1) 기초수학 소개
1-1) 소개
- 컬렉션 프레임워크 이용한 구현(직접구현)
1-2) 경우의 수
- 주사위 예시 경우의 수
- 최대 공약수, 최소공배수
1-3) 순열 / 조합
- 팩토리얼(반복문, Stream)
- m개의 숫자를 이용 n자리 자연수
1-4) 점화식과 재귀함수

- 여러가지 점화식을 재귀함수로 구현
- 최대공약수를 재귀함수로 표현
1-5) 지수와 로그
- Math 클래스 사용한 구현
- 직접 구현
1-6) 알고리즘 복잡도
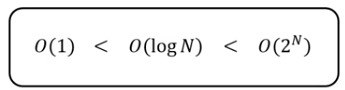
- 시간 복잡도 예시 코드(중요)
- 공간 복잡도 예시 코드
2) 집합
2-1) 정의
-
특정 조건에 맞는 원소들의 모임
-
집합 표현 방법
- 원소 나열법
A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, B={2, 4, 6, 8, 10} - 조건 제시법
A={A|A는 정수, 1<=A<=5}
B={2B|B는 정수, 1<=B<=5} - 벤다이어그램
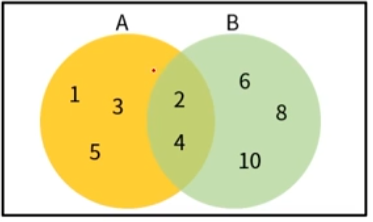
- 원소 나열법
2-2)집합의 종류
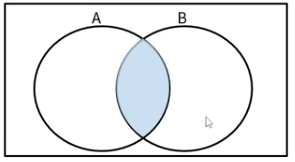
📌교집합
- 두 집합이 공통으로 포함하는 원소로 이루어진 집합
- 𝐴∩𝐵={𝑥 | 𝑥∈𝐴 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑥∈𝐵}
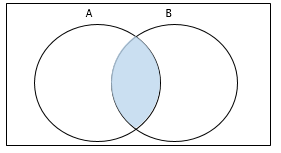
📌합집합
- 어느 하나에라도 속하는 원소들을 모두 모은 집합
- 𝐴∪𝐵={𝑥 | 𝑥∈𝐴 𝑜𝑟 𝑥∈𝐵}
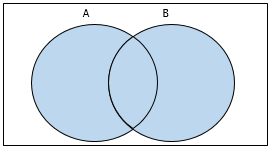
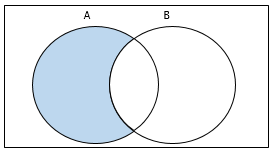
📌차집합
- A(or B)에만 속하는 원소들의 집합
- 𝐴−𝐵={𝑥 | 𝑥∈𝐴 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑥∉𝐵}
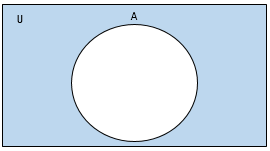
📌여집합
- 전체집합(U)중 A의 원소가 아닌 것들의 집합
- 𝐴^𝑐={𝑥 | 𝑥∈𝑈 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑥∉𝐴}
2-3) 예시
코드
HashSet a = new HashSet(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5));
HashSet b = new HashSet(Arrays.asList(2, 4, 6, 8, 10));📝교집합
a.retainAll(b);
System.out.println("교집합: " + a);📝합집합
a.addAll(b);
System.out.println("합집합: " + a);📝차집합
a.removeAll(b);
System.out.println("차집합: " + a);📝practice
import java.util.ArrayList;
class MySet {
ArrayList<Integer> list;
MySet() {
this.list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
MySet(int[] arr) {
this.list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int item: arr) {
this.list.add(item);
}
}
// 원소 추가 (중복 X)
public void add(int x) {
for (int item: this.list) {
if (item == x) {
return;
}
}
this.list.add(x);
}
// 교집합
public MySet retainAll(MySet b) {
MySet result = new MySet();
for (int itemA: this.list) {
for (int itemB: b.list) {
if (itemA == itemB) {
result.add(itemA);
}
}
}
return result;
}
// 합집합
public MySet addAll(MySet b) {
MySet result = new MySet();
for (int itemA: this.list) {
result.add(itemA);
}
for (int itemB: b.list) {
result.add(itemB);
}
return result;
}
// 차집합
public MySet removeAll(MySet b) {
MySet result = new MySet();
for (int itemA: this.list) {
