전체 요약
프로세스 간의 부모와 자식 관계를 구현하고, 부모가 자식 프로세스의 종료를 대기하는 기능 구현
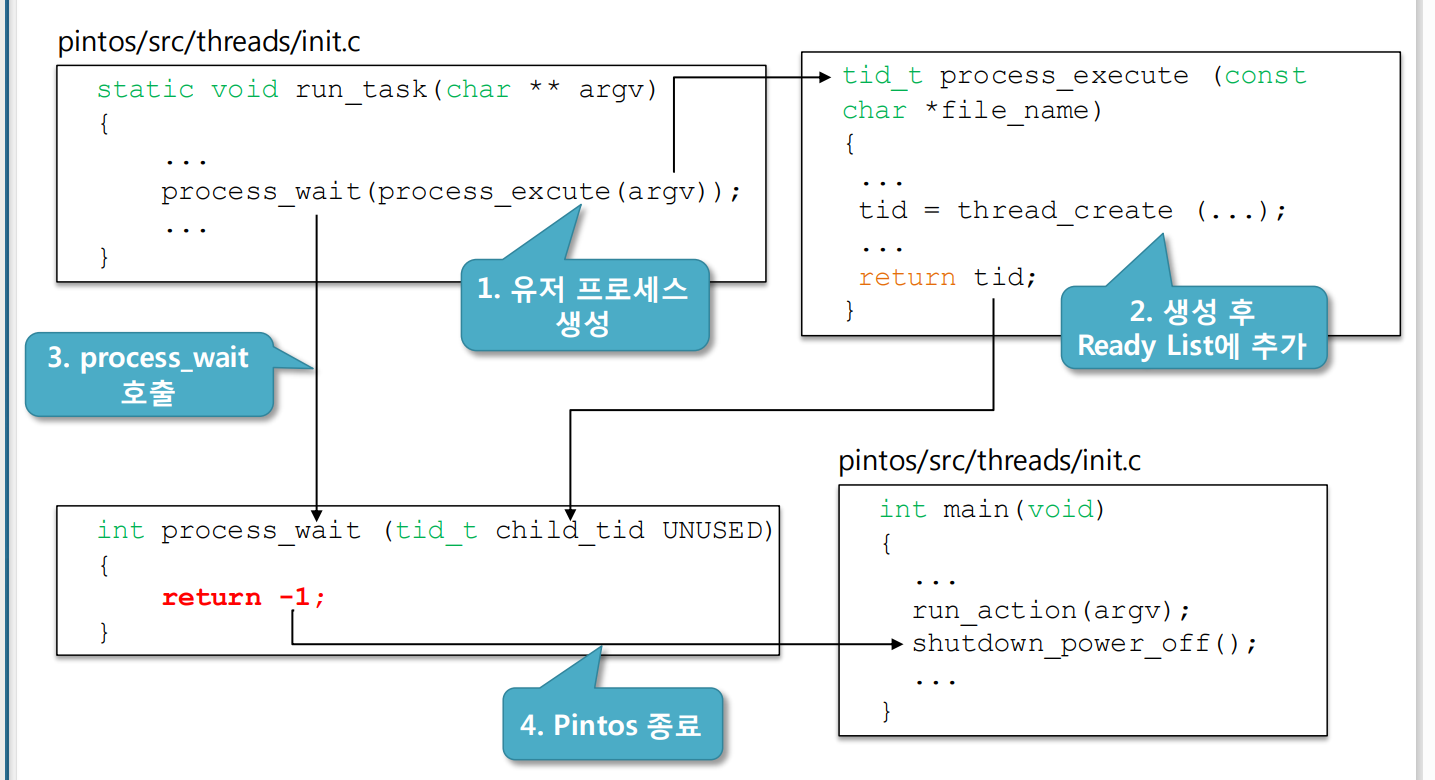
기존 상황
- 부모와 자식의 구분이 없고, 자식 프로세스의 정보를 알지 못하기 때문에, 자식의
시작/종료 전에 부모 프로세스가 종료되는 현상이 발생 프로그램이 실행되지
않음 - 예: init 프로세스는 자식 프로세스의 정보를 알지 못하여, 유저 프로그램이 실행 되기
전에 Pintos를 종료
해야 할 것
