✅ 프로토타입과 객체지향
객체 지향(Object-Oriented Programming): 프로그램을 객체의 집합으로 표현하려는 프로그래밍 패러다임
객체 간 상속inheritance으로 객체 지향 구현, 코드를 재사용한다는 게 핵심
js는 프로토타입을 기반으로 상속을 구현하는 프로토타입 기반 객체지향 언어
js는 클래스가 없어도 객체를 생성 가능, 객체 간 상속관계 설정 가능
c++,java는 클래스 기반 객체지향언어로 클래스로 객체 생성, 클래스를 통해 상속을 해 명확한 상속 구조 존재함
모든 객체는 생성될 때 자신을 생성한 생성자 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티에 연결된 프로토타입 객체를 상속함
객체의 [[prototype]] 내부 슬롯이 프로토타입 객체를 가리킴, 이는 프로토타입 체인의 일부로 동작함
+리터럴 표기법에 의해 생성된 객체도 가상적인 생성자 함수를 가짐
ex) Object, Array, Function, Regexp
아래 메서드로 간접적으로 확인,교체 가능
- Object.getPrototypeOf(객체) 프로토타입 객체를 얻고 싶을때
- Object.setPrototypeOf(프로토타입 교체 당할 객체, 교체할 프로토타입 객체) 프로토타입 객체를 교체하고 싶을 때 (ES6)
⚠ 프로토타입 프로퍼티와 프로토타입
일반 객체는 prototype 프로퍼티를 갖지 않음. 하지만 [[Prototype]]은 가지고 있고, 프로토타입 객체와 연결됨
생성자 함수는 prototype 프로퍼티를 가짐. prototype 프로퍼티는 생성자함수로 생성되는 인스턴스가 상속받는 프로토타입 객체를 참조함
✅ constructor 프로퍼티와 prototype
모든 프로토타입 객체는 자신을 생성한 생성자 함수를 가리키는 constructor 프로퍼티를 가짐
사용자 정의 생성자 함수, 빌트인 생성자 함수 모두, 프로토타입 객체는 생성자 함수 정의 시점에 자동으로 생성돼, 생성자 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티에 바인딩됨. 이후 생성자 함수 or 리터럴 표기법으로 생성된 객체는 자신의 [[Prototype]] 내부 슬롯이 이 프로토타입 객체를 가리키도록 함, 그리고 프로토타입 객체의 constructor 프로퍼티는 해당 생성자 함수를 참조해 연결됨
=> 프로토타입과 생성자 함수는 단독으로 존재할 수 없고 언제나 쌍으로 존재함
function MyConstructor() {}
const obj = new MyConstructor();
// MyConstructor.prototype은 생성자 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티===MyConstructor로 생성된 모든 객체가 상속받는 프로토타입 객체
// Object.getPrototypeOf(obj) 메서드는 obj 객체의 프로토타입 객체를 반환
console.log(MyConstructor.prototype===Object.getPrototypeOf(obj)); // true
// 프로토타입 객체의 constructor 프로퍼티는 생성자 함수를 참조함
console.log(MyConstructor.prototype.constructor === MyConstructor); // true
// obj 객체는 프로토타입 체인을 통해 constructor 프로퍼티에 접근해 자신을 생성한 생성자 함수 참조 가능
console.log(obj.constructor===MyConstructor); // true
// 인스턴스에 constructor 프로퍼티가 직접 정의돼있진 않음
console.log(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(obj,'constructor')); // false프로토타입 체인(참조 루프)이 상호참조에 의해 생성되는 것을 방지하기 위해
프로토타입 체인은 단방향 연결 리스트로 구현돼야 함
즉, 프로퍼티 식별자 검색 방향이 한쪽 방향으로만 흘러야 함
const parent = {};
const child = {};
