1. What is a graph?
-
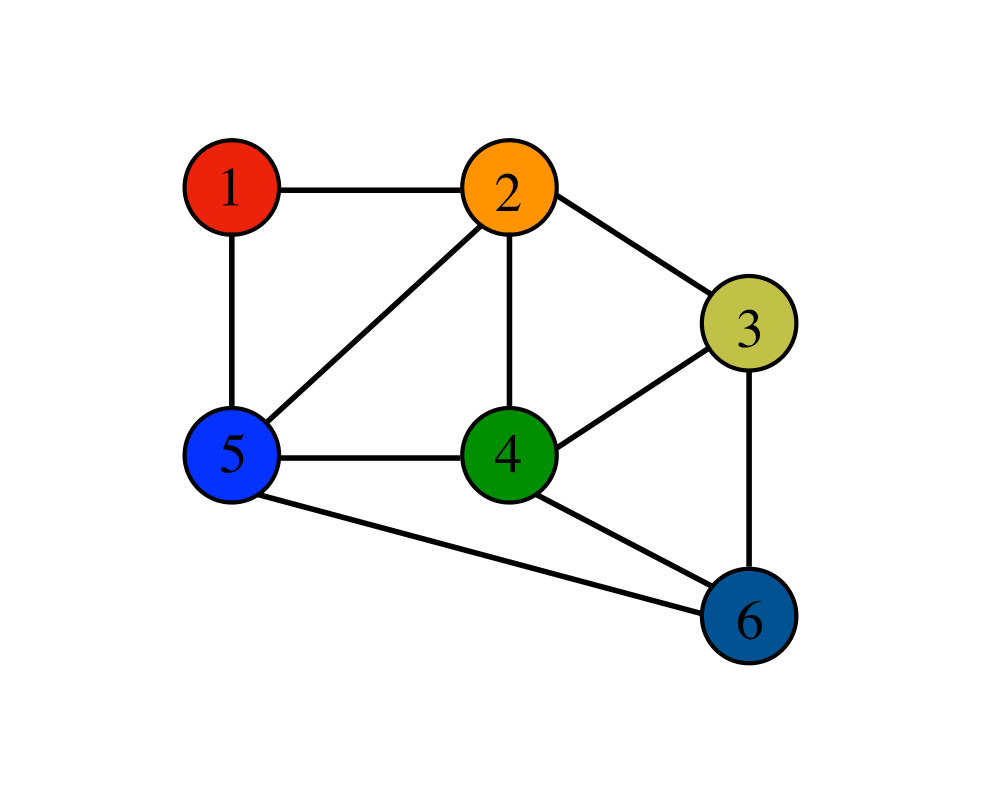
A data structure made up of nodes or vertices and edges or the connections between nodes
-
Typically, a visualization of a graph will be of nodes represented by circles and edges as lines between the circles
Trees vs Graph
-
Trees art just a special kind of graph with one root and only on unique path between any two nodes
-
A graph can go beyond that and have any number of root elements and multiple paths between nodes
2. How can we represent a graph in code?
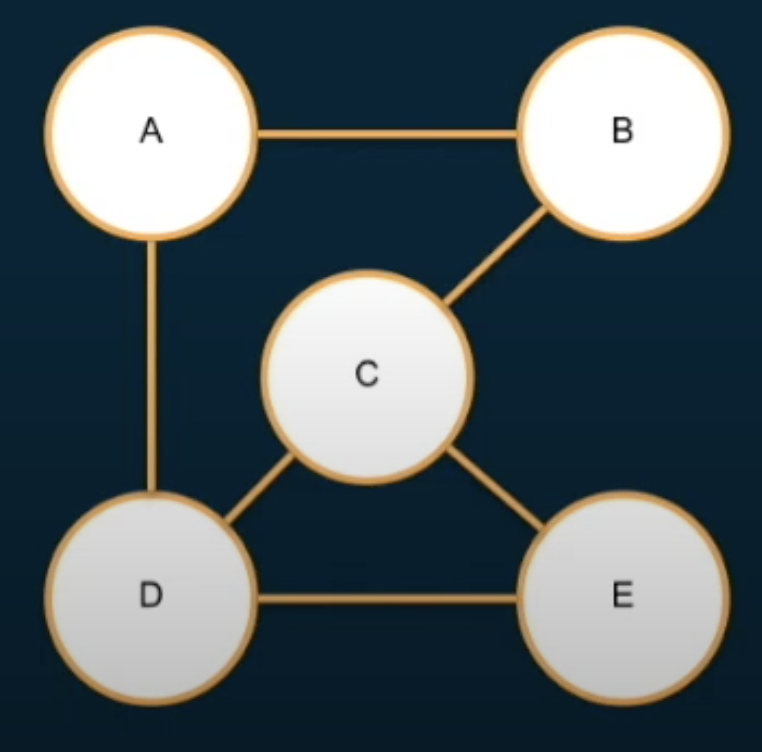
1) Vertex list + Egde list
const vertices = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'];
const edges = [
['A', 'B'],
['A', 'D'],
['B', 'C'],
['C', 'D'],
['C', 'E'],
['D', 'E']
]
// findeAdjacentNodes
const findAdjacentNodes = (node) => {
// Loop through edges array
// Is my node in the connection?
