12) 입출력
12-1) 콘솔 입력
- 입출력 방식 중 콘솔 입력 방법
System.in.read()
InputStreamReader reader = …
BufferedReader br = …
Scanner …12-2) 콘솔 출력
- 입출력 방식 중 콘솔 출력 방법
System.out.println(…);
System.out.print(…);
System.out.printf(…);코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
// referInputStream() 안에 있는 것은 지금은 잘 사용안하지만 알아두면 좋은 것들
public static void referInputStream() throws IOException {
// System.in
System.out.println("== System.in ==");
System.out.print("입력: ");
int a = System.in.read() - '0';
System.out.println("a = " + a);
System.in.read(new byte[System.in.available()]);
// InputStreamReader
System.out.println("== InputStreamReader ==");
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
char[] c = new char[3];
System.out.print("입력: ");
reader.read(c);
System.out.println(c);
// BufferedReader
System.out.println("== BufferedReader ==");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print("입력: ");
String s1 = br.readLine();
System.out.println("s1 = " + s1);
}
// 많이 사용되는 방식
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 입력
// 1-1. 다른 입력 방식 참고
// referInputStream();
// 1-2. Scanner
System.out.println("== Scanner ==");
System.out.print("입력1: ");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(sc.next());
sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("입력2: ");
System.out.println(sc.nextInt()); // int값만 입력 가능
sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("입력3: ");
System.out.println(sc.nextLine()); // 자유자재로 데이터 읽어서 쓸 수 있음
// 참고) 정수, 문자열 변환
int num = Integer.parseInt("12345");
String str = Integer.toString(12345);
// 2. 출력
System.out.println("== 출력 ==");
System.out.println("Hello");
System.out.println("World!");
System.out.print("Hello ");
System.out.print("World!");
System.out.printf("Hello ");
System.out.printf("World!");
System.out.println();
String s = "자바";
int number = 3;
System.out.println(s + "는 언어 선호도 " + number + "위 입니다.");
System.out.printf("%s는 언어 선호도 %d위 입니다.\n", s, number);
System.out.printf("%d\n", 10);
System.out.printf("%o\n", 10);
System.out.printf("%x\n", 10);
System.out.printf("%f\n", 5.2f);
System.out.printf("%c\n", 'A');
System.out.printf("%s\n", "안녕하세요");
System.out.printf("%5d\n", 123); // 5자리 공간 확보하고 내용 출력
System.out.printf("%5d\n", 1234);
System.out.printf("%5d\n", 12345);
System.out.printf("%.2f\n", 1.126123f); // 소수점 2자리까지 반올림
}
}12-3) 파일 출력
- 입출력 방식 중 파일로 출력하는 방법
FileOutputStream …
FileWriter …
PrintWriter …12-4) 파일 입력
- 입출력 방식 중 파일로부터 입력 받는 방법
FileInputStream …
BufferedReader … // 많이 사용코드1
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 파일 쓰기
// FileWriter
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("./memo.txt");
String memo = "헤드 라인\n";
fw.write(memo);
memo = "1월 1일 날씨 맑음\n";
fw.write(memo);
fw.close();
// PrintWriter
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("./memo.txt");
memo = "헤드 라인";
pw.println(memo);
memo = "1월 1일 날씨 맑음";
pw.println(memo);
pw.close();
FileWriter fw2 = new FileWriter("./memo.txt", true); // true 입력하면 이어쓰기가 됨
memo = "1월 2일 날씨 완전 맑음\n";
fw2.write(memo);
fw2.close();
PrintWriter pw2 = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("./memo.txt", true)); // 이어쓰기
memo = "1월 3일 날씨 또 맑음!";
pw2.println(memo);
pw2.close();
// 2. 파일 입력
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("./memo.txt"));
while (true) {