Object.setPrototypeOf(child,parent);
Object.setPrototypeOf(parent,child); // TypeError: Cyclic __proto__ value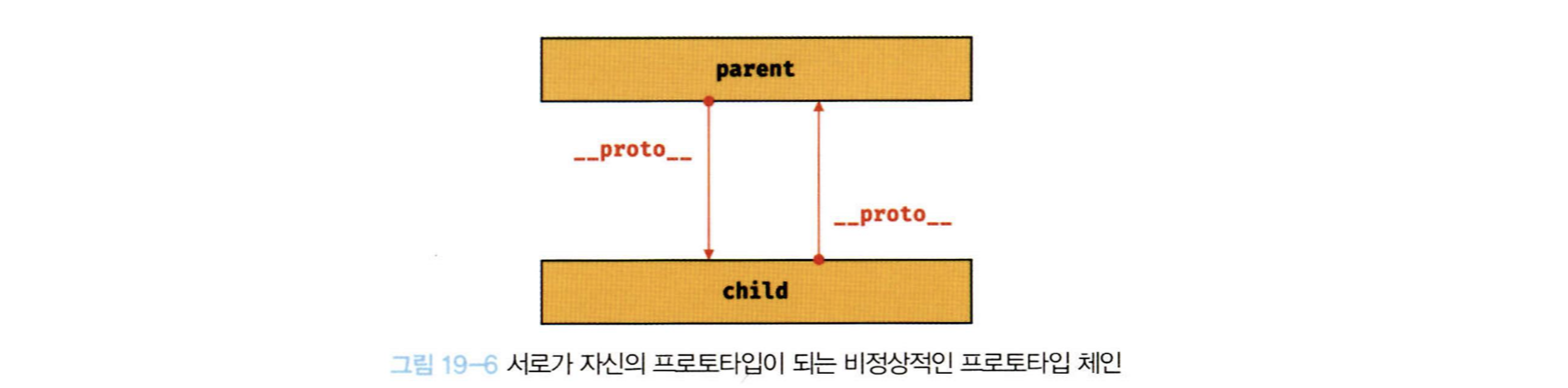
✅ 객체 생성 방식과 프로토타입 결정
객체 생성은 공통적으로 추상 연산 OrdinaryObjectCreate를 사용함
추상 연산 OrdinaryObjectCreate는 자신이 생성할 객체의 프로토타입을 필수 인자로 전달함, 이 인자에 의해 객체의 프로토타입이 결정됨
-
객체 리터럴에 의해 생성된 객체의 프로토타입
js 엔진은 객체 리터럴을 평가해 객체 생성시 추상연산 OrdinaryObjectCreate에 Object.prototoype이 프로토타입으로 넣어 호출
-> 객체 리터럴로 생성된 객체의 프로토타입은 Object.prototoype -
Object 생성자 함수에 의해 생성된 객체의 프로토타입
Object 생성자 함수를 호출해 객체 생성시 추상연산 OrdinaryObjectCreate에 Object.prototoype을 프로토타입으로 넣어 호출
-> Object 생성자 함수로 생성된 객체의 프로토타입은 Object.prototoype -
생성자 함수에 의해 생성된 객체의 프로토타입
new 연산자와 생성자 함수를 호출해 인스턴스를 생성시 추상연산 OrdinaryObjectCreate에 생성자 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티에 바인딩된 객체를 프로토타입으로 넣어 호출
-> 생성자 함수로 생성된 객체의 프로토타입은 생성자 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티에 바인딩돼있는 객체
✅ 프로토타입 체인
: js 엔진은 객체의 프로퍼티에 접근할때 없으면 [[Prototype]] 내부 슬롯의 참조를 따라 자신의 부모(상위) 프로토타입의 프로퍼티를 순차적으로 검색함
프로토타입 체인으로 상속, 프로퍼티 검색을 구현함
프로토타입 체인 최상위에 위치하는 객체(end of prototype chain)는 Object.prototype임
모든 객체는 Object.prototype을 상속받는다는 뜻
Object.prototype의 [[Prototype]] 내부 슬롯 값은 null임
Object.prototype에도 프로퍼티를 검색할 수 없으면 undefined 반환, 에러x
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 프로토타입 메서드
Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log(`Hi! My name is ${this.name}`);
};
const me = new Person('Lee');
// Person.prototype의 프로퍼티 객체엔 constructor 프로퍼티와, sayHello 메서드만 있는데
// Object.prototype의 메서드인 hasOwnProperty도 호출함
// me 객체는 프로토타입 체인을 따라 hasOwnProperty 메서드를 검색해 사용함
console.log(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(me,'name')); // true
console.log(me.foo); //undefined ✅ 오버라이딩과 프로퍼티 섀도잉
const Person = (function () {
// 생성자 함수
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 프로토타입 메서드
Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log(`Hi! My name is ${this.name}`);
};
// 생성자 함수를 반환
return Person;
}());
const me = new Person('Lee');
// 인스턴스 메서드
me.sayHello = function () {
console.log(`Hey! My name is ${this.name}`);
};
