이진 검색 트리를 살펴보기 전에 트리와 이진 트리가 무엇인지부터 알아보자.
Tree
일단 앞써 살펴봤던 그래프와 트리의 차이점을 정리해 놓은 표를 참고하면 이해하기 쉽다.

트리는 방향 그래프 (부모 => 자식) 이고 비순환 그래프이다.
또 그래프와 가장 큰 차이점은 정점 노드가 있는다는 것이다.
그래프는 네트워크 모델이며 트리는 부모 자식관계가 있는 계층 모델이다.
정점의 수가 n개이면 n -1의 간선을 가진다.
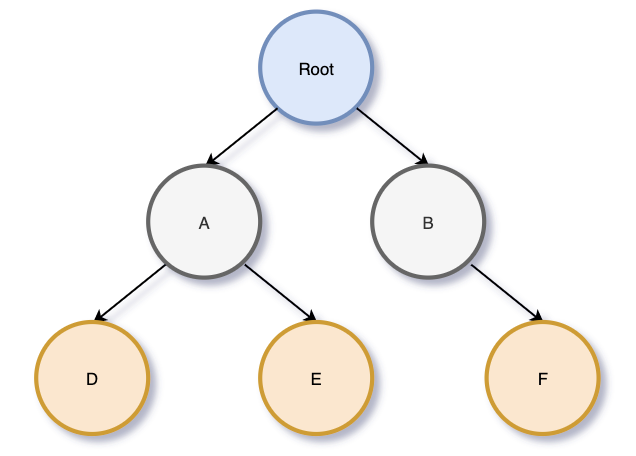
여기서 자식의 수가 항상 2보다 작거나 같은 트리를 이진 트리라고 한다.
여기서 더 나아가 일정한 규칙으로 뻗어나가며 순서가 있는 데이터 구조로 정리한다면 (예: 왼쪽은 작은 숫자 오른쪽은 큰 숫자) 이진 검색 트리라고도 한다.
순서가 있는 데이터들을 찾고 넣을 일이 많을 때 BST를 사용한다.
트리가 Unbalance하게 한쪽으로 치우쳐진다면 검색, 삭제, 삽입에서 O(n)의 시간 복잡도를 갖지만 balance가 잘 맞춰져있다면 O(log n)의 시간 복잡도를 갖는다.
그렇다면 직접 이진 검색 트리를 구현해보자.
class BST {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
insert(value) {
const newVertex = new BST(value);
const recursion = vertex => {
if (vertex.value >= newVertex.value) {
if (!vertex.left) {
vertex.left = newVertex;
} else {
recursion(vertex.left);
}
} else {
if (!vertex.right) {
vertex.right = newVertex;
} else {
recursion(vertex.right);
}
}
};
recursion(this);
}
}
const bsTree = new BST(15);
bsTree.insert(6);
bsTree.insert(23);
bsTree.insert(3);
bsTree.insert(9);
bsTree.insert(19);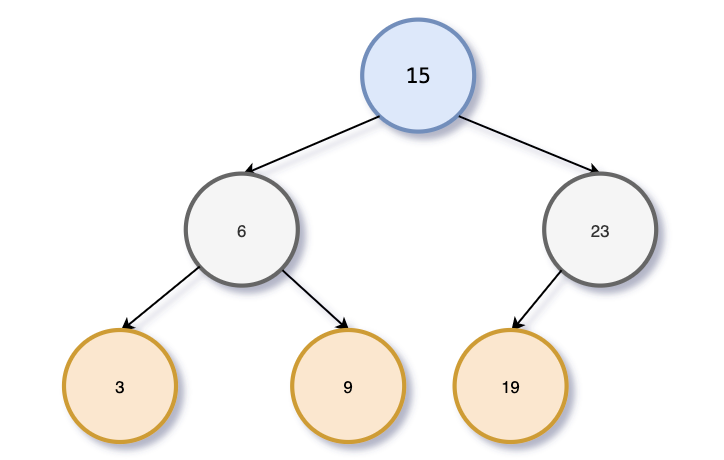
정점이 있는지 확인
contains(value) {
let result = false;
if (this.value === value) return true;
const recursion = vertex => {
if (vertex.value > value) {
if (vertex.left.value === value) {
result = true;
} else {
vertex.left && recursion(vertex.left);
}
} else {
if (vertex.value === value) {
result = true;
} else {
vertex.right && recursion(vertex.right);
}
}
};
recursion(this);
return result;
}
console.log(bsTree.contains(10)); // false
console.log(bsTree.contains(6)); // true
console.log(bsTree.contains(19)); // true
console.log(bsTree.contains(9)); // true