- 프로세스 디스크립터(struct thread)에 부모와 자식필드를 추가하고, 이를
관리하는 함수를 구현
부모 프로세스를 가리키는 포인터 추가
자식 프로세스 : 리스트로 구현
자식 리스트에서 원하는 프로세스를 검색, 삭제하는 함수 구현
- exec(), wait() 구현 (세마포어를 이용)
구현 전 알아야 할 것
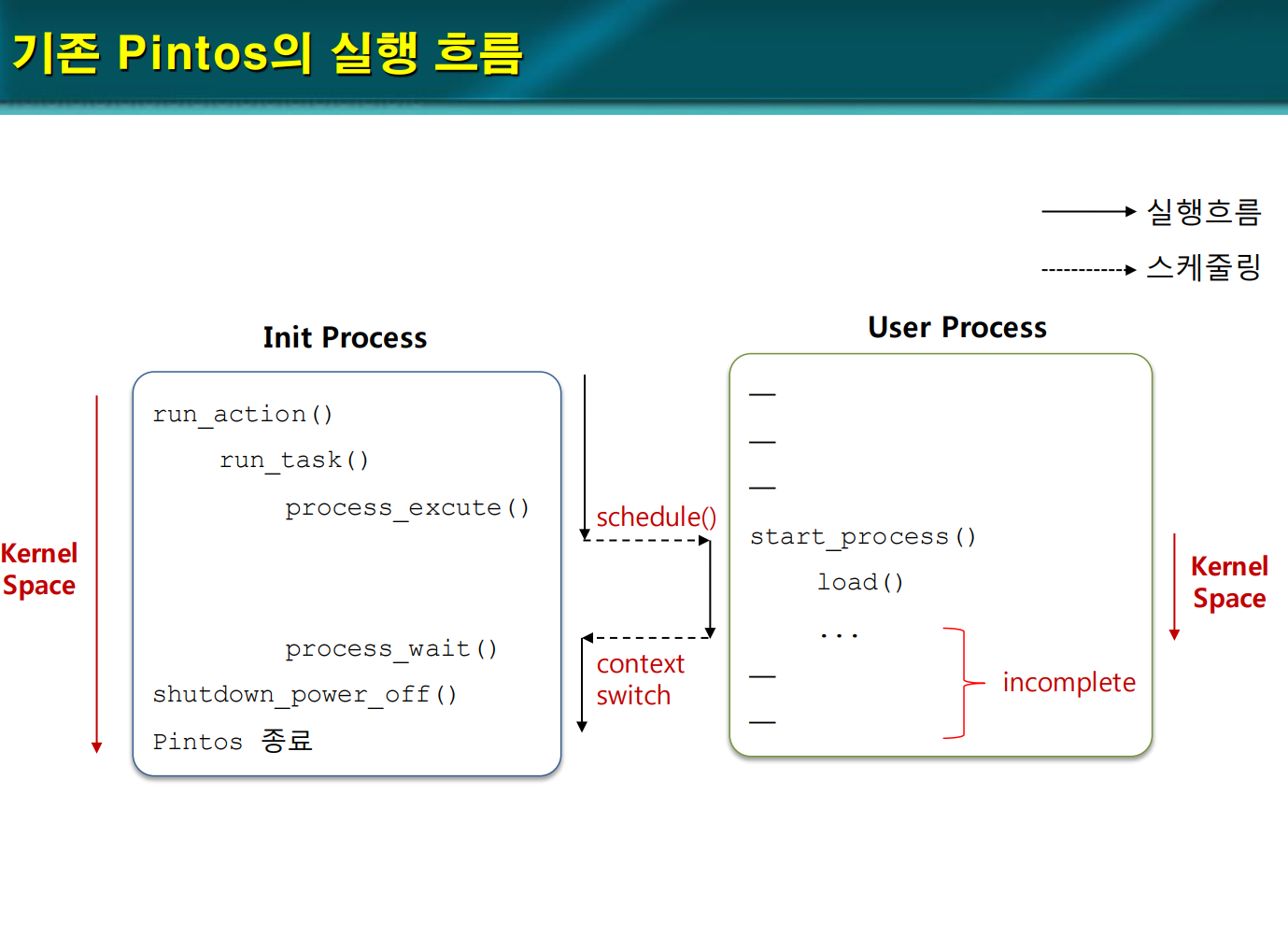
유저 프로그램이 실행 되지 않는 원인
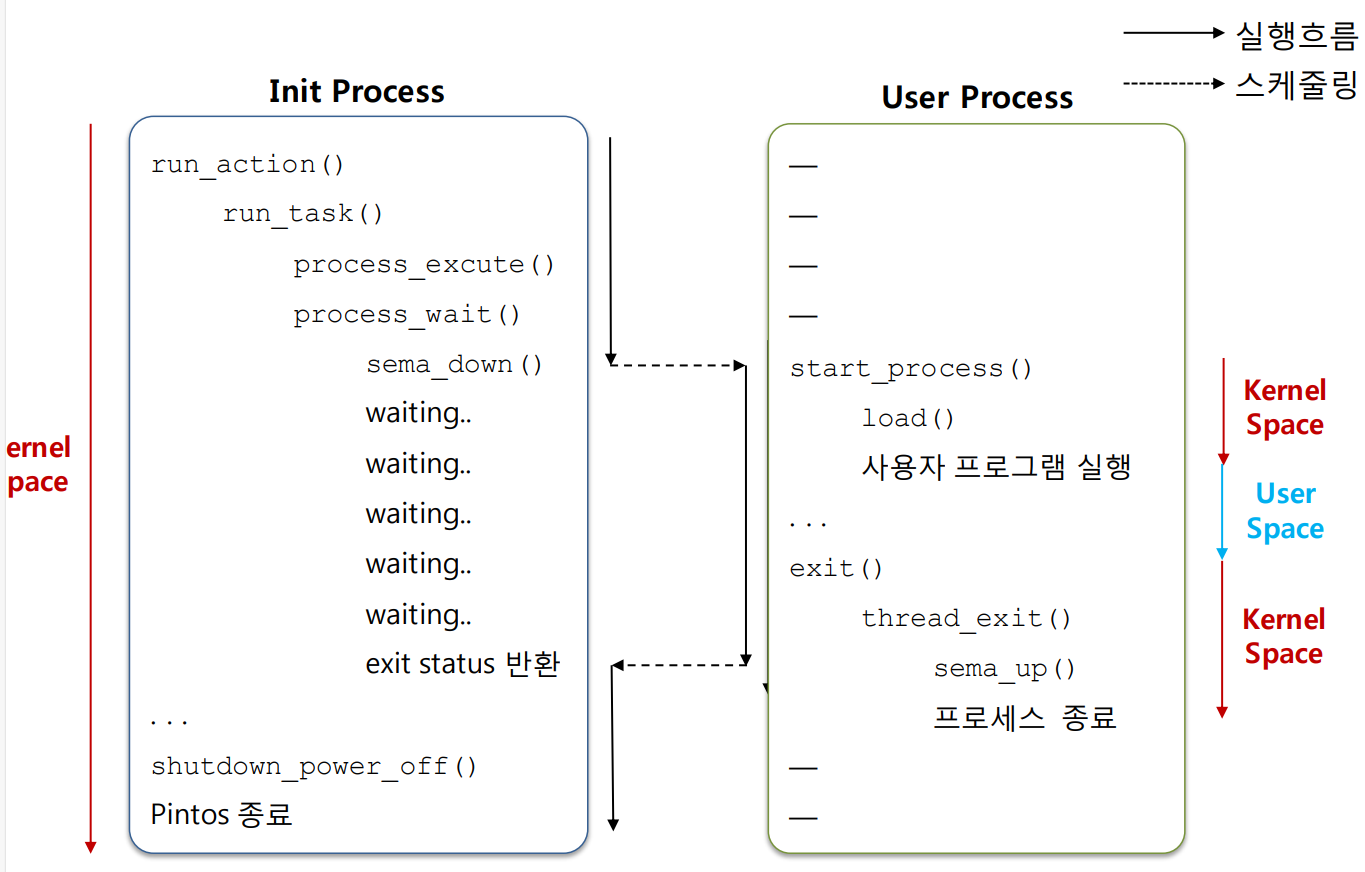
기존 핀토스의 실행 흐름
