원래는 결과(서버에 요청한 데이터), 에러 내용등이 모두 포함된 통합 응답 객체를 만들려고 했는데, 그럴 경우 API 응답 시 불필요한 항목들까지 노출되었다.
{
"result": "T",
"code": "1000",
"msg": "Successful response",
"status": "OK",
"data": {
"cmp_register": "111-11-11112",
"cmp_nm": "테스트용업체",
"cmp_id": "test",
"cmp_pw": "1234",
"tel_front": "010",
"tel_mid": "1111",
"tel_rear": "1111",
"cmp_std": "10",
"join_date": "2022-11-02T15:00:00.000+00:00",
"last_login_date": null,
"withdraw_date": null,
"login_fail_cnt": 0,
"cmp_addr": null
}
// 에러가 없을 시 이 부분은 필요가 없음
"errorCode" : null
"errorMsg" : null
}또한 각 비즈니스 로직에 따라 예상되는 예외를 try~catch로 걸어주어야 했다.
각각 예외들의 상위 Exception 객체로 추려도 양이 많아진다.
그렇다고 최상위 Exception 객체 하나로 catch한다면
유연한 예외 핸들링을 할 수가 없다.
try {
business
} catch (Exception e) {
// 각 에러에 대해 유연한 처리가 불가함
}그래서 ExceptionHandler와 API 응답용 객체(에러 내용이 포함된),
사용자 메시지를 위한 공통 에러를 만들기로 했다.
공통 예외
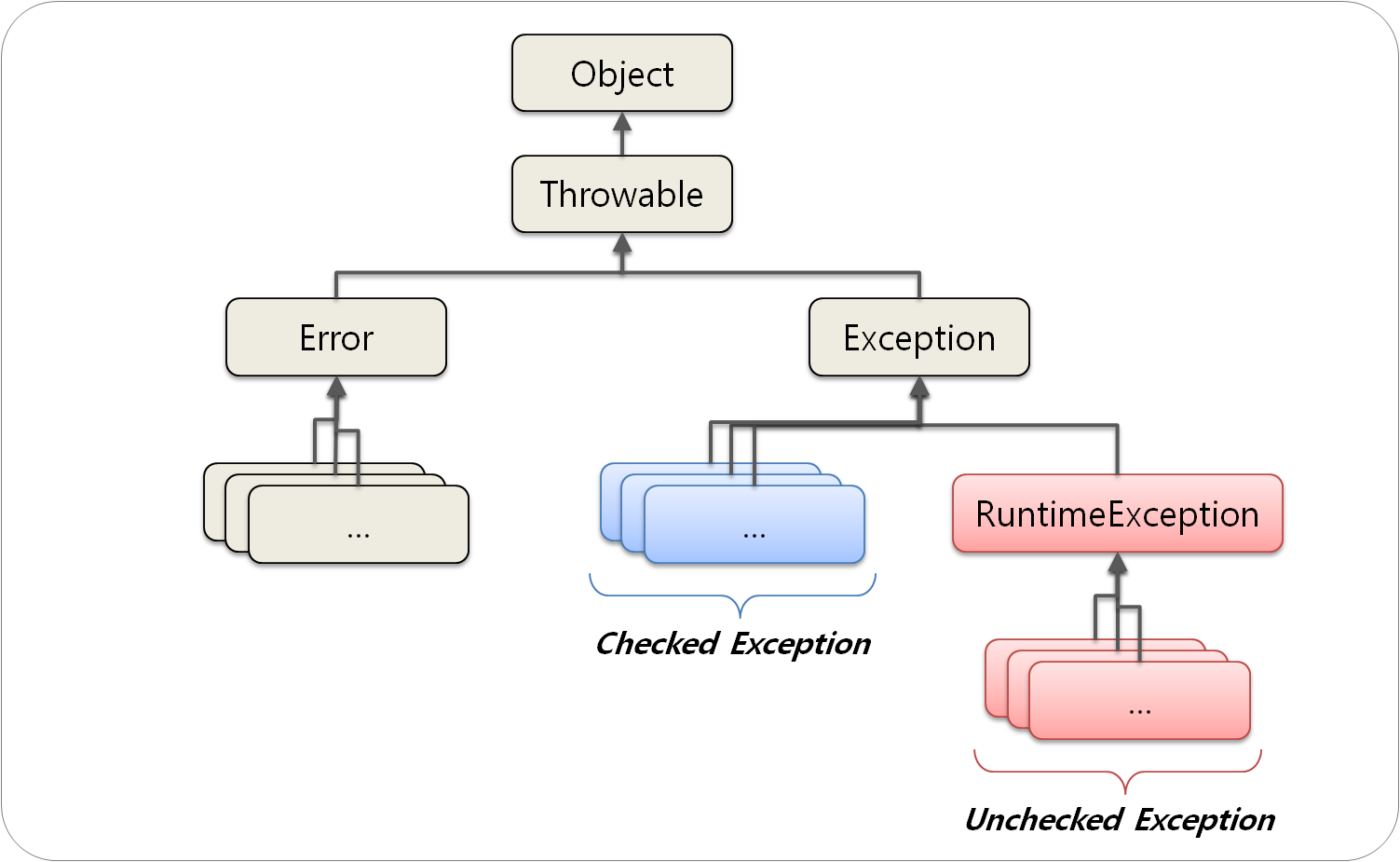
| Checked Exception | Uncheck Exception | |
|---|---|---|
| 트랜잭션 Rollback 여부 | Rollback 안됨 | Rollback 진행 |
| 대표 Exception | IOException, SQLException | NullPointerException, IlligalArgumentException |
Checked Exception
반드시 명시적으로 처리해야 하기 때문에Checked Exception,try~catch로 에러를 잡거나throw를 통해 호출한 메서드로 예외를 던져야 한다.Unchecked Exception
위와 반대로 명시적인 예외 처리를 강제하지 않는다.
