Tabulation 전략
- 문제를 테이블로 시각화
- input값을 토대로 테이블 크기 지정
- 연산을 위한 table 초기값 설정
- 해당 문제의 seed value 찾기 ex) 피보나치 1 => 1
- iterate through the table
- 현재 위치를 토대로 이웃 포지션에 값 전달
1. 피보나치 Tabulation
(1) n만큼 arr 생성
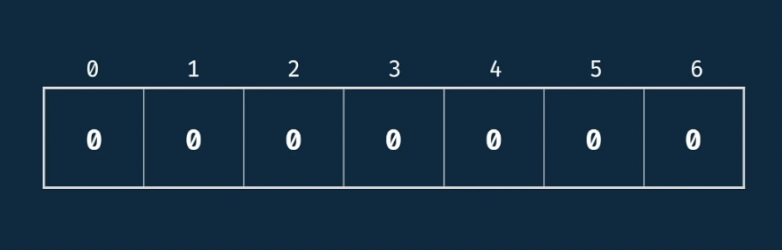
(2) empty arr에 계산의 편의성을 위해 초기값 0 설정
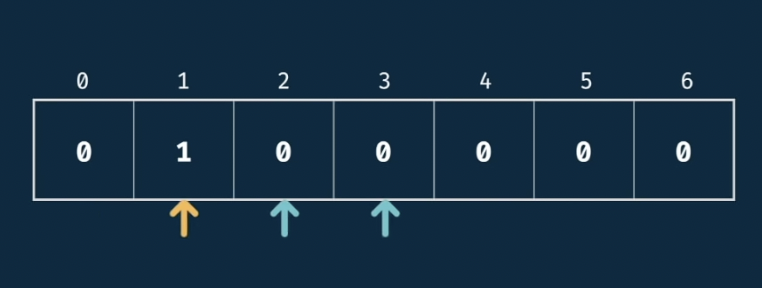
(3) iterator를 이용하여 value 증가

(4) 코드 구현
const fib = (n) => {
const table = Array(n + 1).fill(0);
table[1] = 1;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
table[i + 1] += table[i];
table[i + 2] += table[i];
}
return table[n];
};2. 2D Tabulation
(1) 초기 테이블 visualize
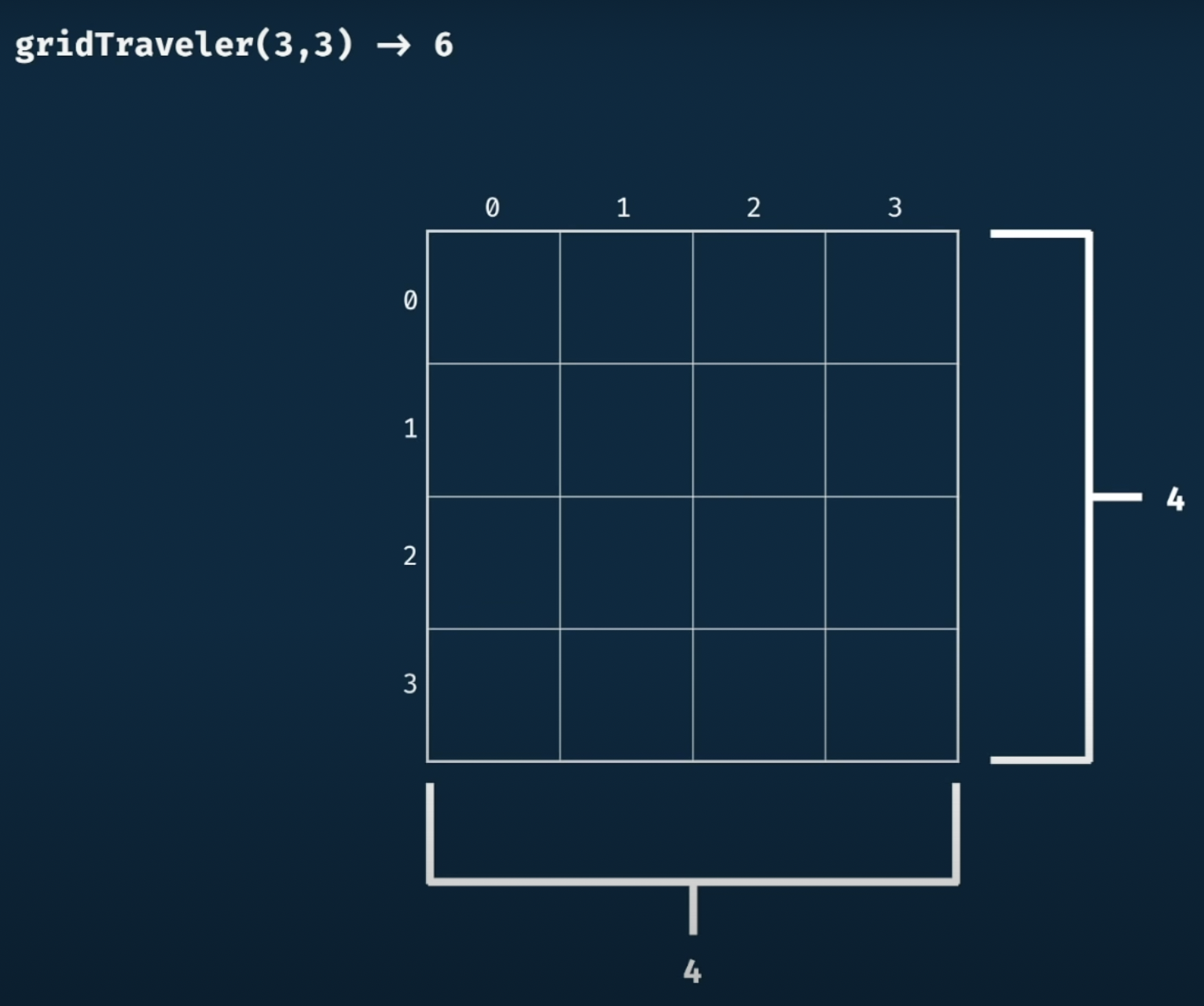
(2) 초기값 설정 ~ 1,1을 가는 경우의 수는 1개 뿐이다.
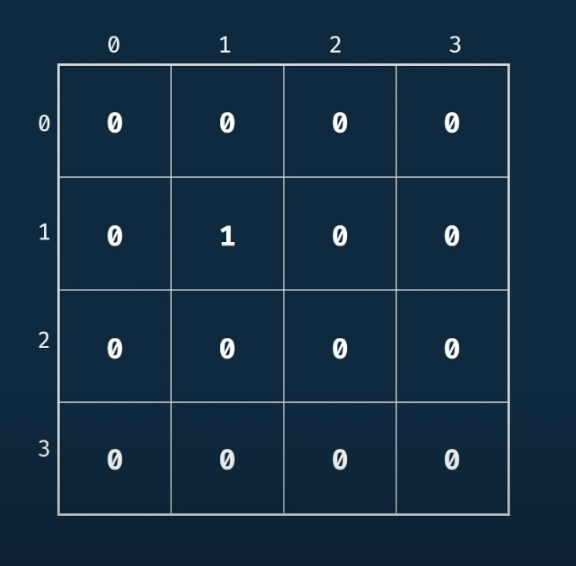