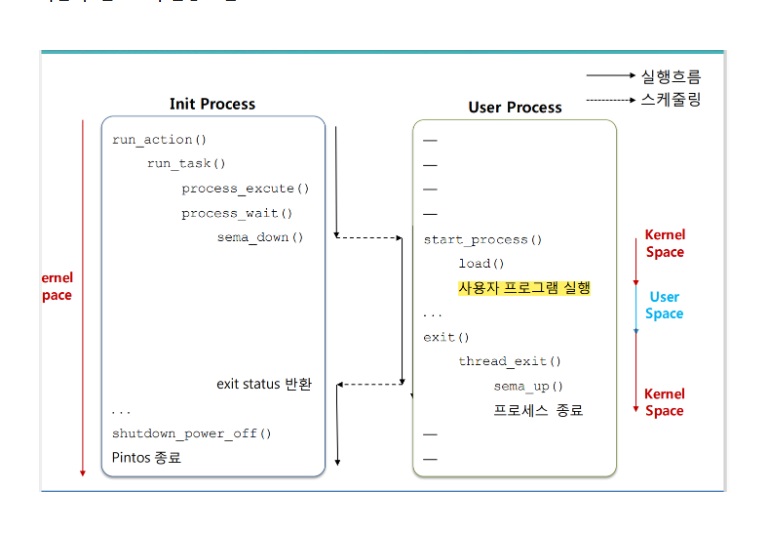
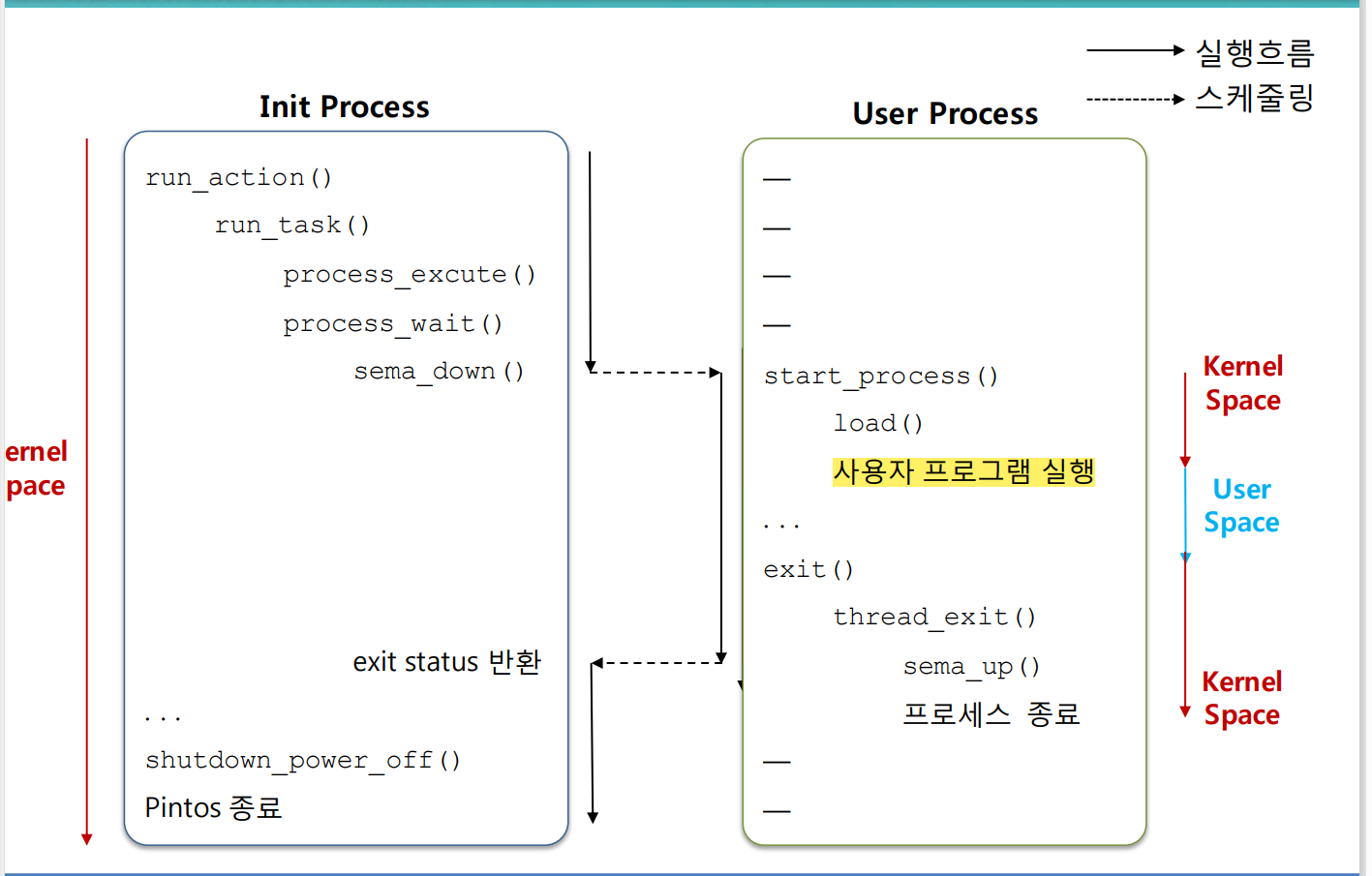
- Init 프로세스가 사용자 프로세스를 실행하고, 사용자 프로세스가 종료될 때까지 대기하며, 모든 작업이 끝나면 시스템을 종료하는 과정을 나타냄
작업 후 핀토스의 실행 흐름
프로세스 and 스레드 복습
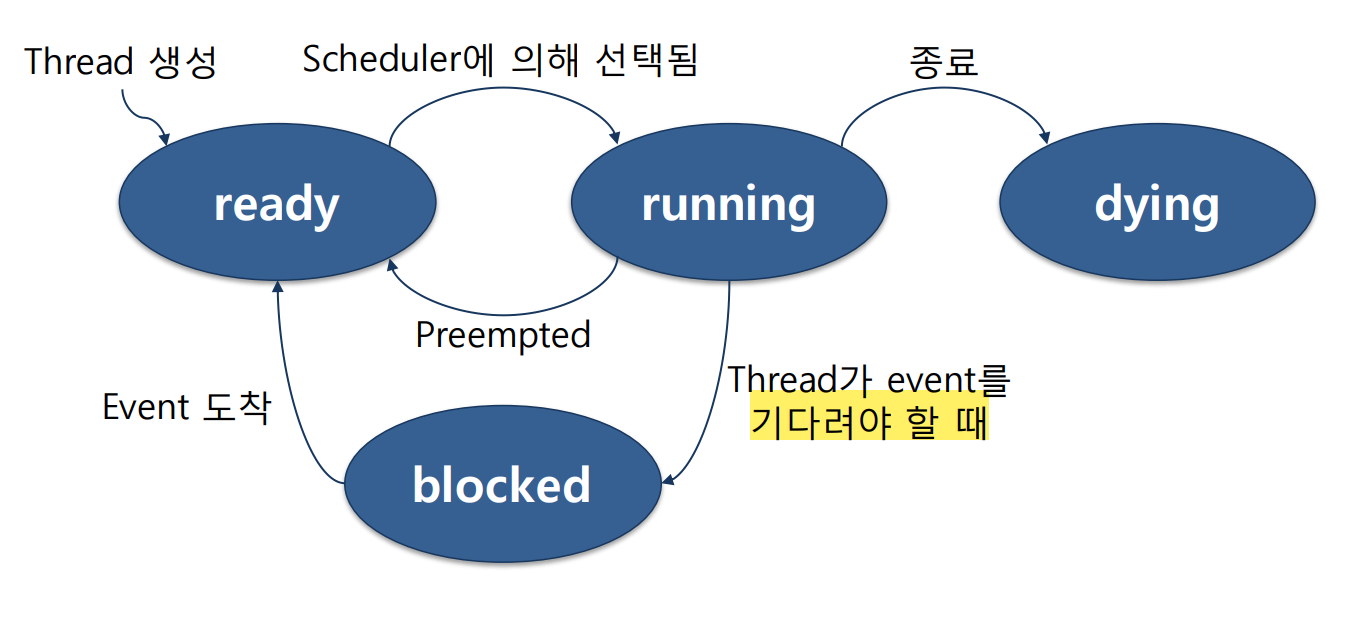
- Pintos의 프로세스는 1개의 스레드로 구성
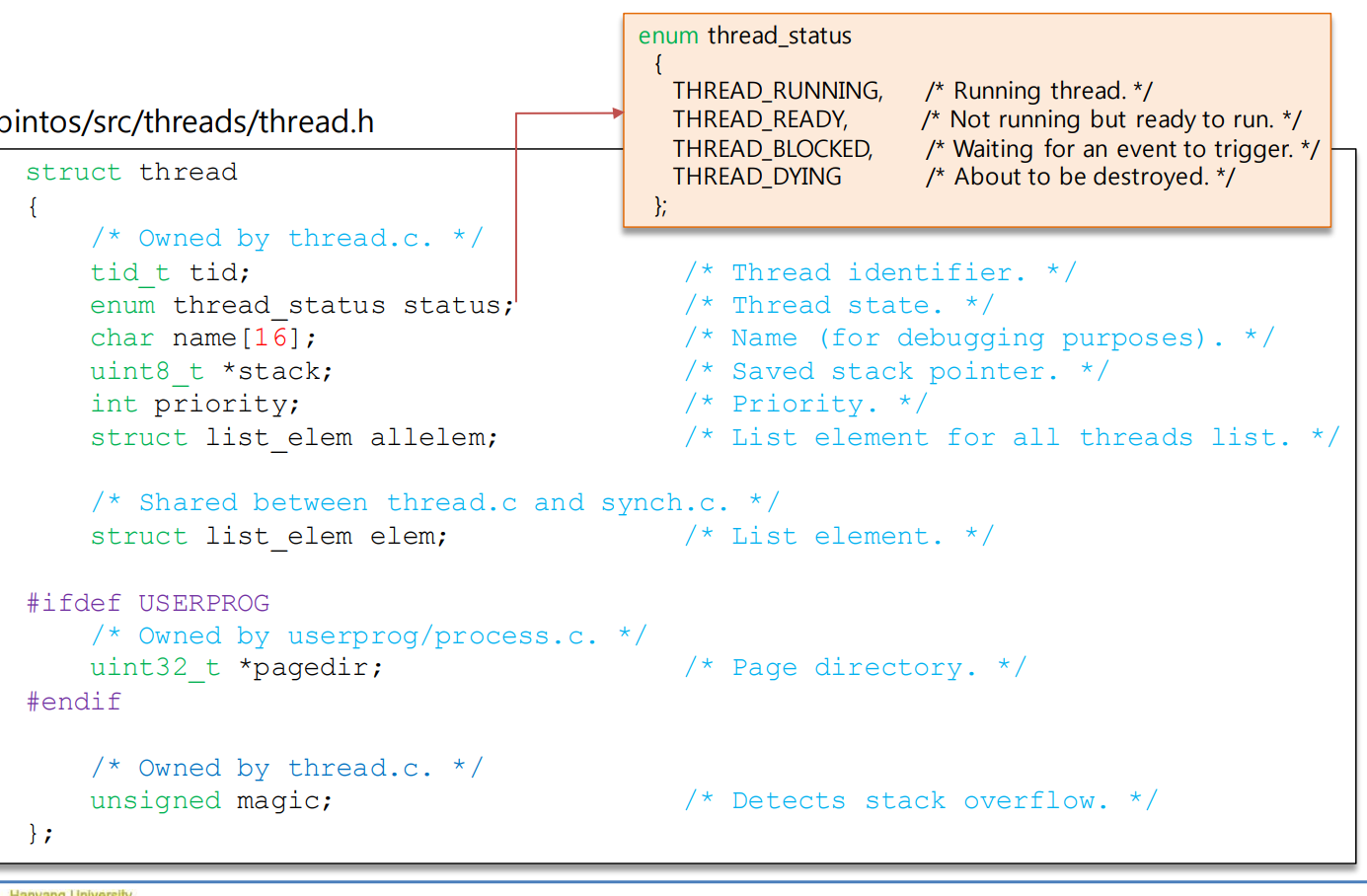
