프로그래머스 Lv1
문제 설명
배열 array의 i번째 숫자부터 j번째 숫자까지 자르고 정렬했을 때, k번째에 있는 수를 구하려 합니다.
예를 들어 array가 [1, 5, 2, 6, 3, 7, 4], i = 2, j = 5, k = 3이라면
- array의 2번째부터 5번째까지 자르면 [5, 2, 6, 3]입니다.
- 1에서 나온 배열을 정렬하면 [2, 3, 5, 6]입니다.
- 2에서 나온 배열의 3번째 숫자는 5입니다.
배열 array, [i, j, k]를 원소로 가진 2차원 배열 commands가 매개변수로 주어질 때, commands의 모든 원소에 대해 앞서 설명한 연산을 적용했을 때 나온 결과를 배열에 담아 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성해주세요.
제한 조건
- array의 길이는 1 이상 100 이하입니다.
- array의 각 원소는 1 이상 100 이하입니다.
- commands의 길이는 1 이상 50 이하입니다.
- commands의 각 원소는 길이가 3입니다.
| array | commands | return |
|---|---|---|
| [1, 5, 2, 6, 3, 7, 4] | [[2, 5, 3], [4, 4, 1], [1, 7, 3]] | [5, 6, 3] |
나의 풀이
function solution(array, commands) { let answer = []; for(let i=0; i<commands.length; i++){ let command = commands[i] let arr = array.slice(command[0]-1,command[1]-1); arr.sort((a, b) => a - b); answer.push(arr[command[2]-1]); } return answer; }
- slice()
arr.slice([begin[, end]])
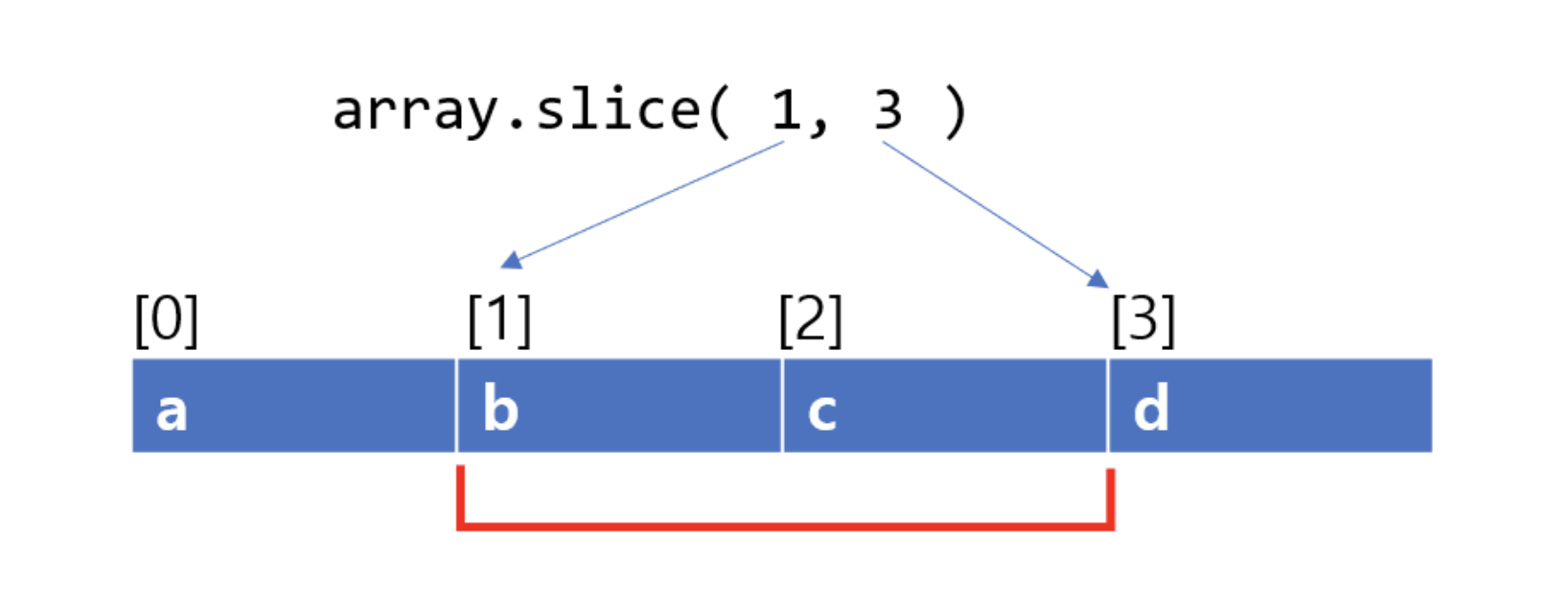
slice 함수는 잘라낼 배열의 시작index와 end index를 파라미터로 받아서,
그 사이의 원소들을 새로운 배열로 만들어서 리턴합니다.
이때 원본 배열인 arr은 변경되지 않습니다.
매개변수
-
begin
: 잘라낼 배열의 시작 index -
end
: 잘라낼 배열의 종료 index
: 🌟 end index의 값은 잘라낼 배열에 포함되지 않습니다.
: end index가 생략되면, begin index부터 배열의 끝까지를 잘라냅니다.
반환 값
: 잘라낸 원소들로 만든 새로운 배열을 리턴합니다.
다른 풀이 #1
function solution(array, commands) { return commands.map(command => { const [sPosition, ePosition, position] = command // ✅ const newArray = array .filter((value, fIndex) => fIndex >= sPosition - 1 && fIndex <= ePosition - 1) .sort((a,b) => a - b) return newArray[position - 1] }) }
- 구조분해 할당
: 구조분해 할당을 통해서 가독성이 좋은 코드를 쓸 수 있었던 것 같다.
const [sPosition, ePosition, position] = command; // ✅
나의 풀이의 command[0], command[1],command[2] 로 표현된 시작값, 끝값, 찾는 값 을 구조분해 할당을 통해서 sPosition, ePosition, position으로 각 인덱스의 의미를 더 명시적으로 나타낼 수 있었다.
- filter()
arr.filter( callback ( element [, index [, array ]])[, thisArg])
⇨매개변수
- callback
: 각 요소를 시험할 함수. true를 반환하면 요소를 유지하고, false를 반환하면 버립니다. 다음 세 가지 매개변수를 받습니다. - element
: 처리할 현재 요소. - index ( Optional )
: 처리할 현재 요소의 인덱스.
array ( Optional )
: filter를 호출한 배열. - thisArg ( Optional )
: callback을 실행할 때 this로 사용하는 값.
⇨ 반환 값
: 테스트를 통과한 요소로 이루어진 새로운 배열. 어떤 요소도 테스트를 통과하지 못했으면 빈 배열을 반환합니다.
- map()
arr.map( callback ( currentValue [, index[, array]])[, thisArg])
⇨ 매개변수
- callback
: 새로운 배열 요소를 생성하는 함수. 다음 세 가지 인수를 가집니다. - currentValue
: 처리할 현재 요소. - index ( Optional )
: 처리할 현재 요소의 인덱스. - array ( Optional )
: map()을 호출한 배열. - thisArg ( Optional )
: callback을 실행할 때 this로 사용되는 값.
⇨ 반환 값
배열의 각 요소에 대해 실행한 callback의 결과를 모은 새로운 배열.