String line = br.readLine(); // 데이터 한줄씩 읽어오기
if (line == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}
}코드2
// Practice
// JamesArthurGosling.txt 파일을 읽은 후 원하는 단어 변경하여 새로 저장해보자.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Practice {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String inputFile = "./JamesArthurGosling.txt";
String outputFile = "./JamesArthurGosling_edit.txt";
// 찾을 단어 / 변경 단어 입력 받기
System.out.print("찾을 단어: ");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String find = sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("변경 단어: ");
String to = sc.nextLine();
// 파일 읽기, 변경 및 저장
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(inputFile));
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(outputFile);
while (true) {
String line = br.readLine();
if (line == null) {
break;
}
String newLine = line.replace(find, to); // 변경 내용
fw.write(newLine + '\n');
}
br.close();
fw.close();
}
}13) 예외 (Exception)
13-1) 정의
- 정상적이지 않은 Case
- 배열의 인덱스 초과
- 없는 파일 열기
- …
- 0으로 나누기
int a = 1 / 0;

13-2) 예외 처리 (Exception Handling)
- 정상적이지 않은 Case에 대한 적절한 처리 방법
13-3) finally
- 예외 발생 여부와 관계없이 항상 실행되는 부분
try {
예외가 발생할 수도 있는 부분;
} catch (예외 case 1) {
예외 case1이 발생해야 실행되는 부분;
} finally {
항상 실행되는 부분;
}13-4) throw, throws
- throw: 예외를 발생 시킴
- throws: 예외를 전가 시킴
… 함수이름 () {
throw new Exception();
}
… 함수이름() throws Exception {
…
}코드1
// Java 프로그래밍 - 예외 처리
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
class NotTenException extends RuntimeException {}
public class Main {
public static boolean checkTen(int ten) {
if (ten != 10) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static boolean checkTenWithException(int ten) {
try {
if (ten != 10) {
throw new NotTenException(); // 예외를 여기서 처리하는게 아니라 밖으로 보냄
}
} catch (NotTenException e) {
System.out.println("e = " + e);
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static boolean checkTenWithThrows(int ten) throws NotTenException {
if (ten != 10) {
throw new NotTenException();
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 예외
// 1-1. 0으로 나누기
System.out.println("== 0으로 나누기 ==");
// int a = 5 / 0;
int a = 0;
try {
a = 5 / 0;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("0으로 나누기 예외 발생");
System.out.println("e = " + e);
} finally {
System.out.println("1-1 연습 종료");
}
// 1-2. 배열 인덱스 초과
System.out.println("== 배열 인덱스 초과 ==");
int[] b = new int[4];
// b[4] = 1;
try {
b[4] = 1;
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("인덱스 초과!");
System.out.println("e = " + e);
}
// 1-3. 없는 파일 열기
System.out.println("== 없는 파일 열기 ==");
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("abc.txt"));
// 2. throw, throws
System.out.println("== checkTen ==");
boolean checkResult = Main.checkTen(10);
System.out.println("checkResult = " + checkResult);
System.out.println("== checkTenWithException ==");
checkResult = checkTenWithException(5);
System.out.println("checkResult = " + checkResult);
System.out.println("== checkTenWithThrows ==");
try {
checkResult = checkTenWithThrows(5);
} catch (NotTenException e) {
System.out.println("e = " + e);
}
System.out.println("checkResult = " + checkResult);
}
}14) 컬렉션 프레임워크 (Collection Framework)
14-1) 정의
- 여러 데이터를 편리하게 관리할 수 있게 만들어 놓은 것
- 자료 구조 및 알고리즘을 구조화
- 대표 인터페이스
- List 인터페이스, Set 인터페이스, Map 인터페이스
