Linked list
단일 연결 리스트
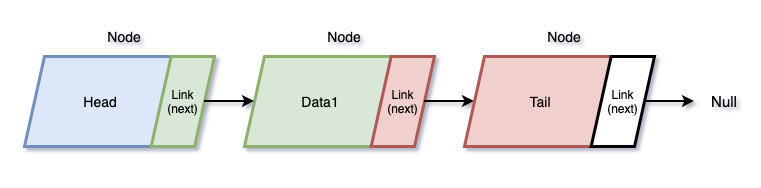
노드라 불리는 객체가 모여 연결 리스트를 구성한다.
각 노드는 next link로 다른 노드와 연결된다. link에서 다음 노드를 참조한다.
인덱스로 요소를 참조할 수 있는 배열과 달리 연결리스트의 요소는 다른요소와의 관계를 통해 원하는 요소를 참조할 수 있다.
연결 리스트를 만드려면 노드 클래스를 따로 만들어야한다.
배열과 연결 리스트 비교
타 언어에서는 배열의 길이가 정해져 있어 배열이 꽉 차면 추가로 데이터를 입력하기 어렵다.
데이터 추가 및 삭제 시 나머지 요소를 이동해야 하므로 어려움이 따른다. (JS는 해당X)
| 종류 | 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|---|
| 배열 | 랜덤 엑세스가 가능 (빠른 접근이 가능하다.) | 메모리 사용이 비효율적이다. 배열 내의 데이터 이동 및 재구성이 어렵다. |
| 연결 리스트 | 동적으로 메모리 사용 가능 데이터 재구성 용이 대용량 데이터 처리 용이 | 특정위치 데이터 검색 불리 메모리 추가 사용 |
ex) 이전 음악 재생, 다음 음악 재생
대표적인 프로퍼티와 메서드는 아래와 같다.
- head, tail : 가장 첫 노드와 마지막 노드
- insert(newNode, target) : 노드를 특정 노드 뒤에 삽입
- remove(target) : 특정 노드를 제거
🎨 그림으로 표현해보기 🎨
- Singly linked list
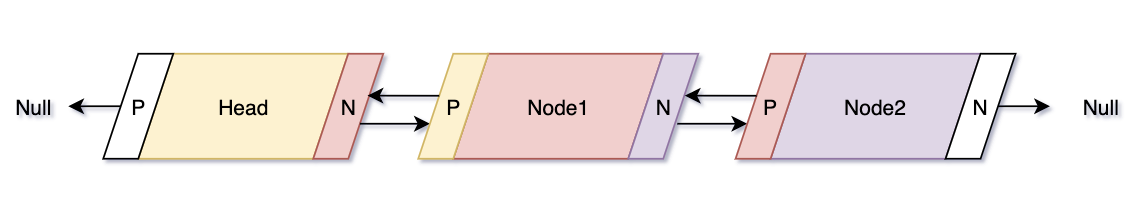
- Doubly linked list
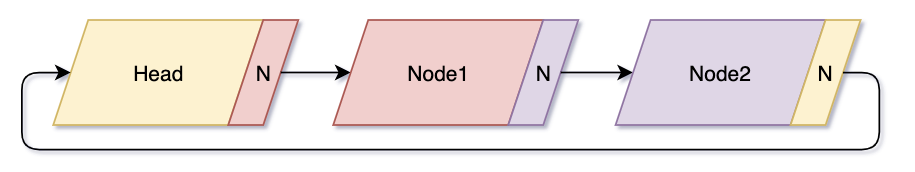
- Circular Linked List
- Insert
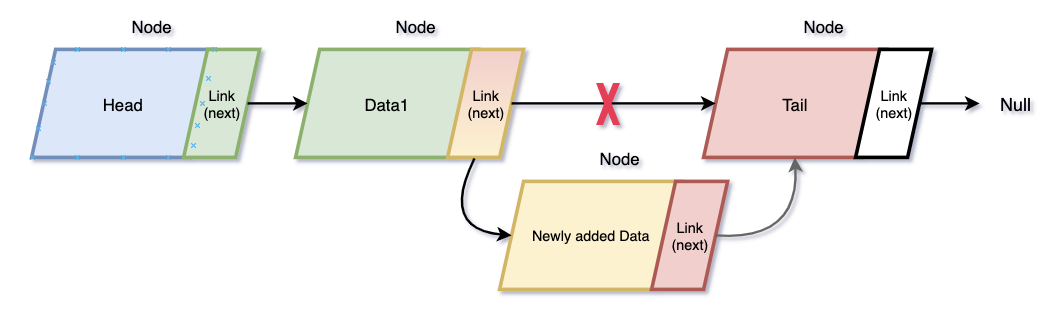
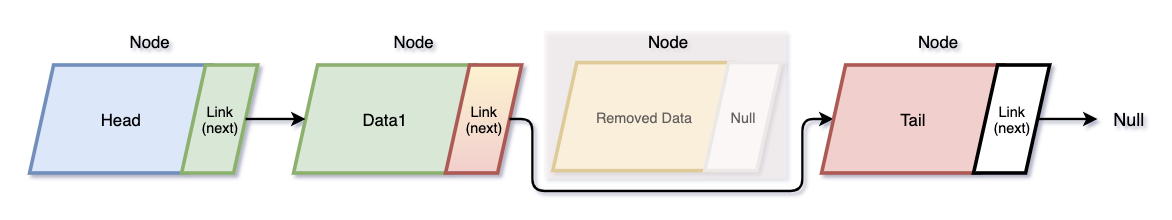
- Remove
💻 Pseudo code 💻
1. Node 클래스 , LinkedList 클래스 생성
2. Node 인스턴스에는 value와 next 프로퍼티 생성
3. insert는 find 헬퍼 함수를 이용해서 특정 요소 뒤에 붙일지 찾아서 특정 요소의 link 수정
그리고 삽입한 node의 link에 특정 요소의 이전 link를 넣어준다.
4. remove는 특정 노드의 이전 노드를 찾는 findPrevious 헬퍼 함수를 이용해 이전 노드를 찾는다.
그리고 이전 노드의 link에 특정 노드의 다음 노드의 link를 넣어준다.
특정 노드의 link 값을 비워줘 참조를 끊어준다.👩💻 구현 👨💻
class Node {
constructor(value, next = null) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
insert(value, target) {
if (!this.head) {
this.head = new Node(value);
this.tail = this.head;
return;
} else {
const currentNode = this.find(target);
