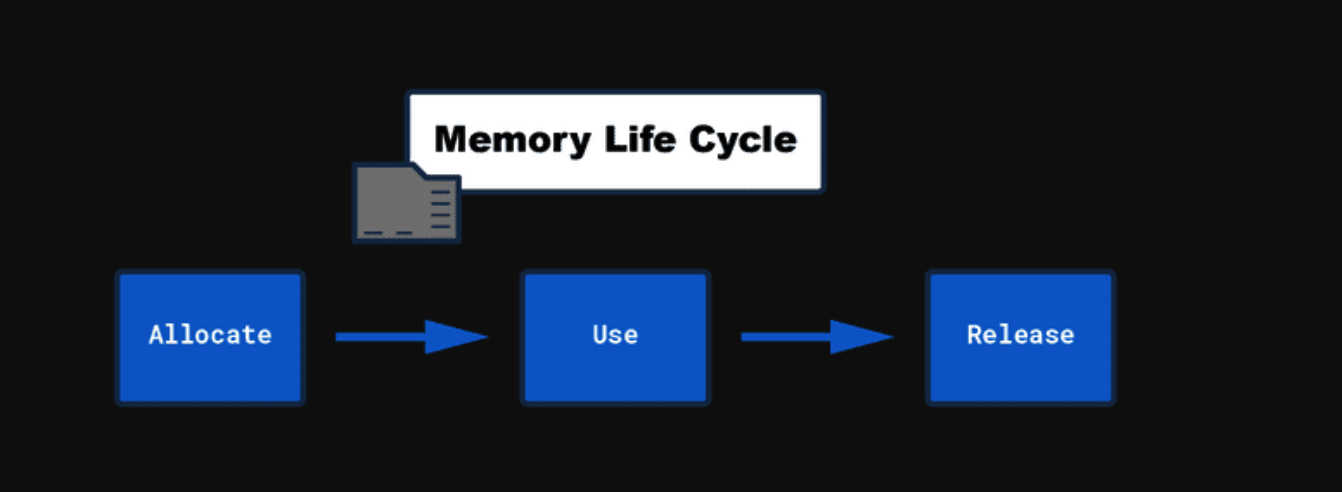
메모리 생명 주기
- Memory Allocate : 메모리 할당
- 우리가 생성한 객체(object)에 필요한 메모리를 할당- 메모리 관리 측면에서의 객체(objects)는 javascript object들만이 아니라 functions, function scopes 까지 포함됨
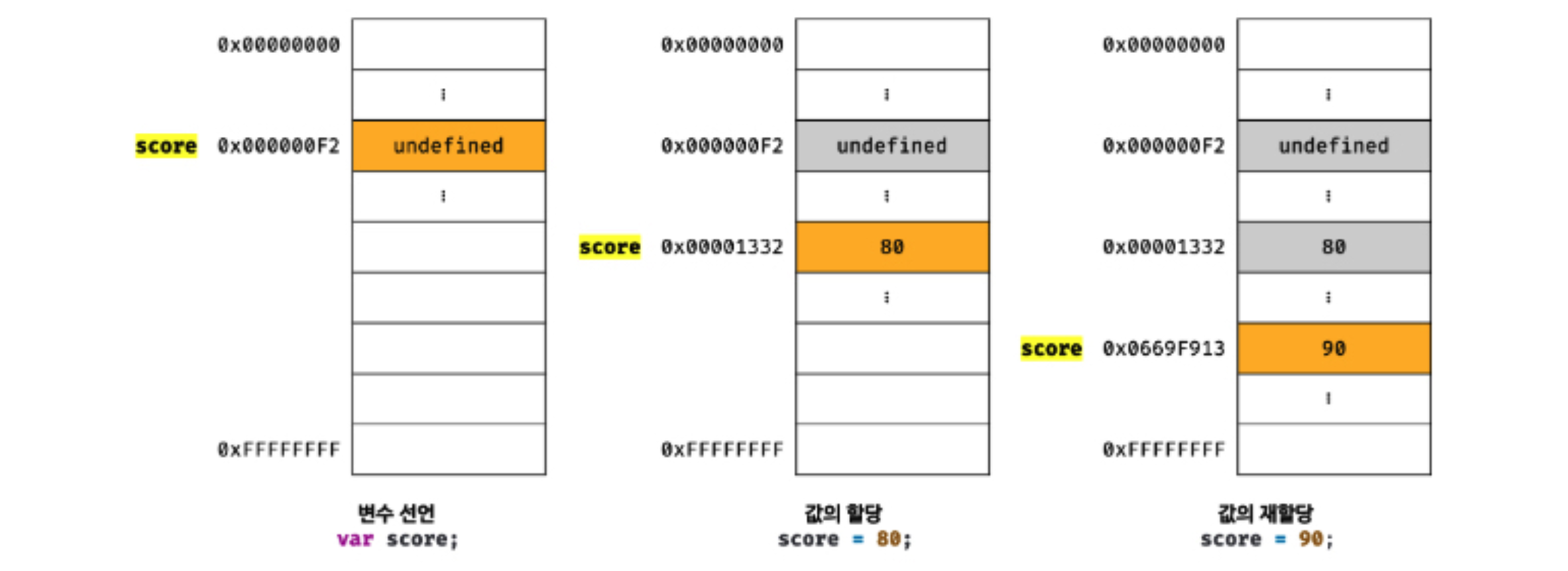
- 변수에 값을 재할당할 때는 기존에 사용하고 있는 메모리 공간을 지우고 재할당하는게 아니라 새로운 메모리 공간을 확보해서 저장함
- Memory Use : 메모리 사용
- 할당된 메모리를 사용하는 것은 기본적으로 그 메모리 내에서 읽거나 쓰는 것을 뜻함
- 이것은 객체의 속성이나 변수의 값을 읽기/쓰기 혹은 함수에 인수를 넘겨줄때에도 일어남.
