주제
- 제목 : Twitter Sentiment Analysis
- 미션 : 감성분석기를 통한 감성분석(SNS를 통해 댓글등을 감성분석하기)
파일 정보
-
트위터의 엔티티 수준 감정 분석 데이터 세트 이며, 데이터세트는 긍정적, 부정적, 중립적으로 세가지 클래스로 되어있습니다. 여기서 중립적은 엔티티와 상관없는것을 중립적이라고 합니다.
-
train.csv
-
validation.csv
라이브러리 및 패키지 설치
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import spacy
import warnings
import re
import string
import random
from wordcloud import WordCloud
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from nltk.tokenize import RegexpTokenizer , TweetTokenizer
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer ,PorterStemmer
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from collections import defaultdict
from collections import Counter
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import one_hot
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# spaCy 라이브러리를 사용하여 en_core_web_sm이라는 사전 훈련된 영어 소형 모델
nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm")
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')데이터로드
df = pd.read_csv('/content/twitter_training.csv')간단하게 데이터 살펴보기
df.sample(7)
df.shape
df.dtypes
df.describe(include='all')(74681,4)


EDA
# 결측값 시각화 표현
CLR = '\033[94m' # Blue
RED = '\033[30m' # Black
RESET = '\033[0m' # Reset color
missing_values_cols = train.isna().sum()[train.isna().sum() > 0].index.to_list()
print(CLR + "Training Dataset Missing Values\n")
for feature in missing_values_cols:
print(
(CLR + feature) + "\t",
(RED + str(train[feature].isna().sum())) + "\t",
(RED + f"{train[feature].isna().sum() / len(train):.1%}" + RESET) + "\t",
(RED + f"{train[feature].dtype}"),
)show_details(df)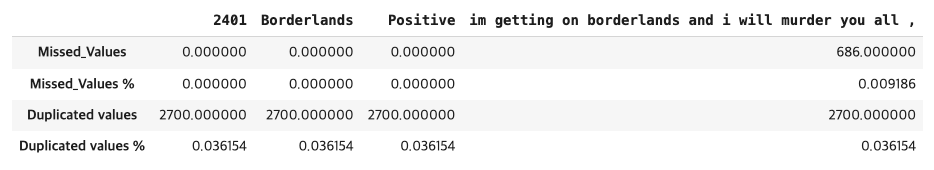
# 결측값과 중복행 제거
df.drop_duplicates(inplace=True)
df.dropna(inplace=True)
show_details(df)
# 컬럼명 변경
df.rename(columns={'2401' : 'Index' , 'Borderlands': 'Land' , 'Positive' : 'Mode'
, "im getting on borderlands and i will murder you all ,": 'Text'}, inplace=True)df.columnsIndex(['Index', 'Land', 'Mode', 'Text'], dtype='object')
# 해당 컬럼에 고유한 값들이 몇 개인지를 셈
print(f'The number of unique lands : {len(df.Land.unique())}')
print('**' * 40)
df.Land.unique()
# 지역의 분포가 거의 동일
lands =df.Land.value_counts()
lands.to_frame()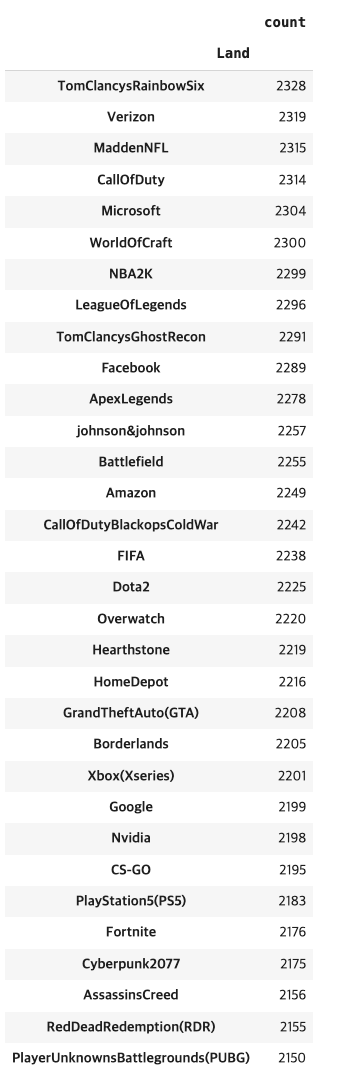
# 2150에서 2328 사이의 범위중 가장높은 10개를 보여줌
sns.set_style('darkgrid')
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
bar = sns.barplot(x=lands.values[:10] ,y=lands.index[:10] , palette='rocket')
bar.bar_label(bar.containers[0])
plt.title('Top 10 Lands')
plt.xlabel('Count')
plt.ylabel('Land')
plt.xlim(0 , 2500)
plt.show()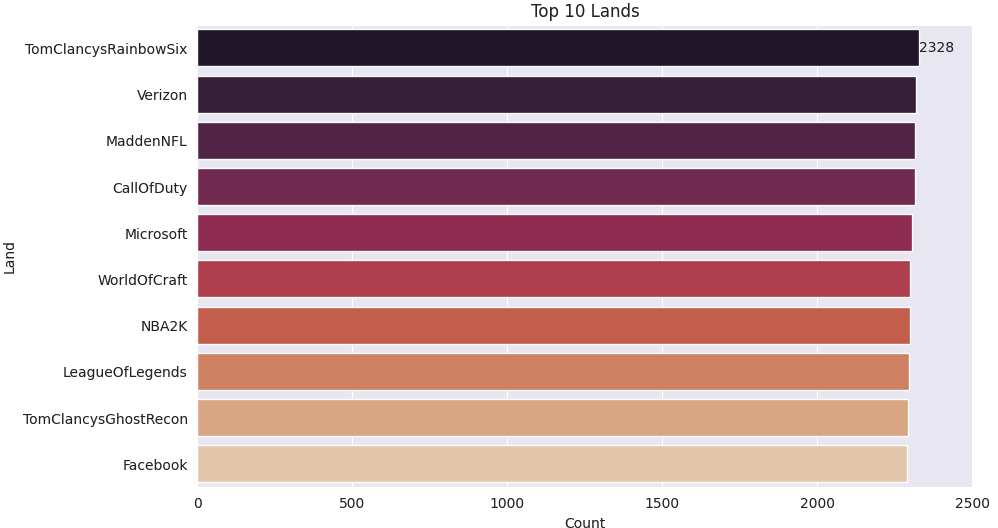
print(f'The unique values of Mode : {len(df.Mode.unique())}')
print('**' * 20)
print(df.Mode.unique())
mode = df.Mode.value_counts()
mode.to_frame().T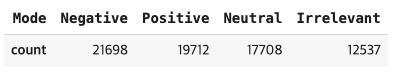
- 부정적 리뷰가 가장 많고 그다음이 긍정, 중립 관련없음으로 나타남
plt.figure(figsize=(6,6))
plt.pie(x = mode.values , labels=mode.keys() ,autopct="%1.1f%%" ,
textprops={"fontsize":10,"fontweight":"bold"},colors=sns.color_palette("pastel"))
plt.title('Mode Distribution')
plt.show()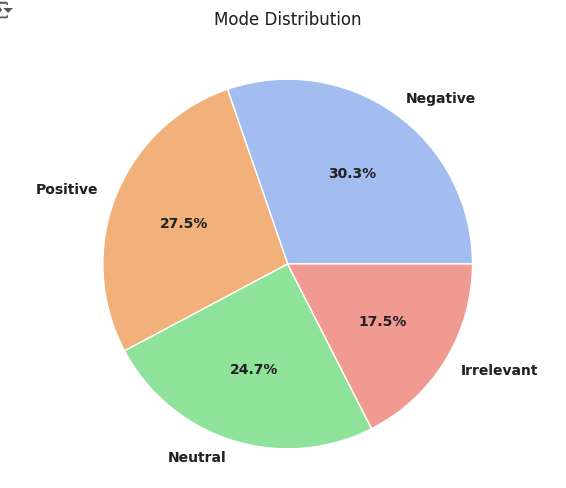
pd.crosstab(df.Mode , df.Land).T.style.background_gradient( subset=['Negative'],cmap='Reds')\
