오늘 풀어볼 문제는 백준 2146
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2146
그래프 이론 알고리즘, 난이도는 골드3
문제 설명
간단하게 설명하면
시작
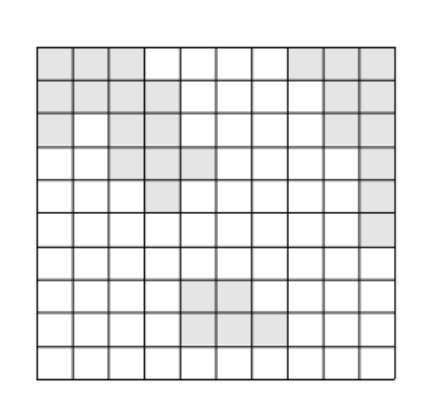
첫번 째 입력 값으로 matrix 의 크기를 입력 받는다. 이때 matrix 는 N X N 이며, N <= 100이다.
다음으로 0과 1로 섬과 바다를 입력 받는다.
문제
두 점을 연결하는 가장 짧은 거리 구하기
풀이
동일한 섬을 연결하는 최단 길이를 구하면 안된다.
무슨 말 이냐면,
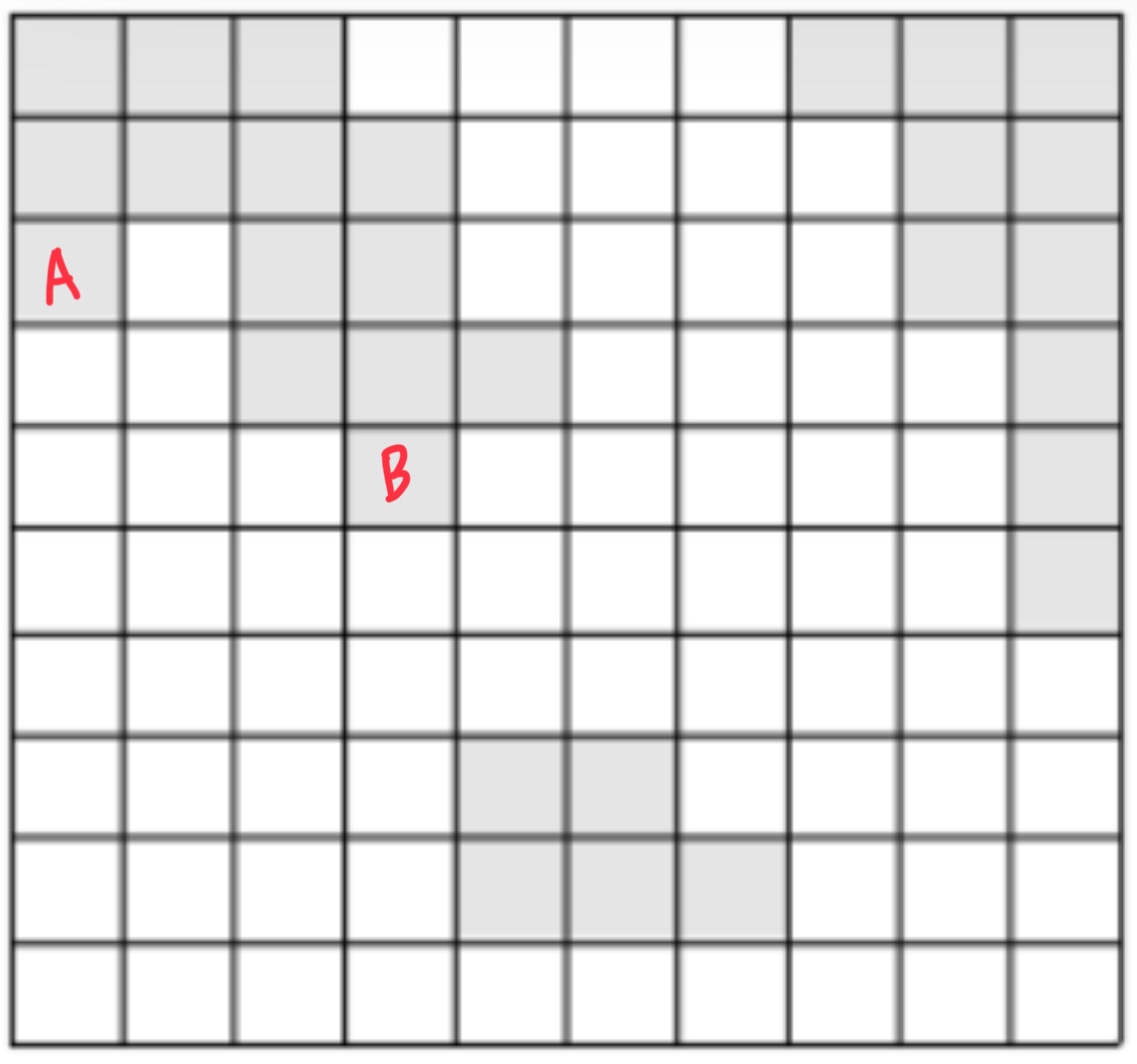
A에서 시작에서 B 를 연결하는 경우는 같은 섬을 연결하는 경우 이므로, 최단 길이가 아니다.
