
KOCW - 양희재 교수님 강의를 기반으로 운영체제 정리
Mutex (Mutual exclusion)
뮤텍스도 세마포어와 마찬가지로 상호배타를 적용하기 위한 소프트웨어 입니다.
뮤텍스는 세마포어와 다르게 Locking 매커니즘을 사용하여 Lock 걸은 프로세스/쓰레드만이 임계 영역을 나갈때 락을 해제할 수 있습니다. 뮤텍스는 임계 영역을 Lock하기 위해 특별한 Key값을 사용하기 때문에 임계 영역에 접근할 수 있는 프로세스/쓰레드 1개로 고정되며 세마포어의 value값을 1로 설정한 것과 유사하게 동작합니다.
Monitor
뮤텍스와 세마포어 보다 고수준 개념의 동기화 도구입니다.
구조
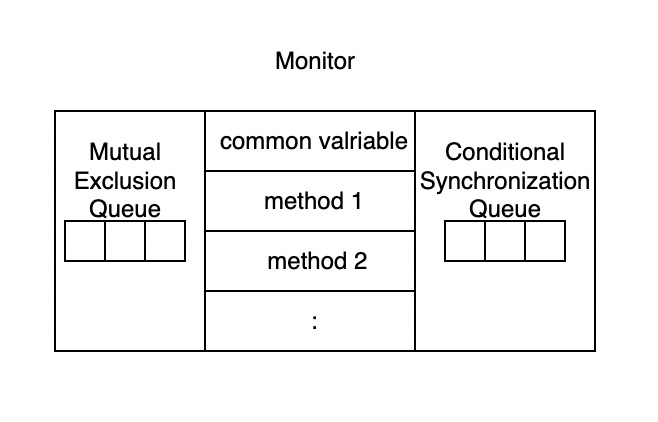
모니터의 구조는 공유자원과 그 공유자원에 접근할 수 있는 여러 함수로 이루어져 있습니다. 세마포어는 한 개의 Queue를 사용한 것과 달리 모니터는 2개의 Queue를 사용하여 각각 상호배타와 조건 동기화를 위해 사용됩니다.
-
공유자원에 접근하는 함수에는 최대 1개의 프로세스/쓰레드만 진입할 수 있고 나머지는 상호배제 큐에서 대기하고 있습니다.
-
접근함수에 진입한 프로세스/쓰레드가
wait()함수를 호출하여 조건 동기 큐로 블락되면 새로운 프로세스/쓰레드가 접근함수로 접근할 수 있습니다. -
새로 접근한 프로세스/쓰레드가
notify()함수를 호출하면 조건 동기 큐에 블락된 프로세스/쓰레드를 깨울 수 있습니다. -
깨워진 프로세스/쓰레드는 현재 프로세스/쓰레드가 끝나면 재진입할 수 있습니다.
자바의 모니터
자바의 모든 객체는 모니터가 될 수 있습니다.
class C {
private int value, ...;
synchronized void f() {
...
}
synchronized void g() {
...
}
void h () {
...
}
}
-
배타동기 : synchronized 키워드 사용하여 지정
-
조건동기 : wait(), notify(), notifyAll() 메소드 사용
g나 f함수에 프로세스/쓰레드가 접근하면 다른 프로세스/쓰레드는 접근할 수 없지만 h함수에는 아무때나 접근할 수 있습니다.
모니터의 Mutual exclusion
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
BankAccount b = new BankAccount();
Parent p = new Parent(b);
Child c = new Child(b);
p.start();
c.start();
p.join();
c.join();
System.out.print("balance = " + b.getBalance());
}
}
class BankAccount {
int balance;
synchronized void deposit(int amount) {
int temp = balance + amount;
System.out.print("+");
balance = temp;
}
synchronized void withdraw(int amount) {
int temp = balance - amount;
System.out.print("-");
balance = temp;
}
int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
class Parent extends Thread {
BankAccount b;
Parent(BankAccount b) {
this.b = b
}
public void run() {
for (int i=0; i<100; i++)
b.deposit(1000);
}
}
class Child extends Thread {
BankAccount b;
Child(BankAccount b) {
this.b = b
}
public void run() {
for (int i=0; i<100; i++)
b.withdraw(1000);
}
}
세마포어와 달리 자바의 모니터 synchronized 키워드를 이용하여 임계영역에 접근하는 프로세스/쓰레드에 상호배타를 적용할 수 있습니다.
모니터의 Ordering
모니터에서 여러 프로세스/쓰레드를 우리가 원하는 순서대로 정하는 방법은 아래와 같습니다.
| P1 | P2 |
|---|---|
| wait() | |
| Section 1 | Section 2 |
| notify() |
P2가 Section2를 실행하기 전에 wait() 메소드를 실행하여 conditional queue에 블락됩니다. P1은 아무 이상없이 Section1이 실행되고 notify() 메소드를 실행하여 conditional queue에 블락된 프로세스/쓰레드를 깨워줍니다.
- 입금 먼저 실행하기
class BankAccount {
int balance;
synchronized void deposit(int amount) {
int temp = balance + amount;
System.out.print("+");
balance = temp;
notify();
}
synchronized void withdraw(int amount) {
while (balance <= 0)
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
int temp = balance - amount;
System.out.print("-");
balance = temp;
}
int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
- 출금 먼저 실행하기
class BankAccount {
int balance;
synchronized void deposit(int amount) {
while (balance == 0)
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
int temp = balance + amount;
System.out.print("+");
balance = temp;
}
synchronized void withdraw(int amount) {
int temp = balance - amount;
System.out.print("-");
balance = temp;
notify();
}
int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
- 입금 출금 교대로 반복하기
class BankAccount {
int balance;
// ture라면 Parent 차례
boolean p_turn = true;
synchronized void deposit(int amount) {
int temp = balance + amount;
System.out.print("+");
balance = temp;
p_turn = false;
// child 깨우기
notify();
// parent 블락
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
}
synchronized void withdraw(int amount) {
// parent 차례라면 child 블락
while (p_turn)
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedExceptione) {}
int temp = balance - amount;
System.out.print("-");
balance = temp;
// parent 깨우기
notify();
p_turn = true;
}
int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
모니터의 전통적 동기화 문제
Producer and Consumer Problem
class Buffer {
int[] buf;
int size, count, in, out;
Buffer(int size) {
buf = new int[size];
this.size = size;
count = int = out = 0;
}
synchronized void insert(int item) {
while (count == size)
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
buf[in] = item;
in = (in + 1) % size;
notify();
count ++;
}
synchronized void remove(int item) {
while (count == size)
try {
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
int item = buf[out];
out = (out + 1) % size;
count --;
notify();
return item;
}
}The Dining Philosopher Problem
젓가락을 세마포어로 구현한것 처럼 모니터로 구현할 수 있습니다.
class Chopstick {
private boolean inUse = false;
synchronized void acquire() throws InterruptedException {
while (inUse)
wait();
inUse = true;
}
synchronized void release() {
inUse = false;
notify();
}
}나머지 부분의 코드는 세마포어와 동일합니다. 모니터로 구현했을 때도 교착상태를 피하기 위해 환형대기 상태를 깨뜨리는 코드가 필요합니다.