(3) 현재위치를 기준으로 오른쪽/아래쪽(이동방향)에 현재값 증가
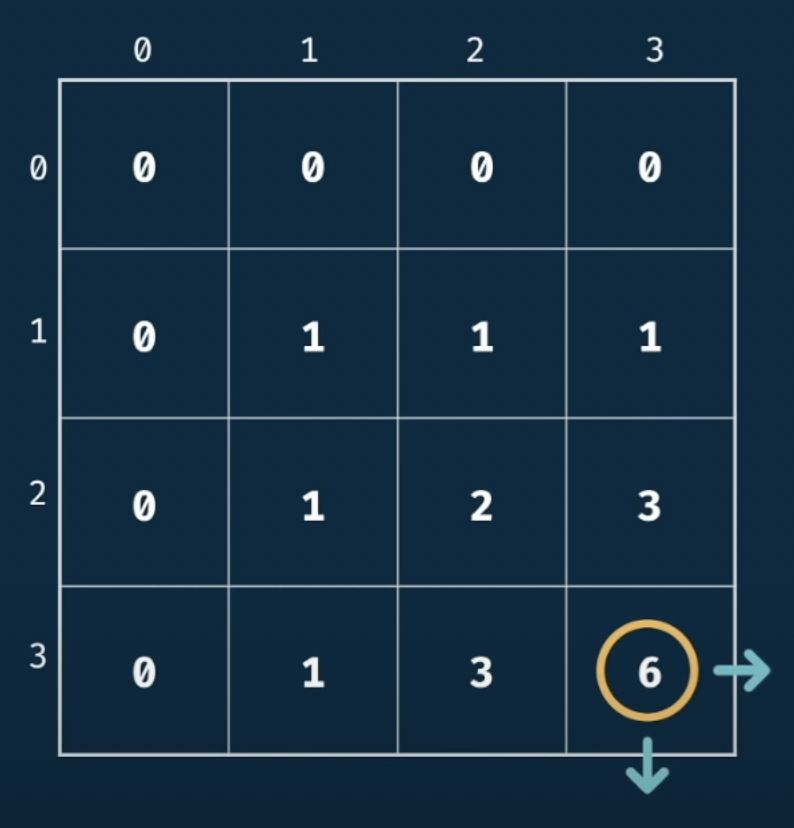
(4) 코드 구현
const gridTraveler = (m, n) => {
const table = Array(m + 1)
.fill()
.map(() => Array(n + 1).fill(0));
table[1][1] = 1;
for (let i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j <= n; j++) {
const current = table[i][j];
if (i + 1 <= n) table[i + 1][j] += current;
if (j + 1 <= m) table[i][j + 1] += current;
}
}
return table[m][n];
};3. CanSum
(1) targetsum의 length + 1만큼 테이블 생성
(2) 초기값 false
(3) targetsum이 0일 경우 true 반환

(4) 코드 구현
const canSum = (targetSum, numbers) => {
let table = Array(targetSum + 1).fill(false);
table[0] = true;
for(let i = 0; i < targetSum; i++) {
if(table[i] === true) {
for (let num of numbers) {
table[i + num] = true;
