EC2 = Elastic Compute Cloud : IaaS
- Virtual machines = EC2
- Virtual drives = EBS (Elastic Block Store)
- Distributing load across machines = ELB (Elastic Load Balancer)
- Auto-Scaling Group = ASG
Sizing / Configuration options
-
OS : Linux / Windows / Mac
-
CPU : Compute power & cores
-
RAM
-
Storage space
- Network-Attached : EBS, EFS
- HW : EC2 Instance Storage
-
Network card : public IP address, speed of card
-
Firewall rules : Security Group
-
Bootstrap script : EC2 User Data : run with root user
- run only once at instance's first start, to automate boot tasks
-
ssh connection
.pem: OpenSSH - mac, linux, Windows10.ppk: PuTTy - Windows 7,8
EC2 instance types
-
aws의 작명규약
ex) m5.2xlarge- m : instance class
- 5 : generation (continuously updated)
- 2xlarge : size within instance class ( more memory, ...)
-
Instance Class
Class purpose use cases General Purpose for diversity of workloads, good balance btwn compute, memory, networking)
•web servers
• code repositoriesCompute Optimized for compute-intensive tasks
• Batch processing workloads
• Media transcoding
• High performance web server
• High performance computing (HPC)
• Dedicated gaming serversMemory Optimized for workloads that process large data sets in memory • High performance, relational/non-relational databases
• Distributed web scale cache stores
• In-memory databases optimized for BI (Business Intelligence)
• Applications performing real-time processing of big unstructured dataStorage Optimized for tasks that require high,sequential read/write access to large data sets on local storage • High frequency OLTP systems
• Relational & NoSQL DB
• Cache for in-memory DB (ex: Redis)
• Distributed file systemsAccelerated Computing - - HPC Optimized
EC2 Instance Purchasing options
1. On-Demand
- 사용한 만큼 가격 발생
- Linux / Windows : 첫 1분 이후 초단위로 청구
- 다른 OS : 1시간 단위로 청구
⇒ 가장 비싼 plan, 선불 요금 X 장기 렌탈 필요 x (X Commitment)
- [추천] 짧고 방해받지 않으며, 예측 가능한 workload
2. Reserved Instance
-
1 & 3년 단위로 렌탈
-
Reserved Instances
-
On-demand 대비 약 72% 할인가
-
Instance Type, Region, Tenancy, OS 등 명시하여 대여
-
요금결제 : 후불 / 부분 선불 / 전부 선불 (먼저 많이 지불할 수록 할인)
-
scope : Regional / Zonal
-
Buy & Sell in the reserved instance marketplace
-
[추천] : 안정적인 앱 사용 / 장기적인 workload
-
-
Convertible Reserved Instances
- 장기적인 workload + flexible한 instance type
- 변경 가능 : EC2 instance type, instance family, OS, scope, tenancy
3. Savings Plans
-
장기사용에 따른 할인
-
특정 사용량에 따라 약정
(ex: 1년 혹은 3년 간 $10/시간)
-
약정 기간 이후 사용량은 On-Demand 가격으로 책정
-
고정 : instance family, Region
-
변경 가능 :
- Instance size (ex: m5.xlarge, m5.2xlarge)
- OS (ex: Linux, Windows, …)
- Tenancy (Host, Dedicated, Default)
*Dedicated Host
- 물리적 서버 자체에 접근 가능, HW의 lovw level까지 가시성 확보 ⇒ 가장 비쌈!
- compliance 요구사항 만족 가능
- 서버를 경계로 하는 자체 라이센스 사용 가능
(socket 단위, core 단위, VM 단위 라이센스 등)
- instance placement 지정 가능
- 구매 옵션
- On-Demand : active한 host 초단위로 계산
- Reserved : 1년 혹은 3년 - 후불 / 부분 선불 / 전체 선불
- [추천]
- 복잡한 라이센싱 모델을 가진 sw (BYOL license)
- 강한 regulatory/compliance가 요구되는 회사
*Dedicated Instances
- Instances run on HW dedicated to you
- 같은 계정 내 다른 instance와 HW 공유 가능
- instance placement 지정 불가
*Capacity Reservations
- 특정 AZ 내 "On-Demand" instances capacity를 예약 (for any duration)
- 필요할 때 언제든 EC2 capacity에 접근 가능
- time commitment 필요 없음 (언제든 생성/중단)
- instance 작동여부와 상관없이 On-Demand rate으로 과금
- Regional Reserved Instance와 Savings Plans과 함꼐 사용 시 할인
- [추천] 단기간, 특정 AZ에 있어야하는 안정적인 workload
* Spot Instances
-
중요한 작업이나 DB의 목적의 workload로는 부적합
-
아주 싸다~! 단기간 workload로 좋음
-
Max spot price (budget) 지정
-
hourly spot price는 수요와 공급에 의해 변동
- current spot price가 max spot price보다 낮으면 instance 보유
- current spot price가 더 비싸지면 2분 간 유예 시간 동안 instance 상태를 결정해야 함
- stop instance : hourly spot price가 max spot price 보다 내려가면 다시 instance 시작
- terminate instance : 아예 종료
- Spot Block : (2021년 7월 기준 신규 고객에게는 Spot Block 서비스 제공 x, 시험에는 나올 수 있음!)**
- 시간을 정해서 지정한 용량을 유지해주는 옵션 - 해당 시간 동안은 Reserved Instance보다 유리
-
[추천] failure에 강한 작업
- ex) Batch Jobs / Data analysis / Image Processing / Any distributed workloads
Spot Instance Request 과금없이 종료하는 법!