각각의 에러코드와 메시지를 담은 열거형 ErrorCode를 만들고,
발생한 에러에 따라 사용자에게 Message를 던져줄 객체를 만들거니까 명시적인 예외처리가 강제되지 않고 롤백이 가능한 Unchecked Exception의 상위 객체인 RuntimeException을 상속받은 객체를 만든다.
ErrorCode.java
public enum ErrorCode {
SUCCESS_RESPONSE("1000", "Successful response", HttpStatus.OK),
DOESNT_EXIST("1001", "DOESNT_EXIST", HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
private String errCode;
private String errMsg;
private HttpStatus status;
private ErrorCode(String errCode, String errMsg, HttpStatus status) {
this.errCode = errCode;
this.errMsg = errMsg;
this.status = status;
}
public String getCode() {
return errCode;
}
public String getErrMsg() {
return errMsg;
}
public HttpStatus getStatus() {
return status;
}
}다른 예제들을 보면 "코드", "메시지"로 만들었는데,
이 프로젝트는 API로 응답하니 각각 에러에 대한 HTTP 상태 코드도 담고 있으면 좋을 것 같아서
코드, 메시지, HTTP 상태까지 3개를 포함한 열거형 상수 클래스를 만들었다.
CommonException.java
public class CommonException extends RuntimeException {
private ErrorCode errorCode;
public CommonException() { super(); }
public CommonException(String message) { super(message); }
public CommonException(Throwable e) { super(e); }
public CommonException(String message, Throwable e) {
super(message, e);
}
public CommonException(ErrorCode errorCode) {
super(errorCode.getCode());
this.errorCode = errorCode;
}
public CommonException(String message, ErrorCode errorCode) {
super(message);
this.errorCode = errorCode;
}
public CommonException(String message, Exception e, ErrorCode errorCode) {
super(message, e);
this.errorCode = errorCode;
}
public String getErrMsg() {
return errorCode.getErrMsg();
}
public String getErrCode() {
return errorCode.getCode();
}
public HttpStatus getStatus() { return errorCode.getStatus();
}
}위의 ErrorCode를 생성자로 가지고 있는 CommonException 클래스다.
Dto dto = testMapper.getSomething(param);
if (dto == null) {
throw new CommonException(ErrorCode.DOESNT_EXIST);
}이런식으로 내가 지정한 에러를 던져줄 수 있다.
에러 응답
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
public class ErrorResponse {
private String message;
private String code;
private HttpStatus status;
public ErrorResponse (Throwable e){
if (e instanceof CommonException) {
CommonException ex = (CommonException)e ;
this.code = ex.getErrCode();
this.message = ex.getErrMsg();
this.status = ex.getStatus();
} else {
CommonException ex = new CommonException(ErrorCode.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
this.code = ex.getErrCode();
this.message = ex.getErrMsg();
this.status = HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
}
public ResponseEntity build() {
ResponseEntity responseEntity = new ResponseEntity<>(this, status);
return responseEntity;
}
}맨 처음엔 이 객체를 바로 return해줬는데, 응답 코드는 200 OK인데
데이터는 에러로 떠서 의도한 바와 맞지 않았다.