// 인스턴스 메서드가 호출됨. 프로토타입 메서드는 인스턴스 메서드에 의해 가려지는 property shadowing 발생
me.sayHello(); // Hey! My name is Lee
// 프로퍼티를 삭제하면 인스턴스 프로퍼티가 삭제되고
delete me.sayHello;
me.sayHello(); // Hi! My name is Lee
// 프로토타입 체인을 통해 프로토타입 프로퍼티는 변경, 삭제되지는 않음
delete me.sayHello;
me.sayHello(); // Hi! My name is Lee
// 🔎 프로토타입 프로퍼티를 변경, 삭제하려면 -> 프로토타입에 직접 접근해야함
// 프로토타입 메서드 변경
Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log(`Hello! My name is ${this.name}`);
};
me.sayHello(); // Hello! My name is Lee
// 프로토타입 메서드 삭제
delete Person.prototype.sayHello;
me.sayHello(); // TypeError: me.sayHello is not a functionproperty shadowing: 인스턴스에 프로토타입 객체의 프로퍼티(메서드포함)와 같은 이름의 프로퍼티를 추가하면 인스턴스 프로퍼티가 프로토타입 객체의 프로퍼티를 오버라이딩해, 프로토타입 객체의 프로퍼티는 가려지는 현상
✅ 직접상속
-
Object.create 사용
객체를 생성하며 명시적으로 프로토타입을 지정해 직접적으로 상속 구현함
추상 연산 OrdinaryObjectCreate를 호출
프로토타입을 지정해 객체를 생성해 객체리터럴에 의해 생성된 객체도 상속받을 수 있음Object.create(프로토타입으로 쓸 객체[, 생성할 객체의 프로퍼티(메서드포함)를 갖는 객체])
// 프로토타입이 null인 객체를 생성, 생성된 객체는 프로토타입 체인의 종점에 위치함
// obj → null
let obj = Object.create(null);
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj) === null); // true
// obj → Object.prototype → null
obj = Object.create(Object.prototype); // === obj={};
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj) === Object.prototype); // true
// 객체 리터럴로 생성한 객체를 직접 상속받음
const myProto = { x: 10 };
// obj → myProto → Object.prototype → null
obj = Object.create(myProto);
console.log(obj.x); // 10
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj) === myProto); // true
// 생성자 함수
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// obj → Person.prototype → Object.prototype → null
obj = Object.create(Person.prototype);
obj.name = 'Lee'; // === obj = new Person('Lee')
console.log(obj.name); // Lee
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj) === Person.prototype); // true- 객체 리터럴 내부에서 --proto-- 접근 연산자 사용 (ES6)
Object.create는 두번째 인자로 프로퍼티를 정의해야하지만 객체 리터럴 내부에서 --proto-- 접근 연산자를 사용해 더 간단하게 프로토타입 명시적으로 지정 가능
const myProto = { x: 10 };
// 객체 리터럴에 의해 객체를 생성하면서 프로토타입을 지정하여 직접 상속받을 수 있음
const obj = {
y: 20,
// 객체를 직접 상속받는다.