.background_gradient(subset=['Positive'] , cmap='Greens')\
.background_gradient(subset=['Irrelevant'] , cmap='BuGn')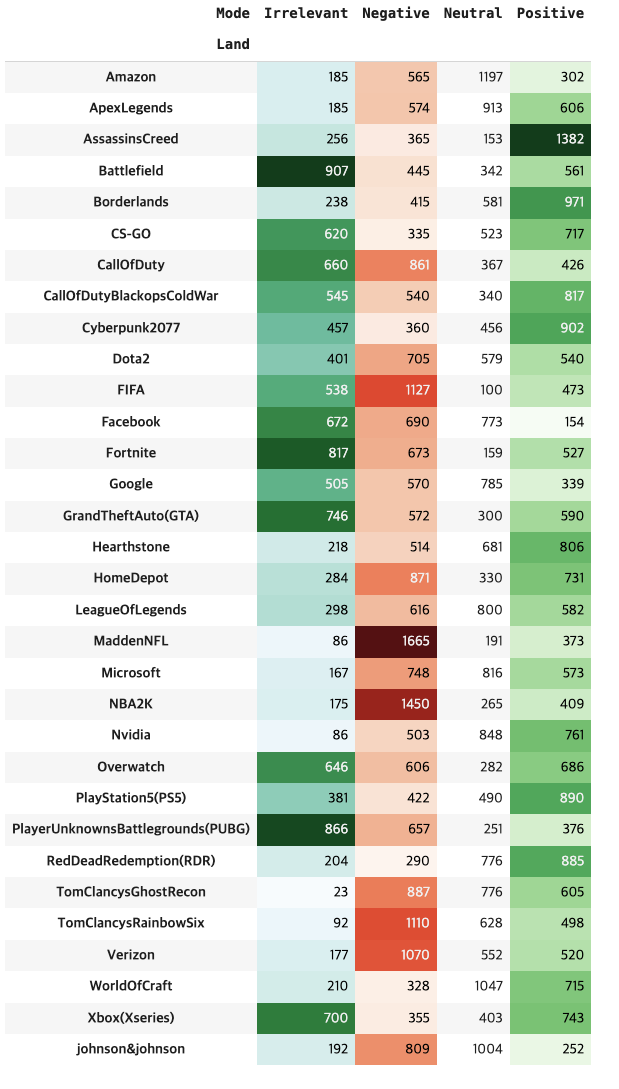
- 각 항목별로 높은 순위로 보여줌
정규화
def clean_emoji(tx):
emoji_pattern = re.compile("["
u"\U0001F600-\U0001F64F" # 감정 표현
u"\U0001F300-\U0001F5FF" # 기호 및 다양한 아이콘
u"\U0001F680-\U0001F6FF" # 교통 수단 및 기호
u"\U0001F1E0-\U0001F1FF" # 국기
u"\U00002702-\U000027B0"
u"\U000024C2-\U0001F251"
"]+", flags=re.UNICODE)
return emoji_pattern.sub(r'', tx)
def text_cleaner(tx):
text = re.sub(r"won\'t", "would not", tx) # 약형을 풀어서 쓰기
text = re.sub(r"im", "i am", tx)
text = re.sub(r"Im", "I am", tx)
text = re.sub(r"can\'t", "can not", text)
text = re.sub(r"don\'t", "do not", text)
text = re.sub(r"shouldn\'t", "should not", text)
text = re.sub(r"needn\'t", "need not", text)
text = re.sub(r"hasn\'t", "has not", text)
text = re.sub(r"haven\'t", "have not", text)
text = re.sub(r"weren\'t", "were not", text)
text = re.sub(r"mightn\'t", "might not", text)
text = re.sub(r"didn\'t", "did not", text)
text = re.sub(r"n\'t", " not", text)
text = re.sub(r"\'re", " are", text)
text = re.sub(r"\'s", " is", text)
text = re.sub(r"\'d", " would", text)
text = re.sub(r"\'ll", " will", text)
text = re.sub(r"\'t", " not", text)
text = re.sub(r"\'ve", " have", text)
text = re.sub(r"\'m", " am", text)
text = re.sub('https?://\S+|www\.\S+', '', text) # URL 제거
text = re.sub(r'[^a-zA-Z0-9\!\?\.\@]',' ' , text) # 특수 기호 처리
text = re.sub(r'[!]+' , '!' , text) # 구두점 정리
text = re.sub(r'[?]+' , '?' , text)
text = re.sub(r'[.]+' , '.' , text)
text = re.sub(r'[@]+' , '@' , text)
text = re.sub(r'unk' , ' ' , text) # unk' 제거
text = re.sub('\n', '', text) # 개행 문자 제거
text = text.lower() # 소문자로 변환
text = re.sub(r'[ ]+' , ' ' , text)
return textrandom.seed(99)
test_text =text_cleaner( random.choice(df['Text']))
test_text = clean_emoji(test_text)
test_text# 텍스트의 특정 단어들을 인식
doc = nlp(test_text)
for chunk in doc.ents:
print(f'{chunk} => {chunk.label_}')- tsushima => GPE
- 2 => CARDINAL
- second => ORDINAL
#Chunking : 단어의 성질에 따라 유사한 단어들을 그룹화
doc = nlp(test_text)
for chunk in doc.noun_chunks:
print(f'{chunk} => {chunk.label_}')- ghost => NP
- tsushima => NP
- the best open world => NP
- red dead redemption => NP
# 형태소 분석 및 품사 태깅을 수행
doc = nlp(test_text)
for token in doc :
print(f'{token} => {token.pos_}')
# Tokenization
# Tokenizer = TweetTokenizer()
Tokenizer=RegexpTokenizer(r'\w+')
test_text_tokenized = Tokenizer.tokenize(test_text)
test_text_tokenized
# df['Text']=df['Text'].apply(lambda x : Tokenizer.tokenize(x))
# CountVectorizer: 문서나 텍스트를 단어 또는 토큰의 빈도 수를 나타내는 벡터로 변환
words = ['ghost','of','tsushima','now','graphically','is','best','open','world','red','dead','redemption','2','one','second','ahead']
counter_vectorizer = CountVectorizer()
transform = counter_vectorizer.fit_transform([test_text]).toarray()
sns.heatmap(transform, annot=True,xticklabels=words,
cbar=False)
transform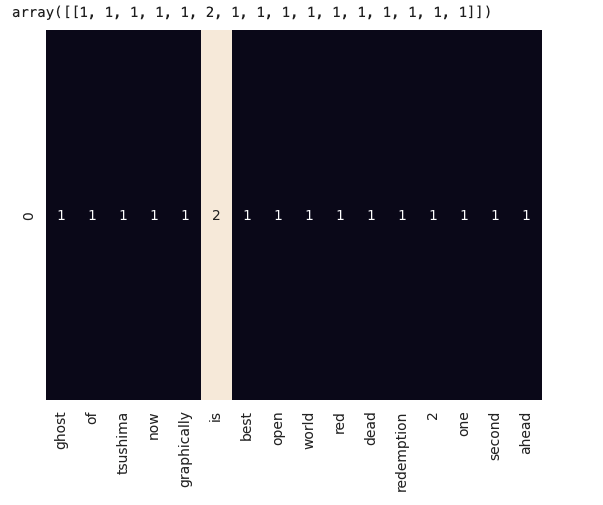
#TF(Term Frequency):특정 단어가 문서에서 얼마나 자주 등장하는지를 나타냄(단어의 등장 횟수를 세고, 이를 문장 내 모든 단어의 수로 나누는 방식입니다.)
