1. 변수와 메모리
프로세스란?
-
프로세스는 실행중인 프로그램이다.
-
프로그램 실행을 위해서는 프로그램의
코드,데이터,스택,힙,U-영역 등이 필요하다. -
프로그램을 실행시키기 위해 필요한 메모리를 모두 합쳐서 프로세스 이미지라고 한다.
-
프로그램 자체가 프로세스는 아니다.
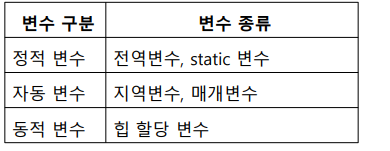
데이터 영역 : static 변수, 전역 변수
스택 영역 : 매개변수, 지역변수
힙 영역 : 동적할당
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int a=1;
static int b =2;
int main()
{
int c= 3;
static int d =4;
char *p;
p = (char *) malloc(40);
fun(5);
}
void fun(int n)
{
int m= 6;
}
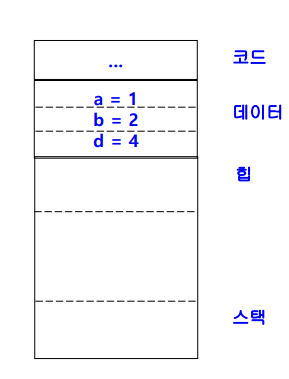
- 프로그램 시작할때 메모리 영역
- static 변수, 전역변수 -> 메모리의 데이터공간에 write
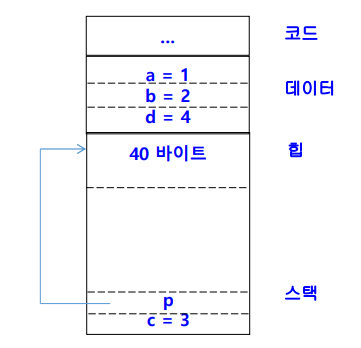
- main() 함수 실행할 때 메모리 영역
-
지역 변수 -> 메모리의 스택 공간에 write
-
동적할당 -> 메모리의 힙 공간에 write
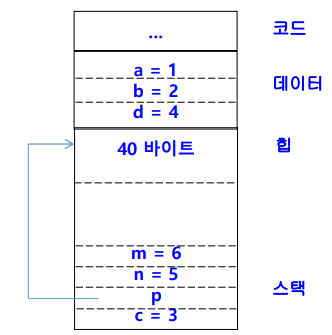
- 함수 fun() 실핼할 때 메모리 영역
- 매개변수 및 지역변수 -> 스택
void fun(int n) { int m = 6; }
2. 동적 할당
동적 메모리 할당
동적 할당을 사용하는 이유
- 필요할때 필요한 만큼만 메모리를 요청해서 사용하고
- 필요없을때 반납하여
- 메모리를 절약한다.
- malloc(), calloc()
: 메모리 할당함수
- realloc()
: 할당된 메모리 크기 변경
- free()
: 메모리 해제
메모리 할당
#include <stdlib.h>
void *malloc(size_t size);
// size 바이트 만큼의 메모리 공간을 할당하며 그 시작주소를 void*형으로 반환한다.
void free(void *ptr);
포인터 p가 가리키는 메모리 공간을 해제한다.- ❗ 힙에 동적 메모리 할당함
ex)
char *ptr;
ptr = (char *) malloc(40);
int *ptr;
ptr = (int *) malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
struct student{
int id;
char name[10];
};
struct student *ptr;
ptr = (struct student *) malloc(sizeof(struct student));
// 또는
typedef struct{
int id;
char name[10];
}student;
student *ptr;
ptr = (student *) malloc(sizeof(student));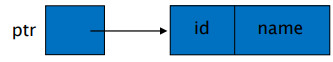
배열 할당
- 같은 크기의 메모리를 여러 개 할당할 경우
#include <stdlib.h>
void *calloc(size_t n, size_t size);
// 크기가 size인 메모리 공간을 n개 할당한다. 값을 모두 0으로 초기화한다. 실패하면 NULL을 반환- 이미 할당된 메모리의 크기 변경
#include <stdlib.h>
void *realloc(void *ptr, size_t newsize);
// ptr이 가리키는 이미 할당된 메모리의 크기를 newsize로 변경calloc() ex)
int *p,*q;
p = malloc(10*sizeof(int));
if (p == NULL)
perror(“malloc”);
q = calloc(10, sizeof(int));
if (q == NULL)
perror(“calloc”);3. 연결 리스트
연결 리스트의 필요성
ex) 여러 학생들의 데이터를 저장하는 경우
-> 배열의 크기를 미리 결정해야 하는 문제점이 있다.
