Map-Reduce engine?
- A Map Reduce engine refers to the software or framework that implements the Map Reduce programming model for processing and analyzing large datasets in a distributed and parallelized manner.
- A map reduce engine automatically paralleizes and distributes the execution of the mapper and reducer functions that charcterize an application.
- It is highly fault tolereant.
Programming model (Paradigm)
- Functional programming approach
1. map
- mapper function is fed one key-value pair and generate the list associated to output value.
- The results of the map phase are hased by key, and written to the store(barrier). The hash divides the map output into 1 bucket per reducer (mod num_of_reducer)
- The engine waits for the map phase on a node to finish (bottle neck point).
input: (in_key, in_value)
output: (out_key, intermediate_value) list2. reducer
- Reducer pull the relevant data from the all different mapper nodes.
- Reduce phase cannot start until the map phase has completed on all nodes.
input: (out_key, intermediate_Value list)
output: out_value list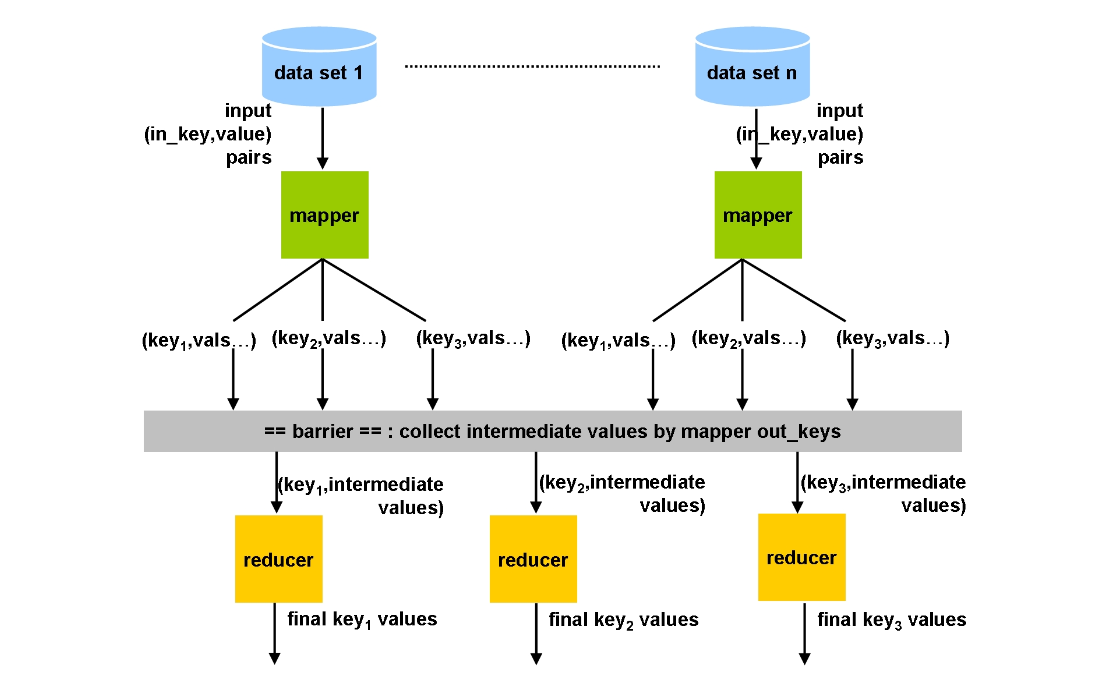
Example: Word Counting
map(String input_key, String input_value)
// input_key: document name
// input_value: document contents
for each word w in input_value:
EmitIntermediate(w, "1");
reduce(String output_key, Iterator Intermediate_values)
// output_key: a word
// output_values: a list of counts
int result = 0;
for each v in intermediate_values:
result += ParseInt(v);
Emit(AsStirng(result));
Map-reduce semantics for Relational Algebraic Operator
1. Selection
-
Selection is capture by the mapper alone, reducer is just the identity function.
-
For
Map: For each t in the input, if C(t) is true, then emit the key-value pair (t, t), i.e., set both key and value to t.
Reduce: For each (t, t) from any of many mappers, emit (t, t). -
The key is hashed to be distributed to reducers.
2. Projection
- Under set semantics, projection must eliminate duplicates.
- For , where is the single input relation to the mapper and isthe se of columns.
Map: For each t in the input, construct t a tuple t' containing only the columns in A and emit the key-value pair (t', t'), i.e., set both key and value to t'.
Reduce: For each t' from any of many mappers, there will be one or more (t', t') pairs (i.e., the reducer takes pairs of the form (t', [t', t', ... , t']), emit exactly one pair (t', t') for each key t' for deduplication.
3. Union
- Union has a merely formatting mapper and a duplicate-eliminating reducer.
- For where and are the input relations, we define:
Map: For each t in the input, emit the key-value pair (t, t), i.e., set both key and value to t.
Reduce: For each key t from any of many mappers, there will be one or two (t, t) pairs (i.e., the reducer takes pairs such as (t, [t]) or (t, [t, t]), emit exactly one pair (t, t) for each key t.
4. Intersection
- Similar to the Union
- For where and are the input relations.
Map: For each t in the input, emit the key-value pair (t, t), i.e., set both key and value to t
Reduce: For each key t from any of many mappers, there will be one or two (t, t) pairs (i.e., the reducer takes pairs such as (t, [t]) or (t [t,t]). If second element is a singleton, emit nothing, otherwise emit exactly one pair (t, t) for each key t.
5. Difference
- The information as to which relation the tuple is from needs to be passed on to the reducer.
- For \ where and are the input relations.
Map: For each t in the input, if t R, emit the key -value pair (t, 'R'), other wise emit the key-value pair (t, 'S'), where the second element may be implemented economically with a single bit to indicate membership in either of the two input relations.
Reduce: For each key t from any of many mappers, if the associated value list is ['R'], then emit exactly one pair (t,t) for each key t, otherwise emit nothing.
6. Natural Join
- For , where and are the input relations with schemas (A, B) and (B, C).
Map: For each t in the input, if t R, emit key-value pair (b, ('R',a)), otherwise emit the key-value pair (b, ('S', c)), where a, b, c are values in the columns A, B, C, rep..
Reduce: For each key b from any of many mappers, the associated value list will be contain pairs of the form ('R', a) or ('S',c ). Then computefor each key b list = [] for each ('R', a) for each ('S', c) list.append((a, b, c)) emit(b, list)
7. Partitioned Aggregation (Group-By)
- Consider the concrete example of a relation to which we apply the operation where is a an aggregation function, the column being aggregated, and the grouping column.
Map: For each tuple (a, b, c) in the input, emit the key-value pair (a, b), i.e., the grouping attribute is the obvious key and, under map-reduce semantics, the desired partition of the input follows from that.
Reduce: For each key a from any of many mappers, there will be one or more (a, b) pairs (i.e., the reducer takes pairs of the form (a, [b1, b2, ..., bn])), emit exactly one pair (a, x) for each key a, where x = ([b1, b2,..., bn]) (e.g., if is Sum, then x = b1+ b2+ ... + bn)
