📌 algorithm만을 위한 C++
I/O template
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
string temp="";
cin >> temp;
cout << temp;
getline(cin,temp);
cout << temp;
return 0;
}✍ vector
C++ STL에는 크게 두 개의 container가 있다. 배열처럼 원소들을 순서대로 보관하는 'Sequence Container'와 key값을 이용하여 대응하는 방식인 'Associative container'이다.
vector는 둘 중 Sequence Container에 속하며, "자동으로 메모리가 할당되는 배열"이라고 이해하면 될 것이다.
vector를 생성하면 heap 메모리에 동적으로 할당된다.
또한 다른 container와 마찬가지로 template을 이용하기 때문에 데이터 타입은 자유롭게 이용할 수 있다.
기본적으로 맨 뒤에서 원소의 삽입과 삭제가 가능하며, 중간에서도 가능하지만 크게 효율적이지 않다.
- 장점
- 배열과 달리 자동으로 메모리를 할당시켜주어 처음부터 원소의 개수를 지정해둘 필요가 없고, 원소의 삽입/삭제 시 효율적인 메모리 관리가 가능하다.
- vector의 중간의 원소를 삭제하거나, vector의 크기를 구하는 작업 등을 알아서 해주는 유용한 멤버 함수들이 많다.
- 동적으로 원소를 추가할 수 있으며 크기가 자동으로 늘어나고, 쉽게 말해 크기가 가변적으로 변하는 배열이다.
- 단점
- 배열 기반의 container이므로 원소의 삽입, 삭제가 자주 수행되면 시간적인 측면에서 비효율적이다.
출처: https://rebro.kr/37 [Rebro의 코딩 일기장:티스토리]
👏 vector의 선언
#include <vector> // vector가 들어있는 헤더파일
vector<int> v; // int타입 벡터 생성
vector<int> v = { 1, 2, 3}; // int형 백터 생성 후 1, 2, 3 으로 초기화
vector<int> v[10]; // int타입 벡터 배열(크기 : 10) 생성
