Coroutine
코루틴 : 루틴의 일종으로서, 협동 루틴이라 할 수 있다.
루틴과 서브 루틴은 서로 비대칭적인 관계이지만, 코루틴들은 완전히 대칭적인, 즉 서로가 서로를 호출하는 관계이다.
-> 어떠한 코루틴이 발동될 때마다 해당 코루틴은 이전에 자신의 실행이 마지막으로 중단되었던 지점 다음의 장소에서 실행을 재개한다.
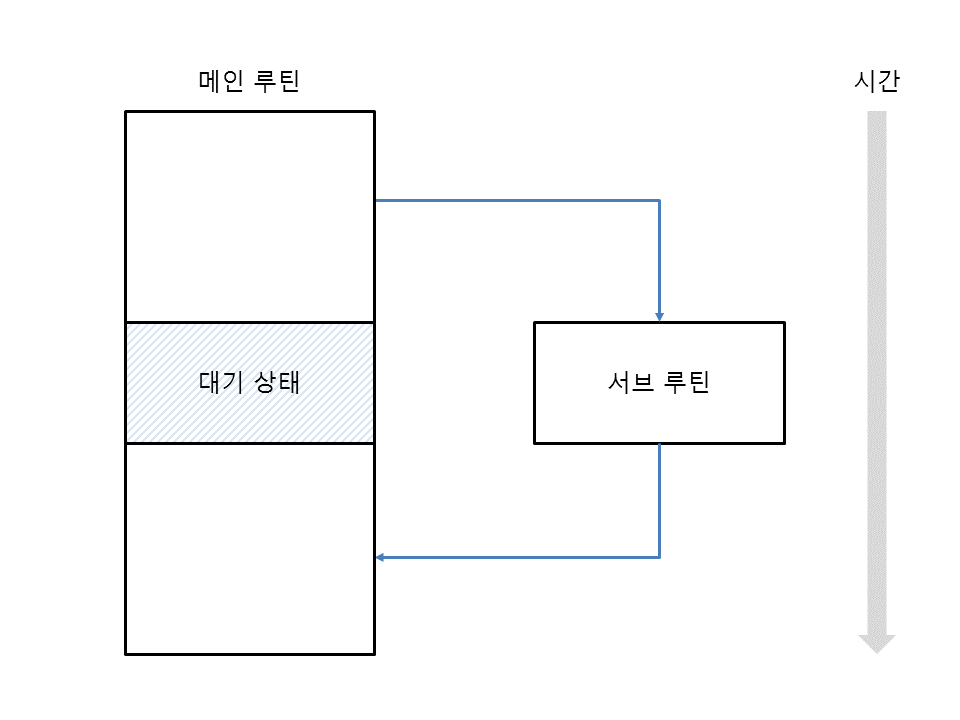
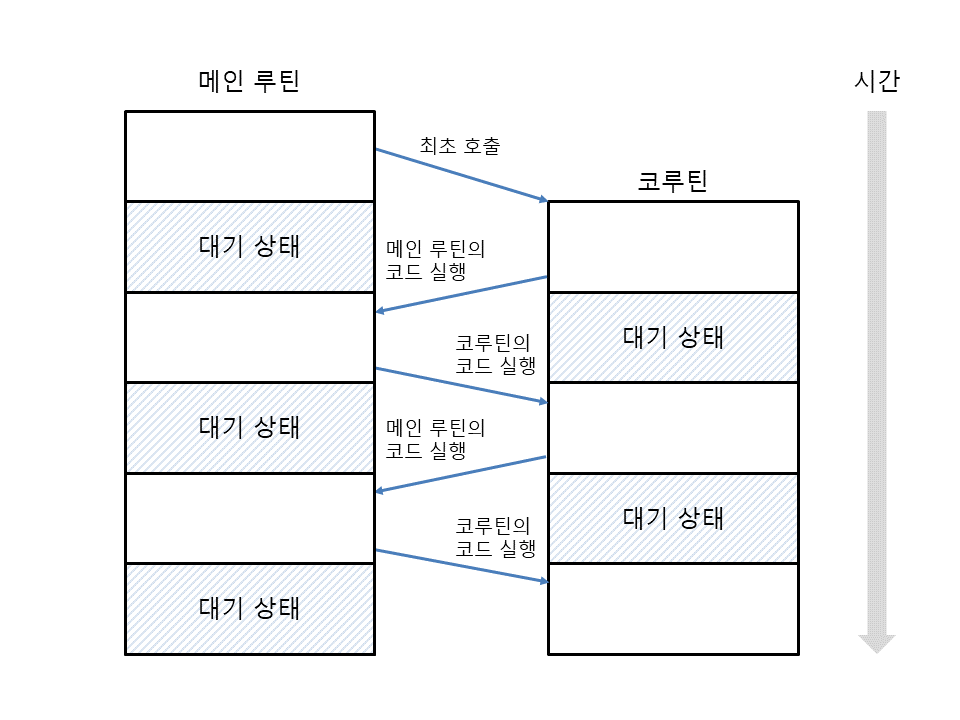
- 일반 함수를 호출하면 코드를 한 번만 실행할 수 있지만, 코루틴은 코드를 여러 번 실행할 수 있습니다.
