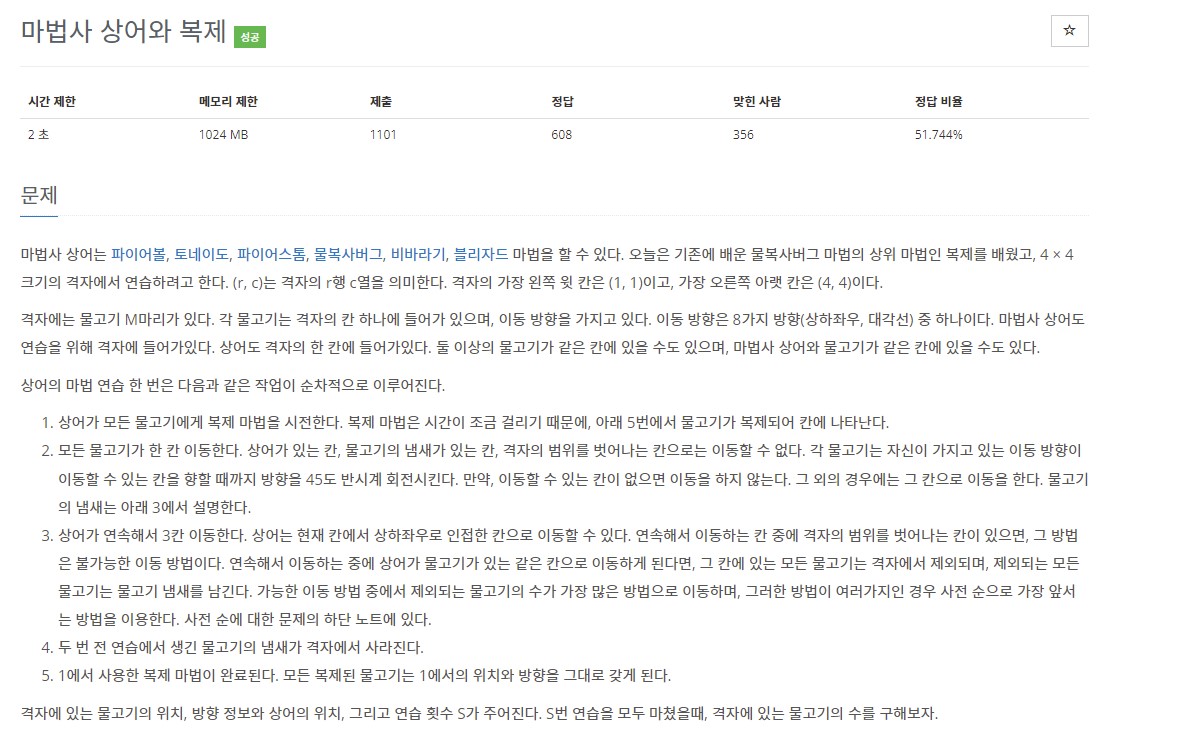
🦈Solution & Idea
- 물고기는 자신의 위치와 방향을 가지고 있고, 상어에게 잡아먹히면 죽는다. 따라서
위치(y,x), 방향(d), 생존여부(alive)의 정보를 담은 구조체를 만든다 - 맵의 한 칸에는 물고기의 번호 (여러 개 가능), 냄새가 저장된다. 따라서 물고기 번호
vector<int> fnum, scent_time을 저장하는 맵을 만들어준다 - 현재 시간을
Time이라고 두고, 물고기가 상어에게 잡혀 사라질 때scent_time=Time을 넣어준다. 그러고 후에 두 번 전 연습에서 생긴 물고기의 냄새가 격자에서 사라질 때,Time-scent_time==2인 경우scent_time=0으로 만들어주는 방법을 사용한다- 함수는 크게 총 6개로
1.start_copy(): 모든 물고기가 복제된다 (이전 물고기의 수를pre_size에 저장)move_fish(): 복제되기 전(pre_size크기만큼) 물고기들이 각각 이동을 한다update_map():map을 초기화해주고 이동한 물고기의 번호를 해당 위치에 넣어준다move_shark(): dfs 중복순열을 만드는 방법을 통해111~444까지의 방향을 만들어주고,해당 방향으로 끝까지 이동이 가능할 때, 잡아 먹을 수 있는 물고기의 수, 방향을vector<pair<int, int>> fishNum에 넣어 우선순위에 맞게 정렬해준다. 우선 순위가 가장 높은 방향으로 이동을 한다.remove_scent(): 현재 시간은Time이다.map의 각 칸에 저장된scent_time이Time-scent_time==2을 만족하면 2번 째 전에 생성된 냄새라는 뜻이므로 0으로 만들어 준다complete_copy(): 1번에서 복제된 물고기들의 번호를map의 해당 위치에 넣어준다.