vector<int> v[] = {{ 1, 2}, {3, 4}}; // int형 백터 배열 생성(행은 가변이지만 열은 고정)
vector<vector<int>> v; // 2차원 백터 생성(행과 열 모두 가변)
vector<int> v(5); // 5개의 원소를 0으로 초기화
vector<int> v(5, 3); // 5개의 원소를 3으로 초기화
vector<int> v2(v); // 벡터 v를 복사하여 벡터v2 생성👏 vector의 insert / erase
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
vector<int> arr;
vector< vector<int> > map;
map.resize(r);
for(int i=0;i<r;i++){
map[i].resize(c);
for(int j=0;j<c;j++){
cin>>map[i][j];
}
}
return 0;
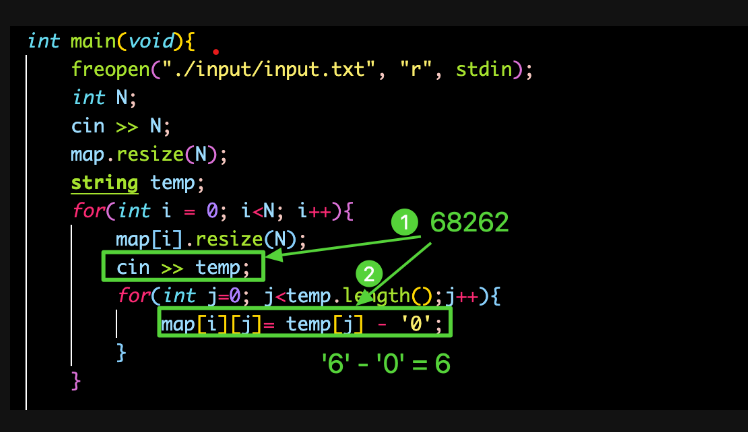
}1. 문자 -> int
2. insert
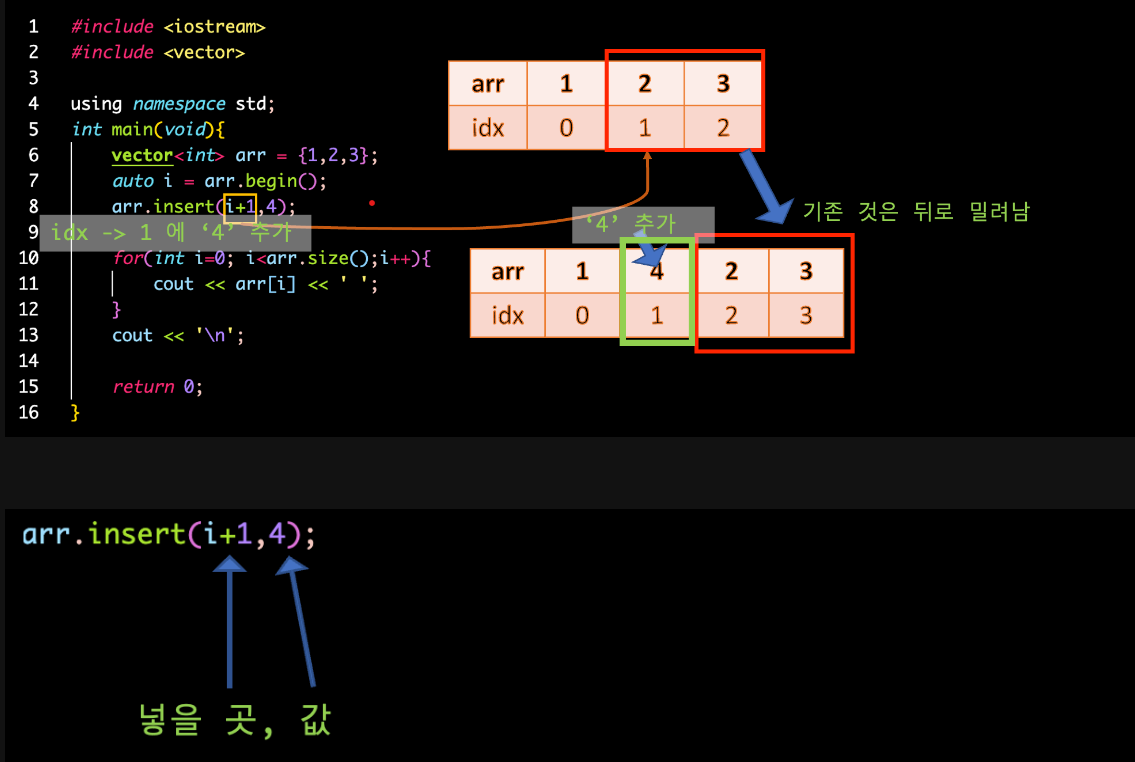
vector<int> arr;
auto i = arr.begin();
arr.insert(i+1,4)v.push_back(10); // 마지막 위치에 숫자 10 추가
vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
it = v.insert(it, 2); //맨앞에 2를 삽입
it = v.insert(it, 2, 3); // 맨앞에 3을 2개 삽입
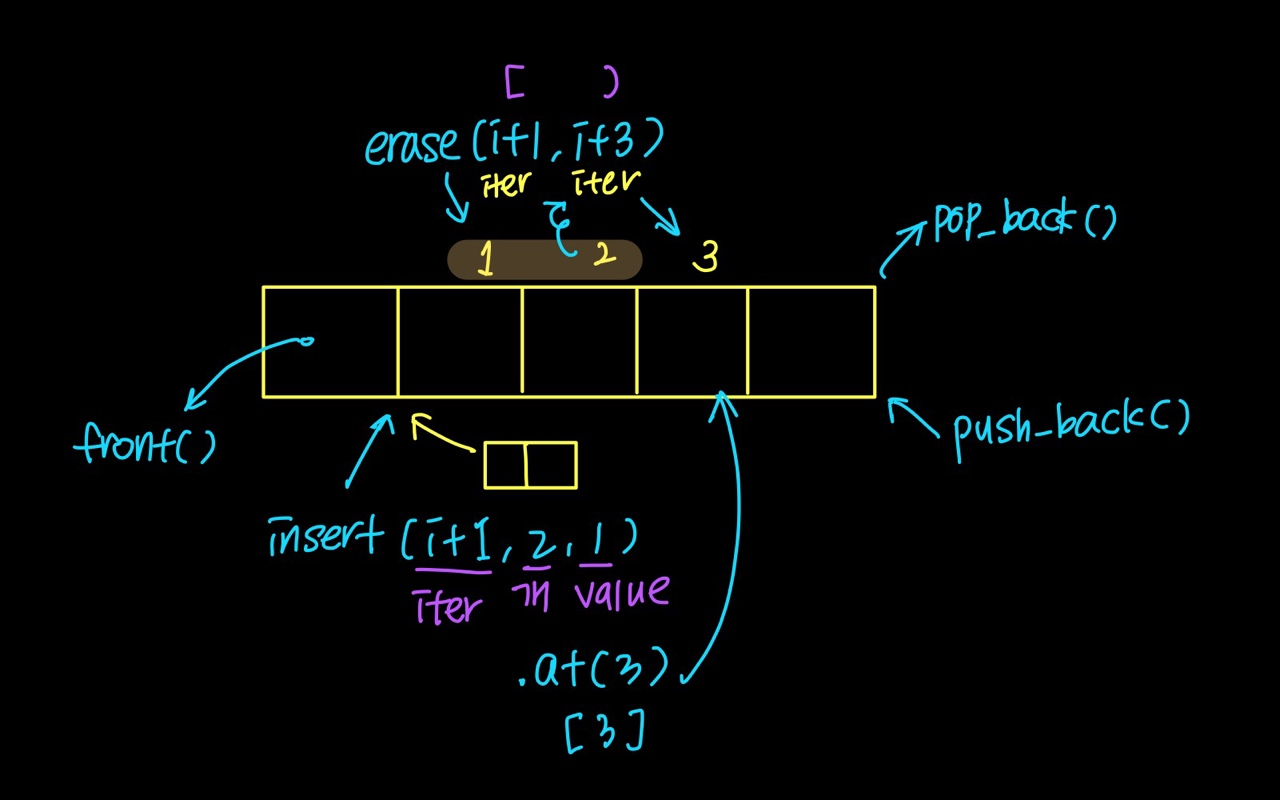
it = v.insert(it+2, 2, 4); // 2번째부터 4를 2개 삽입3. erase

v.pop_back(); // 마지막에 넣은 값 제거
v.erase(vec.begin()+10); // index 10의 값을 제거
v.erase(vec.begin(), vec.begin()+5); // index 0~5의 값을 제거
v.clear(); //모든 값 제거4. push_back(): append
vector<int> a;
a.push_back(1);
a.push_back(2);5. pop_back(): pop