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (currentNode) {
if (currentNode === this.tail) {
this.tail = newNode;
}
newNode.next = currentNode.next;
currentNode.next = newNode;
}
}
}
find(target) {
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode.value !== target) {
if (currentNode.next === null) {
throw new Error("Target is not exist");
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return currentNode;
}
remove(target) {
const toRemove = this.find(target);
if (toRemove === this.head) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return toRemove;
}
const prevTarget = this.findPrevious(target);
if (toRemove === this.tail) {
this.tail = prevTarget;
}
prevTarget.next = toRemove.next;
toRemove.next = null;
return toRemove;
}
findPrevious(target) {
let prevNode = this.head;
if (prevNode === this.find(target)) {
return;
}
while (prevNode.next !== this.find(target)) {
if (prevNode.next === null) {
break;
}
prevNode = prevNode.next;
}
return prevNode;
}
}
const linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.insert("a");
linkedList.insert("b", "a");
linkedList.insert("c", "b");
linkedList.insert("d", "c");
linkedList.insert("f", "d");
linkedList.remove("c");
linkedList.remove("f");
linkedList.remove("a");
console.log(linkedList);
console.log(linkedList.head); // Node {value: "b", next: Node, constructor: Object}
console.log(linkedList.head.next); // Node {value: "d", next: null, constructor: Object}
console.log(linkedList.tail); // Node {value: "d", next: null, constructor: Object}