- Memory Release : 메모리 해제
-
📍 Javascript는 Managed 언어이기 때문에 Allocate와 Release를 알아서 수행한다.
- managed language: 메모리의 할당 및 해제를 위한 메모리 관리 기능을 언어차원에서 담당
- unmanaged language: 개발자가 명시적으로 메모리를 할당하고 해제하기위해 malloc(), free()와 같은 low-level 메모리 제어 기능을 제공
-
메모리 할당 (static allocation vs dynamic allocation)
-
정적 메모리 할당 (static allocation)
- stack - static data를 저장하는 데이터 구조
- 엔진이 컴파일시 데이터의 크기를 알고있는 데이터
- ex) number, string, boolean, undefined, null ..
- 실행 직전 메모리에 할당하는 과정
- 고정된 양의 메모리를 할당하기 때문에 원시값들의 크기에 제한이 있음
- stack - static data를 저장하는 데이터 구조
-
동적 메모리 할당 (dynamic allocation)
- heap - javascript의 object, function을 저장하는 다른 공간
- stack과는 다르게 엔진은 객체에 고정된 양의 메모리를 할당하지 않음
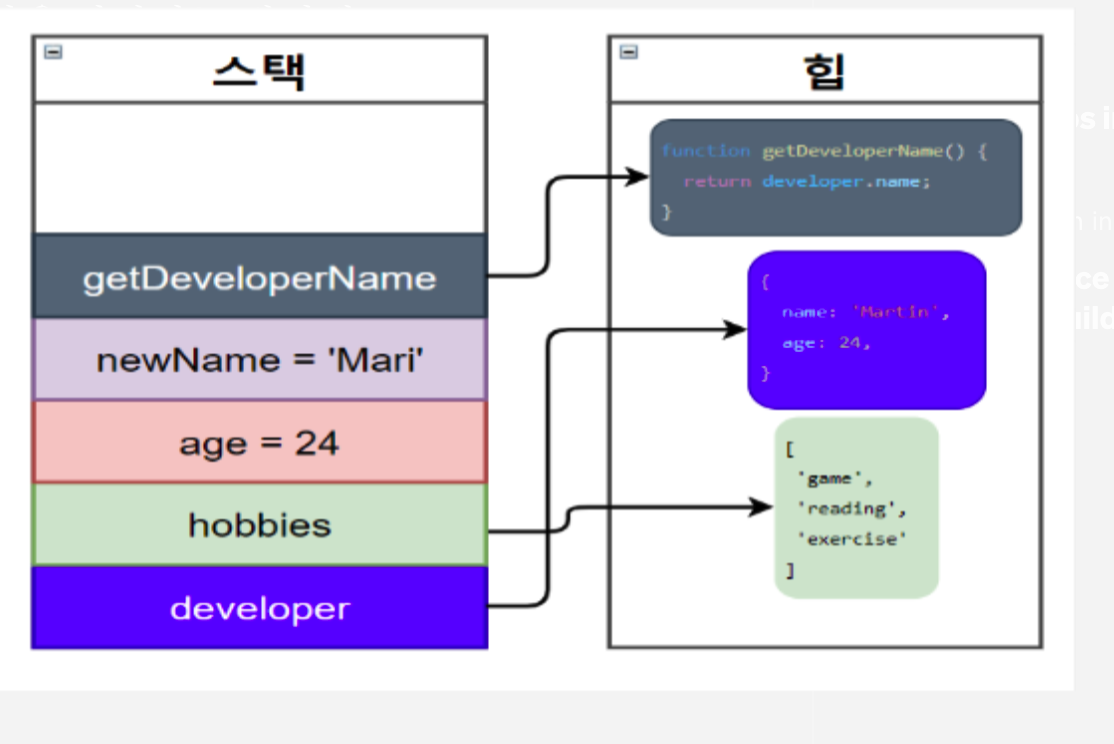
const developer = {
name: 'Martin',
age: 24
}
const hobbies = ['game', 'reading', 'exercise'];
const age = 24;
const newName = 'Mari';
function getDeveloperName() {
return developer.name;
}
위와 같은 코드가 있다고 가정했을 때, 아래와 같이 메모리에 할당이 된다.
