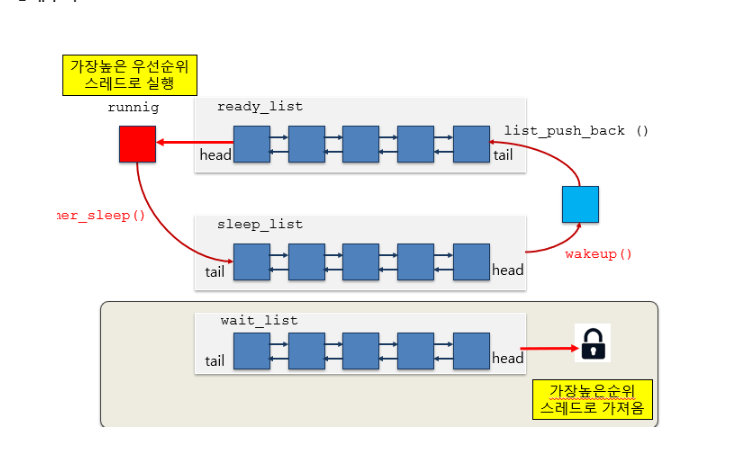
우선 순위 에 따른 스케줄링. 선점으로 구현을 하며, 도네이션 개념을 이용하여 lock + cond + sema 개념을 이용하여 nested, multiple 구현.
상태주기
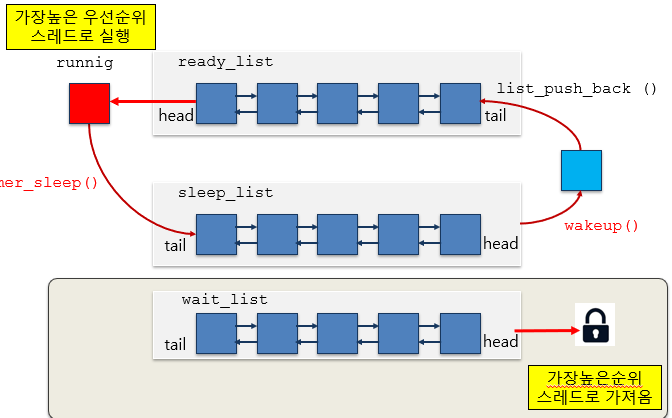
힌트, 기본 개념들
Preemption(선점)
- ready_list에 새로운 스레드를 삽입시 실행중인 스레드와 우선 순위 비교
- 현재 실행 중인 스레드보다 우선순위가 높은 경우 새로 삽입된 스레드를 예약.
Lock : semaphore, condition variable(조건 변수)
- 잠금을 기다리는 스레드 집합 or condition variable에서 스레드를 선택할 때는 우선 순위가 높은 스레드를 선택.
thread_unblock
스레드가 차단 해제되면 ready_list에 우선 순위에 따라 삽입
threads/thread.c
// 스레드들의 priority 값 비교, 내림차순 정렬
bool
cmp_priority(struct list_elem *a, struct list_elem *b, void *aux UNUSED){
return list_entry(a, struct thread, elem)->priority > list_entry(b, struct thread, elem)->priority;
}
void
thread_unblock(struct thread *t)
{
enum intr_level old_level;
old_level = intr_disable ();
ASSERT (t->status == THREAD_BLOCKED); // 현재 t가 차단된 상태인지 확인
// 기존
list_push_back(&ready_list, & t->elem); // ready_list에 뒤에서 부터 넣는다.
// 변경(핵심 코드)
list_insert_ordered(& ready_list, &t->elem, cmp_priority, NULL); // ready 리스트에 우선순위에 따라 삽입
t->status = THREAD_READY;
intr_set_level (old_level); // 인터럽트 레벨을 이전 상태로 복원한다
}thread_yield(void)
현재 스레드는 CPU를 생성하고 우선 순위에 따라 ready_list에 삽입
// 스레드들의 priority 값 비교, 내림차순 정렬
bool
cmp_priority(struct list_elem *a, struct list_elem *b, void *aux UNUSED){
return list_entry(a, struct thread, elem)->priority > list_entry(b, struct thread, elem)->priority;
}
void
thread_yield(void)
{
struct thread *curr = thread_current ();
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable (); // 인터럽트 비활성화
if (curr != idle_thread)
{
// 기존
// list_push_back (&ready_list, &curr->elem); //현재 스레드를 ready_list에 넣음.