boolean containFlag = false;
for (int itemB: b.list) {
if (itemA == itemB) {
containFlag = true;
break;
}
}
if (!containFlag) {
result.add(itemA);
}
}
return result;
}
}
public class Practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
MySet a = new MySet();
a.add(1);
a.add(1);
a.add(1);
System.out.println(a.list);
a.add(2);
a.add(3);
System.out.println(a.list);
a = new MySet(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5});
MySet b = new MySet(new int[]{2, 4, 6, 8, 10});
System.out.println("a: " + a.list);
System.out.println("b: " + b.list);
MySet result = a.retainAll(b);
System.out.println("교집합: " + result.list);
result = a.addAll(b);
System.out.println("합집합: " + result.list);
result = a.removeAll(b);
System.out.println("차집합: " + result.list);
}
}3) 경우의 수
3-1) 정의
어떤 사건에서 일어날 수 있는 경우의 가짓수
- 예시 1) 동전을 던지는 사건 : 경우의 수 2
- 예시 2) 주사위를 던지는 사건 : 경우의 수 6
사건 A가 일어날 경우의 수: n(A)
3-2) 합의 법칙
사건 A 또는 사건 B가 일어날 경우의 수
사건 A와 사건 B의 합의 법칙: n(A ∪ B)
📝예시) 두 개의 주사위를 던졌을 때 합이 3 또는 4의 배수일 경우의 수
-
사건 A: 합이 3의 배수일 경우
3: (1, 2), (2, 1)
6: (1, 5), (2, 4), (3, 3), (4, 2), (5, 1)
9: (3, 6), (4, 5), (5, 4), (6, 3)
12: (6, 6) -
사건 B: 합이 4의 배수일 경우
4: (1, 3), (2, 2), (3, 1)
8: (2, 6), (3, 5), (4, 4), (5, 3), (6, 2)
12: (6, 6)
n(A ∪ B) = n(A) + n(B) – n(A ∩ B)
→ 12 + 9 – 1 = 20
3-3) 곱의 법칙
사건 A와 사건 B가 동시에 일어날 경우의 수
사건 A와 사건 B의 곱의 법칙: n(A x B)
📝예시) 두 개의 주사위 a, b를 던졌을 때 a는 3의 배수, b는 4의 배수인 경우의 수
-
사건 A: a가 3의 배수일 경우
2가지: 3, 6 -
사건 B: b가 4의 배수일 경우
1가지: 4
n(A x B) = n(A) x n(B)
→ 2 x 1 = 2
📝예시1
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 합의 법칙
System.out.println("== 합의 법칙 ==");
// 두 개의 주사위를 던졌을 때 합이 3 또는 4의 배수일 경우의 수
int[] dice1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; // 주사위 정보
int[] dice2 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; // 주사위 정보
int nA = 0; // 3의 배수
int nB = 0; // 4의 배수
int nAandB = 0; // 공통 부분 세기 위한 변수
for (int item1: dice1) {
for (int item2: dice2) {
if ((item1 + item2) % 3 == 0) {
nA += 1;
}
if ((item1 + item2) % 4 == 0) {
nB += 1;
}
if ((item1 + item2) % 12 == 0) {
nAandB += 1;
}
}
}
System.out.println("결과: " + (nA + nB - nAandB));
HashSet<ArrayList> allCase = new HashSet<ArrayList>();
for (int item1: dice1) {
for (int item2 : dice2) {
if ((item1 + item2) % 3 == 0 || (item1 + item2) % 4 == 0) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(item1, item2));
