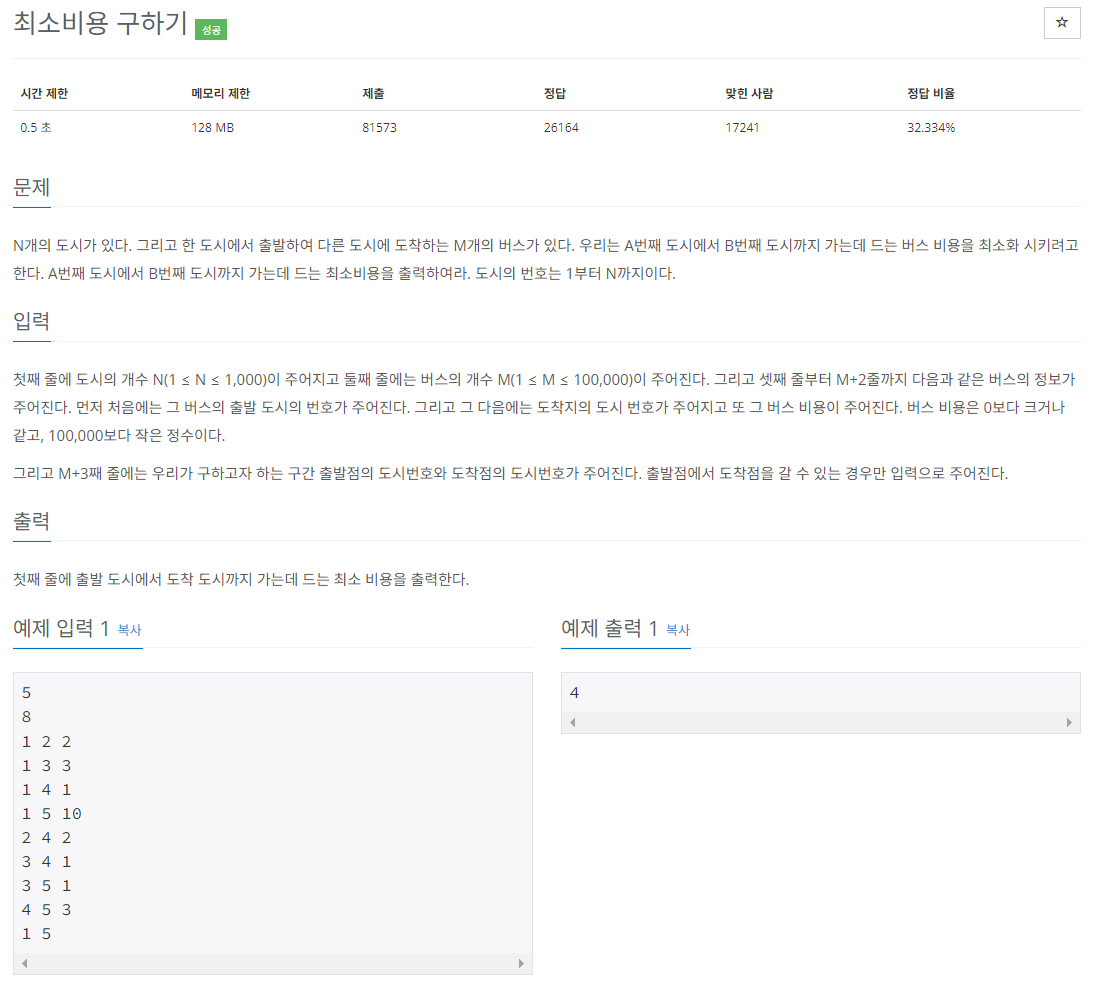
풀이 방법
다익스트라 알고리즘의 기본 방법을 사용하는 문제였다.
다익스트라(Dijstra) 알고리즘은
- 그래프의 최단 경로를 구하는 알고리즘
- 하나의 정점에서 다른 모든 정점까지의 최단 거리를 구해준다.
- 음수 가중치는 처리하지 않는다.
PriorityQueue를 사용하면 시간 복잡도를 까지 낮출 수 있다.
기본 동작으로는
출발지로부터 가장 거리가 짧은 정점을 방문하면서 이전의 기록한 값보다 작으면 갱신해주면 된다.
소스 코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
class Node implements Comparable<Node>{
int idx;
int weight;
public Node(int to, int weight) {
this.idx = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) { //정렬
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
}
public class Main {
static List<List<Node>> graph;
static int[] dist;
static boolean[] visited;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int m = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
//초기화
graph = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
dist = new int[n+1];
visited = new boolean[n+1];
//그래프 구성
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
int from = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int to = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int weight = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
graph.get(from).add(new Node(to,weight));
}
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
int start = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int end = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
Dijkstra(start,end);
System.out.println(dist[end]);
}
private static void Dijkstra(int start, int end) {
PriorityQueue<Node> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
queue.add(new Node(start,0));
Arrays.fill(dist,Integer.MAX_VALUE); //최대 값으로 배열 초기화(최소를 구하기에)
dist[start] = 0; //자기 자신은 거리가 0
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int curIdx = queue.remove().idx;
if(visited[curIdx]) continue;
visited[curIdx] = true;
for(Node next : graph.get(curIdx)){
//현재 노드에서 시작점과의 거리 + 다음 노드까지의 가중치가
//다음 노드에서 시작점과의 거리보다 작으면
if(!visited[next.idx] && dist[next.idx] > dist[curIdx] + next.weight){
dist[next.idx] = dist[curIdx] + next.weight; //다음 노드 최소 거리 업데이트
queue.add(new Node(next.idx, dist[next.idx]));
}
}
}
}
}