}
}
}
return table[targetSum];
}3. CanSum
(1) targetsum의 length + 1만큼 테이블 생성
(2) 초기값 false
(3) targetsum이 0일 경우 true 반환

(4) 코드 구현
const canSum = (targetSum, numbers) => {
let table = Array(targetSum + 1).fill(false);
table[0] = true;
for(let i = 0; i < targetSum; i++) {
if(table[i] === true) {
for (let num of numbers) {
table[i + num] = true;
}
}
}
return table[targetSum];
}4. HowSum
(1) 초기 값 null
(2) 0 번째 index의 경우 빈배열
(3) 해당 numbers의 각 값을 table에 적용 후 roop

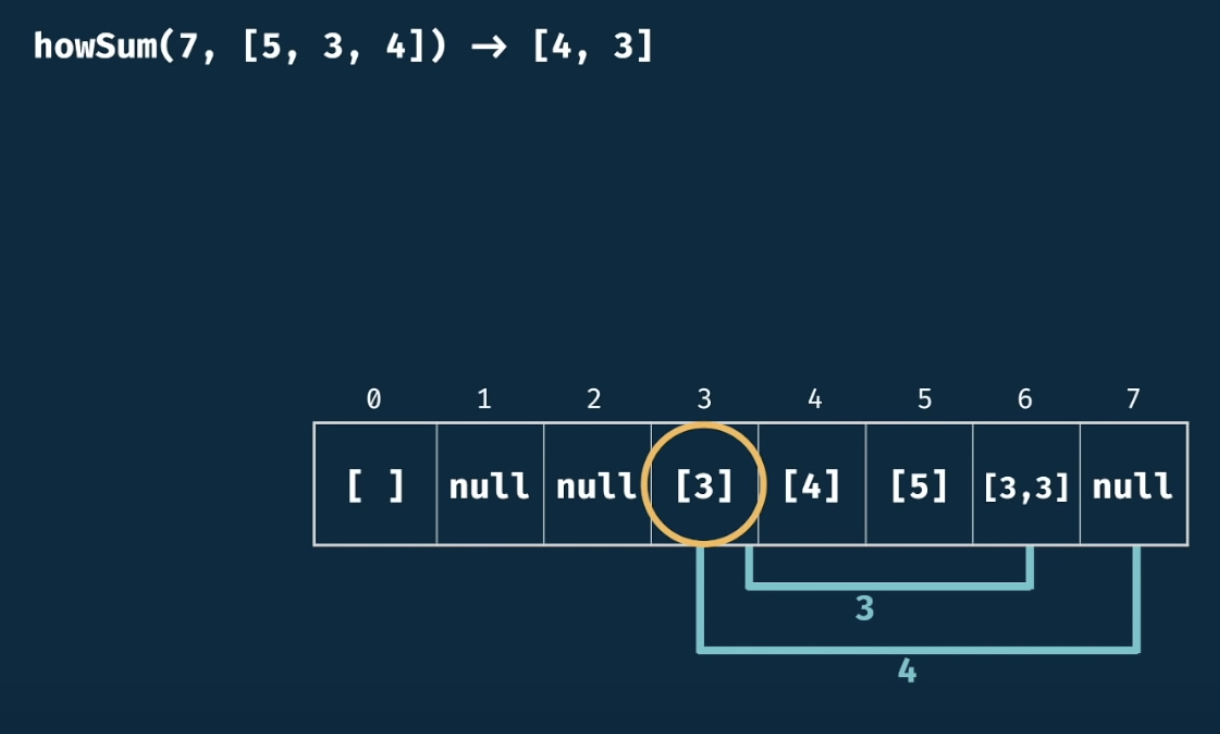
(4) 코드 구현
const howSum = (targetSum, numbers) => {
const table = Array(targetSum + 1).fill(null);
table[0] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < targetSum; i++) {
if (table[i] !== null) {