-
Spot Instance request 종류 : One-time / persistent
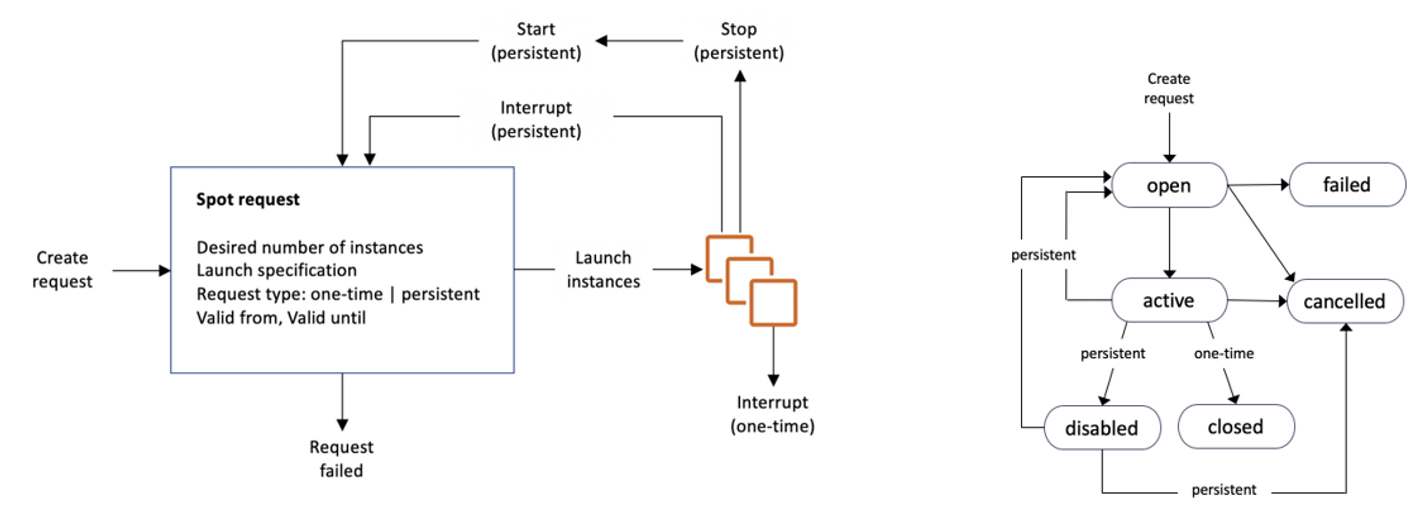
-
Spot Instance 종료시키기 when persistent request
- request 상태가
open/active/disabled중 하나
(failed,cancelled,closed는 종료 불가) - Cancel spot instance
- 동작 중인 instance를 별도로 직접 terminate
(request 취소 ≠ instance 종료)
- request 상태가
Spot Fleets
- 최저가에 Spot Instance를 request하는 것을 자동화
-
Budget, capacity, launch pool 정의
- launch pool : Instance type, OS, AZ 지정
-
가격 제한과 Target capacity를 만족하도록 instance를 구축
-
budget 한도에 도달했을 때 instance 구축 중단
-
- Spot instance 구축 위한 구성 전략
- 최저가 : pool 내 가장 최저가
(가격 최적화, 단기 workload용) - diversified : 모든 pool에 걸쳐 분산 구축
(good availability, 장기 workload용) - capacity Optimized : 필요한 instance들을 수용할 수 있는 적합한 capacity를 가진 pool 선택
- 최저가 : pool 내 가장 최저가
Security Groups
- 방화벽 역할 : EC2를 오고 가는 트래픽 관리
Allow규칙 정의- 관리 대상 :
- Access to Ports
- Authorized IP ranges - IPv4, IPv6
- Inbound network (default : all blocked)
- Outbound network (default : all authorized)
- 관리 대상 :
- IP 참조 가능
- 여러 Instance들에 attach 가능
- region/VPC 내에서만 유효
- SSH 접근 관련 SG 별도로 관리하는 것이 유리함
Classic Ports
| 22 | SSH (Secure Shell) | log into a Linux instance |
|---|---|---|
| 21 | FTP (File Transfer Protocol) | upload files into a file share |
| 22 | SFTP (Secure FTP) | upload files using SSH |
| 80 | HTTP | access unsecured websites |
| 443 | HTTPS | access secured websited |
| 3389 | RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) | lgo into a Windows instance |
SSH (Secure SHell)
| SSH | Putty | EC2 Instance Connect (web browser @ AWS) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mac | O | O | |
| Linux | O | O | |
| Windows < 10 | O | O | |
| Windows ≥ 10 | O | O | O |
※ IP - IPv4 / IPv6, Private IP / Public IP
-
IPv4 : 32bit , still most common format (강좌에서 주로 다룰 주소)
- [0-255].[0-255].[0-255].[0-255]
-
IPv6 : 128bit, 고정header, 암호화 기능 기본
-
Public IP
- can be identified on the internet
- must be unique
- can be geo-located easily
-
Private IP
- can only be identified on a private network
- unique accross the private network
- 2 diff private networks can have same private IPs
- machines connect to internet by NAT + internet gateway (as a proxy)
- only a certain range of IPs can be used as private IP
Elastic IP
: fixed public IPv4 for your instance (only 1 instance)
- with Elastic IP address, you can mask the failure of an instance/software by rapidly remapping the address to another instance in your account
- 5개 제한 있지만, AWS에 늘려달라고 요청할 수 있음
- AVOID ELASTIC IP : often reflect poor architectural decision ⇒ use a random public IP and register a DNS name to it ⇒ or use a Load Balancer & don’t use a public IP
EC2 Placement Groups