thread 구조체
부모 and 자식 프로세스의 관계
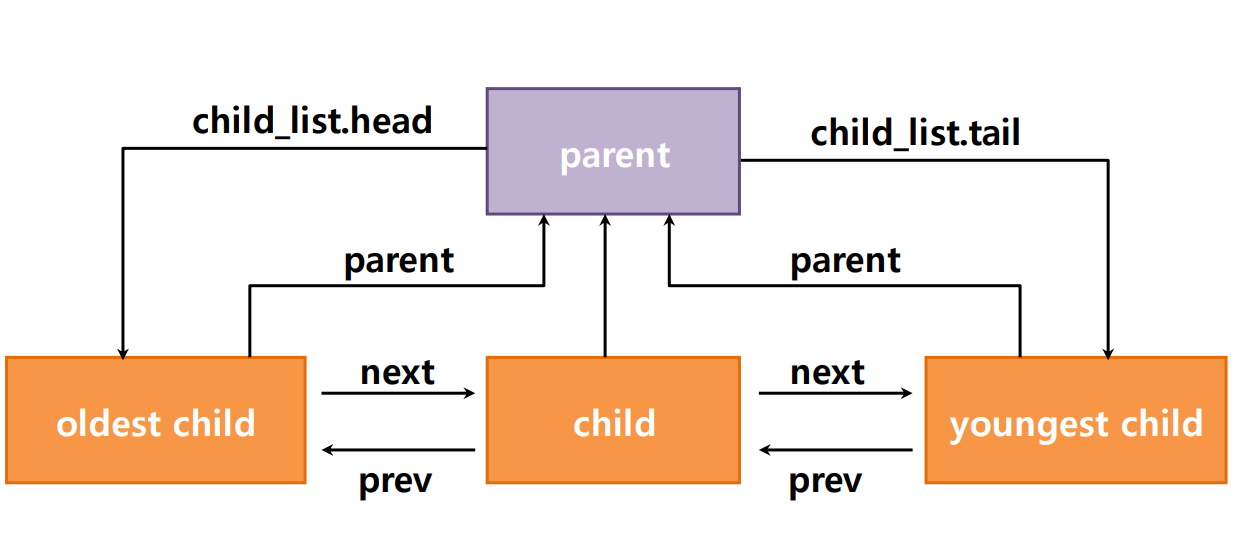
- 부모 프로세스는
child_list를 통해 자식 프로세스들의 리스트를 관리. - 자식 프로세스들은
next와prev포인터를 통해 이중 연결 리스트로 연결. 이는 자식 프로세스들을 순차적으로 탐색하거나 삽입/삭제하는 데 유리. - 부모 프로세스와 자식 프로세스 간의 관계는 부모 프로세스의
child_list필드와 자식 프로세스의parent필드로 관리.