- 함수의 코드를 실행하는 지점을
진입점(entry point)이라고 하는데, 코루틴은 진입점이 여러 개인 함수입니다.
- 코루틴 바깥에서 값을 받아오면서 값을 다시 바깥으로 전달하는 방법
- 변수 = (yield 변수)
- 변수 = next(코루틴객체) -> 코드는 실행하지만 값은 보내지 않는다.
- 변수 = 코루틴객체.send() -> 코드를 실행하고 값을 보낸다.
generator : next 함수를 반복 호출하여 값을 얻어낸다.
coroutine : next 함수를 한번만 호출한 뒤 send로 값을 주고 받는 방식이다.
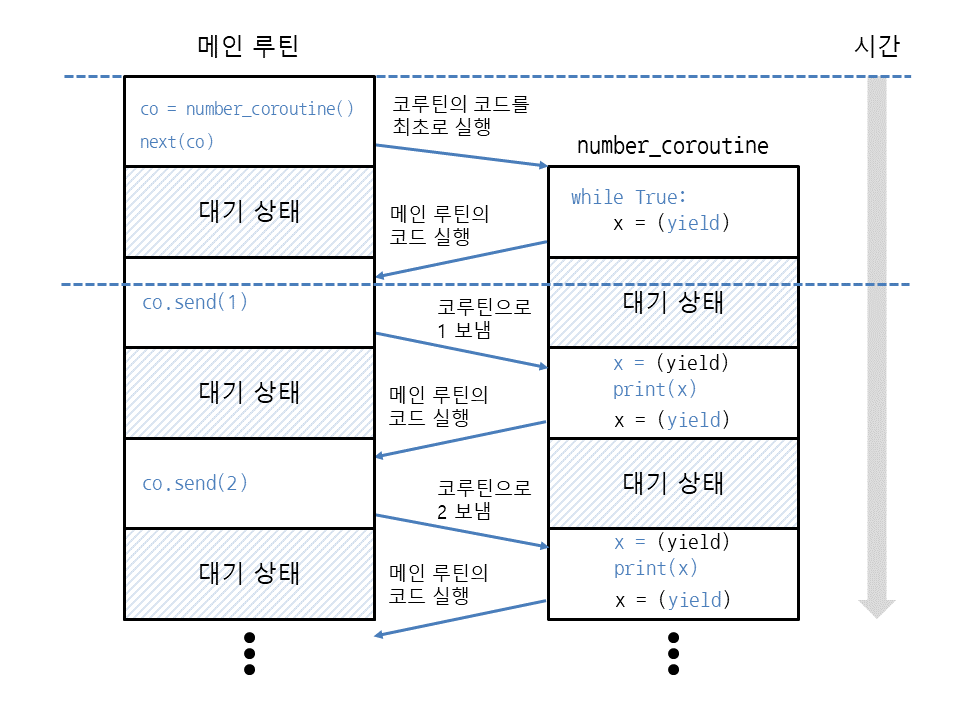
def number_coroutine():
while True:
x = (yield)
print(x)
co = number_coroutine()
next(co)
co.send(1)
co.send(2)
co.send(3)
def number_coroutine():
while True:
x = (yield)
print(x, end=' ')
co = number_coroutine()
next(co)
for i in range(20):
co.send(i)
co.close()
- 코루틴 객체에서 close메소드를 호출하면 코루틴이 종료될 때
GeneratorExit 예외가 발생한다. -> 이 예외를 처리하면 코루틴의 종료 시점을 알 수 있다.
def number_coroutine():
try:
while True:
x = (yield)
print(x, end=' ')
except GeneratorExit:
print()
print('코루틴 종료')
co = number_coroutine()
next(co)
for i in range(20):
co.send(i)
co.close()
- 코루틴 안에 예외를 발생시키는
throw메소드를 사용하여 코루틴을 종료시킬 수 있다.