#IDF(Inverse Document Frequency):는 특정 단어가 말뭉치에서 얼마나 흔하게 또는 드물게 등장하는지를 나타냄(말뭉치 내에서 해당 용어가 전체 문서에서 얼마나 중요한지를 측정하는 값입니다.)
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
words = ['ghost','of','tsushima','now','graphically','is','best','open','world','red','dead','redemption','2','one','second','ahead']
TF_IDF = TfidfVectorizer()
transform = TF_IDF.fit_transform([test_text]).toarray()
sns.heatmap(transform, annot=True,xticklabels=words,
cbar=False)
transform 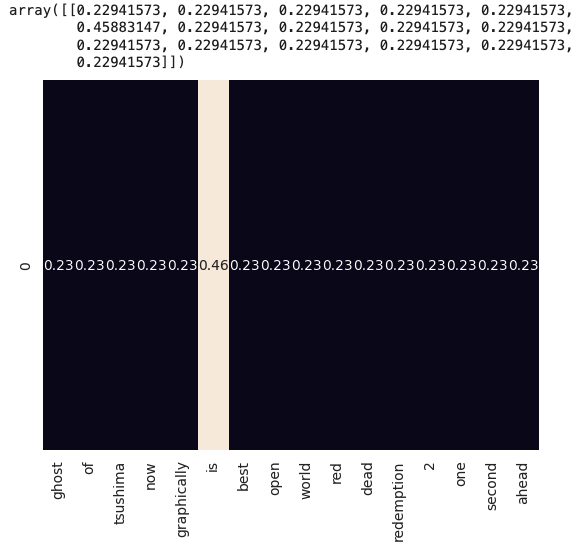
#N-grams : N개의 연속된 단어들의 시퀀스를 의미
def n_grams(text, n):
return [text[i:i+n] for i in range(len(text)-n+1)]
cleaned = test_text_tokenized
n_grams(cleaned, 3)
# Stop words : 언어에서 매우 흔히 사용되는 단어들
stopwords_list = stopwords.words('english')
print(f'There are {len(stopwords_list) } stop words')
print('**' * 20 , '\n20 of them are as follows:\n')
for inx , value in enumerate(stopwords_list[:20]):
print(f'{inx+1}:{value}')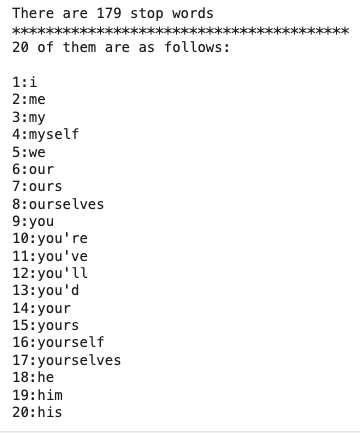
# Punctuation count(구두점개수)
def make_corpus(kind):
corpus = []
for text in df.loc[df['Mode']==kind]['Text'].str.split():
for word in text:
corpus.append(word)
return corpus%%time
stop = stopwords.words('english')
sentiments = list(df.Mode.unique())
for inx , value in enumerate(sentiments):
corpus = make_corpus(value)
dic = defaultdict(int)
for word in corpus:
if word in stop:
dic[word] += 1
top = sorted(dic.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)[:10]
x, y = zip(*top)
plt.title(f'{value} ')
plt.bar(x , y)
plt.show()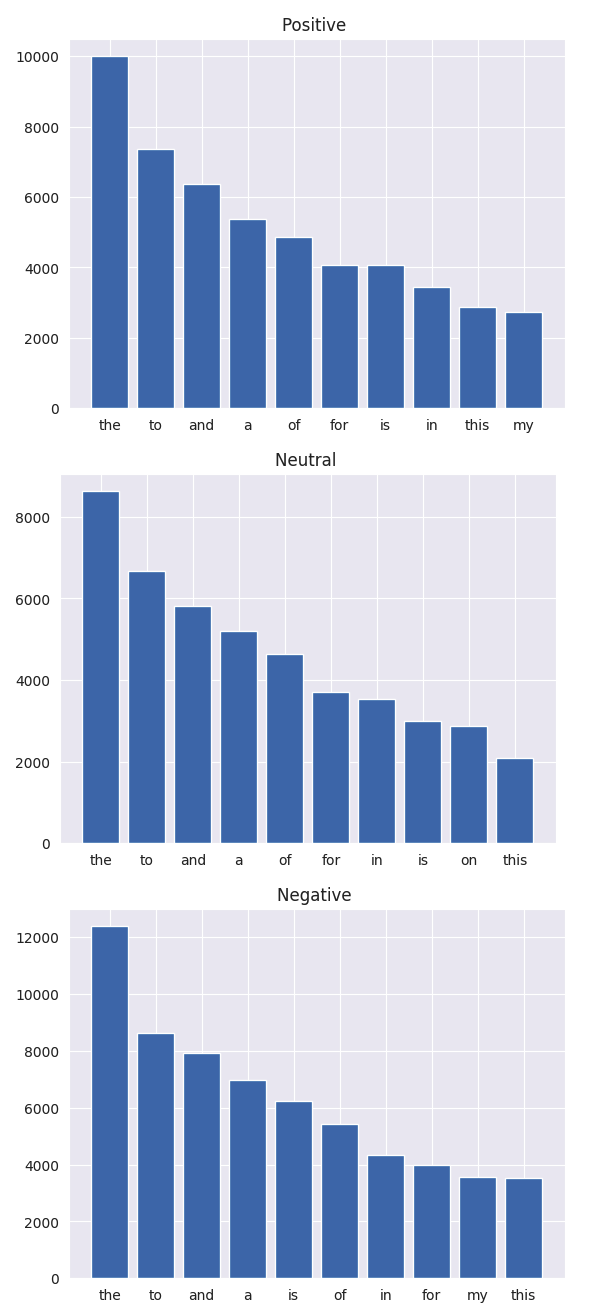
# 텍스트 정제
# df['Text'] = df['Text'].apply(lambda x : clean_emoji(x))
df['Text'] = df['Text'].apply(lambda x : text_cleaner(x))
df['Text']= df['Text'].apply(lambda x : Tokenizer.tokenize(x))
df['Text'].to_frame()
전처리
# Lemmatization : 자연어 처리(NLP) 모델에서 단어를 그 근본적인 의미로 분해하여 유사성을 식별하는 텍스트 전처리 기법
# Stemming : 단어를 그 기본 형태(루트 형태)로 줄이는 자연어 처리 기법
nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm")
doc = nlp(test_text)
for token in doc :
print(f'{token} => {token.lemma_}')
# lemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer()
Stemmer = PorterStemmer()
def stopwords_cleaner(text):
# word = [lemmatizer.lemmatize(letter) for letter in text if letter not in stopwords_list]
word = [Stemmer.stem(letter) for letter in text if letter not in stopwords_list]
peasting = ' '.join(word)
return peasting
df['Text'] = df['Text'].apply(lambda x : stopwords_cleaner(x))
# stopwords_cleaner(Tokenizer.tokenize(df.Text[100]))
워드클라우드
positive_reviews = df[df['Mode'] == 'Positive']['Text']
pos = ' '.join(map(str, positive_reviews))
pos_wordcloud = WordCloud(width=1500, height=800,
background_color='black',
stopwords=stopwords_list,
min_font_size=15).generate(pos)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(pos_wordcloud)
plt.title('Word Cloud for Positive Reviews')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
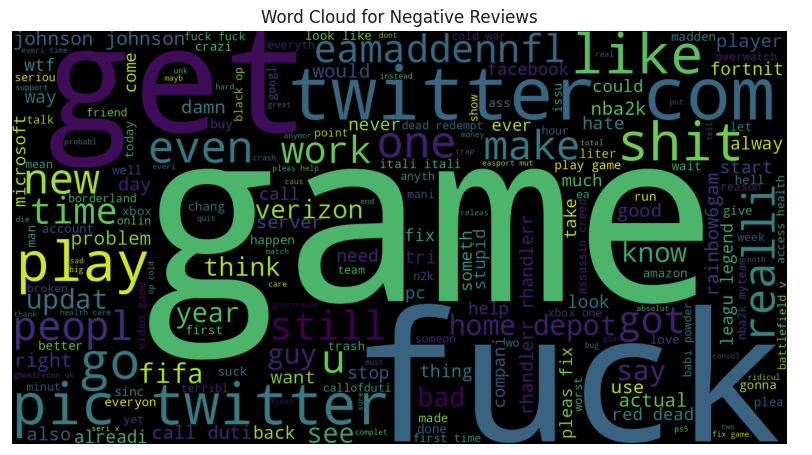
positive_reviews = df[df['Mode'] == 'Negative']['Text']
neg = ' '.join(map(str, positive_reviews))