allCase.add(list);
}
}
}
System.out.println("결과: " + allCase.size());
// 2. 곱의 법칙
System.out.println("== 곱의 법칙 ==");
// 두 개의 주사위 a, b를 던졌을 때 a는 3의 배수, b는 4의 배수인 경우의 수
nA = 0;
nB = 0;
for (int item1: dice1) {
if (item1 % 3 == 0) {
nA++;
}
}
for (int item2: dice2) {
if (item2 % 4 == 0) {
nB++;
}
}
System.out.println("결과: " + (nA * nB));
}
}📝예시2
약수 구하기, 두 수의 최대공약수와 최소공배수 구하기
활용) 1~10의 수 중 A의 약수 또는 B의 약수인 경우의 수
활용) 1~10의 수 중 A의 약수이면서 B의 약수인 경우의 수
public class Practice {
// 약수
public ArrayList getDivisor(int num) {
ArrayList result = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 1; i <= (int)num/2; i++) {
if (num % i == 0) {
result.add(i);
}
}
result.add(num);
return result;
}
// 최대 공약수
// GCD: the Greatest Common Denominator
public int getGCD(int numA, int numB) {
int gcd = -1;
ArrayList divisorA = this.getDivisor(numA);
ArrayList divisorB = this.getDivisor(numB);
for (int itemA: (ArrayList<Integer>)divisorA) {
for (int itemB: (ArrayList<Integer>)divisorB) {
if (itemA == itemB) {
if (itemA > gcd) {
gcd = itemA;
}
}
}
}
return gcd;
}
// 최소 공배수
// LCM: the Lowest Common Multiple
public int getLCM(int numA, int numB) {
int lcm = -1;
int gcd = this.getGCD(numA, numB);
if (gcd != -1) {
lcm = numA * numB / gcd;
}
return lcm;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int number1 = 10;
int number2 = 6;
Practice p = new Practice();
ArrayList l1 = p.getDivisor(number1); // 10: 1, 2, 5, 10
ArrayList l2 = p.getDivisor(number2); // 6: 1, 2, 3, 6
System.out.println("l1 = " + l1);
System.out.println("l2 = " + l2);
System.out.println("최대 공약수: " + p.getGCD(number1, number2));
System.out.println("최대 공배수: " + p.getLCM(number1, number2));
}
}4) 순열
4-1) 팩토리얼 (Factorial)
1에서 n까지 모든 자연수의 곱 (n!)
1! = 1
2! = 1 x 2
3! = 1 x 2 x 3
𝑛!=𝑛(𝑛−1)(𝑛−2)⋯1
4-2) 순열 (Permutation)
- 순서를 정해서 나열
- 서로 다른 n개 중에 r개를 선택하는 경우의 수 (순서 O, 중복 X)
- 예시) 5명을 3줄로 세우는 방법
- 예시) 서로 다른 4명 중 반장, 부반장 뽑는 방법
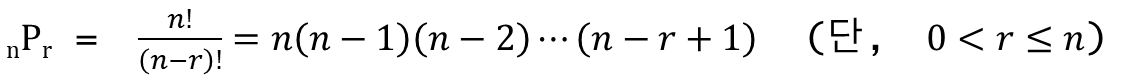
4-3) 중복 순열
서로 다른 n개 중에 r개를 선택하는 경우의 수 (순서 O, 중복 O)
- 예시) 서로 다른 4개의 수 중 2개를 뽑는 방법 (중복 허용)
- 예시) 후보 2명, 유권자 3명일 때 기명 투표 방법
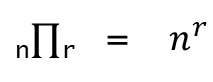
4-4) 원 순열
원 모양의 테이블에 n개의 원소를 나열하는 경우의 수
- 예시) 원 모양의 테이블에 3명을 앉히는 경우
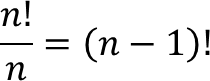
📝예시1
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 팩토리얼
System.out.println("== 팩토리얼 ==");
// 5!