list 자료구조
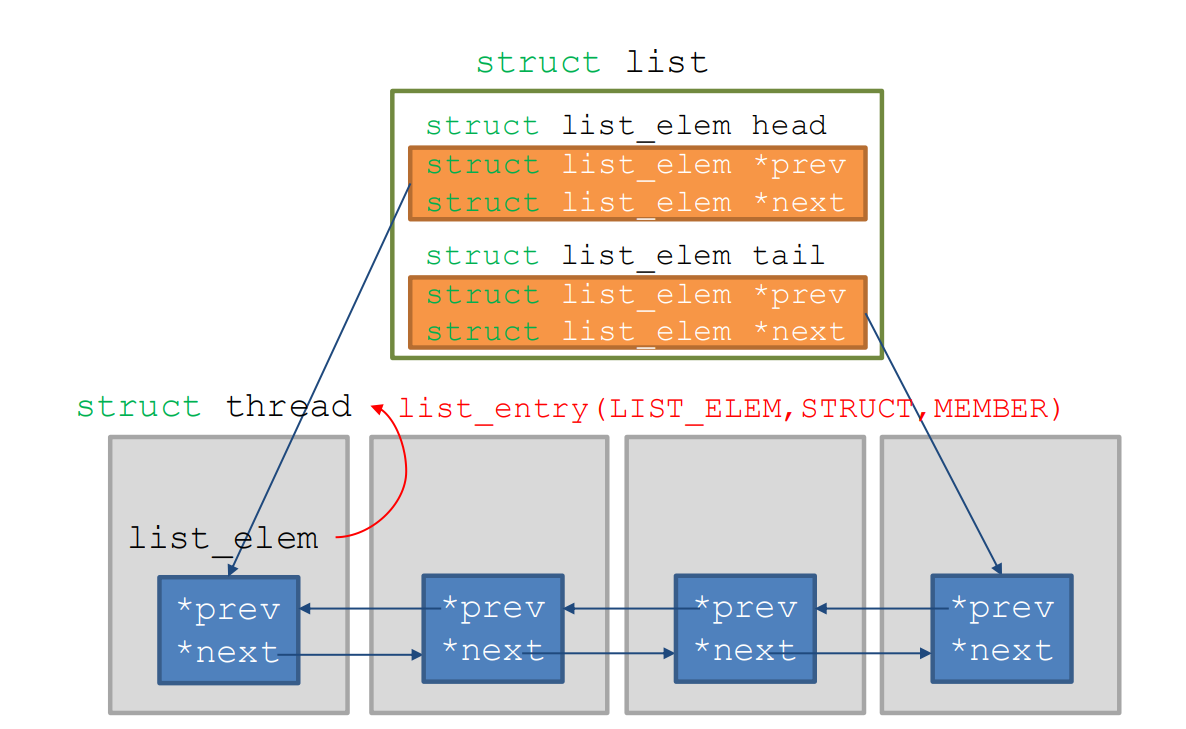
구현해야 할 것
System Call함수들
exec
자식 프로세스를 생성하고 프로그램을 실행
구현 전 힌트
- process_execute() 함수를 호출하여 자식 프로세스 생성
- 생성된 자식 프로세스의 프로세스 디스크립터를 검색
- 자식 프로세스의 프로그램이 적재될 때까지 대기
- 프로그램 적재 실패 시 -1 리턴
- 프로그램 적재 성공 시 자식 프로세스의 tid 리턴
exec 코드 흐름
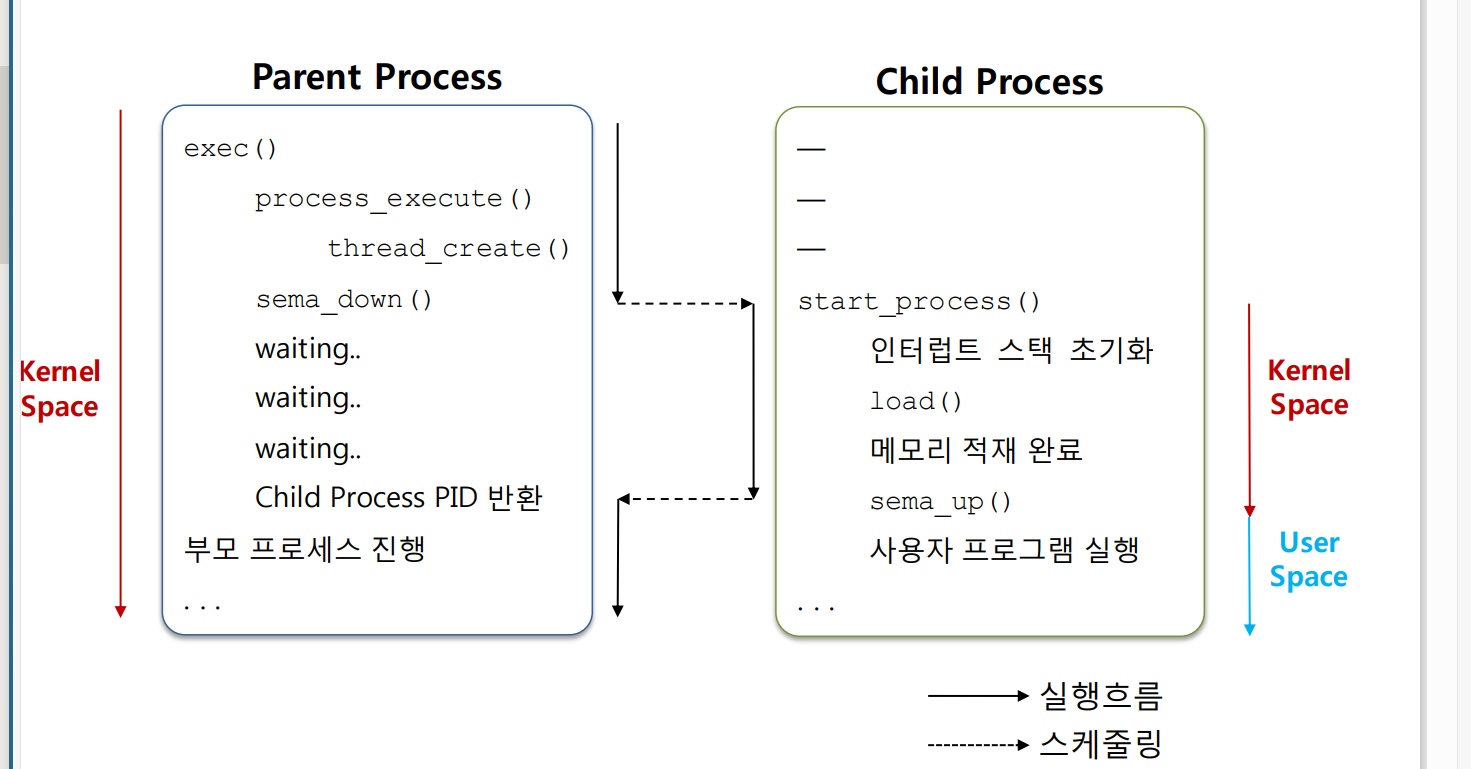
- 부모 프로세스가 자식 프로세스를 생성하고, 자식 프로세스가 준비되면 이를 통보받아 자신의 작업을 계속 진행하는 방식으로, 프로세스 간의 동기화를 한다.