pos_wordcloud = WordCloud(width=1500, height=800,
background_color='black',
stopwords=stopwords_list,
min_font_size=15).generate(neg)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(pos_wordcloud)
plt.title('Word Cloud for Negative Reviews')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
positive_reviews = df[df['Mode'] == 'Neutral']['Text']
Neutral = ' '.join(map(str, positive_reviews))
pos_wordcloud = WordCloud(width=1500, height=800,
background_color='black',
stopwords=stopwords_list,
min_font_size=15).generate(Neutral)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(pos_wordcloud)
plt.title('Word Cloud for Neutral Reviews')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()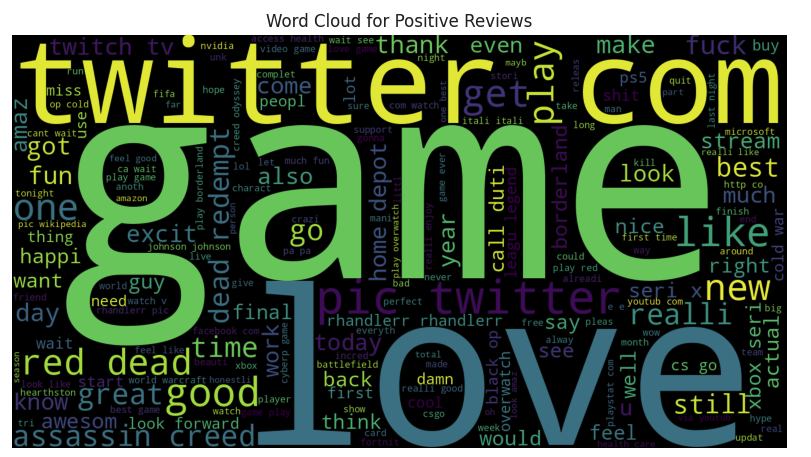

#여러 감정(sentiment) 유형별로 자주 사용되는 단어를 시각화
for inx , value in enumerate(sentiments):
counter = Counter(make_corpus(value))
most_common = counter.most_common()
x = []
y = []
for word, count in most_common[:40]:
if word not in stop:
x.append(word)
y.append(count)
sns.barplot(x=y, y=x, orient='h')
plt.title(f'{value} most used words')
plt.show()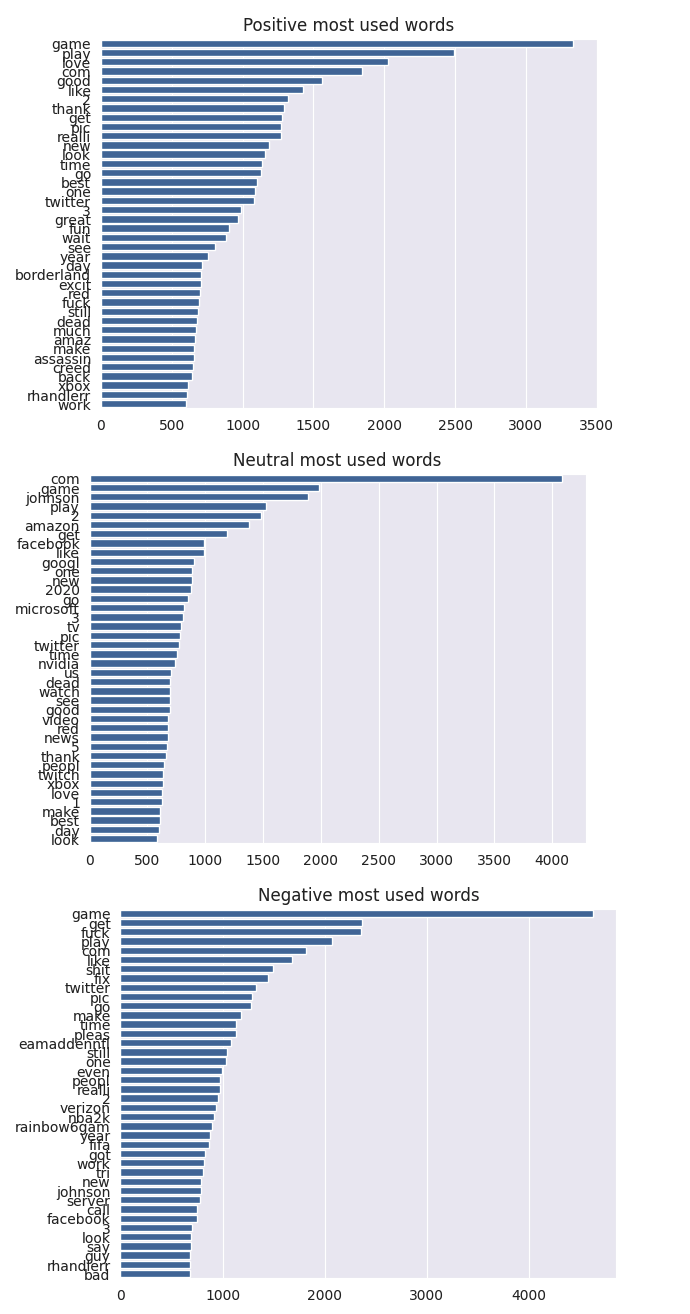
len_text = [len(tx) for tx in df['Text'].to_list()]
print(f'Max Length : {np.max(len_text)}')
print(f'Min Length : {np.min(len_text)}')
print(f'Mean Length : {round(np.mean(len_text),2)}')
print(f'Std Length : {round(np.std(len_text),2)}')
print(f'Mew + 2sigma : {round(np.mean(len_text)+ 2 *np.std(len_text),2)}')
df['sentiments'] = df['Mode'].replace({'Positive' : 1 , 'Negative' : 0 ,'Neutral':2 , 'Irrelevant' : 2 }) # Replace '<CorrectColumnName>' with 'Mode'
df.sample(10)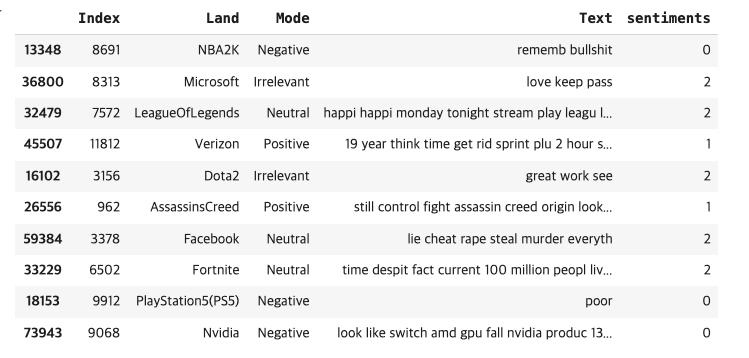
#텍스트와 감정(sentiment) 데이터를 PyTorch의 데이터셋 형태로 구성
class Dataset:
def __init__(self,text,sentiment):
self.text = text
self.sentiment = sentiment
def __len__(self):
return len(self.text)
def __getitem__(self,item):
text = self.text[item,:]
target = self.sentiment[item]
return {
"text": torch.tensor(text,dtype = torch.long),
"target": torch.tensor(target,dtype = torch.long)
}
def load_vectors(fname):
fin = open(fname , encoding="utf8")
data = {}
for line in fin:
tokens = line.split()
data[tokens[0]] = np.array([float(value) for value in tokens[1:]])
return data
def create_embedding_matrix(word_index,embedding_dict):
embedding_matrix = np.zeros((len(word_index)+1,300))
for word, i in word_index.items():
if word in embedding_dict:
embedding_matrix[i] = embedding_dict[word]
return embedding_matrix모델학습
Bidirectional LSTM
class sentimentBiLSTM(nn.Module):
#inherited from nn.Module
def __init__(self, embedding_matrix, hidden_dim, output_size):
#initializing the params by initialization method
super(sentimentBiLSTM, self).__init__()
self.embedding_matrix = embedding_matrix
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
num_words = self.embedding_matrix.shape[0]
embed_dim = self.embedding_matrix.shape[1]
# craetinh embedding layer
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=num_words,embedding_dim=embed_dim)