// 변경(핵심 코드)
list_insert_ordered(&ready_list, & curr->elem, cmp_priority, NULL);
}
do_schedule (THREAD_READY); // 스케줄러에게 현재 스레드가 ready_list에 추가되었음을 알림
intr_set_level (old_level); // 인터럽트 복원
}thread_set_priority
현재 스레드의 우선순위를 new_priority로 변경. ready_list 재정렬
threads/thread.c
// 선점 구현 코드
void
thread_preemption(void)
{
if(!list_empty(&ready_list) && (thread_current ()->priority < list_entry(list_front(&ready_list), struct thread, elem)->priority))
thread_yield();
}
void
thread_set_priority (int new_priority)
{
thread_current ()->priority = new_priority;
thread_preemption(); // 리스트 앞 부분과 비교해서 read_list의 값이 더 클 경우 yield
}sema와 cond의 구조체
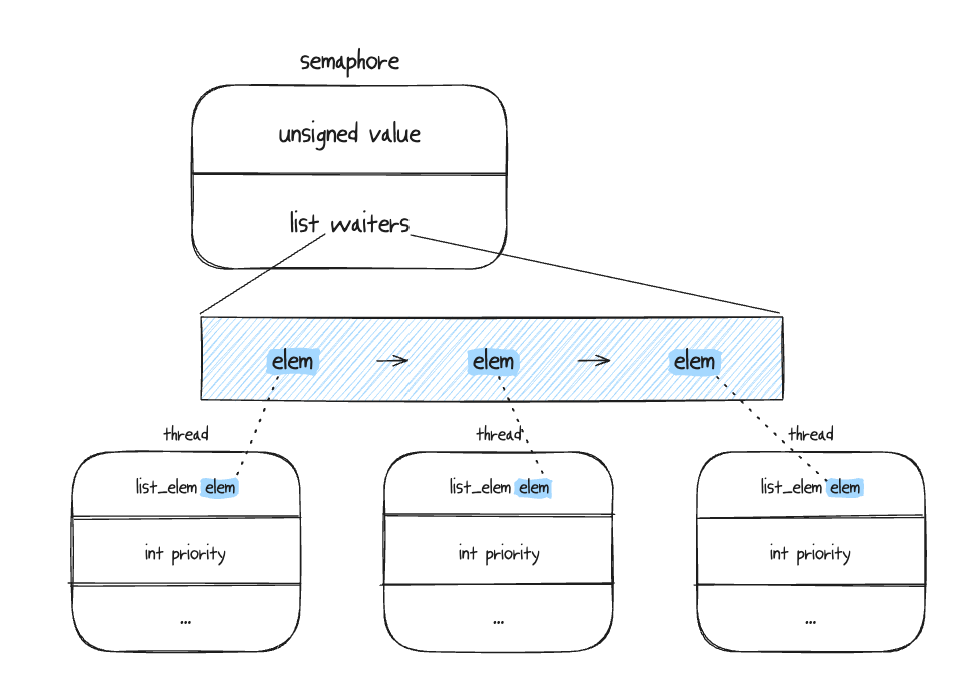
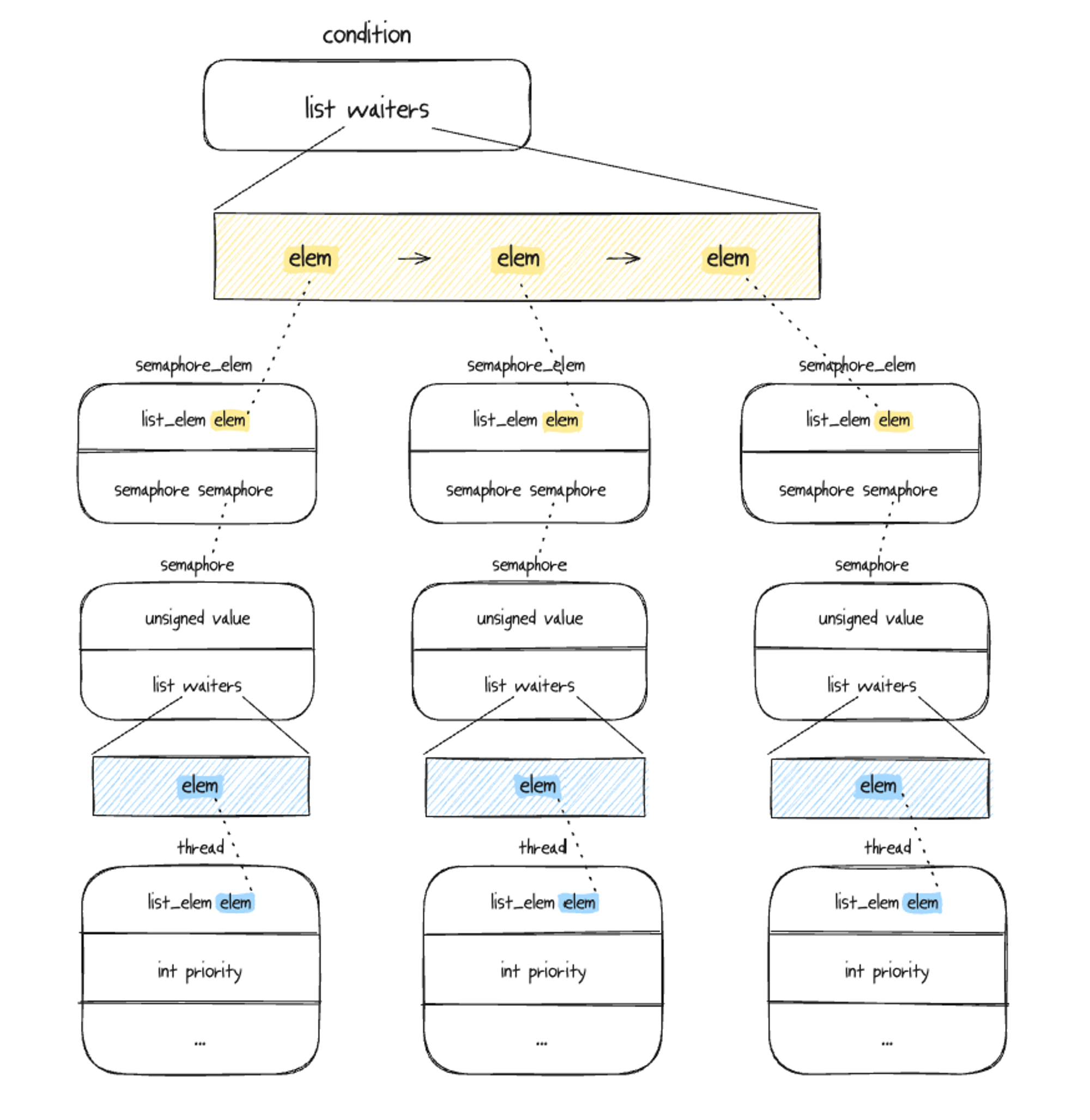
이렇게 다르기 때문에 스레드들의 우선순위값을 비교해주는 cmp 함수들을 sema와 cond에 다르게 사용하는 것이다.
우선 순위에 따라 wait_list 스레드를 삽입 하도록 수정.
sema_down(struct semaphore *sema)
request 세마포어를 흭득한 경우 값을 1만큼 증가.
threads/synch.c
// 스레드들의 priority 값 비교, 내림차순 정렬
bool
cmp_priority(struct list_elem *a, struct list_elem *b, void *aux UNUSED){
return list_entry(a, struct thread, elem)->priority > list_entry(b, struct thread, elem)->priority;
}
threads/synch.c
// 세마포어 Request 세마포어를 흭득한 값을 1만큼 decrease
// 값이 0이하이면 현재 스레드를 wait 리스트에 추가하고 블록
sema_down (struct semaphore *sema)
{
enum intr_level old_level;
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable ();
old_level = intr_disable (); // 비활성화
while (sema->value == 0) {
list_push_back (&sema->waiters, &thread_current ()->elem);
thread_block ();
// 기존
// list_push_back (&sema->waiters, &thread_current ()->elem);
// 변경
list_insert_ordered(&sema->waiters, &thread_current()->elem , cmp_priority, NULL);
thread_block (); // 현재 스레드를 블록 상태로 전환
}
sema->value--;
intr_set_level (old_level);
intr_set_level (old_level); // 활성화
}cond_wait(struct semaphore *sema)
조건 변수로 신호를 받을 때까지 기다립니다.