-> 크기를 미리 결정하여 새로운 학생을 받을수 없다.
❗ 연결리스트를 사용하면 해결 가능

struct student{
int id;
char name[20];
struct student *next;
};
struct student *ptr;
ptr = (struct student *) malloc(sizeof(struct student));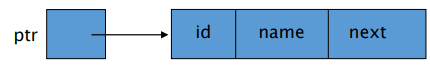
ex) stud2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 학생 정보를 입력받아 연결리스트에 저장하고 학생 정보를 역순으로 출력
int main()
{
int count = 0, id;
char name[20];
struct student *p, *head = NULL;
printf("학번과 이름을 입력하세요 \n");
while(scanf("%d %s",id,name)==2)
{
p = (struct student *) malloc(sizeof(struct student));
if( p == NULL )
{
perror("malloc");
exit(1);
}
p -> id = id;
strcpy(p->name,name);
p->next = head;
head = p;
}
printf("\n * 학생 정보(역순) *\n");
p = head;
while(p!= NULL)
{
count ++;
printf("학번 : %d 이름: %s\n",p->id,p->name);
p = p->next;
}
printf("총 %d 명입니다. \n",count);
exit(0);
}
4. 메모리 관리 함수
#include <string.h>
void *memset(void *s, int c, size_t n);
//s에서 시작하여 n 바이트만큼 바이트 c (char)로 설정한 다음에 s를 반환한다.
int memcmp(const void *s1, const void *s2, size_t n);
// s1과 s2에서 첫 n 바이트를 비교해서, 메모리 블록 내용이 동일하면 0을 반환하고 s1이 s2보다 작으면 음수를 반환하고, s1이 s2보다 크다면 양수를 반환한다.
void *memchr(const void *s, int c, size_t n);
// s가 가리키는 메모리의 n 바이트 범위에서 문자 c를 탐색한다. c와 일치하는 첫 바이트에 대한 포인터를 반환하거나,c를 찾지 못하면 NULL을 반환한다.
void *memmove(void *dst, const void *src, size_t n);
// src에서 dst로 n 바이트를 복사하고, dst를 반환한다.
void *memcpy(void *dst, const void *src, size_t n);
// src에서 dst로 n 바이트를 복사한다. 두 메모리 영역은 겹쳐지지 않는다. 만일 메모리 영역을 겹쳐서 쓰길 원한다면 memmove() 함수를 사용해라. dst를 반환한다.EX)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char str[32]="Do you like Linux?";
char *ptr,*p;
ptr = (char *) malloc(32);
memcpy(ptr, str, strlen(str));
puts(ptr);
memset(ptr+12,'l',1);
puts(ptr);
p = (char *) memchr(ptr,'l',18);
puts(p);
memmove(str+12,str+7,10);
puts(str);
}핵심개념
- 지역변수와 매개변수 -> 스택에 자동할당, 동적변수 -> 힙에 할당
- 동적할당을 사용하는 이유는 필요할 때 필요한 만큼만 메모리를 요청해서 사용하여 메모리를 절약하기 위함이다.
- malloc()함수는 메모리를 할당할때 사용하고 free는 할당한 메모리를 해제할때 사용한다.
- malloc() 함수는 메모리 할당에 성공하면 할당된 메모리의 시작주소를 반환하고 실패하면 NULL을 반환한다.