## initializes the weights of the embedding layer to the pretrained embeddings in
## embedding_matrix. It first converts embedding_matrix to a PyTorch tensor and
## wraps it in an nn.Parameter object, which makes it a learnable parameter of the model.
self.embedding.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor(embedding_matrix,dtype=torch.float32))
self.embedding.weight.requires_grad = False
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(embed_dim,hidden_dim,bidirectional=True,batch_first=True)
#it is multuplied by 2 becuase it is bi_directional if one-sided it didnt need.
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim*2, output_size)
#we need a forward function to model calculate the cost and know how bad the params is .
# However , it can be written in a line of code but if we want to track it it is easier way.
def forward(self, x):
embeds = self.embedding(x)
lstm_out,_ = self.lstm(embeds)
lstm_out = lstm_out[:, -1]
out = self.fc(lstm_out)
return out
y = df.sentiments.values
train_df,test_df = train_test_split(df,test_size = 0.2, stratify = y)
# 80% 훈련 20 % 테스트 설정
# 모델 하이퍼파라미터와 학습 장치(GPU/CPU)를 설정
MAX_LEN = 167
BATCH_SIZE = 32
hidden_dim = 64
output_size = 3
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device("cuda")
else:
device = torch.device("cpu")
print(f'Current device is {device}')
# PyTorch와 TensorFlow의 텍스트 전처리 및 데이터 로더 설정
tokenizer = tf.keras.preprocessing.text.Tokenizer()
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(df.Text.values.tolist())
xtrain = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(train_df.Text.values)
xtest = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(test_df.Text.values)
xtrain = tf.keras.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences(xtrain,maxlen = MAX_LEN)
xtest = tf.keras.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences(xtest,maxlen = MAX_LEN)
train_dataset = Dataset(text=xtrain,sentiment=train_df.sentiments.values)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,drop_last=True)
valid_dataset = Dataset(text=xtest,sentiment=test_df.sentiments.values)
valid_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(valid_dataset,batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,drop_last=True)
one_batch = next(iter(train_loader))
one_batch
embedding_dict = load_vectors('/content/glove.6B.300d.txt')
embedding_matrix = create_embedding_matrix(tokenizer.word_index,embedding_dict)
model = sentimentBiLSTM(embedding_matrix, hidden_dim, output_size)
model = model.to(device)
print(model)
# 모델 학습 준비
torch.manual_seed(42)
torch.cuda.manual_seed(42)
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# schedul_learning = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer=optimizer , milestones=[6] ,
# gamma=0.055)
def acc(pred,label):
pred = pred.argmax(1)
return torch.sum(pred == label.squeeze()).ite
clip = 5
epochs = 9
valid_loss_min = np.Inf
# train for some number of epochs
epoch_tr_loss,epoch_vl_loss = [],[]
epoch_tr_acc,epoch_vl_acc = [],[]
for epoch in range(epochs):
# for getting loss and accuracy for train
train_losses = []
train_acc = 0.0
#put model on train mode
model.train()
correct = 0
# initialize hidden state
for data in train_loader:
#get text and target
inputs = data['text']
labels = data['target']
#put them on GPU and right dtypes
inputs = inputs.to(device,dtype=torch.long)
labels = labels.to(device,dtype=torch.float)
#gradient becomes zero=> avoid accumulating
model.zero_grad()
output = model(inputs)
# calculate the loss and perform backprop
loss = criterion(output, labels.long())
loss.backward()
train_losses.append(loss.item())
# accuracy
accuracy = acc(output,labels)
train_acc += accuracy
#`clip_grad_norm` helps prevent the exploding gradient problem in LSTMs
nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), clip)
optimizer.step()
# for getting loss and accuracy for valiadtion
val_losses = []
val_acc = 0.0
#put model on evaluation mode
model.eval()
for data in valid_loader:
#get text and target
inputs = data['text']
labels = data['target']
#put them on GPU and right dtypes
inputs = inputs.to(device,dtype=torch.long)
labels = labels.to(device,dtype=torch.float)
#gradient becomes zero=> avoid accumulating
model.zero_grad()
output = model(inputs)
output = model(inputs)
#Loss calculating
val_loss = criterion(output, labels.long())
#append Loss to the above list
val_losses.append(val_loss.item())
# calculating accuracy
accuracy = acc(output,labels)
val_acc += accuracy
epoch_train_loss = np.mean(train_losses)
#using schedule lr if you need
# schedul_learning.step()
# schedul_learning
#appending all accuracy and loss to the above lists and variables
epoch_val_loss = np.mean(val_losses)
epoch_train_acc = train_acc/len(train_loader.dataset)
epoch_val_acc = val_acc/len(valid_loader.dataset)
epoch_tr_loss.append(epoch_train_loss)
epoch_vl_loss.append(epoch_val_loss)
epoch_tr_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
epoch_vl_acc.append(epoch_val_acc)
print(f'Epoch {epoch+1}')
print(f'train_loss : {epoch_train_loss} val_loss : {epoch_val_loss}')
print(f'train_accuracy : {epoch_train_acc*100} val_accuracy : {epoch_val_acc*100}')
if epoch_val_loss <= valid_loss_min:
#each time that model(params) get better you can save the model(you have to enter a path ou you pc and save with pt file)
# torch.save(model.state_dict(), r'C:\Users\payama\Desktop\Projects kaggle\NLP\vectors features\BidirectionalLSTM.pt')
# print('Validation loss decreased ({:.6f} --> {:.6f}). Saving model ...'.format(valid_loss_min,epoch_val_loss))
print(f'Validation loss decreased ({valid_loss_min} --> {epoch_val_loss}) Saving model ...')