- number, string과 같은 원시타입은 스택에 쌓이고
- hobbies, developer, getDeveloper와 같은 object, function은 힙에 저장이 된다.
- 모든 변수들은 스택을 먼저 가리키게 되고 원시값이 아닌 경우 스택에서는 힙의 객체에 대한 참조를 가지고 있다.
- 힙의 메모리는 정렬되어있지 않기 때문에 스택에 참조를 유지해야함
가비지 컬렉션 (Garbage Collection)
javascript에서는 무언가(객체, 문자열 등)가 생겨날 때 메모리가 할당되며 이들이 더이상 사용되지 않을때는 ‘자동으로' 메모리가 반환되는데, 이러한 과정을 가비지컬렉션(garbage collection) 이라 한다.
- 변수/데이터가 더 필요하지 않을때 → 가비지 변수, 또는 가비지 데이터가 됨.
- 가비지 컬렉션 메커니즘은 수동과 자동 두 가지 범주로 나뉨
- C/C++ → 수동 메커니즘 사용 : 메모리 할당/해제를 수동으로 함.
- javascript → 자동 메커니즘 사용
메모리 누수 (Memory Leak)
- 프로그램에서 사용했다가 더이상 필요하지 않지만 아직 OS나 메모리 풀에 반환되지 않은 메모리 조각들
- 부주의 또는 일부 프로그램 오류로 인해 더 사용되지 않는 메모리를 해제하지 못하는 것
- 어떤 변수가 100M의 메모리를 점유한다고 할 때, 이 변수가 사용되지 않더라도 수동 또는 자동으로 해제되지 않아 계속 메모리를 점유하는 것
- ex)
- 의도치 않게 생성된 전역 변수
strict mode에서 javascript는 예상치 못한 전역 변수 생성을 방지할 수 있는 훨씬 엄격한 파싱을 시도함 → 자바스크립트 파일의 상단에 use strict를 사용하면 회피 가능function foo(arg) { bar = 'some text'; // window.bar = 'some text'; 와 동일하다. // 또는 this.bar = 'some text'; } - 클로저의 잘못된 사용
var theThing = null
var replaceThing = function () {
var originalThing = theThing
// 상위 스코프인 originalThing을 참조하는 스코프를 갖게됨
// 동시에 theThing 도 참조하게됨.
var unused = function () {
if (originalThing) console.log('hi')
}
//
theThing = {
longStr: new Array(1000000).join('*'),
someMethod: function () {
console.log(someMessage)
},
}
}
setInterval(replaceThing, 1000)- DOM에서 벗어난 요소 참조
var elements = {
button: document.getElementById('button'),
image: document.getElementById('image')
};
function doStuff() {
elements.image.src = 'http://example.com/image_name.png';
}
function removeImage() {
// image는 body 요소의 바로 아래 자식임
document.body.removeChild(document.getElementById('image'));
// 이 순간까지 #button 전역 요소 객체에 대한 참조가 아직 존재함
// 즉, button 요소는 아직도 메모리 상에 있고 가비지컬렉터가 가져갈 수 없음
}- 해제하지 않은 타이머
var serverData = loadData();
setInterval(function() {
var renderer = document.getElementById('renderer');
if(renderer) {
renderer.innerHTML = JSON.stringify(serverData);
}
}, 5000); // 매 5초 마다 실행- renderer를 5초마다 참조해서 존재하는 경우 dom element를 innerHTML로 변경 시키고 있음.
- 그런데 해당 element가 만약 바뀌었거나 삭제 되었다면, renderer 안에 그려지게 될 serverData가 더이상 참조 될 일이 없어짐.
- 하지만 5초마다 계속 참조 하고 있기 때문에 메모리 누수가 발생할 수 있음.
- 해결 방법
- 아래와 같이 setInterval의 return 값을 받아 clearInterval의 인자로 넘겨서 호출한다.
const timer = setInterval() => {...}, 5000);
clearInterval(timer);