for (let num of numbers) {
table[i + num] = [...table[i], num];
}
}
}
return table[targetSum];
}
console.log(howSum(7,[2,3]));4. BestSum
(1) 초기값 null 및 0 번째 index [] 설정
(2) roop 돌면서 length 비교
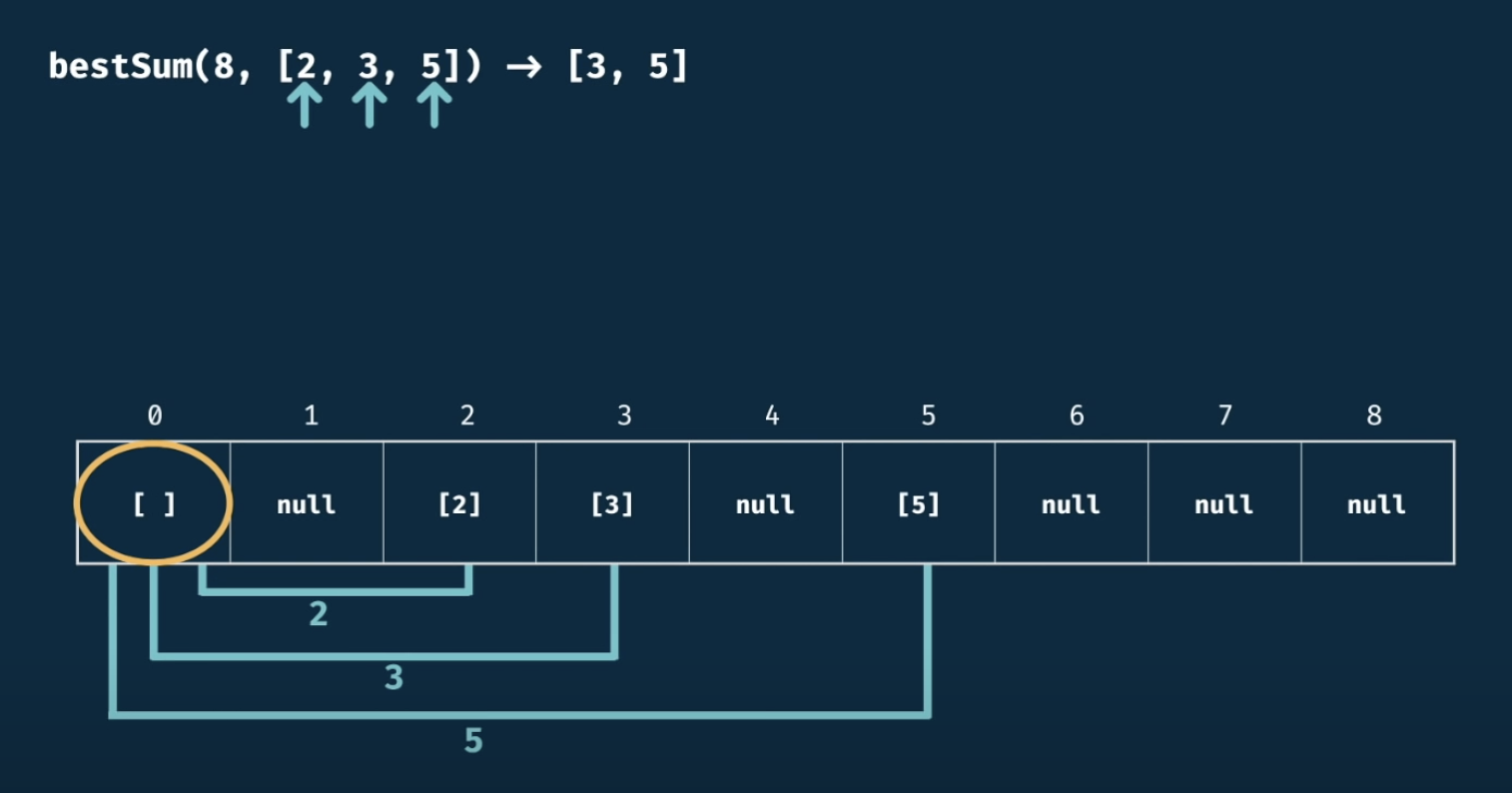
(3) 코드 구현
const bestSum = (targetSum, numbers) => {
const table = Array(targetSum + 1).fill(null);
table[0] = [];
for (let i = 0; i <= targetSum; i++) {
if (table[i] !== null) {
for (let num of numbers) {
const combination = [...table[i], num];
// length 비교 및 초기값 설정을 위해 조건문 설정
if (!table[i + num] || table[i + num].length > combination.length) {
table[i + num] = combination;
}
}
}
}
return table[targetSum];
}
console.log(bestSum(7,[2,3,7]));4. CanConstruct
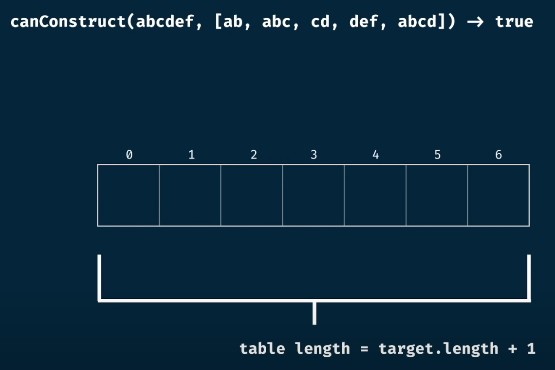