# save model if better result happends
valid_loss_min = epoch_val_loss
print(30 * '==' , '>')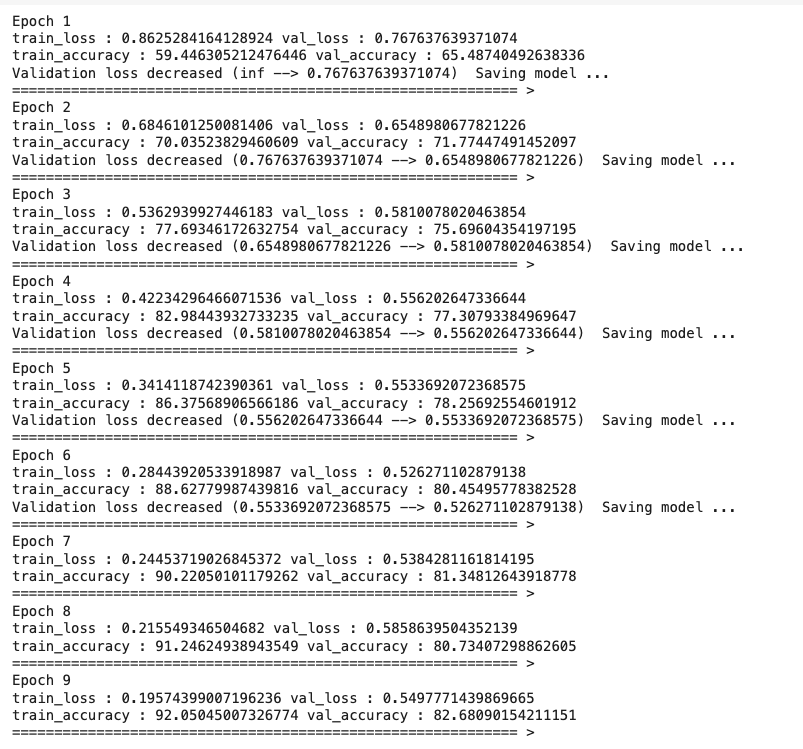
# 결과치 시각화
plt.figure(figsize=(7,5))
plt.plot(range(1,10),epoch_tr_acc , label='train accuracy')
plt.scatter(range(1,10),epoch_tr_acc)
plt.plot(range(1,10),epoch_vl_acc , label='val accuracy')
plt.scatter(range(1,10),epoch_vl_acc)
plt.title('Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
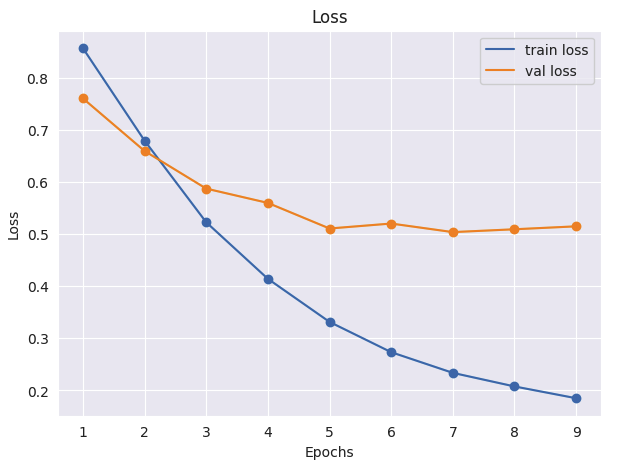
plt.figure(figsize=(7,5))
plt.plot(range(1,10),epoch_tr_loss , label='train loss')
plt.scatter(range(1,10),epoch_tr_loss )
plt.plot(range(1,10),epoch_vl_loss , label='val loss')
plt.scatter(range(1,10),epoch_vl_loss)
plt.title('Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()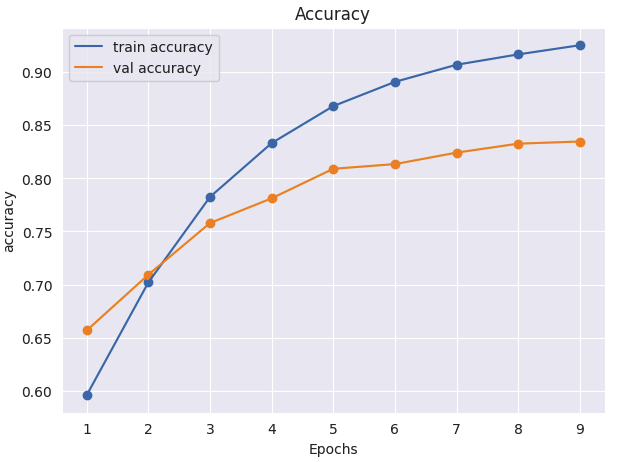
Bert 모델
# BERT 모델로 학습
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import numpy as np
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertModel
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import tensorflow as tf
# 데이터셋 클래스 정의
class Dataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, text, sentiment):
self.text = text
self.sentiment = sentiment
def __len__(self):
return len(self.text)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return {'text': self.text[idx], 'target': self.sentiment[idx]}
class SentimentBERT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, output_size):
super(SentimentBERT, self).__init__()
# BERT 모델과 토크나이저 로드
self.tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
self.bert = BertModel.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
# BERT의 출력 크기는 768
self.fc = nn.Linear(768, output_size)
def forward(self, x):
# x가 이미 토큰화된 경우
if isinstance(x, dict):
outputs = self.bert(**x)
else:
# 입력 문장을 토큰화하고 인덱스로 변환
inputs = self.tokenizer(x, return_tensors='pt', padding=True, truncation=True)
inputs = {k: v.to(self.bert.device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
outputs = self.bert(**inputs)
# BERT의 마지막 은닉 상태 가져오기
last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
# 마지막 토큰의 은닉 상태 사용
out = self.fc(last_hidden_states[:, -1, :])
return out
# 데이터 준비
y = df.sentiments.values
train_df, test_df = train_test_split(df, test_size=0.2, stratify=y)
MAX_LEN = 167
BATCH_SIZE = 32
output_size = 3
# 디바이스 설정
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device("cuda")
else:
device = torch.device("cpu")
print(f'Current device is {device}')
# 모델 초기화
model = SentimentBERT(output_size)
model = model.to(device)
print(model)
# 시드 설정
torch.manual_seed(42)
torch.cuda.manual_seed(42)
# 옵티마이저 및 손실 함수 설정
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 정확도 계산 함수
def acc(pred, label):
pred = pred.argmax(1)
return torch.sum(pred == label.squeeze()).item()
clip = 5
epochs = 9
valid_loss_min = np.Inf
# 학습 루프
epoch_tr_loss, epoch_vl_loss = [], []
epoch_tr_acc, epoch_vl_acc = [], []
for epoch in range(epochs):
train_losses = []
train_acc = 0.0
# 모델을 학습 모드로 설정
model.train()
correct = 0
for data in train_loader:
inputs = data['text']
labels = data['target']
# BERT 토크나이저는 문자열 리스트를 입력으로 받음
inputs = list(inputs) # 텐서를 리스트로 변환
inputs = [str(i) for i in inputs] # 각 요소를 문자열로 변환
labels = labels.to(device, dtype=torch.float)
model.zero_grad()
output = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(output, labels.long())
loss.backward()
train_losses.append(loss.item())
accuracy = acc(output, labels)
train_acc += accuracy
nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), clip)
optimizer.step()
val_losses = []
val_acc = 0.0
model.eval()
for data in valid_loader:
inputs = data['text']
labels = data['target']
# inputs가 이미 문자열 리스트이므로 추가 변환이 필요 없음
labels = labels.to(device, dtype=torch.float)
model.zero_grad()
output = model(inputs) # 직접 inputs를 전달
val_loss = criterion(output, labels.long())
val_losses.append(val_loss.item())
accuracy = acc(output, labels)
val_acc += accuracy
epoch_train_loss = np.mean(train_losses)
epoch_val_loss = np.mean(val_losses)
epoch_train_acc = train_acc / len(train_loader.dataset)
epoch_val_acc = val_acc / len(valid_loader.dataset)
epoch_tr_loss.append(epoch_train_loss)
epoch_vl_loss.append(epoch_val_loss)
epoch_tr_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
epoch_vl_acc.append(epoch_val_acc)
print(f'Epoch {epoch+1}')
print(f'train_loss : {epoch_train_loss} val_loss : {epoch_val_loss}')
print(f'train_accuracy : {epoch_train_acc*100} val_accuracy : {epoch_val_acc*100}')
if epoch_val_loss <= valid_loss_min:
print(f'Validation loss decreased ({valid_loss_min} --> {epoch_val_loss}) Saving model ...')
valid_loss_min = epoch_val_loss
print(30 * '==', '>')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 정확도 시각화
plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))
plt.plot(range(1, epochs + 1), epoch_tr_acc, label='Train Accuracy')
plt.scatter(range(1, epochs + 1), epoch_tr_acc)
plt.plot(range(1, epochs + 1), epoch_vl_acc, label='Validation Accuracy')
plt.scatter(range(1, epochs + 1), epoch_vl_acc)
plt.title('Accuracy over Epochs')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 손실 시각화
plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))
plt.plot(range(1, epochs + 1), epoch_tr_loss, label='Train Loss')
plt.scatter(range(1, epochs + 1), epoch_tr_loss)
plt.plot(range(1, epochs + 1), epoch_vl_loss, label='Validation Loss')
plt.scatter(range(1, epochs + 1), epoch_vl_loss)
plt.title('Loss over Epochs')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
- 결과치가 좋지 않아서 변경을 주었다.