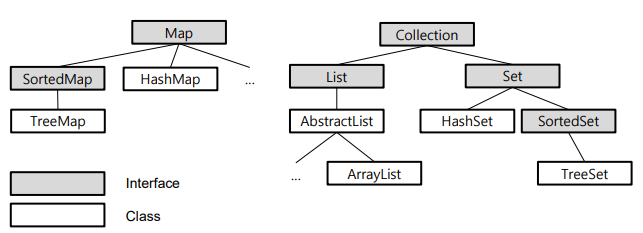
- List 인터페이스, Set 인터페이스, Map 인터페이스
14-2) List 인터페이스
- 순서가 있는 데이터의 집합
- 데이터 중복 허용
- 대표 구현 클래스
ArrayListLinkedListVector
ArrayList list1 = new ArrayList();
LinkedList list2 = new LinkedList();
Vector v = new Vector();14-3) Set 인터페이스
- 순서가 없는 데이터의 집합
- 데이터의 중복 허용 하지 않음
- 대표 구현 클래스
HashSetTreeSet
HashSet set1 = new HashSet();
TreeSet set2 = new TreeSet();14-4) Map 인터페이스
- 키와 값의 쌍으로 이루어진 데이터 집합
- 순서를 유지 하지 않음
- 대표 구현 클래스
HashMapTreeMap
HashMap map1 = new HashMap();
TreeMap = map2 = new TreeMap();코드1
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. List
// 1-1. ArrayList
ArrayList list1 = new ArrayList();
list1.add(1);
list1.add(2);
list1.add(3);
System.out.println("list1 = " + list1); // 결과 : list1 = [1, 2, 3]
list1.remove(Integer.valueOf(2));
System.out.println("list1 = " + list1); // 결과 : list1 = [1, 3]
list1.add(0, 10);
System.out.println("list1 = " + list1); // 결과 : list1 = [10, 1, 3]
System.out.println("list1.size() = " + list1.size()); // 결과 : list1.size() = 3
System.out.println("list1.contains(1) = " + list1.contains(1)); // 결과 : list1.contains(1) = true
System.out.println("list1.indexOf(10) = " + list1.indexOf(10)); // 결과 : list1.indexOf(10) = 0
// 1-2. LinkedList
System.out.println("== LinkedList ==");
LinkedList list2 = new LinkedList();
list2.add(1);
list2.add(2);
list2.add(3);
System.out.println("list2 = " + list2); // 결과 : list2 = [1, 2, 3]
list2.addFirst(10);
list2.addLast(20);
System.out.println("list2 = " + list2); // 결과 : list2 = [10, 1, 2, 3, 20]
list2.remove(Integer.valueOf(1));
System.out.println("list2 = " + list2); // 결과 : list2 = [10, 2, 3, 20]
list2.removeFirst();
list2.removeLast();
System.out.println("list2 = " + list2); // 결과 : list2 = [2, 3]
System.out.println("list2.size() = " + list2.size()); // 결과 : list2.size() = 2
// 2. Set
// 2-1. HashSet
System.out.println("== HashSet ==");
HashSet set1 = new HashSet();
set1.add(1);
set1.add(2);
set1.add(3);
System.out.println("set1 = " + set1); // 결과 : set1 = [1, 2, 3]
set1.remove(1);
System.out.println("set1 = " + set1); // 결과 : set1 = [2, 3]
set1.add(2);
set1.add(3);
System.out.println("set1 = " + set1); // 결과 : set1 = [2, 3]
System.out.println("set1.size() = " + set1.size()); // 결과 : set1.size() = 2
System.out.println("set1.contains(2) = " + set1.contains(2)); // 결과 : set1.contains(2) = true
// 2-2. TreeSet
System.out.println("== TreeSet ==");
TreeSet set2 = new TreeSet();
set2.add(1);
set2.add(2);
set2.add(3);
System.out.println("set2 = " + set2); // 결과 : set2 = [1, 2, 3]
set2.remove(2);
System.out.println("set2 = " + set2); // 결과 : set2 = [1, 3]
set2.clear();
System.out.println("set2 = " + set2); // 결과 : set2 = []
set2.add(10);
set2.add(5);
set2.add(15);
set2.add(15);
System.out.println("set2 = " + set2); // 결과 : set2 = [5, 10, 15]
System.out.println("set2.first() = " + set2.first()); // 결과 : set2.first() = 5
System.out.println("set2.last() = " + set2.last()); // 결과 : set2.last() = 15
System.out.println("set2.lower(10) = " + set2.lower(10)); // 결과 : set2.lower(10) = 5
System.out.println("set2.higher(10) = " + set2.higher(10)); // 결과 : set2.higher(10) = 15
// 3. Map
// 3-1. HashMap
System.out.println("== HashMap ==");
HashMap map1 = new HashMap();
map1.put(1, "kiwi");
map1.put(2, "apple");
map1.put(3, "mango");