따라서 ResponseEntity의 body에 응답용 데이터와 상태코드를 담아서 리턴하도록 메서드를 만들어주었다.
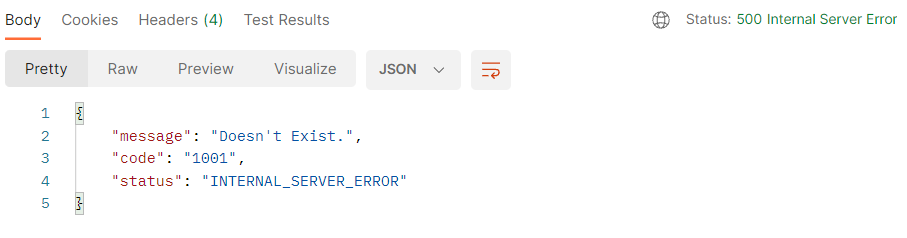
에러 발생 시 이렇게 응답한다.
ExceptionHandler
@ExceptionHandler를 사용하기 위해
@ControllerAdvice를 먼저 클래스 상단에 선언해주어야 한다.
@ControllerAdvice와@RestControllerAdvice는 전역적으로 예외를 처리할 수 있는 어노테이션입니다. 각각 Spring 3.2, Spring 4.3부터 제공하고 있습니다.@Controller어노테이션이 붙은 컨트롤러에서 발생하는 예외를 처리할 수 있습니다.
@ControllerAdvice는 컨트롤러에 대해@ExceptionHandler,@InitBinder,@ModelAttribute가 적용된 메소드에 AOP를 적용하기 위해 고안되었습니다.
또한,@Component가 포함되어 있기 때문에, Bean으로 관리됩니다.
@RestControllerAdvice는 @ControllerAdvice + @ResponseBody로
응답을 JSON으로 내려준다는 특징이 있다.
나는 위에서 만든 에러 객체를 리턴할 것이므로, @RestControllerAdvice를 사용했다.
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(CommonException.class)
public ResponseEntity handleCommonException(CommonException e) {
ErrorResponse res = new ErrorResponse(e);
return res.build();
}
/*
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity handleException(Exception e) {
do Something...
}
*/
}Service 로직에서 에러 발생 시 ExceptionHandler를 통해 에러를 받아
사용자가 받을 에러 메시지와 에러 코드, HTTP 상태 코드를 리턴해준다.
또한 각각의 예외 클래스들에 따라서 별도의 로직을 작성할 수 있다.
다만...
Global Exception Handling은 좋은 패턴이지만 모든 예외를 Global Exception Handler에서만 처리하는 것은 좋지 않다.
Runtime Exception이 이미 발생할 발생할 것임을 알고서도 해당 메서드를 꼭 사용해야 하는 경우에는 이미 Global Exception Handler에 등록이 되어 있더라도 해당 메서드 내에서try~catch로 예외에 대한 적절한 처리를 하는게 맞을 수도 있다.즉, Global Exception Handling은 한 가지의 선택지가 될 수 있는 것이지 모든 처리를 반드시 여기서 하라는 의미는 아니다.
Global Exception Handler를 사용하면 좋은 케이스
RuntimeException에 대한 DefaultHandler를 지정할 때
NullPointerException같은 일일히 예상할 수 없는 Unchecked Exception에 대해 DefaultHandler를 지정하게 되면 일관된 응답을 기대할 수 있다.
로깅도 용이하며, 프로그램이 뻗는 상황도 방지할 수 있을 것이다.- 여러 곳에서 비슷한 예외가 발생하고 이에 대해 일관된 처리가 필요 하거나, 일관된 응답이 필요할 때
- 최상위 Uncheck인
RuntimeException에 대한 핸들러가 이미 존재한다 해도, 그 자식인 다른 Exception에 대한 핸들러를 지정해서 조금 더 구체적으로 예외 상황을 처리하는 것이 필요할 때가 있다.
- 최상위 Uncheck인
Check/Unchecked Exception에 대한 처리 로직을 한 곳으로 모으고 싶을 때try~catch를 하는 부분이 지저분하거나, throw를 해서 메서드 시그니쳐가 지저분해지는 것을 막을때
참조
https://travelbeeee.tistory.com/454
https://www.nextree.co.kr/p3239/
https://chanos.tistory.com/entry/Spring-%EC%A0%84%EC%97%AD-%EC%98%88%EC%99%B8-%EC%B2%98%EB%A6%AC%EB%A5%BC-%EC%9C%84%ED%95%9C-ControllerAdvice%EC%99%80-RestControllerAdvice
https://umbum.dev/896