- 함수는 크게 총 6개로
🦈Initialize
- 물고기, 상어, 맵에 대한 정보
struct FISH {
int y, x;
int d;
bool alive = true;
};
vector<FISH> fish;
struct SHARK {
int y, x;
};
SHARK shark;
struct MAP_INFO {
vector<int> fnum;
int scent_time=0;
};
MAP_INFO map[5][5];- 상어가
111~444사이의 각 위치로 이동했을 때, 총 먹는 물고기 수와 방향을 저장하는vector<pair<int, int>> fishNum를 만들고 이를 우선 순위에 따라 정렬하기 위해compare함수를 만든다
bool compare(pair<int, int>& A, pair<int, int>& B) {
if (A.first == B.first)
return A.second < B.second;
else return A.first > B.first;
}🦈1. start_copy()
- 물고기가 복제되기 전 물고기의 사이즈를
pre_size에 저장해주고 살아있는 물고기들만 차례대로fish에 추가해준다
void start_copy() {
pre_size = fish.size();
int idx = pre_size;
for (int i = 0; i < pre_size; i++) {
if (fish[i].alive == false) continue;
int y = fish[i].y;
int x = fish[i].x;
int d = fish[i].d;
fish.push_back({ y,x,d,true });
}
}🦈2. move_fish()
0번~pre_size-1번 물고기 중 살아있는 물고기만 움직임을 수행한다- 다음 칸이 범위를 벗어나지 않고, 다른 물고기의 냄새가 있지 않고
(map[ny][nx].scent_time==0), 상어와 같은 위치가 아닐 때 이동수행 - 그런 경우가 없다면 45도 방향을 바꾸어 다시 이동을 수행한다
- 이동이 끝난 후에는 물고기의 방향을 다시 재설정해준다 (도중에 물고기의 방향이 바뀌었을 수 있기 때문에)
void move_fish() {
for (int i = 0; i < pre_size; i++) {
if (fish[i].alive == false) continue;
int y = fish[i].y;
int x = fish[i].x;
int d = fish[i].d;
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
int ny = y + dy[d];
int nx = x + dx[d];
if (ny > 0 && nx > 0 && ny <= 4 && nx <= 4) {
if (map[ny][nx].scent_time==0) {
if (!(ny == shark.y && nx == shark.x)) {
fish[i].y = ny;
fish[i].x = nx;
break;
}
}
}
d = d - 1;
if (d < 0) d = 7;
}
fish[i].d = d;
}
}🦈3. update_map()
- 각
map에서 물고기의 번호를 저장하는 부분을 초기화해주고0번~pre_size-1까지 물고기를 맵에 업데이트 해준다
void update_map() {
//clear map
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= 4; j++)
map[i][j].fnum.clear();
//add fish to map
for (int i = 0; i < pre_size; i++) {
if (fish[i].alive == false) continue;
int y = fish[i].y;
int x = fish[i].x;
map[y][x].fnum.push_back(i);
}
}🦈4. move_shark()
- 중복 순열을 구하는 dfs 함수를 만들어 int selected[3]에 차례대로 이동 방향이 저장되게 한다
- 3가지 이동방향이 모두 정해졌을 때, move() 함수에서 해당 방향으로 이동했을 경우 끝까지 이동이 가능한지, 가능하다면 몇 마리의 물고기를 먹는지를 조사한다.