System.out.println("map1 = " + map1); // 결과 : map1 = {1=kiwi, 2=apple, 3=mango}
map1.remove(2);
System.out.println("map1 = " + map1); // 결과 : map1 = {1=kiwi, 3=mango}
System.out.println("map1.get(1) = " + map1.get(1)); // 결과 : map1.get(1) = kiwi
// 3-2. TreeMap
System.out.println("== TreeMap ==");
TreeMap map2 = new TreeMap();
map2.put(10, "kiwi");
map2.put(5, "apple");
map2.put(15, "mango");
System.out.println("map2 = " + map2); // 결과 : map2 = {5=apple, 10=kiwi, 15=mango}
System.out.println("map2.firstEntry() = " + map2.firstEntry()); // 결과 : map2.firstEntry() = 5=apple
System.out.println("map2.firstKey() = " + map2.firstKey()); // 결과 : map2.firstKey() = 5
System.out.println("map2.lastEntry() = " + map2.lastEntry()); // 결과 : map2.lastEntry() = 15=mango
System.out.println("map2.lastKey() = " + map2.lastKey()); // 결과 : map2.lastKey() = 15
System.out.println("map2.lowerEntry(10) = " + map2.lowerEntry(10)); // 결과 : map2.lowerEntry(10) = 5=apple
System.out.println("map2.higherEntry(10) = " + map2.higherEntry(10)); // 결과 : map2.higherEntry(10) = 15=mango
}
}코드2
import java.util.*;
public class Practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
for (int i = 0; set.size() < 6; i++) {
int num = (int)(Math.random() * 45) + 1;
set.add(num);
}
LinkedList list = new LinkedList(set);
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println("로또 번호: " + list);
}
}15) 람다식
15-1) 람다 표현식 (Lambda Expression)
- 메소드 대신 하나의 식으로 표현하는 것
- 익명 함수 (Anonymous function)

15-2) 람다식 장점
- 일반적으로 코드가 간결해짐
- 코드 가독성이 높아짐
- 생산성이 높아짐
15-3) 람다식 단점
- 재사용이 불가능 (익명)
- 디버깅 어려움
- 재귀함수로는 맞지 않음
코드1
interface ComputeTool {
public abstract int compute(int x, int y);
// public abstract int compute2(int x, int y);
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//일반적인 함수
ComputeTool cTool1 = new ComputeTool() {
@Override
public int compute(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
};
System.out.println(cTool1.compute(1, 2));
// 람다식
ComputeTool cTool2 = (x, y) -> { return x + y; };
System.out.println(cTool2.compute(1, 2));
}
}
인터페이스에 추상메소드가 두개인 경우 익명클래스는 오버라이딩하면 되는데 람다식의 경우 사용이 제한됨
코드2
interface CompareTool {
public abstract int getMaxNum(int num1, int num2);
}
public class Practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
CompareTool cTool = new CompareTool() {
@Override
public int getMaxNum(int num1, int num2) {
return num1 > num2? num1 : num2;
}
};
System.out.println(cTool.getMaxNum(10, 11));
// 람다식으로 작성
CompareTool cTool2 = (num1, num2) -> { return num1 > num2? num1 : num2; };
System.out.println(cTool2.getMaxNum(10, 11));
}
}16) 스트림
16-1) 정의
- 배열, 컬렉션 등의 데이터를 하나씩 참조하여 처리 가능한 기능
- for문의 사용을 줄여 코드를 간결하게 함
- 스트림은 크게 3가지로 구성
Stream 생성중개 연산최종 연산
데이터소스객체.Stream생성().중개연산().최종연산();
16-2) 스트림 생성
-
배열 스트림
String[] arr = new String[]{"a", "b", "c"};
Stream stream = Arrays.stream(arr); -
컬렉션 스트림
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
Stream stream = list.stream();
16-3) 스트림 중개연산
- Filtering
- filter 내부 조건에 참인 요소들을 추출
IntStream intStream = IntStream.range(1, 10).filter(n -> n % 2 == 0);
- filter 내부 조건에 참인 요소들을 추출
- Mapping
- map 안의 연산을 요소별로 수행
IntStream intStream = IntStream.range(1, 10).map(n -> n + 1);
- map 안의 연산을 요소별로 수행
16-4) 스트림 최종연산
- Sum, Average
IntStream.range(1, 5).sum()
IntStream.range(1, 5).average().getAsDouble() - min, max