threads/synch.c
bool
cmp_sema_priority(const struct list_elem *a, const struct list_elem *b, void *aux UNUSED)
{
// 세마포어 요소 추출
struct semaphore_elem *sema_a = list_entry(a, struct semaphore_elem, elem);
struct semaphore_elem *sema_b = list_entry(b, struct semaphore_elem, elem);
// 기다리는 스레드 목록 추출
struct list *waiters_a = &(sema_a->semaphore.waiters);
struct list *waiters_b = &(sema_b->semaphore.waiters);
// 가장 높은 우선순위 스레드 추출
struct thread *s_a = list_entry(list_begin(waiters_a), struct thread, elem);
struct thread *s_b = list_entry(list_begin(waiters_b), struct thread, elem);
// 우선순위 비교
return s_a->priority > s_b->priority;
}
void
cond_wait (struct condition *cond, struct lock *lock)
{
struct semaphore_elem waiter;
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
sema_init (&waiter.semaphore, 0);
// list_push_back (&cond->waiters, &waiter.elem);
list_insert_ordered(& cond->waiters, & waiter.elem, cmp_sema_priority, NULL);
lock_release (lock);
sema_down (&waiter.semaphore);
lock_acquire (lock);
}
wait_list 우선순위에 따라 정렬
wait_list에서 스레드의 우선순위를 변경하는 경우 고려
sema_up(struct semaphore *sema)
세마포어를 해제시에 and 값을 1씩 늘리기.
threads/synch.c
sema_up (struct semaphore *sema) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
old_level = intr_disable (); // 인터럽트 비활성화
if (!list_empty (&sema->waiters))
{
// 핵심 코드(정렬)
list_sort(&sema->waiters, cmp_priority, NULL);
thread_unblock (list_entry (list_pop_front (&sema->waiters), struct thread, elem));
sema->value++;
thread_preemption(); // 선점
intr_set_level (old_level); // 인터럽트 활성화
}
cond_signal(struct condition cond, struct lock lock UNUSED)
조건 변수에서 대기 중인 우선순위가 가장 높은 스레드에 신호를 보낸다.
threads/synch.c
void
cond_signal (struct condition *cond, struct lock *lock UNUSED) {
ASSERT (cond != NULL);
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
if (!list_empty (&cond->waiters)){
list_sort(&cond->waiters, cmp_sema_priority, NULL);
sema_up (&list_entry (list_pop_front (&cond->waiters), struct semaphore_elem, elem)->semaphore);
}Donation
선점인 상황에서 프로세스에 실행중인 스레드를 보호하기 위해 락의 개념을 활용하여 우선순위를 기부하는 것
init_thread(struct thread t, const char name, int priority)
스레드 초기화 함수(우선 기부를 위한 데이터 구조 초기화)
// 스레드 초기화 함수
static void
init_thread (struct thread *t, const char *name, int priority) {
ASSERT (t != NULL);
ASSERT (PRI_MIN <= priority && priority <= PRI_MAX);
ASSERT (name != NULL);
memset (t, 0, sizeof *t);
t->status = THREAD_BLOCKED;
strlcpy (t->name, name, sizeof t->name);
t->tf.rsp = (uint64_t) t + PGSIZE - sizeof (void *);
// priority 구현
t->priority = priority; // 우선순위 부여
t->magic = THREAD_MAGIC;
// priority 구현
t->original_priority = priority; // 원래 우선 순위로 되돌리기
t->wait_on_lock = NULL; // 락을 소유하고 있는 스레드 초기화
list_init(&t->donations); // 기부 받은 우선순위 리스트 초기화
}lock_acquire(struct lock *lock)
현재 우선순위를 저장하고 기부한 스레드를 목록에 유지(복수기부)
구현 전 힌트
- Lock를 사용할 수 없는 경우 잠금 주소를 저장.
- 현재 우선순위를 저장하고 기부한 스레드를 목록에 유지 (복수 기부).
