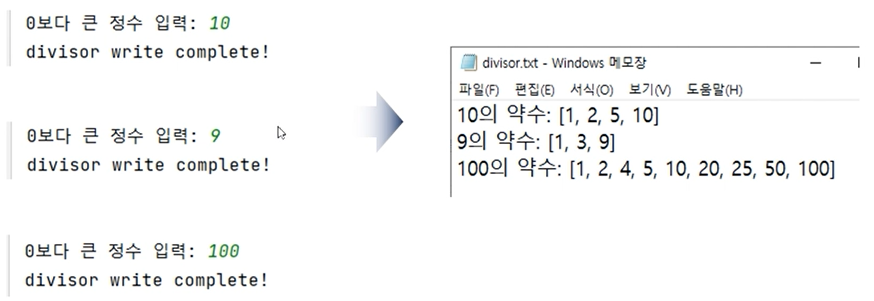
- 사용자가 입력한 숫자의 약수를 텍스트 파일에 기록해 보자.
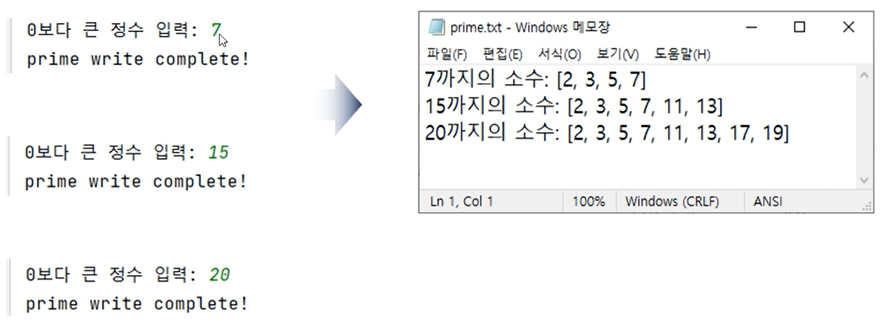
- 사용자가 입력한 숫자까지의 소수를 텍스트 파일에 기록해 보자.
# 약수
inputNumber = int(input('0보다 큰 정수 입력 : '))
divisor = []
for number in range(1, (inputNumber + 1)):
if inputNumber % number == 0:
divisor.append(number)
if len(divisor) > 0:
try:
with open('C:/PythonTxt/divisor.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(f'{inputNumber}의 약수 : ')
f.write(f'{divisor}\n')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
else:
print('divisor write complete!!')
# 소수
inputNumber = int(input('0보다 큰 정수 입력 : '))
prime = []
for number in range(2, (inputNumber+1)):
flag = True
for n in range(2, number):
if number % n == 0:
flag = False
break
if flag:
prime.append(number)
if len(prime) > 0:
try:
with open('C:/PythonTxt/prime.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(f'{inputNumber}까지의 소수 : ')
f.write(f'{prime} \n')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
else:
print('prime write complete!!')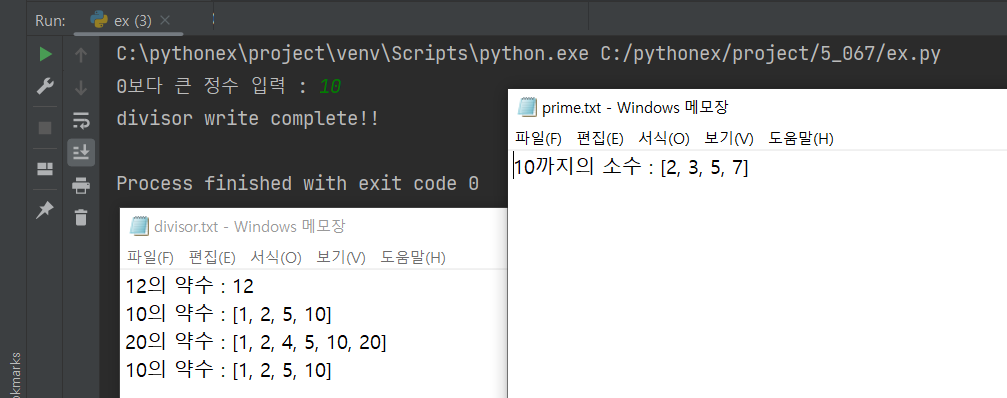
28번
- 두개의 수를 입력하면 공약수를 텍스트 파일에 작성해보자.