int n = 5;
int result = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
result *= i;
}
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println(IntStream.range(2, 6).reduce(1, (x, y) -> x * y));
// 2. 순열
System.out.println("== 순열 ==");
// 5명을 3줄로 세우는 경우의 수
n = 5;
int r = 3;
result = 1;
for (int i = n; i >= n - r + 1; i--) {
result *= i;
}
System.out.println("result = " + result);
// 3. 중복 순열
System.out.println("== 중복 순열 ==");
// 서로 다른 4개의 수 중 2개를 뽑는 경우의 수 (중복 허용)
n = 4;
r = 2;
result = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
result *= n;
}
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println(Math.pow(n, r));
// 4. 원 순열
System.out.println("== 원 순열 ==");
// 원 모양의 테이블에 3명을 앉히는 경우의 수
n = 3;
result = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
result *= i;
}
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
}
📝예시2
1, 2, 3, 4 를 이용하여 세자리 자연수를 만드는 방법 (순서 O, 중복 x)의 각 결과를 출력하시오
public class Practice {
void permutation(int[] arr, int depth, int n, int r) {
if (depth == r) {
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
for (int i = depth; i < n; i++) {
swap(arr, depth, i);
permutation(arr, depth + 1, n, r);
swap(arr, depth, i);
}
}
void swap(int[] arr, int depth, int idx) {
int tmp = arr[depth];
arr[depth] = arr[idx];
arr[idx] = tmp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4};
Practice p = new Practice();
p.permutation(arr, 0, 4, 3);
}
}📝예시3
1, 2, 3, 4 를 이용하여 세자리 자연수를 만드는 방법 (순서 O, 중복 x)의 각 결과를 출력하시오
방법1
public class Practice1 {
void permutation(int[] arr, int depth, int n, int r) {
if (depth == r) {
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
for (int i = depth; i < n; i++) {
swap(arr, depth, i);
permutation(arr, depth + 1, n, r);
swap(arr, depth, i);
}
}
void swap(int[] arr, int depth, int idx) {
int tmp = arr[depth];
arr[depth] = arr[idx];
arr[idx] = tmp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4};
Practice1 p = new Practice1();
p.permutation(arr, 0, 4, 3);
}
}방법2
public class Practice2 {
void permutation(int[] arr, int depth, int n, int r, boolean[] visited, int[] out) {
if (depth == r) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(out));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (visited[i] != true) {
visited[i] = true;
out[depth] = arr[i];
permutation(arr, depth + 1, n, r, visited, out);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4};
boolean[] visited = new boolean[4];
int[] out = new int[3];
Practice2 p = new Practice2();
p.permutation(arr, 0, 4, 3, visited, out);
}
}5) 조합 (Combination)
5-1) 정의
서로 다른 n개 중에서 r개를 선택하는 경우의 수 (순서 X, 중복 X)
- 예시) 서로 다른 4명 중 주번 2명 뽑는 방법
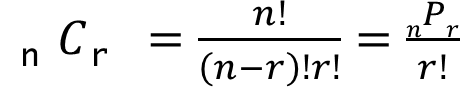
단, 0<𝑟≤𝑛
5-2) 중복 조합
서로 다른 n개 중에서 r개를 선택하는 경우의 수 (순서 X, 중복 O)
- 예시) 후보 2명, 유권자 3명일 때 무기명 투표 방법
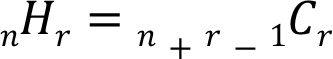
📝예시1
public class Main {
int getNumOfCombination(int n, int r) {
int pResult = 1;
for (int i = n; i >= n - r + 1; i--) {
pResult *= i;
}
int fResult = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= r; i++) {
fResult *= i;
}
return pResult / fResult;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 조합
System.out.println("== 조합 ==");
int n = 4;
int r = 2;
int pResult = 1;
for (int i = n; i >= n - r + 1; i--) {
pResult *= i;
}
int fResult = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= r; i++) {
fResult *= i;
}
System.out.println(pResult / fResult);
// 2. 중복 조합
System.out.println("== 중복 조합 ==");
n = 2;