vector<pair<int, int>> fishNum에 (물고기의 수, 이동방향)의 쌍이 저장된다- 가장 우선 순위가 높은 방향으로 이동을 진행한다
(dfs함수와 move함수는 아래 전체 코드에서)
void move_shark() {
/*
choose 3directions &
order by removed fish num, direction
*/
dfs(0);
sort(fishNum.begin(), fishNum.end(), compare);
int cnt = fishNum[0].first;
int order = fishNum[0].second;
int ny, nx;
int divisor = 100;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int d = (order / divisor);
order = order - (d * divisor);
divisor /= 10;
ny = shark.y + sdy[d];
nx = shark.x + sdx[d];
if (map[ny][nx].fnum.size() != 0) {
for (int j = 0; j < map[ny][nx].fnum.size(); j++) {
int f = map[ny][nx].fnum[j];
fish[f].alive = false;
}
map[ny][nx].fnum.clear();
map[ny][nx].scent_time = Time;
}
shark.y = ny;
shark.x = nx;
}
}🦈5. remove_scent()
- 현재 시간 Time을 기준으로 2번 째 전에 생성된 냄새들을 제거해준다
- 모두 제거를 완료한 후 현재 시간을 늘려준다
void remove_scent() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 4; j++) {
if (Time-map[i][j].scent_time==2) {
map[i][j].scent_time = 0;
}
}
}
Time++;
}🦈6. complete_copy()
- 1번에서 복제된 물고기 즉,
pre_size~fish.size()-1의 물고기들을map에 업데이트 해준다
void complete_copy() {
for (int i = pre_size; i < fish.size(); i++) {
int y = fish[i].y;
int x = fish[i].x;
map[y][x].fnum.push_back(i);
}
}Source Code
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
const int dy[] = { 0,-1,-1,-1,0,1,1,1};
const int dx[] = { -1,-1,0,1,1,1,0,-1};
const int sdy[] = {0,-1,0,1,0 };
const int sdx[] = {0,0,-1,0,1 };
using namespace std;
struct FISH {
int y, x;
int d;
bool alive = true;
};
vector<FISH> fish;
struct SHARK {
int y, x;
};
SHARK shark;
struct MAP_INFO {
vector<int> fnum;
int scent_time=0;
};
MAP_INFO map[5][5];
int tmp[5][5];
int pre_size = 0;
int Time = 1;
int M, S;
int ret = 0;
int selected[3];
vector<pair<int, int>> fishNum;
bool compare(pair<int, int>& A, pair<int, int>& B) {
if (A.first == B.first)
return A.second < B.second;
else return A.first > B.first;
}
void complete_copy() {
for (int i = pre_size; i < fish.size(); i++) {
int y = fish[i].y;
int x = fish[i].x;
map[y][x].fnum.push_back(i);
}
}
void remove_scent() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 4; j++) {
if (Time-map[i][j].scent_time==2) {
map[i][j].scent_time = 0;
}
}
}
Time++;
}
void move() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= 4; j++)
tmp[i][j] = map[i][j].fnum.size();
int cnt=0,order = 0;
int y = shark.y;
int x = shark.x;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int dir = selected[i];
int ny = y + sdy[dir];
int nx = x + sdx[dir];
if (ny <= 0 || nx <= 0 || ny > 4 || nx > 4) return;
if (tmp[ny][nx] != 0) {
cnt += map[ny][nx].fnum.size();