- control over the EC2 Instances are going to be placed within the AWS infrastructure
- when creating a placement group, specify 1 of 3 strategies for the group :
-
Cluster
-
grouped together in a low-latency HW setup within the same rack within a single AZ
-
Use Case :
- Big Data job that needs to complete fast
- Application that needs extremely low latency, high network throughput⨁ high performance : 10 Gbps bandwidth btwn instances
Θ high risk : If the rack fails, all instances fails at the same time
-
-
Spread
-
spreads instances across underlying HW ( Instances on diff physical HW )
-
Use Case :
- applications that needs high availability
- critical application where instances must be isolated from failure from one another⨁ span across AZs , Reduced risk of simultaneous failure
Θ limited to max 7 instances per AZ per placement group
(ex: 1 region w/ 3 AZ ⇒ 7 instances in each AZ ⇒ total 21 instances in that region)
<br/
-
-
Partition : spread instances across many diff partitions within an AZ
(rely on diff sets of racks of HW, EC2 )-
EC2 instances get access to partition information as meta data
-
spread groups are just single individual instances spread through different racks or AZs, partition placement group : made of several instances on each partition)
-
Use Cases : HDFS, HBase, Cassandra, Kafka
⨁ can span across multiple AZs in the same region
⨁ Scales to 100s of EC2 instances per group
Θ partition failure can affect many EC2, but won’t affect other partitions
-
-
Elastic Network Interfaces (ENI)
-
logical component in a VPV that represents virtual network card
⇒ gives EC2 access to the network (EC2 밖에서도 사용됨) -
ENI can have following attributes:
- Primary private IPv4 , 1개 이상의 secondary IPv4
- 1 Elastic IP (IPv4) per private IPv4
- 1 public IPv4
- 1개 이상의 security groups
- Mac 주소
-
bound to specific AZ
-
Failover를 위해 ENI를 독립적으로 생성하여 다른 instance로 옮길 수 있음 (“attach them on the fly” )
- Failover : the redirection of traffic from a primary system to a secondary system
(백업 목적) 원래 등록되어있던 instance에 문제 발생 시 private IP가 다른 instance로 이동함
- Failover : the redirection of traffic from a primary system to a secondary system
EC2 Hibernate
- Stop & Terminate
- Stop : data on EBS (disk) is kept intact(not injured) in the next start
- Terminate : if you set root volume to be destroyed w/ instance, it will be destroyed
(if not set to be destroyed, it will be kept)
- Start
- 1st start : OS boots up ⇒ User Data script is run
- following starts : OS boots up ⇒ applications start / caches get warmed up
⇒ takes time
- EC2 Hibernate
- write in-memory (RAM) state to a file in the root EBS volume ⇒ RAM state preserved!