- Donate priority
threads/thread.c
lock_acquire (struct lock *lock) {
// 입력 조건 확인
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (!lock_held_by_current_thread (lock)); // 현재 스레드가 이미
// 현재 스레드 가져오기
struct thread *current_thread = thread_current();
// 락 소유자가 있는 경우 우선순위 기부 처리 - nested donataion 처리.
if(lock->holder != NULL) // NULL이 아니다? 그러면 다른 스레드가 소유하고 있다는 뜻이다.
{
if(lock->holder->priority < current_thread->priority)
{
current_thread->wait_on_lock = lock; // 현재 스레드는 'wait_on_lock' 필드에 이 락을 저장
// 락 소유자의 'donations' 리스트에 현재 스레드를 우선순위에 따라 삽입
list_insert_ordered(&lock->holder->donations, ¤t_thread->d_elem, donation_cmp_priority, NULL);
// 우선순위 기부 처리(nested donataion)
while (current_thread->wait_on_lock != NULL) {
// 락 소유자 가져오기
struct thread *holder = current_thread->wait_on_lock->holder;
// 우선순위 비교 및 업데이트
if (holder->priority < current_thread->priority)
{
// 락 소유자의 우선순위를 > 현재 스레드의 우선순위에 기부
holder->priority = current_thread->priority;
//현재스레드 = 락 소유자로 변경
current_thread = holder;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
}lock_release(struct lock *lock)
잠금이 해제되면 기부 목록에서 잠금이 설정된 스레드를 삭제하고 우선 순위를 올바르게 설정
구현 전 힌트
- 잠금이 해제되면 기부목록에서 잠금이 설정된 스레드를 삭제하고 우선 순위를 올바르게 설정
threads/thread.c
void
lock_release (struct lock *lock) {
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
struct list_elem *e;
struct thread *current_thread_donation = &thread_current()->donations;
// 현재 스레드가 소유한 'donations'리스트를 순회하며, 'wait_on_lockl'이 해제하려는 'lock'인 스레드를 찾기 = 기부 목록에서 기부된 스레드 제거
for(e = list_begin(current_thread_donation); e != list_end(current_thread_donation); e = list_next(e))
{
// 기부 목록에서 스레드 추출
struct thread *t = list_entry(e, struct thread, d_elem);
// 특정 락을 기다리는지 확인
if (t->wait_on_lock == lock)
{
list_remove(&t->d_elem);
}
}
//우선 순위 복원(왜? 단순히 원래 우선순위로 간다면, 남아있는 다른 락이 뺐긴다)
thread_current()->priority = thread_current()->original_priority;
// 기부받은 우선순위 확인 및 조정(multiple donation 처리)
if(!list_empty(current_thread_donation)) //현재 스레드가 기부받은 우선순위가 있는지 확인
{
// 최대 기부 우선순위 찾기.
struct thread *max_donor = list_entry(list_front(current_thread_donation), struct thread, d_elem);
// 우선순위 조정
if(max_donor->priority > thread_current()->priority) // 기부받은 스레드의 우선순위가 현재 스레드의 우선순위보다 높은경우
{
thread_current()->priority = max_donor->priority; // 현재 스레드의 우선순위를 기부받은 우선 순위로 설정
}
}
lock->holder = NULL;
sema_up (&lock->semaphore);
}
thread_set_priority (int new_priority)
현재 스레드의 우선순위를 new_priority로 변경
구현 전 힌트
- 기부를 고려한 우선순위 설정
thread_set_priority (int new_priority)
{
// 1. 현재 실행 중인 스레드 가져오기
struct thread *curr = thread_current();
// 원래 우선 순위 설정
curr->original_priority = new_priority;
// update_priority_for_donations();
// 3. 조건 확인 및 우선순위 설정
if(list_empty(&curr->donations) || new_priority > curr->priority) // 새로운 우선순위가 현재 우선순위보다 높은지
{
// 4. 우선순위 업데이트
curr->priority = new_priority;
}
else
{
curr->priority = list_entry(list_front(&curr->donations), struct thread,d_elem)->priority;
}
thread_preemption(); //리스트 앞 부분과 비교해서 read_list의 값이 더 클 경우 yield
}출처 : 카이스트, 한양대 핀토스