tid_t
exec(const char *cmd_line)
{
check_address(cmd_line);
tid_t child_tid = process_create_initd(cmd_line);
struct thread *child_thread = get_child_process(child_tid);
if (child_thread == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
sema_down(&child_thread->sema_load);
if (child_thread->is_program_loaded)
{
return;
}
else
{
return child_thread->exit_status = -1;
}
}wait
자식 프로세스가 모두 종료될 때까지 대기
구현 전 힌트
- 자식 프로세스의 프로세스 디스크립터 검색
- 예외 처리 발생시 -1 리턴
- 자식프로세스가 종료될 때까지 부모 프로세스 대기(세마포어 이용)
- 자식 프로세스 디스크립터 삭제
- 자식 프로세스의 exit status 리턴
wait 흐름
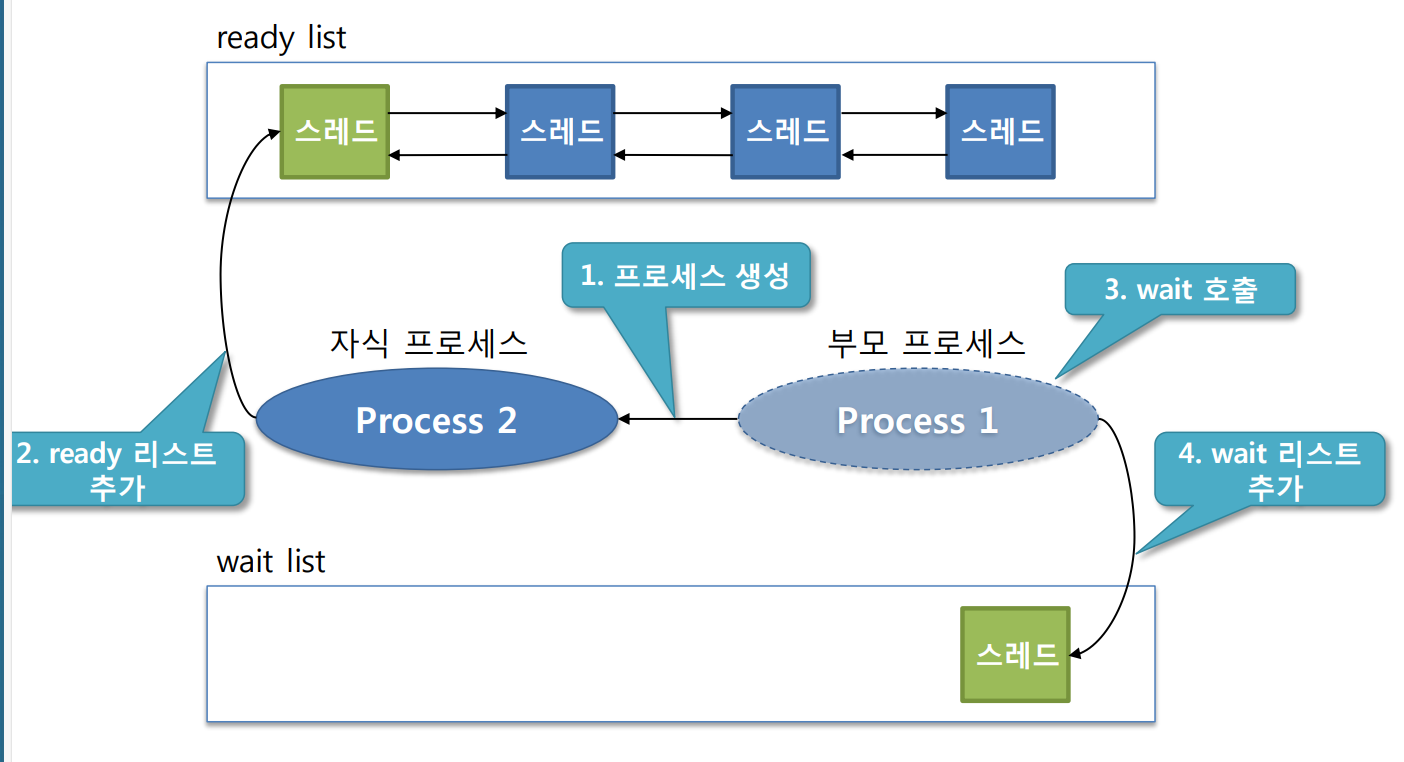
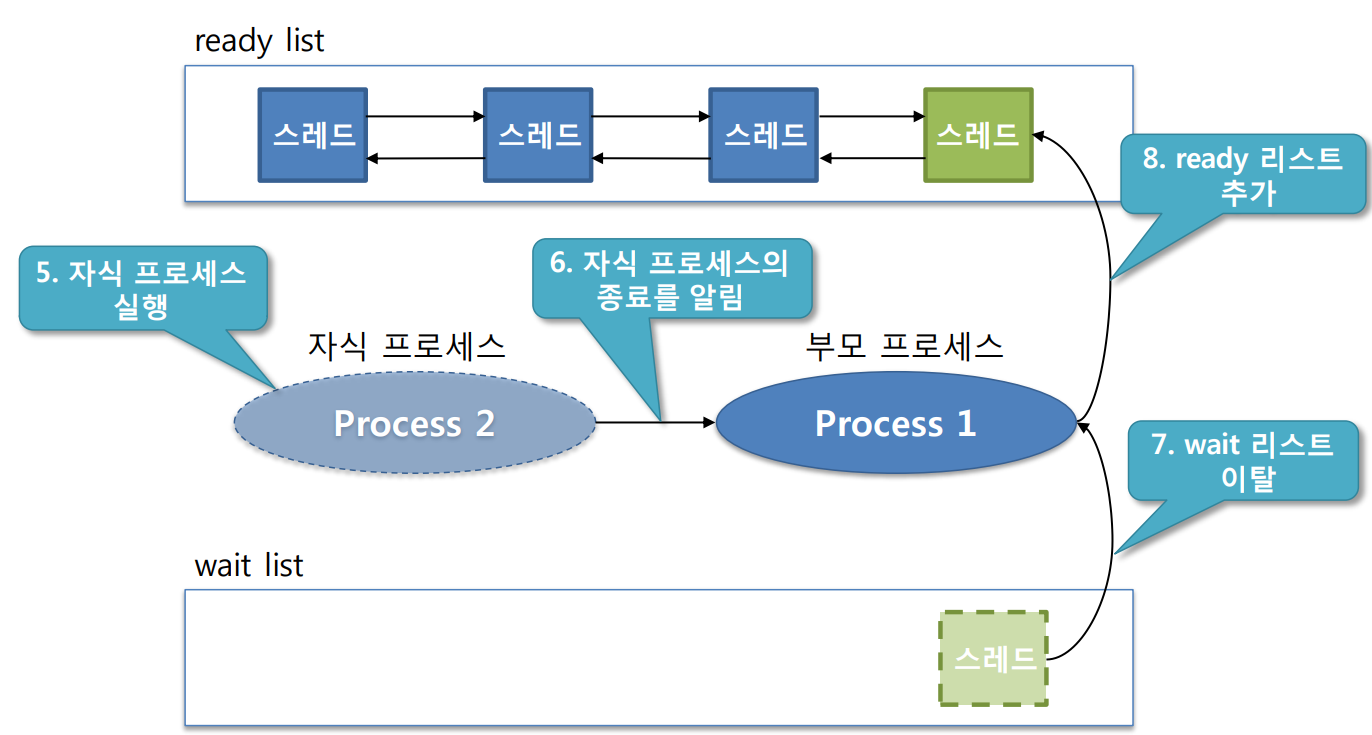