// If yes, push the other node in pair, into adjacentNodes array
// If no, keep looping
const adjacentNodes = [];
for (let edge of edges) {
const nodeIdx = edge.indexOf(node);
if (nodeIdx > -1) {
let adjacentNode = nodeIdx === 0 ? edge[1] : edge[0]
adjacentNodes.push(adjacentNode);
}
}
return adjacentNodes;
};
const isConnected = (node1, node2) => {
return edges.some((edge) => {
return edge.indexOf(node1) > -1 && edge.indexOf(node2) > -1
})
};2) Ajacency Matrix
- A 2-D array filled out with 1's and O's where each array represents a node and each index in the subarray, represents a potentail connection to another node
- The value at adjacencyMatrix[node1][node2] indicates where there is a connection between node1 and node2
const vertices = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'];
const vertexIdxs = {
'A': 0,
'B': 1,
'C': 2,
'D': 3,
'E': 4,
};
const adjacenyMatrix = [
[0,1,0,1,0],
[1,0,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,1,1],
[1,0,1,0,1],
[0,0,1,1,0],
];
// findAdjacencies
const findAdjacencies = (node) => {
const adjacentNodes = [];
// get the row in the matrix
// loop through the row
// if there is 1, push that node
// otherwise skip
for (let i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) {
let nodeVertext = vertexIdxs[node];
if(adjacenyMatrix[nodeVertext][i] === 1) {
adjacentNodes.push(vertices[i]);
}
}
return adjacentNodes;
}
// isConnected
const isConnected = (node1, node2) => {
const nodeIdx1 = vertexIdxs[node1];
const nodeIdx2 = vertexIdxs[node2];
return !!adjacenyMatrix[nodeIdx1][nodeIdx2];
};
3) Ajacency List
- For every node, store a list of what nodes it's connecte to
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.edgeList = [];
}
connect(node) {
this.edgeList.push(node);
node.edgeList.push(this);
}
getAdjacentNodes() {
return this.edgeList.map(edge => edge.value);
}
isConnect(node) {
return this.edgeList.map(edge => edge.value).indexOf(node.value) > -1;
}
}
class Graph {
constructor(nodes) {
this.nodes = [...nodes];
}
addToGraph(node) {
this.nodes.push(node);
}
}
const nodeA = new Node('A');
const nodeB = new Node('B');
const nodeC = new Node('C');
const nodeD = new Node('D');
const nodeE = new Node('E');
const graph = new Graph([nodeA, nodeB, nodeC, nodeD, nodeE]);
nodeA.connect(nodeB);
nodeA.connect(nodeD);
nodeB.connect(nodeC);
nodeC.connect(nodeD);
nodeC.connect(nodeE);
nodeD.connect(nodeE);
// for (let node of graph.nodes) {
// console.log(`Node ${node.value}`);
// for (let connectedNode of node.edgeList) {
// console.log(`Node ${node.value} is connected to ${connectedNode.value}`);
// }
// }
console.log(nodeA.getAdjacentNodes());
console.log(nodeA.isConnect(nodeB));참고: Graph Data Structure with 3 Javascript Implementations - codebyte