- optimizer 수정
- 배치크기
- 모델 아키텍처 수정
- 과적합 방지를 위해 L2 정규화 추가
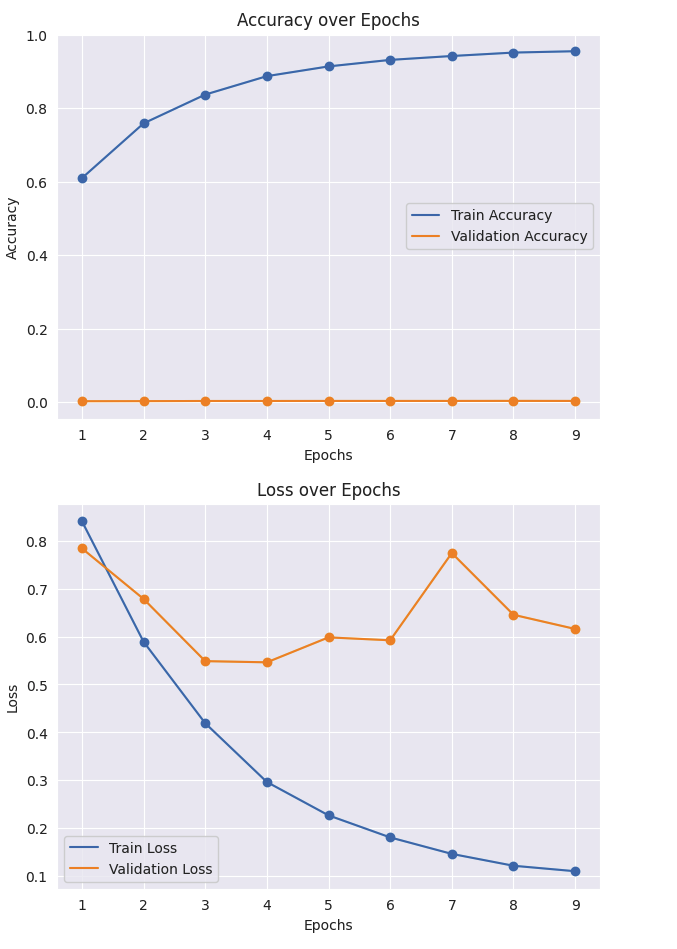

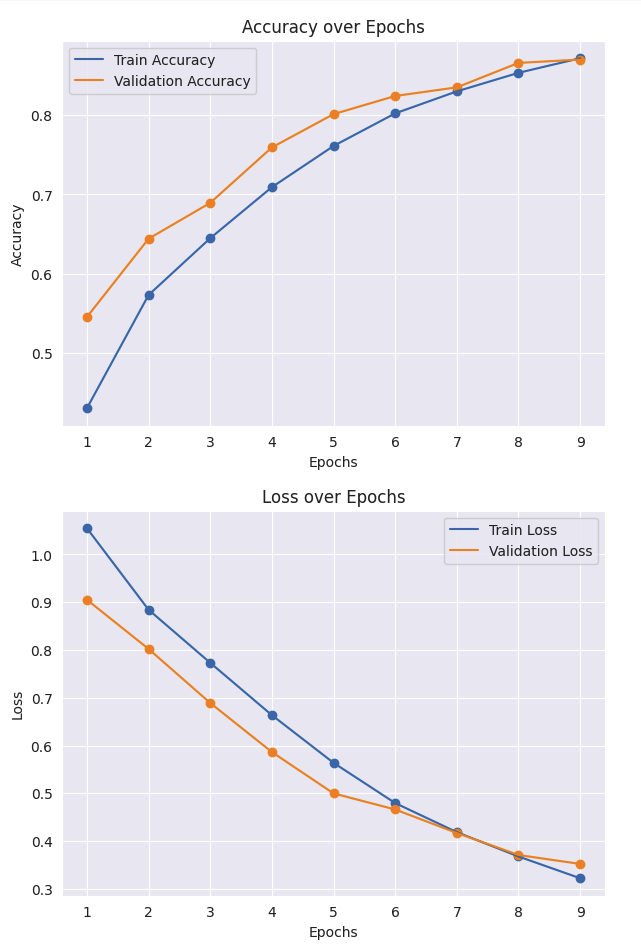
- Train 은 훨씬 좋아졌으나 Validation은 변화가 별로 좋지않아 추가적으로 개선해야할거같음
최종코드
# BERT 모델로 학습
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import numpy as np
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertModel
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import tensorflow as tf
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, RandomSampler, SequentialSampler
from sklearn.utils.class_weight import compute_class_weight
from tqdm import tqdm
import random
# BERT 토크나이저 설정
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
# 하이퍼파라미터 설정
MAX_LEN = 128
BATCH_SIZE = 32
ACCUMULATION_STEPS = 2
EPOCHS = 9
LEARNING_RATE = 2e-5
WEIGHT_DECAY = 1e-2
WARMUP_STEPS = 0.1
GRADIENT_CLIP = 1.0
output_size = 3
# 디바이스 설정
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# Dataset 클래스 정의
class Dataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, text, sentiment):
self.text = text
self.sentiment = sentiment
def __len__(self):
return len(self.text)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
text = str(self.text[idx])
encoding = tokenizer.encode_plus(
text,
add_special_tokens=True,
max_length=MAX_LEN,
return_token_type_ids=False,
padding='max_length',
truncation=True,
return_attention_mask=True,
return_tensors='pt',
)
return {
'text': encoding['input_ids'].flatten(),
'attention_mask': encoding['attention_mask'].flatten(),
'target': torch.tensor(self.sentiment[idx], dtype=torch.long)
}
# 데이터 로더 생성 함수
def create_data_loader(df, tokenizer, max_len, batch_size):
dataset = Dataset(
text=df.Text.values,
sentiment=df.sentiments.values
)
return DataLoader(
dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
num_workers=2,
pin_memory=True,
shuffle=True
)
# 모델 정의
class SentimentBERT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, output_size, dropout_rate=0.3):
super(SentimentBERT, self).__init__()
self.bert = BertModel.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout_rate)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(768, 512)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, 256)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(256, output_size)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.layer_norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(512)
self.layer_norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(256)
def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask):
outputs = self.bert(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
pooled_output = outputs.pooler_output
x = self.fc1(pooled_output)
x = self.layer_norm1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.layer_norm2(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
logits = self.fc3(x)
return logits
# 시드 설정
def set_seed(seed_value=42):
torch.manual_seed(seed_value)
torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed_value)
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed_value)
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
np.random.seed(seed_value)
random.seed(seed_value)
set_seed(42)
# 데이터 준비
y = df.sentiments.values
train_df, test_df = train_test_split(df, test_size=0.2, stratify=y, random_state=42)
# 클래스 가중치 계산
class_weights = compute_class_weight('balanced', classes=np.unique(y), y=y)
class_weights = torch.tensor(class_weights, dtype=torch.float).to(device)
# 데이터 로더 생성
train_loader = create_data_loader(train_df, tokenizer, MAX_LEN, BATCH_SIZE)
valid_loader = create_data_loader(test_df, tokenizer, MAX_LEN, BATCH_SIZE)