따라서 해당 문제를 풀기 위해서는
1. 각 섬을 구분하는 과정
2. 한 섬에서 다른 섬까지의 최단 거리 구하는 과정
이렇게 두 과정이 필요하다.
각 섬을 구분하기
그냥 간단하게 BFS든 DFS든 탐색해서 라벨링 하면 된다.
한 섬에서 다른 섬까지의 최단 거리 구하기
라벨링이 되었으면 이제 다른 섬 까지의 최단 거리를 구해야 하는데
최단 거리 이므로 BFS 를 사용할거임
일단 섬의 가장자리 그러니까 바다와 연결된 부분을 구해야 한다.
1번 섬부터 상하좌우를 확인하면서 바다와 연결된 섬의 가장 자리면 queue에 push 한다.
해당 과정이 끝나면 1번 섬의 가장자리 칸 들이 queue 에 들어있게 된다.
이때 queue 는 구조체로 해당 칸의 행, 열, 거리 정보를 담는다.
while(!queue.isempty())동안 BFS를 한다.
다른 섬을 찾으면 min_value 를 업데이트하고 해당 조건을 break 한다.
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<climits>
using namespace std;
const int dx[] = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
const int dy[] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
vector<vector<int>> temp;
int min_value = INT_MAX;
int island;
void set_temp(const vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
queue<pair<int, int>> qu;
int count = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix.size(); j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == 1 && temp[i][j] == 0) {
qu.push({ i, j });
temp[i][j] = count;
while (!qu.empty()) {
auto current = qu.front();
qu.pop();
int col = current.first;
int row = current.second;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int nx = col + dx[k];
int ny = row + dy[k];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < matrix.size() && ny >= 0 && ny < matrix.size() && matrix[nx][ny] == 1 && temp[nx][ny] == 0) {
qu.push({ nx, ny });
temp[nx][ny] = count;
}
}
}
count++;
}
}
}
island = count - 1;
}
struct node {
int col;
int row;
int cost;
};
void answer(const vector<vector<int>>& temp) {
for (int init = 1; init <= island; init++) {
queue<node> qu;
vector<vector<bool>> visited(temp.size(), vector<bool>(temp.size(), false));
for (int i = 0; i < temp.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < temp.size(); j++) {
if (temp[i][j] == init) {
visited[i][j] = true;
bool is_boundary = false;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int nx = i + dx[k];
int ny = j + dy[k];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < temp.size() && ny >= 0 && ny < temp.size() && temp[nx][ny] == 0) {
is_boundary = true;
break;
}
}
if (is_boundary)
qu.push({ i, j, 0 });
}
}
}
while (!qu.empty()) {
auto current = qu.front();
qu.pop();
if (current.cost >= min_value)
continue;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = current.col + dx[i];
int ny = current.row + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= temp.size() || ny < 0 || ny >= temp.size() || visited[nx][ny])
continue;
if (temp[nx][ny] != 0 && temp[nx][ny] != init) {
min_value = min(min_value, current.cost);
break;
}
if (temp[nx][ny] == 0) {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
qu.push({ nx, ny, current.cost + 1 });
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<vector<int>> matrix(n, vector<int>(n));
temp.resize(n, vector<int>(n));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
cin >> matrix[i][j];
}
}
set_temp(matrix);
answer(temp);
cout << min_value;
}
설명이 좀 부실하긴 한데(주석도 없음^^) 뭐 암튼 이렇게 풀었다.
오랜만에 푸니까 시간이 좀 걸렸다.
일주일에 두 문제는 풀어야지.... 노력해보겠음
