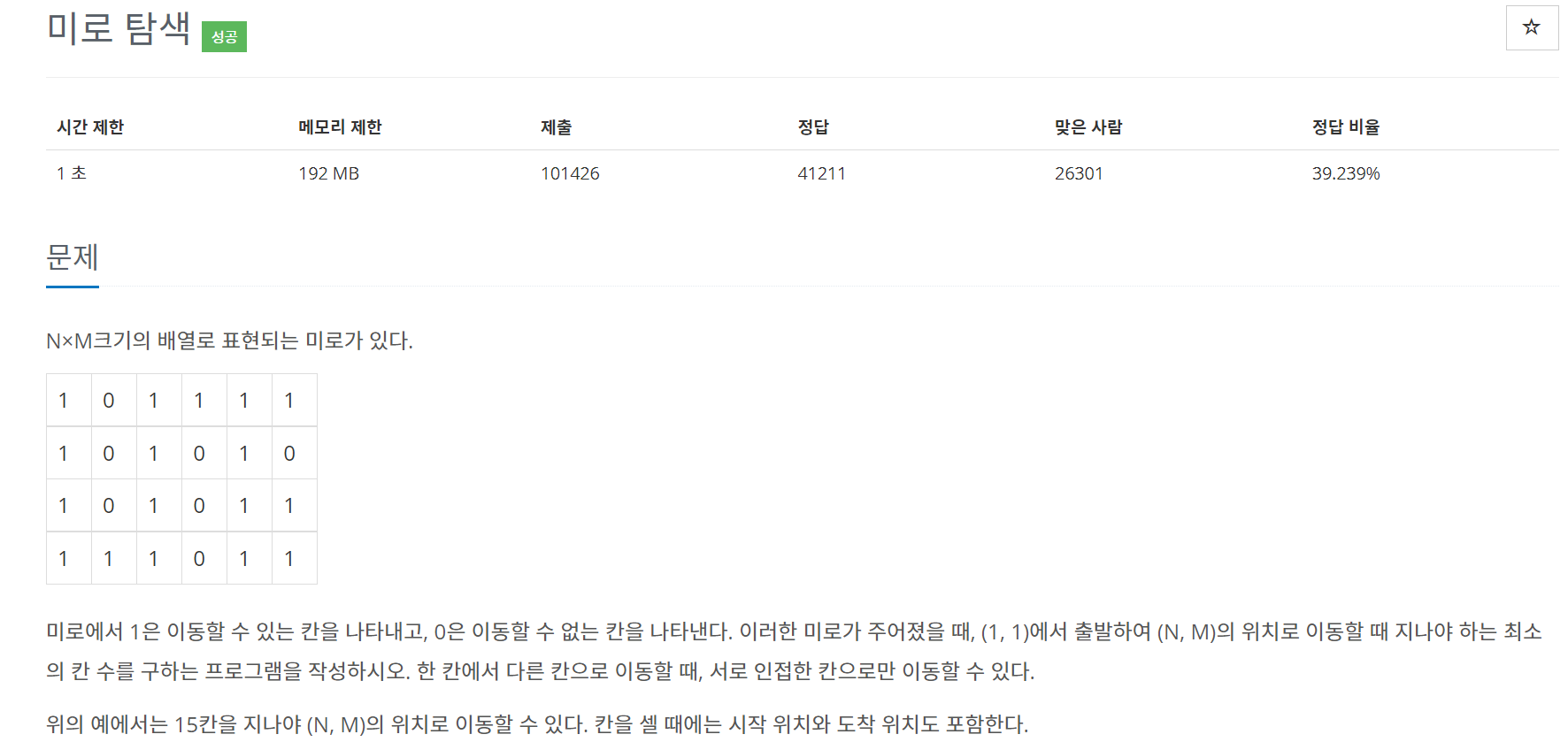
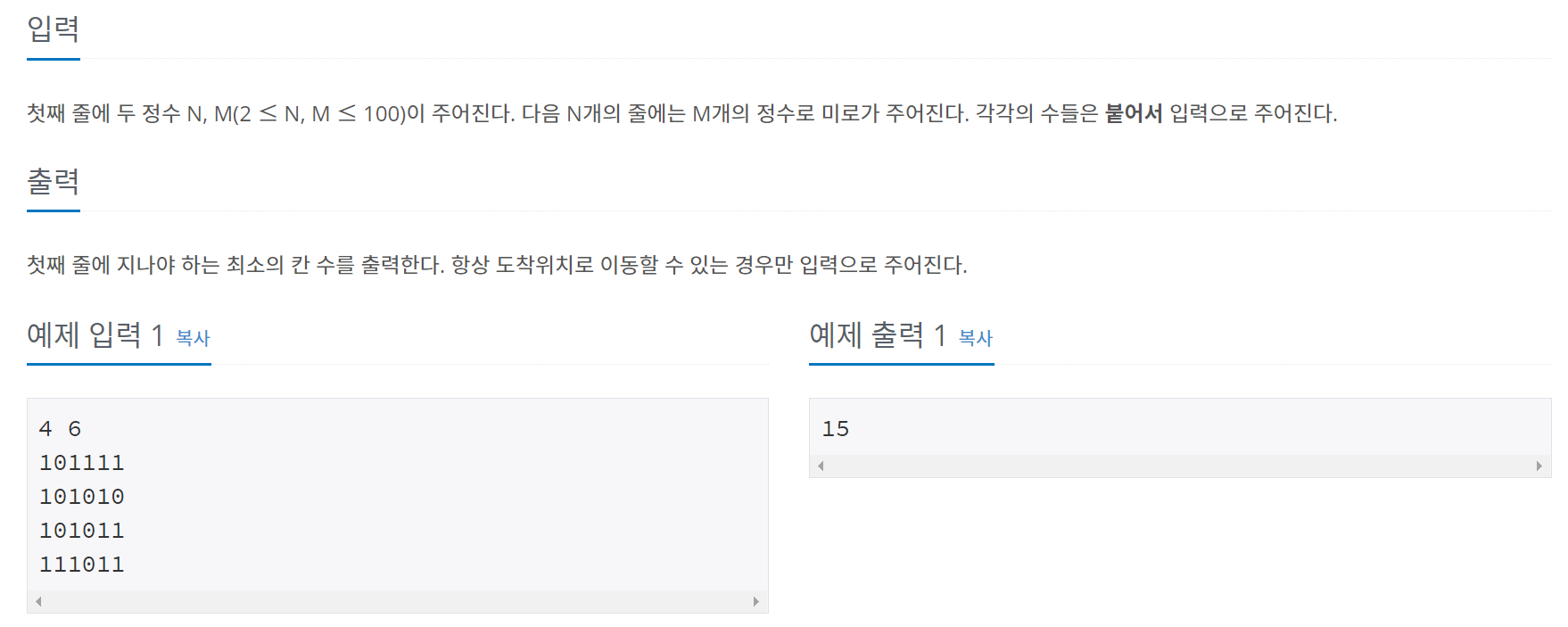
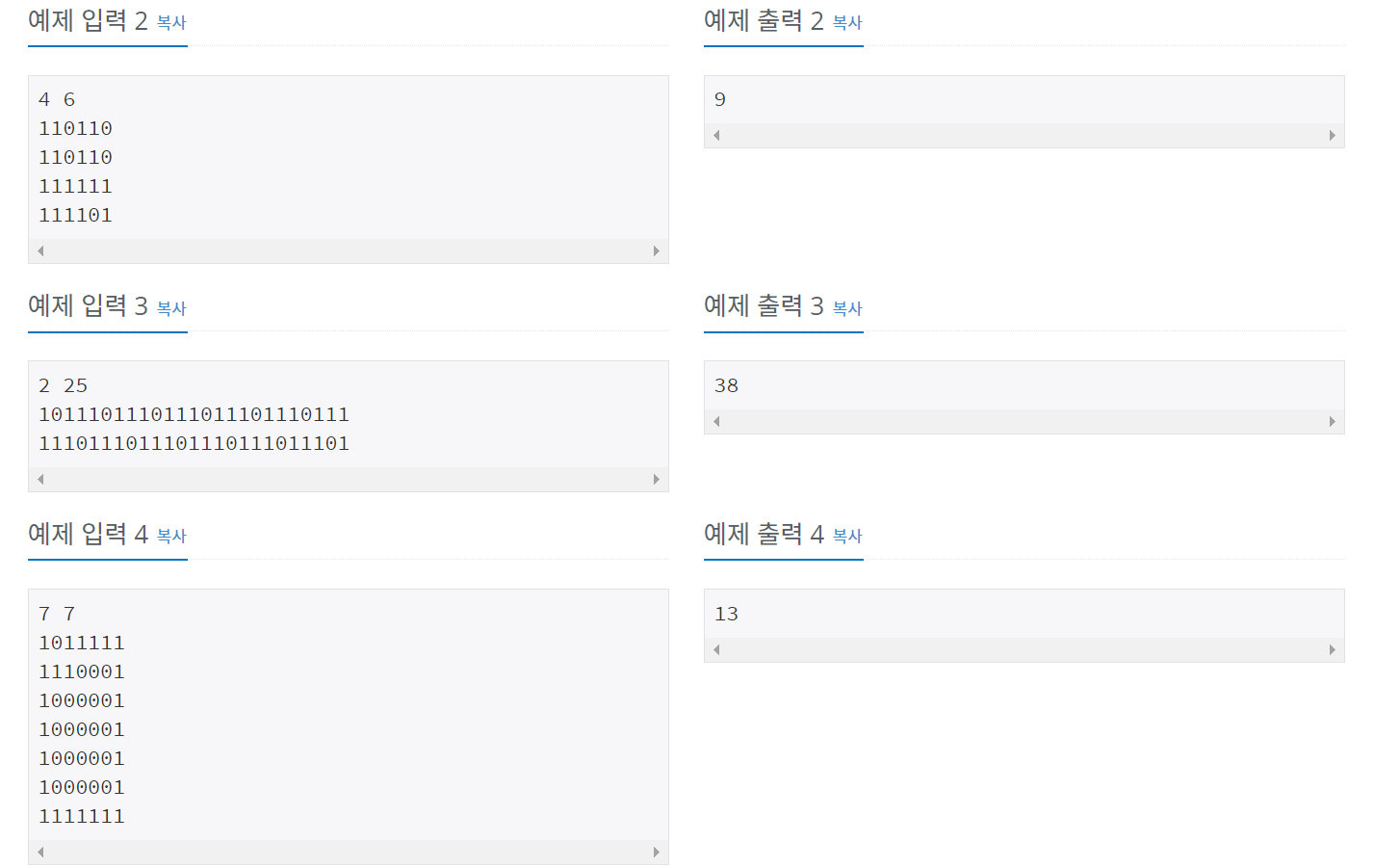
BFS 정답 코드
import java.awt.Point;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class No2178_미로탐색 {
static boolean visited[][];
static Queue<Point> queue = new LinkedList<>();
static int[] dx = {0,0,-1,1};
static int[] dy = {1,-1, 0,0};
static int N,M;
static int[][] maze;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String temp[] = br.readLine().split(" ");
N = Integer.parseInt(temp[0]); //세로
M = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]); //가로
maze = new int[N][M];
visited = new boolean[N][M];
for (int i=0;i<N;i++) {
String s = br.readLine();
for (int j=0;j<M;j++) {
maze[i][j] = s.charAt(j)-'0';
}
}
bfs(0,0);
System.out.println(maze[N-1][M-1]);
}
public static void bfs(int i, int j) {
queue.add(new Point(i,j));
visited[j][i] = true;
outLoop :
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Point current = queue.poll();
for (int h=0;h<4;h++) {
int nx= current.x+dx[h];
int ny = current.y+dy[h];
// if (nx==M-1 && ny==N-1) {
// break outLoop;
// }
if (nx>=0 && ny>=0 && nx<M && ny<N) {
if (visited[ny][nx]==false && maze[ny][nx]==1){
visited[ny][nx]=true;
queue.add(new Point(nx,ny));
maze[ny][nx]=maze[current.y][current.x]+1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
기본적인 bfs문제이다. 처음에 나는 cnt변수를 따로 두어서 하나씩 증가시켰는데, 이렇게 하면 연결되어있는 모든 1을 다 찾기 때문에 답이 나오지 않는다.
따라서 cnt를 따로두지 않고 maze[현재값]+=maze[이전값]+1 하면 된다. 그러면 각 칸에는 각 칸에 도달하기 위한 최단거리가 저장되고, 결과적으로 maze[N-1][M-1]에는 무조건 답이 저장되어 있게된다.
dfs로 풀면 시간초과가 난다고 한다. 이렇게 최단거리를 구하는 문제는 bfs로 접근하는것이 좋다.