// obj → myProto → Object.prototype → null
__proto__: myProto
};
/* ===
const obj = Object.create(myProto, {
y: { value: 20, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true }
});
*/
console.log(obj.x, obj.y); // 10 20
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj) === myProto); // true✅ 프로퍼티 존재 확인
const person = {
name: 'Lee',
address: 'Seoul'
};
// 1️⃣ in 연산자 : 객체와, 객체가 상속받은 프로토타입의 프로퍼티(메서드포함)에 특정 프로퍼티가 존재하는지 확인
// 프로퍼티 키를 나타내는 문자열 `in` 객체로 평가되는 표현식
// person 객체에 name 프로퍼티가 존재함
console.log('name' in person); // true
// person이 상속받은 Object.prototype에 toString 메서드가 존재함
console.log('toString' in person); // true
// 2️⃣ Reflect.has 메서드 (ES6) - in 연산자와 동일하게 동작함
console.log(Reflect.has(person,'address')); // true
// 3️⃣ Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty 메서드 - 프로퍼티 키가 객체 고유의 프로퍼티 키인 경우 true를 반환, 객체가 상속받은 프로토타입의 프로퍼티 키인 경우 false 반환
console.log(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(person, 'name')); // true
console.log(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(person, 'toString')); // false✅ 프로퍼티 열거
for..in 문 : 객체의 프로토타입 체인이 모든 프로토타입의 프로퍼티(메서드포함) 중 프로퍼티 어트리뷰트 [[Enumerable]]이 true인 프로퍼티를 순회하며 열거함
`for` (변수 선언문 `in` 객체) {...}const person = {
name: 'Lee',
address: 'Seoul',
__proto__: { age: 20 }
};
for (const key in person) {
console.log(key + ': ' + person[key]);
}
/*
name: Lee
address: Seoul
age: 20
*/객체의 프로퍼티만 열거하려면 Object.keys, Object.values, Object.entries 메서드를 사용
const person = {
name: 'Lee',
address: 'Seoul',
__proto__: { age: 20 }
};
// ✔ Object.keys는 객체 자신의 enumerable란 프로퍼티 키를 배열로 반환함
console.log(Object.keys(person)); // ["name", "address"]
// ✔ Object.values는 객체 자신의 enumerable란 프로퍼티 값을 배열로 반환함 (ES8)
console.log(Object.values(person)); // ["Lee", "Seoul"]
// ✔ Object.entries는 객체 자신의 enumerable란 프로퍼티 키-값 쌍을 배열로 반환함 (ES8)
Object.entries(person).forEach(([key, value]) => console.log(key, value));
/*
name Lee
address Seoul
*/
+정적 프로퍼티,정적 메서드
: 생성자 함수(객체임)가 소유한 프로퍼티, 메서드
생성자 함수가 생성한 인스턴스로는 참조, 호출 불가
function Foo() {}
// 프로토타입 메서드
Foo.prototype.x = function () {
console.log('x');
};
const foo = new Foo();
// 프로토타입 메서드를 호출하려면 인스턴스를 생성해야 함
foo.x(); // x
// 정적 메서드
Foo.x2 = function () {
console.log('x');
};
// 생성자 함수에 추가한 정적 프로퍼티/메서드는 생성자 함수로 참조/호출
// 인스턴스 생성하지 않아도 호출 가능
Foo.x2(); // x
// 정적 프로퍼티/메서드는 생성자 함수가 생성한 인스턴스로 참조/호출할 수 없음
// 인스턴스로 참조/호출할 수 있는 프로퍼티/메서드는 프로토타입 체인 상에 존재해야 함
foo.x2(); // TypeError: foo.x2 is not a functionObject.create 메서드는 Object 생성자 함수의 정적 메서드 -> Object 생성자함수가 생성한 객체로 호출 불가
Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty 메서드는 Object.prototype의 메서드 -> 모든 객체가 호출 가능
참고자료
모던 자바스크립트 Deep Dive