코드 구현
const canConstruct = (target, wordBank) => {
const table = Array(target.length + 1).fill(false);
table[0] = true;
for (let i = 0; i <= target.length; i++) {
if (table[i] === true) {
for (let word of wordBank) {
// word문자가 일치하는 경우 해당 테이블 true
if (target.slice(i, i + word.length) === word) {
table[i + word.length] = true;
}
}
}
console.log(table);
}
return table[target.length];
};
console.log(canConstruct("abcdef", ["ab", "abc", "cd", "def", "abcd"]));4. CountConstruct

코드 구현
const countConstruct = (target, wordBank) => {
const table = Array(target.length + 1).fill(0);
table[0] = 1;
for (let i = 0; i < target.length; i++) {
for (let word of wordBank) {
if (target.slice(i, i + word.length) === word) {
table[i + word.length] += table[i];
}
}
}
return table[target.length];
};
console.log(countConstruct("purple", ["purp", "p", "ur", "le", "purpl"]));
4. AllConstruct
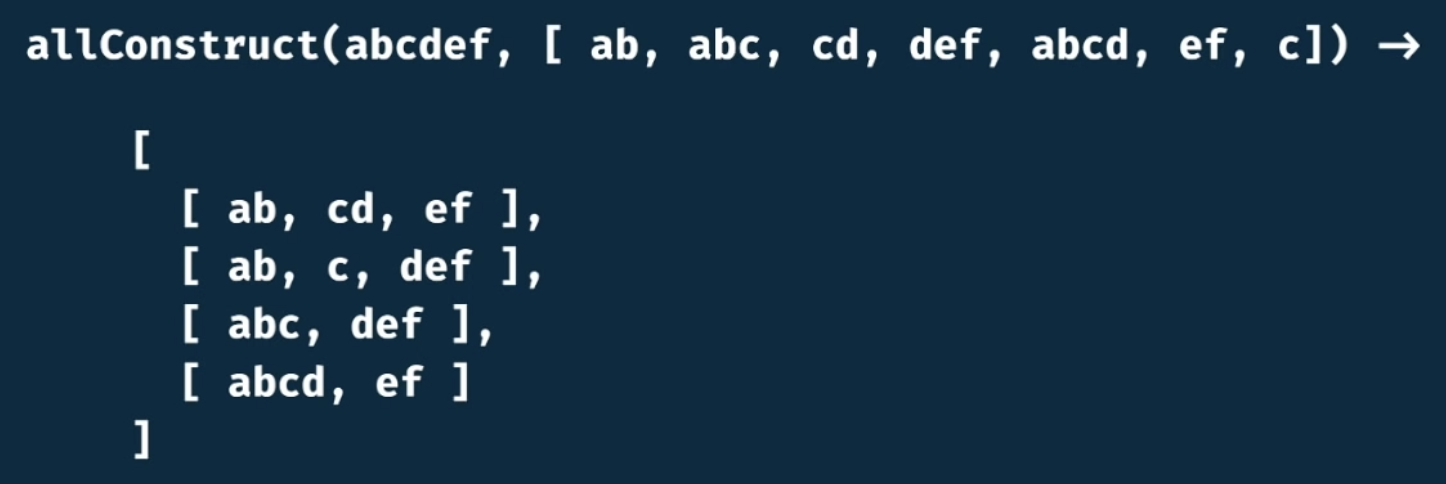

코드 구현
const allConstruct = (target, wordBank) => {
const table = Array(target.length + 1)
.fill()
.map(() => []);
table[0] = [[]];
for (let i=0; i <= target.length; i++) {
for (let word of wordBank) {
if (target.slice(i, i + word.length) === word) {
const newCombinations = table[i].map(subArray => [...subArray, word]);
table[i + word.length].push(...newCombinations);
}
}
}
return table[target.length];
}
console.log(allConstruct("abcdef", ["ab", "abc", "cd", "def", "abcd", "ef", "c"]));참고 : freecodecamp - dynamic programming