👏 vector의 입출력
- 이중 for문으로 값을 넣어준다.
- .resize()로 배열의 크기를 할당해준다.
📢 행과 열 크기가 같을때 (2차 배열 모양이 정사각형)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector< vector<int> >map; //선언만 해준 상황(비어있는 상태)
int N;
int main(void) {
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
cin >> N;
map.resize(N); //N이라는 사이즈를 할당해줌
for (int i = 0; i < map.size(); i++) {
map[i].resize(N); //열에만 있는 상황
for (int j = 0; j < map[i].size(); j++) {
cin >> map[i][j]; //행과 같이 map에 입력
cout << map[i][j] << ' '; //입력과 동시에 출력 ' '
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}📢 행과 열 크기가 다를때 (2차 배열 모양이 직사각형)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector< vector<int> >map; //선언만 해준 상황(비어있는 상태)
int R,C;
int main(void) {
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
cin >> R; //행
cin >> C; //열
string temp="";
map.resize(R); //행 값으로 크기 할당
for (int i = 0; i < map.size(); i++) {
map[i].resize(C); //열 값으롷 크기 할당
cin >> temp;
for (int j = 0; j < temp.length(); j++) {
map[i][j]=temp[j]-'0';
}
}
...출처 : https://velog.io/@markyang92/cpp https://coding-factory.tistory.com/596