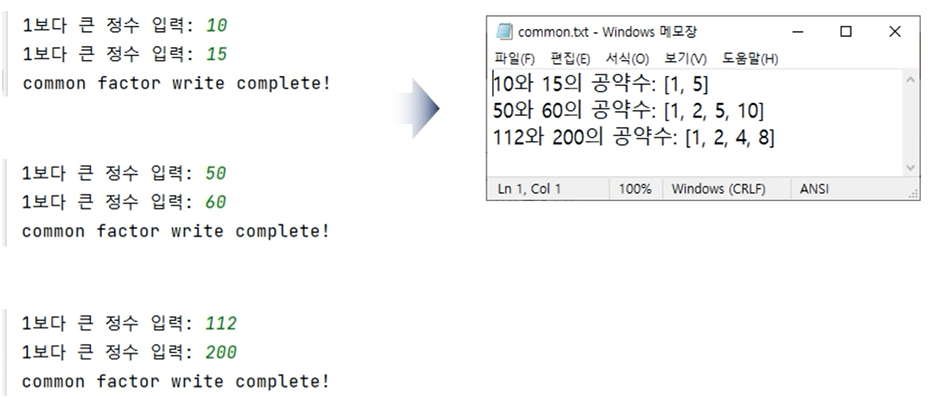
# 수 두개의 공약수
num1 = int(input('1보다 큰 정수 입력 : '))
num2 = int(input('1보다 큰 정수 입력 : '))
common = []
for i in range(1, (num2+1)):
if num1 % i == 0 and num2 % i == 0:
common.append(i)
if len(common) > 0:
try:
with open('C:/PythonTxt/common.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(f'{num1}과 {num2}의 공약수 :')
f.write(f'{common} \n')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
else:
print('common factor write complete!!')
# 수 두개의 최대 공약수
num1 = int(input('1보다 큰 정수 입력 : '))
num2 = int(input('1보다 큰 정수 입력 : '))
maxComNum = 0
for i in range(1, (num2+1)):
if num1 % i == 0 and num2 % i == 0:
maxComNum = i
try:
with open('C:/PythonTxt/maxComNum.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(f'{num1}과 {num2}의 최대 공약수 : {maxComNum} \n')
except Exception as e:
print(e)
else:
print('maxComNum factor write complete!!')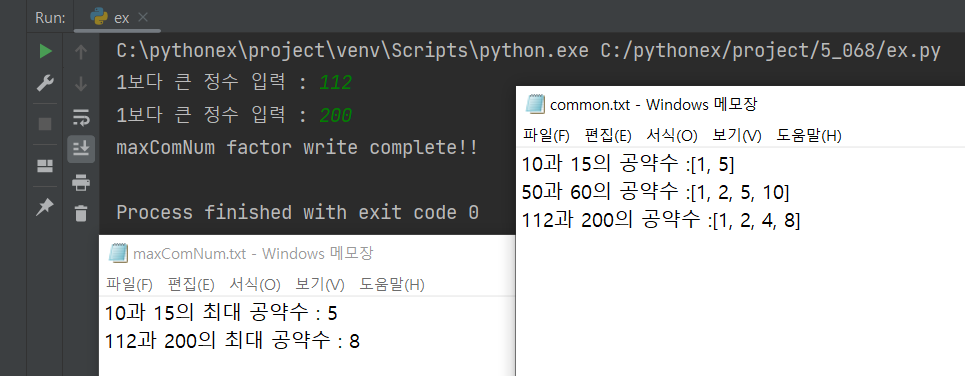
29번
- 섬마을에 과일, 생선, 야채를 판매하는 배가 다음 주기로 입항한다고 할 때, 모든 배가 입항하는 날짜를 텍스트 파일에 기록해보자.
