Promise, async / await
앞에서 살펴본 내용 (자바스크립트 비동기 처리) 마지막 부분에서 콜백 함수들을 순차적으로 계속 사용하면 가독성이 떨어지고 에러 처리가 복잡해지는 콜백 지옥에 대해서 설명했다.
이러한 콜백 지옥에서 벗어나기 위해 Promise, async / await에 대해 순서대로 알아보자.
Promise
const increaseAndPrint = (number, callback) => {
setTimeout(() => {
let increased = number + 1;
console.log(increased);
if (callback) {
callback(increased);
}
}, 1000);
}
increaseAndPrint(0, n =>
increaseAndPrint(n, n =>
increaseAndPrint(n, n =>
increaseAndPrint(n, n =>
increaseAndPrint(n)
)
)
)
);이러한 콜백 지옥을 해결하기 위해 등장한 Promise의 기본적인 동작은 이러하다.
Promise는 언젠가 완료가 되는 작업의 결과 값을 담는 상자와 같은 역할을 하는 객체이다.
상자가 만들어질 때는 안에 어떠한 내용이 들어갈지 모를 수도 있다. 그래서 then이라는 메소드를 통해 콜백을 등록하고 작업이 끝났을 때 결과 값을 상자 안에 있는 결과 값을 꺼내 추가 작업을 할 수 있다.
Promise 생성자를 통해서 Promise 객체를 만들 수 있다. 생성자 함수의 첫 번째 인수에는 resolve가 들어가고 콜백 안에서 resolve를 호출하면 resolve에 인수로 준 값이 곧 Promise 라는 상자에 들어가 있는 최종적인 결과 값이다.
두 번째 인수에는 reject 함수가 들어가고 비동기 작업에서 에러가 발생했을 때 호출하는 함수이다.
const increaseAndPrint = n => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
const value = n + 1;
if (value === 5) {
const error = new Error();
error.name = "Value is five";
reject(error);
return;
}
console.log(value);
resolve(value);
}, 1000);
});
};
increaseAndPrint(0).then(n =>
increaseAndPrint(n).then(n =>
increaseAndPrint(n).then(n =>
increaseAndPrint(n).then(n =>
increaseAndPrint(n)
.then(n => increaseAndPrint(n))
.catch(e => console.error(e))
)
)
)
);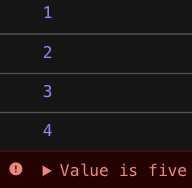
위의 코드를 설명하자면 처음 1초 동안은 Promise 객체는 결과값이 없는 상태이다. 그리고 1초가 지나면 resolve 함수가 호출되어 Promise 객체는 결과 값을 갖는 객체가 된다. 거기서 then 메소드에 콜백함수로 increaseAndPrint를 넘겨서 1초-2초 사이에는 1의 결과 값을 가지고 있다가 다시 총 2초가 지나면 resolve 함수가 호출되어 Promise 객체에는 2라는 결과 값이 들어가게 된다. 여기서 알 수 있는 점은 then 메소드 자체도 Promise 객체를 반환한다는 것이다. 이렇게 계속 진행이 되고 value의 값이 5가 되었을 때 reject 함수로 넘긴 에러를 catch 메서드를 이용해 가져온다.
const posts = [
{ title: "Post One", body: "This is post one" },
{ title: "Post Two", body: "This is post two" }
];
const getPosts = () => {
setTimeout(() => {
let output = "";
posts.forEach((post, index) => {
output += `<li>${post.title}</li>`;
});
document.body.innerHTML = output;
}, 1000);
};
const creaetPost = post => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
posts.push(post);
const error = false;
if (!error) {
resolve();
} else {
reject("Error: Something went wrong");
}
}, 2000);
});
};
creaetPost({ title: "Post Three", body: "This is post Three" })
.then(getPosts)
.catch(err => console.error(err));
이런식으로 포스트를 생성하고 그 다음 포스트를 가져오는 흐름을 Promise를 사용해 처리할 수 있다.
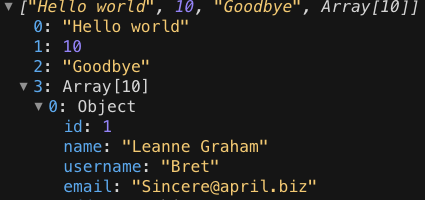
Promise.all
Promise.all 메소드는 인수로 들어온 이터러블 객체에 있는 모든 Promise 객체가 완료되었을 때 그 자신도 완료되는 새 Promise 객체를 반환한다.
const promise1 = Promise.resolve("Hello world");
const promise2 = 10;
const promise3 = new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
setTimeout(resolve, 2000, "Goodbye")
);
const promise4 = fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users").then(res =>
res.json()
);
Promise.all([promise1, promise2, promise3, promise4]).then(values => {
console.log(values);
});
Promise.race
Promise.race는 제일 처음 완료되는 Promise 객체를 반환한다.
Promise.race([promise1, promise2, promise3, promise4]).then(values => {
console.log(values);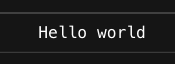
async / await
Promise를 사용하는 비동기 프로그래밍 방식은 콜백 지옥에 비해 상당히 좋아졌지만 여전히 콜백을 사용해야하는 단점이 있다. 따라서 ES2017에서 나온 비동기 함수(Async function)을 사용해 동기적 코드와 비슷한 구조를 갖는 비동기적 코드를 짤 수가 있다.
비동기 함수는 항상 Promise 객체를 반환한다는 특징이 있다. 결과값은 비동기 함수 내에서 무엇을 반환하느냐에 따라서 결정된다.
const foo = async () => {
return "Hello World";
};
foo().then(v => console.log(v));
비동기 함수에서는 await 키워드를 사용한다. await은 then과 비슷한 기능을 하며 await 뒤에 오는 Promise가 결과값을 가질 때까지 함수의 실행을 중단시킨다.
const sleep = speed => {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`${speed * 1000}초 지났습니다.`);
resolve();
}, speed * 1000);
});
};
const foo = async () => {
await sleep(2);
console.log("1차 실행");
await sleep(2);
const done = await Promise.resolve("종료");
console.log(done);
};
foo();
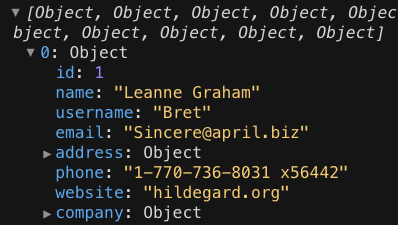
const fetchUsers = async () => {
const res = await fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users");
const data = await res.json();
console.log(data);
};
fetchUsers();