tmp[ny][nx] = 0;
}
y = ny;
x = nx;
}
order = selected[0] * 100 + selected[1] * 10 + selected[2];
fishNum.push_back(make_pair(cnt, order));
}
void dfs(int cnt) {
if (cnt == 3) {
move();
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
selected[cnt] = i;
dfs(cnt + 1);
}
}
void move_shark() {
/*
choose 3directions &
order by removed fish num, direction
*/
dfs(0);
sort(fishNum.begin(), fishNum.end(), compare);
int cnt = fishNum[0].first;
int order = fishNum[0].second;
int ny, nx;
int divisor = 100;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int d = (order / divisor);
order = order - (d * divisor);
divisor /= 10;
ny = shark.y + sdy[d];
nx = shark.x + sdx[d];
if (map[ny][nx].fnum.size() != 0) {
for (int j = 0; j < map[ny][nx].fnum.size(); j++) {
int f = map[ny][nx].fnum[j];
fish[f].alive = false;
}
map[ny][nx].fnum.clear();
map[ny][nx].scent_time = Time;
}
shark.y = ny;
shark.x = nx;
}
}
void update_map() {
//clear map
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= 4; j++)
map[i][j].fnum.clear();
//add fish to map
for (int i = 0; i < pre_size; i++) {
if (fish[i].alive == false) continue;
int y = fish[i].y;
int x = fish[i].x;
map[y][x].fnum.push_back(i);
}
}
void move_fish() {
for (int i = 0; i < pre_size; i++) {
if (fish[i].alive == false) continue;
int y = fish[i].y;
int x = fish[i].x;
int d = fish[i].d;
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
int ny = y + dy[d];
int nx = x + dx[d];
if (ny > 0 && nx > 0 && ny <= 4 && nx <= 4) {
if (map[ny][nx].scent_time==0) {
if (!(ny == shark.y && nx == shark.x)) {
fish[i].y = ny;
fish[i].x = nx;
break;
}
}
}
d = d - 1;
if (d < 0) d = 7;
}
fish[i].d = d;
}
}
void start_copy() {
pre_size = fish.size();
int idx = pre_size;
for (int i = 0; i < pre_size; i++) {
if (fish[i].alive == false) continue;
int y = fish[i].y;
int x = fish[i].x;
int d = fish[i].d;
fish.push_back({ y,x,d,true });
}
}
void solution() {
while (S--) {
start_copy();
move_fish();
update_map();
move_shark();
remove_scent();
complete_copy();
fishNum.clear();
}
}
void input() {
cin >> M >> S;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int y, x, d;
cin >> y >> x >> d;
fish.push_back({ y,x,d - 1,true});
}
int sy, sx;
cin >> sy >> sx;
shark.y = sy;
shark.x = sx;
}
int main() {
input();
solution();
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < fish.size(); i++) {
if (fish[i].alive == true) cnt++;
}
printf("%d\n", cnt);
}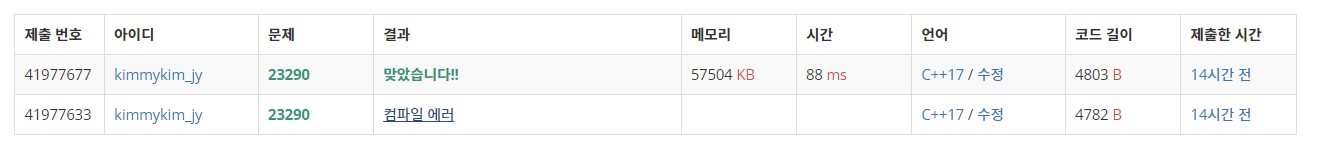
전에는 이렇게 지문이 긴 문제를 받으면 당황했지만 그냥 차근 차근 시키는대로 구현하면 되니까 이런 문제가 더 나은 것 같다.. 물론 익숙해지기 전까지는 엄청 삽질을 많이하고 디버깅 하느라 많은 시간을 할애지만 😥..
