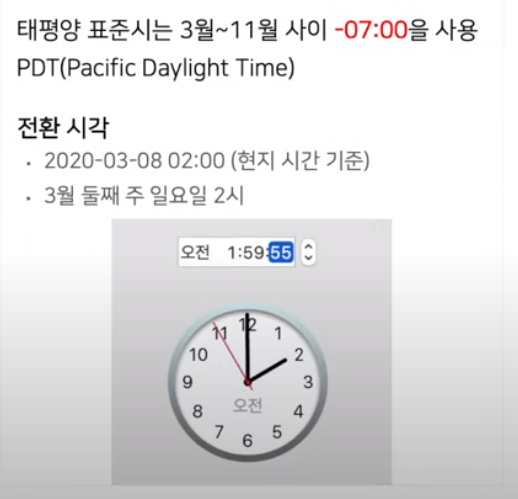
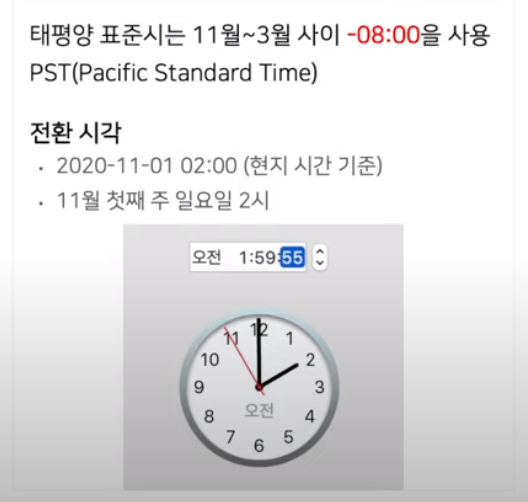
1) 타임존(시간대)
2) 서머타임 : 여름에는 1시간을 앞당겨 생활하고 겨울에는 1시간을 늦춘다.
ex) 태평양 표준시는 -8시간으로 하다가 해가 길어지면(여름이 되면) -7시간으로 바꾼다. (겨울에는 1시간 더 시간이 늦어지고 여름에는 1시간 더 시간이 빨라진다.)
목표 : 각 나라마다 시간대가 다르고 서머타임을 가진 나라들이 존재한다. 써머타임이 있는 나라를 알아보고 그때의 런던 GMT와의 시간 차이를 비교해보자
Intl.DateTimeFormat 사용하기
Intl.DateTimeFormat은 언어에 맞는 날짜 및 시간 서식을 지원하는 객체의 생성자입니다.
const formatter = new Intl.DateTimeFormat('en-us', {
hourCycle: 'h23',
year : 'numeric',
month : 'numeric',
day : 'numeric',
hour : 'numeric',
minute : 'numeric',
second : 'numeric',
timeZone : 'America/Los_Angeles'
});사용법
console.log(formatter.formatToParts(new Date('2020-12-14T10:00:00+09:00')));[
{ type: 'month', value: '12' },
{ type: 'literal', value: '/' },
{ type: 'day', value: '13' },
{ type: 'literal', value: '/' },
{ type: 'year', value: '2020' },
{ type: 'literal', value: ', ' },
{ type: 'hour', value: '17' },
{ type: 'literal', value: ':' },
{ type: 'minute', value: '00' },
{ type: 'literal', value: ':' },
{ type: 'second', value: '00' }
]
위의 결과를 유용하게 사용하기 위해서 홀수번째에 집중할 필요가 있다.
function parts(a){
const typetopos = ['year','month','day','hour','minute','second'];
let count=0;
let p=[];
for(let i=0;i<a.length;i++)
{
for(let j=0;j<a.length;j++)
{
if (a[j].type == typetopos[count]) {
p.push(a[j].value);
count++;
}
}
}
return p;
}다음의 parts 함수를 통해 순서에 맞게 year -> month -> day -> hour -> minute ->second 순으로 p 배열에 나열을 한다.
console.log(parts(formatter.formatToParts(new Date('2020-12-14T10:00:00+09:00'))));이것의 결과는 결국 [ '2020', '12', '13', '18', '00', '00' ] 이렇게 나타난다.
즉 한국에서 12월 14일 오전 10시였다면 미국의 타임존을 기준으로는 12월 13일 오후 6시가 된다.
UTC와 비교하기
얻어낸 시간을 바탕으로 비교하면 얼마나 시간이 차이나는지 알 수 있다.
function getOff(parts,date)
{
const [y,M,d,h,m,s]=parts;
const utc = new Date(Date.UTC(y,M-1,d,h,m,s)); //그냥 utc알기위한 용 (M-1)에 크게 의미부여 x
const offset= (utc-date)/60/1000;
return offset;
}위의 함수를 통해 가져온 시간과 parts는 현재 우리나라의 시간에서 얻어낸 Los에서의 배열로 된 정보이고 이를 utc틀을 위해서 바꾸고 date는 현재 우리나라에서의 시간을 런던의 GMT에 맞춘것이다.
즉 parts를 통해 utc를 만들어낸 값에서 date를 빼면 시간이 나타난다.
1) parts => Los의 정보를 담은 배열
2) utc => Los의 정보를 담은 utc 틀 형태 (배열 형태 X)
3) date => 현재 우리나라의 시간을 기준으로 런던의 GMT
ex) date가 '2020-12-14T10:00:00' 이면 알아서 지금 '2020-12-14T01:00:00'로 바뀌게 된다. '2020-12-14T10:00:00+09:00' 이게 좀 더 확실하다. => 우리나라의 경우 10시이지만 +09:00이므로 이를 같이 써주는게 낫다.
정리
원하는 한국시간을 기준으로 Intl을 통해 원하는 나라의 현재 시간을 알아 낸다.
한국시간을 기준으로 런던의 GMT를 얻어내 원하는 나라와의 시간 차이를 계산하면 그 나라가 여름과 겨울에 시간차이가 있나 알 수 있고 이를 통해 써머타임의 유무 그리고 런던의 GMT와의 차이를 알 수있다.
const formatter = new Intl.DateTimeFormat('en-us', {
hourCycle: 'h23',
year : 'numeric',
month : 'numeric',
day : 'numeric',
hour : 'numeric',
minute : 'numeric',
second : 'numeric',
timeZone : 'America/Los_Angeles'
});
function parts(a){
const typetopos = ['year','month','day','hour','minute','second'];
let count=0;
let p=[];
for(let i=0;i<a.length;i++)
{
for(let j=0;j<a.length;j++)
{
if (a[j].type == typetopos[count]) {
p.push(a[j].value);
count++;
}
}
}
return p;
}
function getOff(parts,date)
{
const [y,M,d,h,m,s]=parts;
const utc = new Date(Date.UTC(y,M-1,d,h,m,s));
const offset= (utc-date)/60/1000;
return offset;
}
const december = new Date('2020-12-14T10:00:00');
const august = new Date('2020-08-14T10:00:00');
console.log(getOff(parts(formatter.formatToParts(new Date('2020-12-14T10:00:00+09:00'))),december));
console.log(getOff(parts(formatter.formatToParts(new Date('2020-08-14T10:00:00+09:00'))),august));
이를 통해서 결과로
-480
-420
가 나타나는데 즉 12월에는 8시간이 런던기준으로 차이가 나고 8월에는 7시간이 차이가 난다.