1. Decorator란
'다른 함수'를 인수로 받고,
그 '다른 함수'에 기능을 추가/수정하고,
마찬가지로return 함수의 형태를 갖는 함수/객체를 의미한다.
('다른 함수'가 정의된 부분을 수정할 필요가 없다.)
정의만 읽고 모든 걸 이해하려고 하면 너무 어렵다.
예시를 통해 알아가 보자.
2. Decorator 예시
1) Decorator 미사용
# decorator_function는 '다른 함수'를 인수로 받고 있다.
def decorator_function(another_function):
def inner_function():
return another_function() # <---- '다른 함수'를 실행!
return inner_function
def display():
print(f'이건 {display.__name__}함수입니다.')
# 아래 부분은 지난 시간에 봤던 예제들의 방법과 동일
# waiting for to be executed
decorated_display = decorator_function(display)
# 드디어 함수 실행(호출)!!!!
decorated_display()2) Decorator 사용
def decorator_function(another_function):
def inner_function():
return another_function()
return inner_function
# decorator 사용
@decorator_function
def display():
print(f'이건 {display.__name__}함수입니다.')
display()
# 이 아래 코드는 주석처리
# decorated_display = decorator_function(display)decorator를 사용해서
1) Decorator 미사용 예제와 같은 결과를 만들어 냈다.
이처럼 decorator는 쉽게 함수를 추가하여 구현하게 도와준다.
무엇보다도
def display():
print(f'이건 {display.__name__}함수입니다.')이 함수를 조금의 수정도 하지 않았다는 것이다.
좀 더 이해를 돕기위해 위의 예제의 inner_function 부분을 수정해보겠다.
def decorator_function(another_function):
def inner_function():
print(f'{another_function.__name__}함수가 실행되기 바로 직전입니다.')
return another_function()
return inner_function
@decorator_function
def display():
print(f'이번엔 display 함수입니다.')
display()
결과
display함수가 실행되기 바로 직전입니다.
이건 display 함수입니다.
decorator에 대해 다시 말해보자면
위의 display()는
display= decorator_function(display)와 같은 역할을 한다.
3) 인자가 있는 Decorator