r = 3;
int hResult = new Main().getNumOfCombination(n + r - 1, r);
System.out.println(hResult);
}
}📝예시2
1, 2, 3, 4 를 이용하여 세자리 자연수를 만드는 방법 (순서 X, 중복 x)의 각 결과를 출력하시오
public class Practice {
void combination(int[] arr, boolean[] visited, int depth, int n, int r) {
if (r == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (visited[i]) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
if (depth == n) {
return;
}
visited[depth] = true;
combination(arr, visited, depth + 1, n, r - 1);
visited[depth] = false;
combination(arr, visited, depth + 1, n, r);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4};
boolean[] visited = {false, false, false, false};
Practice p = new Practice();
p.combination(arr, visited, 0, 4, 3);
}
}
6) 점화식과 재귀함수
6-1) 점화식 (Recurrence)
어떤 수열의 일반항을 그 이전의 항들을 이용하여 정의한 식
- 예시) 피보나치 수열
1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, …
F1 = F2 = 1, Fn+2 = Fn+1 + Fn
6-2) 재귀함수
어떤 함수가 자신을 다시 호출하여 작업을 수행하는 방식
반환타입 함수이름 (매개 변수) {
종료 조건
…
함수이름(…)
} 📝예시1
public class Main {
static int recursion1(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
return 3 * recursion1(n - 1);
}
static int recursion2(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
return n + recursion2(n - 1);
}
static int recursion3(int n) {
if (n < 3) {
return 1;
}
return recursion3(n - 2) + recursion3(n -1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 점화식 -> 반복문, 재귀함수
System.out.println("== 점화식/재귀함수 연습1 ==");
// 1, 3, 9, 27, ... 의 n번째 수
int n = 4;
int result = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
result = 1;
} else {
result *= 3;
}
}
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(recursion1(n));
System.out.println("== 점화식/재귀함수 연습2 ==");
// 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, ... 의 n번째 까지의 합
n = 5;
result = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++) {
result += i;
}
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(recursion2(n));
System.out.println("== 점화식/재귀함수 연습3 ==");
// 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, ...의 n번 째 수
n = 6;
result = 0;
int a1 = 1;
int a2 = 1;
if (n < 3) {
result = 1;
} else {
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
result = a1 + a2;
a1 = a2;
a2 = result;
}
}
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(recursion3(n));
}
}📝예시2
팩토리얼을 재귀함수로 구현하시오.
public class Practice1 {
static int factorial(int n) {
if (n == 1) {
return 1;
}
return n * factorial(n - 1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
System.out.println(factorial(1));
System.out.println(factorial(2));
System.out.println(factorial(3));
System.out.println(factorial(4));
System.out.println(factorial(5));
}
}📝예시3
최대공약수를 재귀함수로 구현하시오.
public class Practice2 {
static int gcd(int a, int b) {
if (a % b == 0) {
return b;
}
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
System.out.println(gcd(3, 5));
System.out.println(gcd(2, 6));
System.out.println(gcd(8, 12));
}
}7) 지수와 로그
7-1) 제곱, 제곱근, 지수
제곱근 제곱
- 같은 수를 두 번 곱함 - 거듭 제곱: 같은 수를 거듭하여 곱함
(= root, √)
- a를 제곱하여 b가 될 때 a를 b의 제곱근이라고 함
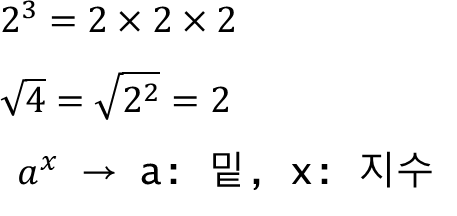
7-2) 로그


📝예시1
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 제곱, 제곱근, 지수
System.out.println("== 제곱 ==");
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 3));
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, -3));
System.out.println(Math.pow(-2, -3));
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 30));
System.out.printf("%.0f\n", Math.pow(2, 30));