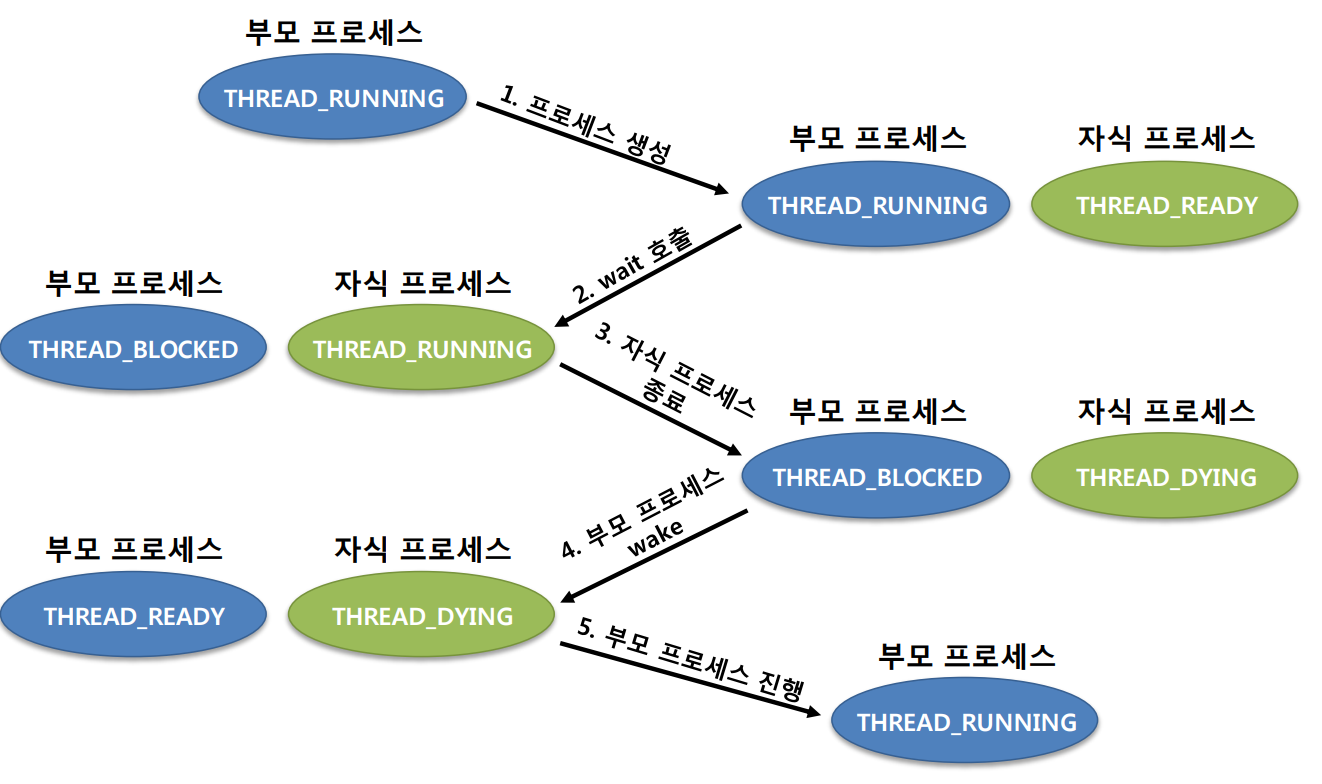
wait 코드 흐름
process_wait 이용
int
wait(tid_t tid)
{
process_wait(tid);
}int
process_wait(tid_t child_tid UNUSED)
{
// child_tid에 해당하는 자식 프로세스를 검색.
struct thread *t = get_child_process(child_tid);
if (t == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
// 자식 프로세스를 찾은 경우, 자식 프로세스가 종료될 때까지 대기
sema_down(&t->sema_exit);
// 자식 프로세스의 종료 상태 가져옴
int exit_s = t->exit_status;
// 자식 프로세스 제거
remove_child_process(t);
return exit_s;
}exit - 수정
정상적으로 종료가 됐는지 확인하기 위해 exit_status 저장
void
exit(int status)
{
struct thread *cur = thread_current(); // 현재 실행중인 스레드 가져오기
cur->exit_status = status; // 프로세스 디스크립터에 exit status 저장.