IntStream.range(1, 5).min().getAsInt();
IntStream.range(1, 5).max().getAsInt();
코드1
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 스트림 생성
// 1-1. 배열 스트림
System.out.println("== 배열 스트림 == ");
String[] arr = new String[]{"a", "b", "c"};
System.out.println("== fori ==");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
System.out.println("== forEach ==");
for (String item: arr) {
System.out.println(item);
}
// 스트림으로 바꿔서 출력
System.out.println("== Stream ==");
Stream stream1 = Arrays.stream(arr);
stream1.forEach(System.out::println);
// 1-2. 컬렉션 스트림
System.out.println("== 컬렉션 스트림 ==");
ArrayList list1 = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
System.out.println("list1 = " + list1);
Stream stream2 = list1.stream();
stream2.forEach(System.out::println);
// stream2.forEach(num -> System.out.println("num = " + num));
// 1-3. 스트림 builder
System.out.println("== 스트림 builder ==");
Stream streamBuild = Stream.builder().add("a").add("b").add("c").build();
streamBuild.forEach(System.out::println);
// 1-4. 스트림 generate
System.out.println("== 스트림 generate ==");
Stream streamGenerate = Stream.generate( () -> "abc" ).limit(3);
streamGenerate.forEach(System.out::println);
// 1-5. 스트림 iterate
System.out.println("== 스트림 iterate ==");
Stream streamIterate = Stream.iterate(10, n -> n * 2).limit(3);
streamIterate.forEach(System.out::println);
// 1-6. 기본 타입 스트림
System.out.println("== 기본타입 스트림 ==");
IntStream intStream = IntStream.range(1, 5);
intStream.forEach(System.out::println);
// 2. 스트림 중개 연산
// 2-1. Filtering
System.out.println("== Filtering ==");
IntStream intStream2 = IntStream.range(1, 10).filter(n -> n % 2 == 0);
intStream2.forEach(System.out::println);
// 2-2. Mapping
System.out.println("== Mapping ==");
IntStream intStream3 = IntStream.range(1, 10).map(n -> n + 1);
intStream3.forEach(n -> System.out.print(n + " "));
System.out.println();
// 2-3. Sorting
System.out.println("== Sorting ==");
IntStream intStream4 = IntStream.builder().add(5).add(1).add(3).add(4).add(2).build();
IntStream intStreamSort = intStream4.sorted();
intStreamSort.forEach(System.out::println);
// 3. 최종 연산
// 3-1. Sum, Average
System.out.println("== sum, average ==");
int sum = IntStream.range(1, 5).sum();
double average = IntStream.range(1, 5).average().getAsDouble();
System.out.println(sum);
System.out.println(average);
// 3-2. Min, Max
System.out.println("== min, max ==");
int min = IntStream.range(1, 5).min().getAsInt();
int max = IntStream.range(1, 5).max().getAsInt();
System.out.println(min);
System.out.println(max);
// 3-3. reduce
System.out.println("== reduce ==");
Stream<Integer> stream3 = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)).stream();
System.out.println(stream3.reduce((x, y) -> x + y).get());
// 3-4. forEach
System.out.println("== forEach == ");
IntStream.range(1, 10).filter(n -> n == 5).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}코드2
public class Practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 예제: 1~10 숫자 중 짝수 들의 합
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int sum = 0;
for (int num: arr) {
if (num % 2 == 0) {
sum += num;
}
}
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
// 스트림으로 구현
int sum2 = IntStream.range(1, 11).filter(x -> x % 2 == 0).sum();
System.out.println("sum2 = " + sum2);
}
}