- when launching instance
- root EBS volume must be encrypted
- Use cases:
- long-running processing
- saving RAM state (RAM ≤ 150GB)
- Services that take up time to initialize
- good to know,,,,,, :
- Hibernate supports many kinds of instance families, instance RAM Sizes, Instance Sizes, all kinds of instances(on-demand, reserved, spot)
- Root Volume must be a large & encrypted EBS
- can not be hibernated more than 60 days
- write in-memory (RAM) state to a file in the root EBS volume ⇒ RAM state preserved!
※ EC2 Instance Storage Section : EBS, EC2 Instance store, EFS
EBS Volume (Elastic Block Store)
: network drive you can attach to your instance while they run
-
uses network to communicate the instance ⇒ latency might occur
-
can be detached from an instance and attached to another one quickly
-
allows your instance to persist data even after termination
-
some EBS can be “multi-attached” to more than 1 instances
(mostly mounted at 1 instance at a time) -
bound to AZ ⇒ use snapshots to move volume across AZ
-
provisioned capacity : size in GBs and IOPS (I/O Ops Per Second - 저장장치의 속도 측정 단위)
⇒ EBS Volume의 용량을 provision할 때 명시해야 하지만 나중에 늘릴 수 있음 -
Free tier : 30 GB of free EBS storage of type General Purpose(SSD) or Magnetic per month
EBS : Delete on Termination attribute
- controls the EBS behavior when an EC2 instance terminates, by AWS console / AWS CLI
Delete on Terminationby Default :- root EBS volume : enabled (deleted on termination)
- any other attached EBS volume : disabled (not deleted on termination)
- Use case : preserve root volume when instance is terminated (exam scenario)
EBS Snapshots
-
backup (snapshot) of EBS volume at a point in time
-
X necessary to detach volume to do snapshot, but recommended
-
Can copy snapshots across AZ or Region
-
Features :
- EBS Snapshot Archive
- move snapshot to “archive tier” : 75% cheaper
- takes 24~72 hours for restoring (restore : to bring back existence)
- Recycle Bin for EBS Snapshots
- setup rules to retain deleted snapshots so you can recover after accidental deletion
- specify retention from 1 day ~ 1 year (retention : **the ability to keep and hold)**
- Fast Snapshot Restore (FSR)
- Force full initialization of snapshot to have x latency on the first use (cost $$$)
- good when snapshot is very big and need a quick instance initialization
- Force full initialization of snapshot to have x latency on the first use (cost $$$)
- EBS Snapshot Archive
EBS Volume Types
- SSD (Solid State Drive) vs HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
- Types - depending on Size / Throughput / IOPS
-
st1 (Low cost HDD) : for frequently accessed, throughput-intensive workloads
-
s1 (Lowest cost HDD)* : for less frequently accessed workloads
- HDD EBS features
⇒ only gp2/gp3, io1/io2 can be used as boot volumes
-
gp2 / gp3 (SSD) : General Purpose SSD volume
- cost effective & low latency ⇒ balance price & performance
- 1 GiB ~ 16Tib
- ex) system boot volumes, virtual desktops, Development and test env’ts
- gp3 (newer ver.)
- Baseline of 3,000 IOPS and throughput of 125 MiB/s
- Can increase IOPS up to 16,000 and throughput up to 1000 MiB/s independently
- gp2 (older ver.)