System.out.println("== 제곱근 ==");
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(16));
System.out.println(Math.pow(16, 1.0/2));
System.out.println(Math.pow(16, 1.0/4));
// 참고) 절대 값
System.out.println("== 절대 값 ==");
System.out.println(Math.abs(5));
System.out.println(Math.abs(-5));
// 2. 로그
System.out.println("== 로그 ==");
System.out.println(Math.log(2.7182818284590452353602874713527));
System.out.println(Math.log10(1000));
System.out.println(Math.log(4) / Math.log(2));
}
}📝예시2
제곱과 제곱근을 Math 없이 구현하기
public class Practice {
static double pow(int a, double b) {
double result = 1;
boolean isMinus = false;
if (b == 0) {
return 1;
} else if (b < 0) {
b *= -1;
isMinus = true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) {
result *= a;
}
return isMinus ? 1 / result : result;
}
static double sqrt(int a) {
double result = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
result = (result + (a / result)) / 2;
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Test code
System.out.println("== Math pow ==");
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 3));
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, -3));
System.out.println(Math.pow(-2, -3));
System.out.println("== My pow ==");
System.out.println(pow(2, 3));
System.out.println(pow(2, -3));
System.out.println(pow(-2, -3));
System.out.println("== Math sqrt ==");
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(16));
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(8));
System.out.println("== My sqrt ==");
System.out.println(sqrt(16));
System.out.println(sqrt(8));
}
}8) 알고리즘 복잡도
8-1) 복잡도 (Complexity)
알고리즘 성능을 나타내는 척도
시간 복잡도 (Time Complexity)
- 알고리즘의 필요 연산 횟수
공간 복잡도 (Space Complexity)
- 알고리즘의 필요 메모리
시간 복잡도와 공간 복잡도는 Trade-off 관계
8-2) 시간 복잡도 (Time Complexity)
어떤 문제를 해결하기 위한 알고리즘의 필요 연산 횟수
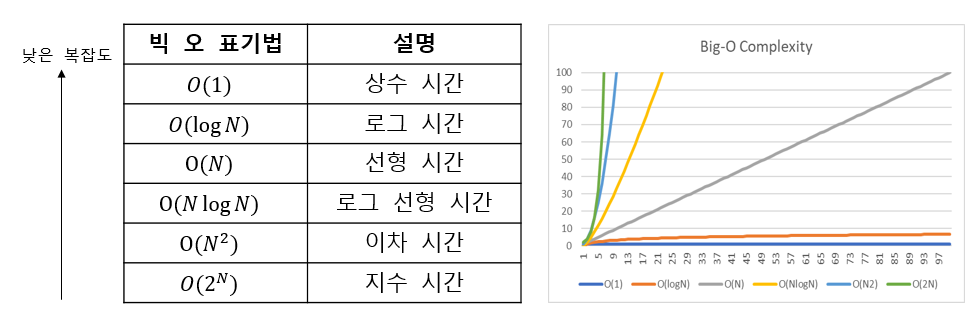
8-3) 공간 복잡도
어떤 문제를 해결하기 위한 알고리즘의 필요 메모리 사용량
빅오 표기법을 통해 나타냄
- 일반적으로 메모리 사용량 기준은 MB 단위
int[] a = new int[1000]; // 4KB
int[][] a = new int[1000][1000] // 4MB
📝예시
public class Main {
static int fibonacci(int n) {
if (n < 3) {
return 1;
}
return fibonacci(n - 2) + fibonacci(n - 1);
}
static int factorial(int n) {
if (n < 1) {
return 1;
}
return n * factorial(n - 1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 시간 복잡도
System.out.println("== 시간 복잡도 ==");
// O(1)
System.out.println("== O(1) ==");
System.out.println("hello");
// O(logN)
System.out.println("== O(logN) ==");
for (int i = 1; i < 16; i*=2) {
System.out.println("hello");
}
// O(N)
System.out.println("== O(N) ==");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.println("hello");
}
// O(NlogN)
System.out.println("== O(NlogN) ==");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < 8; j*=2) {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
// O(N^2)
System.out.println("== O(N^2) ==");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
System.out.print("hello ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// O(2^N)
System.out.println("== O(2^N) ==");
// 피보나치 재귀
// 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, ...
System.out.println(fibonacci(6));
// 2. 공간 복잡도
System.out.println("== 공간 복잡도 ==");
// O(N)
System.out.println("== O(N) ==");
int n = 3;
System.out.println(factorial(n));
// O(1)
System.out.println("== O(1) ==");
int result = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
result *= i;
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}