# 모델 초기화
model = SentimentBERT(output_size=output_size, dropout_rate=0.3)
model = model.to(device)
# BERT 레이어 동결
for param in model.bert.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
# 마지막 4개의 트랜스포머 레이어와 풀링 레이어의 파라미터를 학습 가능하게 설정
for param in model.bert.encoder.layer[-4:].parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
for param in model.bert.pooler.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
# 옵티마이저 설정
optimizer = optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=LEARNING_RATE, weight_decay=WEIGHT_DECAY)
# 손실 함수 설정
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=class_weights)
# 정확도 계산 함수
def acc(pred, label):
pred = torch.argmax(pred, dim=1)
return (pred == label).float().mean().item()
# 학습률 스케줄러 설정
total_steps = len(train_loader) * EPOCHS
scheduler = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup(optimizer,
num_warmup_steps=int(WARMUP_STEPS * total_steps),
num_training_steps=total_steps)
# 그래디언트 클리핑 함수
def clip_gradients(model, clip_value=GRADIENT_CLIP):
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=clip_value)
# 학습 루프
VALID_LOSS_MIN = np.Inf
epoch_tr_loss, epoch_vl_loss = [], []
epoch_tr_acc, epoch_vl_acc = [], []
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
print(f'Epoch {epoch+1}/{EPOCHS}')
print('-' * 10)
# 3번째 에포크 후에 마지막 3개 레이어를 해제
if epoch == 3:
for param in model.bert.encoder.layer[-3:].parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
print("Unfreezing last 3 BERT layers")
# 학습 단계
model.train()
train_loss, train_acc = 0, 0
train_pbar = tqdm(train_loader, desc="Training")
for step, data in enumerate(train_pbar):
input_ids = data['text'].to(device)
attention_mask = data['attention_mask'].to(device)
labels = data['target'].to(device)
outputs = model(input_ids, attention_mask)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss = loss / ACCUMULATION_STEPS
loss.backward()
if (step + 1) % ACCUMULATION_STEPS == 0:
clip_gradients(model, GRADIENT_CLIP)
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
scheduler.step()
train_loss += loss.item() * ACCUMULATION_STEPS
train_acc += acc(outputs, labels)
train_pbar.set_postfix({'train_loss': train_loss / (step + 1), 'train_acc': train_acc / (step + 1)})
# 검증 단계
model.eval()
val_loss, val_acc = 0, 0
val_pbar = tqdm(valid_loader, desc="Validation")
with torch.no_grad():
for step, data in enumerate(val_pbar):
input_ids = data['text'].to(device)
attention_mask = data['attention_mask'].to(device)
labels = data['target'].to(device)
outputs = model(input_ids, attention_mask)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
val_loss += loss.item()
val_acc += acc(outputs, labels)
val_pbar.set_postfix({'val_loss': val_loss / (step + 1), 'val_acc': val_acc / (step + 1)})
# 에포크 결과 계산
train_loss /= len(train_loader)
train_acc /= len(train_loader)
val_loss /= len(valid_loader)
val_acc /= len(valid_loader)
epoch_tr_loss.append(train_loss)
epoch_vl_loss.append(val_loss)
epoch_tr_acc.append(train_acc)
epoch_vl_acc.append(val_acc)
print(f'Train Loss: {train_loss:.4f} Acc: {train_acc*100:.2f}%')
print(f'Val Loss: {val_loss:.4f} Acc: {val_acc*100:.2f}%')
# 모델 저장
if val_loss < VALID_LOSS_MIN:
print(f'Validation loss decreased ({VALID_LOSS_MIN:.6f} --> {val_loss:.6f}). Saving model ...')
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'best_model.pt')
VALID_LOSS_MIN = val_loss
print()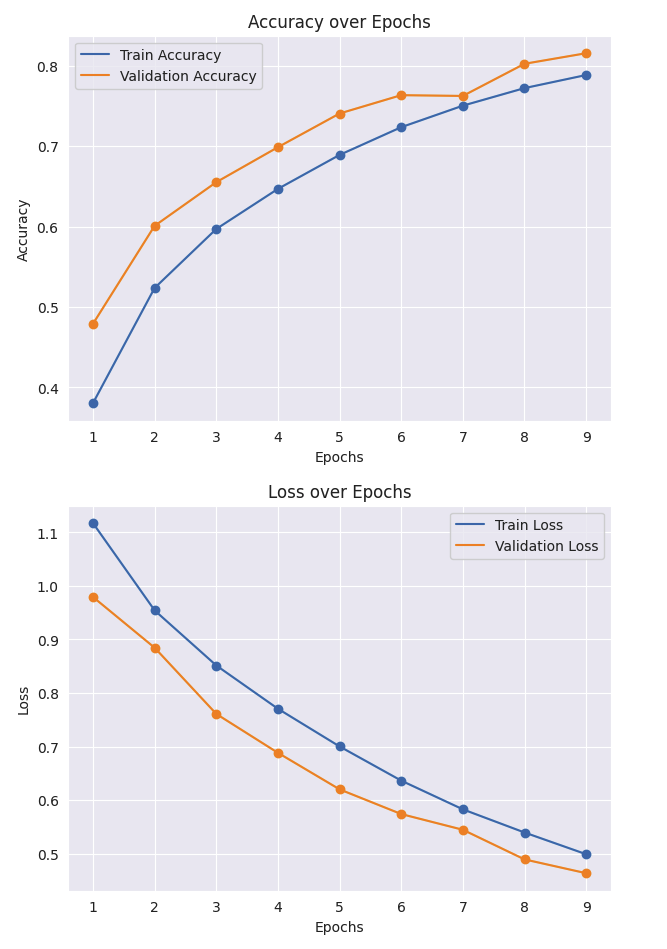
- 전체적으로 많이 좋아졌다.
bert-large-cased 변경해보기
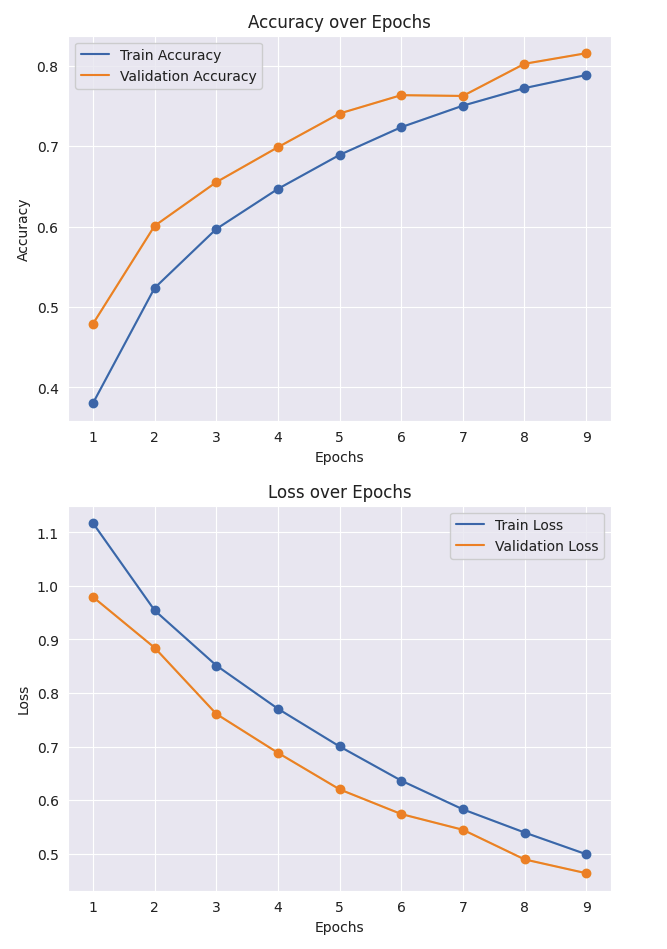
기본 모델보다 성능이 떨어졌다.(예상 데이터가 부족해서 그런거같다.....)