def sum_coroutine():
try:
total = 0
while True:
x = (yield)
total += x
except RuntimeError as e:
print(e)
yield total
co = sum_coroutine()
next(co)
for i in range(20):
co.send(i)
print(co.throw(RuntimeError, '예외로 코루틴 끝내기'))
- 첫번째 예제 코드는 greeting에 문자열이 send 보낼때 마다 계속 더해지는 문제가 있습니다. 다음과 같이 send 호출시마다 good morning, good afternoon, good evening 이 출력되도록 코드를 수정해보세요
import time
def coroutine_test():
greeting = "good"
while True:
text = (yield greeting)
print("text= ", end= ""), print(text)
greeting += text
if __name__ == "__main__":
cr = coroutine_test()
print("cr=", end=""), print(cr)
next(cr)
time.sleep(2)
print("send 1")
print(cr.send("morning"))
time.sleep(2)
print("send 2")
print(cr.send("afternoon"))
time.sleep(2)
print("send 3")
print(cr.send("evening"))
time.sleep(2)
def coroutine_test():
greeting = "good"
while True:
text = (yield greeting)
print(greeting + text)
if __name__ == "__main__":
cr = coroutine_test()
print("cr=", end=""), print(cr)
next(cr)
time.sleep(2)
print("send 1")
cr.send("morning")
time.sleep(2)
print("send 2")
cr.send("afternoon")
time.sleep(2)
print("send 3")
cr.send("evening")
time.sleep(2)
def coroutine_test():
greeting = "good"
while True:
text = (yield greeting)
print("text = ", end=""), print(text)
greeting = "good"
greeting += text
if __name__ == "__main__":
cr = coroutine_test()
print("cr=", end=""), print(cr)
next(cr)
time.sleep(2)
print("send 1")
print(cr.send("morning"))
time.sleep(2)
print("send 2")
print(cr.send("afternoon"))
time.sleep(2)
print("send 3")
print(cr.send("evening"))
time.sleep(2)
- 두번째 코드를 coroutine 과 asyncio 를 활용하여 구현해 보세요. asyncio에는 비동기 처리를 위한 event loop가 존재하고 여기에 코루틴을 등록해서 사용하는 구조로 되어있습니다
def coroutine_1():
return_value = 0
while True:
input_value = (yield return_value)
return_value = input_value + 1
def coroutine_2():
return_value = 0
while True:
input_value = (yield return_value)
return_value = input_value + 1
if __name__ == "__main__":
ret_value = 0
c1 = coroutine_1()
c2 = coroutine_2()
next(c1)
next(c2)
while ret_value < 100000000:
ret_value = c1.send(ret_value)
ret_value = c2.send(ret_value)
print("ret_value =", end=""), print(ret_value)
print("end of main")
asyncio(Asynchronous I/O)
- 비동기 프로그래밍을 위한 모듈이며 CPU 작업과 I/O를 병렬로 처리하게 해줍니다.
- 고수준으로 구조화된 네트워크 구조에 적합하다.
- 코루틴들을 동시에 실행하고 실행을 제어한다.
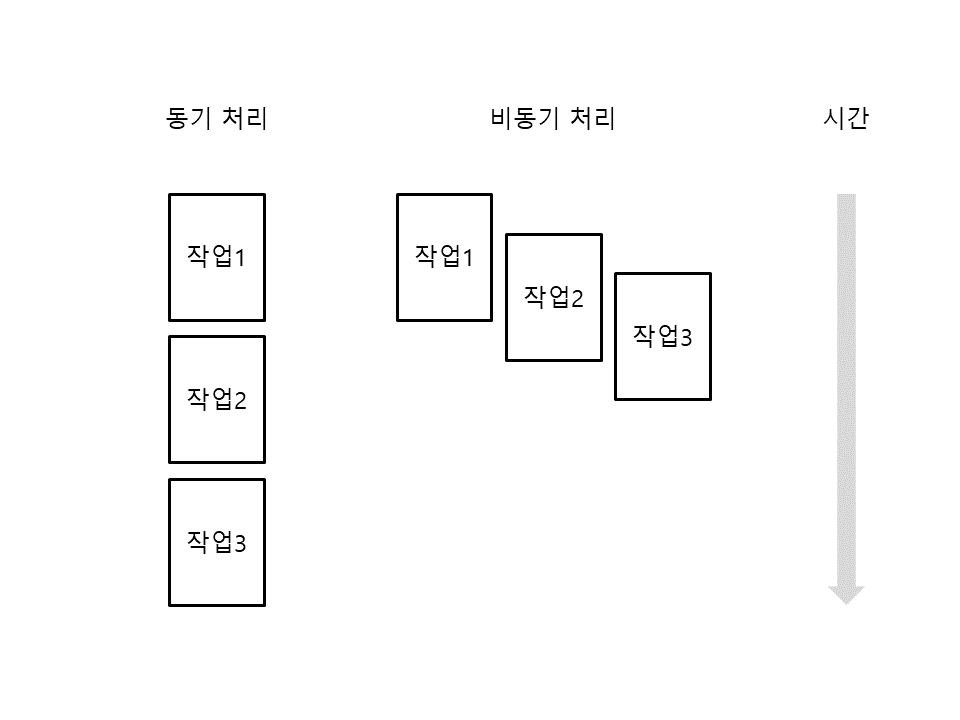
- 동기 처리 : 특정 작업이 끝나면 다음 작업을 처리하는 순차처리 방식
- 비동기 처리 : 여러 작업을 처리하도록 예약한 뒤 작업이 끝나면 결과를 받는 방식
import asyncio
async def coroutine_1(num):
result_value = 0
while result_value < num:
result_value += 1
return result_value
async def coroutine_2(num):
result_value = 0
while result_value < num:
result_value += 1
return result_value
async def main():
one = await coroutine_1(50000000)
two = await coroutine_2(50000000)
print("ret_value=", end="")
print(one+two)
print("end of main")
if __name__ == "__main__":
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(main())
loop.close()