다음과 같이 name_decorator decorator에 "정우성"을 parameter로 적용하여 greeting을 호출하시오.
@name_decorator("정우성")
def greeting():
return "Hello, "
greeting()
결과"Hello, 정우성"
def name_decorator(*args):
def decorator(func):
def wrapper():
hello = func()
name = args[0]
return hello + name
return wrapper
return decorator
# decorator 옆에 '인자'가 있는 경우
@name_decorator("정우성")
def greeting():
return "Hello, "
print(greeting())3)번 예제 보충 설명
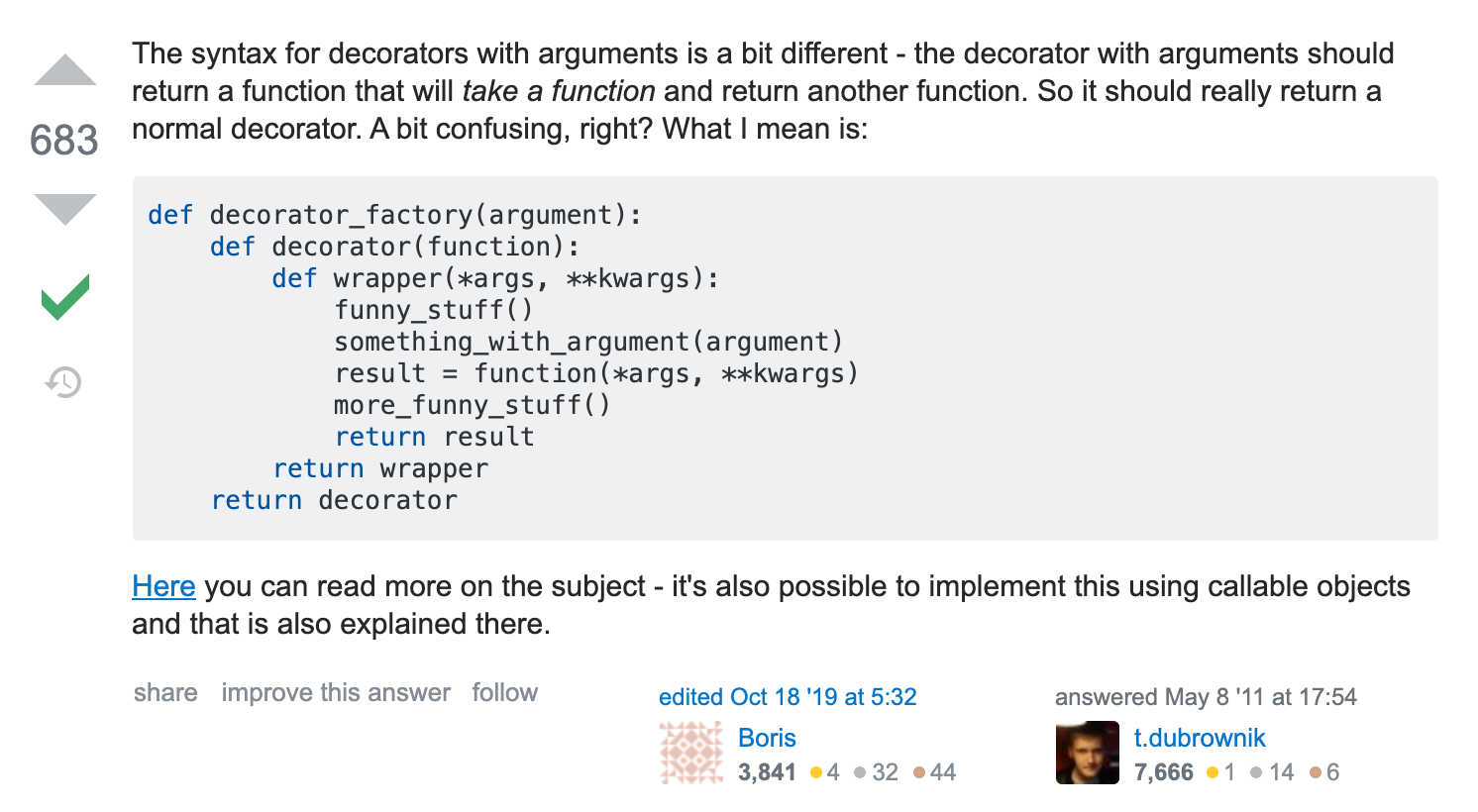
argument(인자)가 있는 name_decorator 함수는
return decorator 가 필요하다.(필요충분조건)
왜냐하면 매개변수 func에 greeting함수를 아직 못넘겨줬기 때문이다.
인수가 없는 경우엔
@name_decorator 는
greeting = name_decortator(greeting)을 대체한 것이다.
인수가 있는 경우엔
@name_decorator("정우성")의 프로세스는
1) 매개변수 *args에 "정우성"을 전달하고
2)return decorator가 실행되고 (위의 코드 확인!)
3) 그제서야 우리가 알고있던 인수가 없던 decorator 처럼
진행되는 것이다.
4) 기본함수가 3가지인 경우
기본함수(add, sub, multiply) 3개와 Decorator 함수
def outer_decorator_func(*args):
def decorator_func(func):
def wrapper():
print(f'{func.__name__}함수 작동중....')
result = func(args)
print(result)
return wrapper
return decorator_func
@outer_decorator_func(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9)
def add(args):
total = 0
for arg in args:
total += arg
return total
add()
@outer_decorator_func(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9)
def sub(args):
total = 0
for arg in args:
total -= arg
return total
sub()
@outer_decorator_func(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9)
def multiply(args):
total = 0
for arg in args:
total *= arg
return total
multiply() - One step at a time - 