(첫 입항일은 2021년 1월 1일 오전 10시로 한다.)
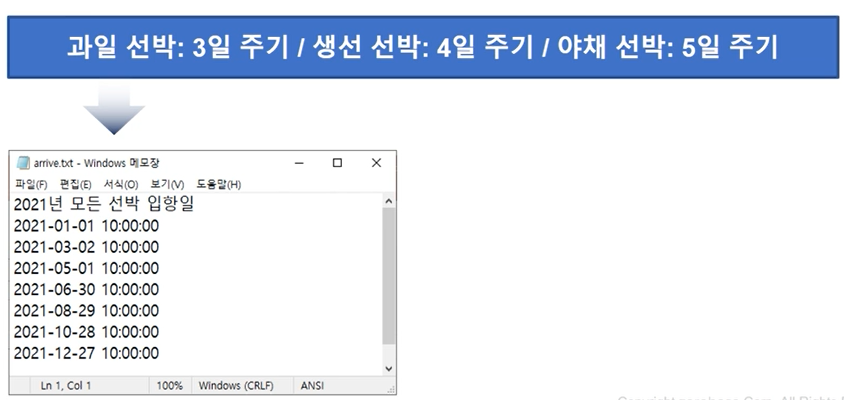
ship1 = 3
ship2 = 4
ship3 = 5
maxDay = 0
for i in range(1, (ship1 + 1)):
if ship1 % i == 0 and ship2 % i == 0:
maxDay = i
minDay = (ship1 * ship2) // maxDay
newDay = minDay
for i in range(1, (newDay + 1)):
if newDay % i == 0 and ship3 % i == 0:
maxDay = i
minDay = (newDay * ship3) // maxDay
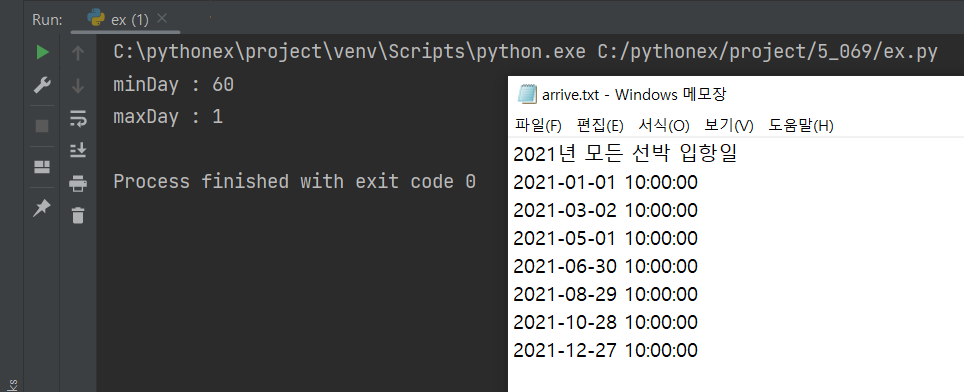
print(f'minDay : {minDay}')
print(f'maxDay : {maxDay}')
from datetime import datetime
from datetime import timedelta
n = 1
baseTime = datetime(2021, 1, 1, 10, 0, 0) # 기준점을 잡기위해 datetime로 기준 날짜를 입력
baseTime
with open('C:/PythonTxt/arrive.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(f'2021년 모든 선박 입항일 \n')
f.write(f'{baseTime} \n')
nextTime = baseTime + timedelta(days=minDay)
while True:
with open('C:/PythonTxt/arrive.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(f'{nextTime} \n')
nextTime = nextTime + timedelta(days=minDay)
if nextTime.year > 2021:
break