- Small gp2 volumes can burst IOPS to 3,000
- Size of the volume and IOPS are linked, max IOPS is 16,000
- 3 IOPS per GB, means at 5,334 GB we are at the max IOPS
-
io1 / io2 (SSD) : Provisioned IOPS - Highest-performance SSD volume
- for mission-critical low-latency or high-throughput workloads
- Critical business applications with sustained IOPS performance
- applications that need more than 16,000 IOPS
- Great for databases workloads (sensitive to storage perf and consistency)
- Supports EBS Multi-attach
- io1/io2 (4 GiB - 16 TiB)
- Max PIOPS: 64,000 for Nitro EC2 instances & 32,000 for other
- Can increase PIOPS independently from storage size
- io2 have more durability and more IOPS per GiB (at the same price as io1)
- io2 Block Express (4 GiB – 64 TiB):
- Sub-millisecond latency
- Max PIOPS: 256,000 with an IOPS:GiB ratio of 1,000:1
- for mission-critical low-latency or high-throughput workloads
-
EBS Multi-Attach - io1/io2 family
-
Attach the same EBS volume to multiple EC2 instances in the same AZ
⇒ Each instance has full Read & Write permissions to high-performance volume
-
Up to 16 EC2 Instances at a time
-
Must use a file system that’s cluster-aware (not XFS, EX4, etc…)
-
Use Cases:
- Achieve higher application availability in clustered Linux applications (ex: Teradata)
- Applications must manage concurrent write operations
EBS Encryption
- list of encryption in an encrypted EBS volume :
- Data at rest inside the volume
- All data flow btwn the instance and the volume
- All snapshots
- All volumes created from the snapshot
- Encryption and decryption are handled transparently (user has nothing to do)
- minimal impact on latency
- EBS Encryption leverages keys from KMS (AES-256)
- Copying an unencrypted snapshot allows encryption
Encrypt an unencrypted EBS volume
- Create EBS Snapshot of the volume
- Using copy, encrypt the EBS snapshot
- create new EBS volume from the encrypted snapshot ⇒ encrypted snapshot
- attach encrypted volume to original instance
AMI = Amazon Machine Image
: customization of an EC2 instance -
-
add your own software, configuration, OS, monitoring, …
-
all software is pre-packaged ⇒ faster boot / faster configuration time
-
built for specific region & can be copied across regions
-
types
- Public AMI : AWS provided
- Your own AMI : you make and maintain them yourself
- AWS Marketplace AMI : AMI someone else made (and potentially sells)
-
Creating AMI from an EC2 instance
- Start an EC2 instance and customize it
- stop the instance for data integrity
- Build an AMI : this will also create EBS snapshots
- Launch instance from AMI
EC2 Instance Store : high-performance HW attached volume
- EBS volumes : network drives → “limited performance”
- Features :
- Better I/O performance
- lose storage if stopped (ephemeral - lasting for a very short time)
- good for buffer / cache / scratch data / temporary content
- risk of data loss if HW fails
- Backups / Replication are your responsiblity
Amazon EFS : Elastic File System
: Managed NFS (Network File System) that can be mounted on many EC2
- work w/ EC2 instance in multi-AZ
- Highly available, scalable, pay per use, expensive (3 * gp2)
NFSv4.1protocol- use Security to control access to EFS
- compatible w/ Linux based AMI (
Windows) - Encryption at rest using KMS
- standard file system on Linux - POSIX - has standard file API
- X plan capacity in advance - File system scales automatically
- Scale
- 1000s of concurrent NFS clients, 10 GB+ /s throughput
- Grow to Petabyte-scale network file system, automatically
- Use cases :
- Content management
- web serving
- data sharing
- wordpress
EFS - Storage Classes at EFS creation time
- Availability and Durability
- Standard (구 Regional) : Multi-AZ
- great for prod
- One Zone : One AZ
- great for development
- backup enabled by default
- compatible with IA (EFS One Zone-IA)
- Over 90% in cost s뜐avings
- Standard (구 Regional) : Multi-AZ
- Storage Classes - Tiers : move files to a different tier after a few days (lifecycle management feature)
- Standard Tier : for frequently accessed files
- EFS-IA (Infrequent Access Tier) : cost to retrieve files, lower price to store
- Must use Lifecycle Policy to enable EFS-IA
- Must use Lifecycle Policy to enable EFS-IA
- Performance Modes
- General Purpose (default) : latency-sensitive use cases (web server, CMS, etc…)
- Max I/O – higher latency, throughput, highly parallel (big data, media processing)
- Throughput Mode
1. Bursting : growing in throughputs as we have more storage
2. Provisioned : set your throughput regardless of storage size
3. Elastic : automatically scales throughput up or down based on your workloads
- Used for unpredictable workloads
EBS vs EFS
| EBS | EFS | |
|---|---|---|
| Attachment & Availability | 1 instance (Except multi-attach io1/io2 Bound to AZ | Mounting 100s of instances across AZ |
| IO | gp2 : IO increases if disk size increases io1 : can increase IO independently | - share website files (WordPress) - only for Linux Instances (POSIX) |
| Feature | Migrate EBS across AZ : take snapshot →restore snapshot to another AZ EBS backups use IO ⇒ shouldn’t run backups while your application is handling a lot of traffic) Termination : Root EBS Volumes of instances get terminated by default if the EC2 instance gets terminated. | - EFS has a higher price point than EBS - Can leverage EFS-IA for cost savings |