printf("%s: exit(%d)\n", cur->name, status);
thread_exit();
}그 외 함수들
구조체 (thread) - 수정
프로세스 디스크립터에 프로세스의 정보 추가
// thread.h 파일에
// struct thread{ } 여기에 추가
struct thread *parent_process;
struct list_elem child_elem;
struct list child_list;
bool is_program_loaded;
bool is_program_exit;
struct semaphore sema_load;
struct semaphore sema_exit;
int exit_status; 자료구조 - 수정
스레드 생성 시 자식 리스트 초기화
// thread.c 파일에
// init_thread 함수에 추가
list_init(&t->child_list);자료구조 - 수정
생성된 프로세스 디스크립터 정보 초기화
// thread.c 파일에
// thread_create 함수에 추가
struct thread *cur = thread_current();
t->parent_process = cur;
t->is_program_loaded = false;
t->is_program_exit = false;
sema_init(&t->sema_load, 0);
sema_init(&t->sema_exit, 0);
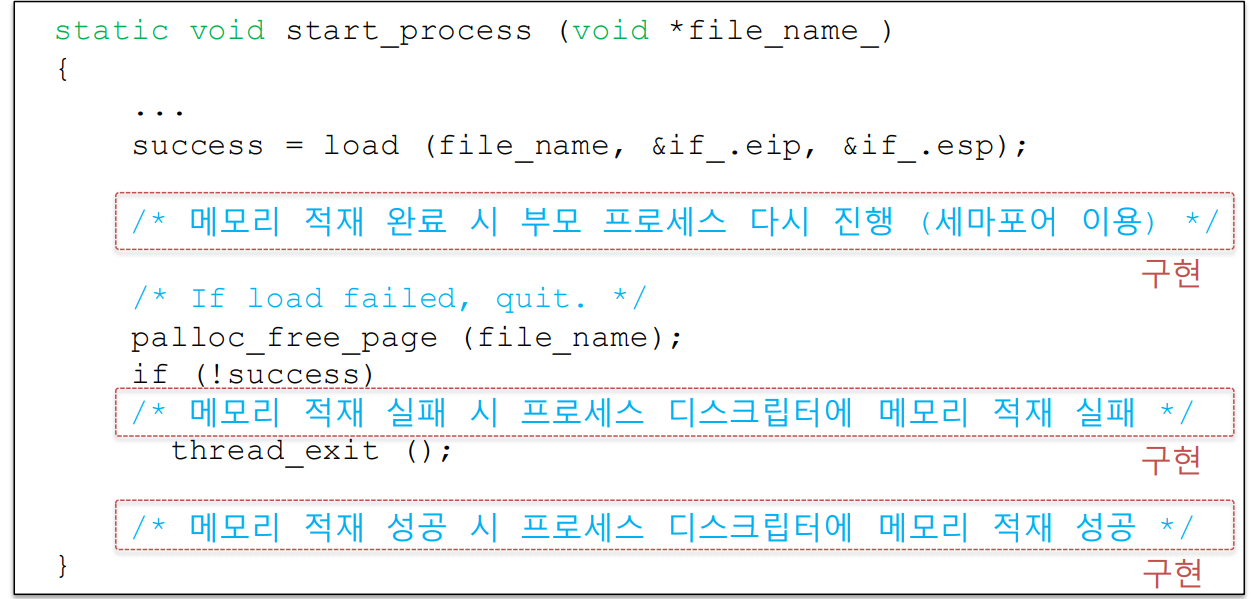
list_push_back(&cur->child_list, &t->child_elem); process_exec - 수정
부모 프로세스 대기 상태 이탈 구현. 메모리 적재 완료 시 부모 프로세스 다시 진행(세마포어 이용)
구현 전 힌트
int process_exec(void *f_name)
{
char *file_name = f_name;
bool success;
/* We cannot use the intr_frame in the thread structure.
* This is because when current thread rescheduled,
* it stores the execution information to the member. */
// 인터럽트 프레임 초기화
struct intr_frame _if;
_if.ds = _if.es = _if.ss = SEL_UDSEG;
_if.cs = SEL_UCSEG;
_if.eflags = FLAG_IF | FLAG_MBS;
/* We first kill the current context */
// 현재 컨텍스트 종료
process_cleanup();
/* And then load the binary */
/* add code - gdy_pro2*/
char *token;
char *save_ptr;
int count = 0;
char *parse[128];
// 인자 파싱
for (token = strtok_r(file_name, " ", &save_ptr); token != NULL;
token = strtok_r(NULL, " ", &save_ptr))
{
parse[count] = token;
count++;
}
/* 프로그램을 메모리에 적재 */
success = load(parse[0], &_if);
thread_current() ->is_program_loaded = success;
// 파일 디스크립터 구현
// 메모리 적재 완료 시 부모 프로세스 다시 진행(세마포어 진행)
sema_up(&thread_current()->sema_load); //
argument_stack(parse, count, &_if.rsp;
_if.R.rsi = _if.rsp + sizeof(void *);
_if.R.rdi = count;
/* If load failed, quit. */
// argument_stack으로 parse를 전달해준 이후에 palloc_free_page를 통해 file_name이 가리키는 메모리를 해제한다.
palloc_free_page(file_name);
// 로드 실패 처리
if (!success){
return -1;
}
/* Start switched process. */
do_iret(&_if); // 인터럽트 반환 명령을 사용하여 새로운 사용자 모드 프로그램 실행
NOT_REACHED();
}get_child_process
자식 프로세스 검색
구현 전 힌트
- 자식 리스트에 접근하여 프로세스 디스크립터 검색
- 해당 pid가 존재하면 프로세스 디스크립터 반환
- 리스트에 존재하지 않으면 NULL 리턴
struct
thread *get_child_process(int tid)
{
struct thread *current_thread = thread_current();
struct list_elem *e;
for(e = list_begin(¤t_thread->child_list); e != list_end(¤t_thread->child_list); e = list_next(e))
{
struct thread *child_thread = list_entry(e, struct thread, child_elem);
if (child_thread->tid == tid)
{
return child_thread; // 해당 pid가 존재하면 프로세스 디스크립터 반환
}
}
return NULL; // 리스트에 존재하지 않으면 NULL 리턴.
}remove_child_process
부모 프로세스 제거
구현 전 힌트
- 자식 리스트에서 제거
- 프로세스 디스크립터 메모리 해제
void
remove_child_process(struct thread *cp)
{
struct thread *parent = thread_current();
if(cp == NULL)
{
return;
}
// 자식 리스트에서 제거
list_remove(&cp->child_elem);
// 프로세스 디스크립터 메모리 해제.
palloc_free_page(cp);
}