[TIL] Linked List
Linked List
컴퓨터에 자료를 저장하는 구조의 한종류이다. 일렬로 연결된 데이터를 저장할 때 사용된다.
예) A에서 B로 넘어갈때 A에 B의 주소가 있다. 배열과 비교하면, 배열들은 전체 방 크기를 한번 정하면 늘리거나 줄일 수가 없다. 하지만 링크드 리스트는 데이터를 중간에 삽입하고 싶다면, A와 B사이에 임의로 추가할 수가 있다.
Array List
메모리 안에 연속적으로 붙어있는 형태.
Linked List
메모리 안에 임의로 차지하고 있지만 그 하나하나가 연결이 되어 있다.
(아래사진 참조)
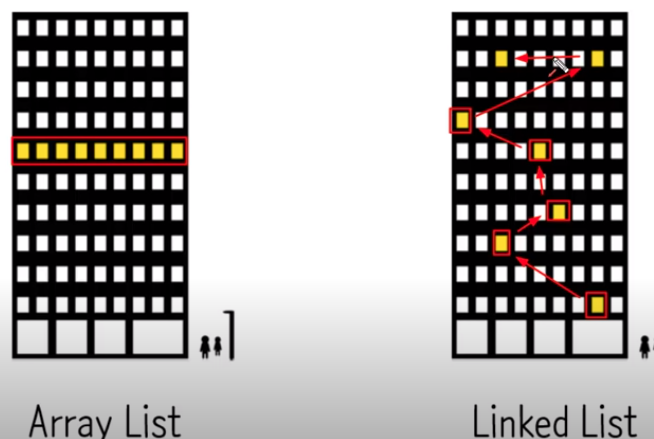
Linked List의 형태:
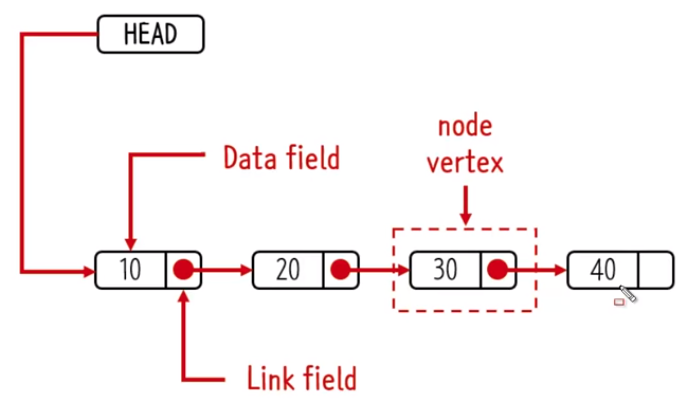
사진 속 점선을 차지하고 있는 부분이 하나의 node, 그리고 사진 속에는 총 4개의 node가 있다.
"node vertex" 안에는 'data field'와 'link field'가 존재한다.
Singly linked list(단일 연결 리스트)
Singly linked list는 각 노드에 자료 공간과 한 개의 포인터 공간(다음 노드의 주소를 담는 공간)이 있고, 각 노드의 포인터는 다음 노드를 가리킨다.
# Node 클래스 선언
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# Singly linked list 클래스 선언
class SinglyLinkedList(object):
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.count = 0
# Add new node at the end of the linked list
def append(self, node):
if self.head == None:
self.head = node
else:
cur = self.head
while cur.next != None:
cur = cur.next
cur.next = node
# return first index of data in the linked list
def getdataIndex(self, data):
curn = self.head
idx = 0
while curn:
if curn.data == data:
return idx
curn = curn.next
idx += 1
return -1
# Add new node at the given index
def insertNodeAtIndex(self, idx, node):
"""
A node can be added in three ways:
1) At the front of the linked list.
2) At a given index.
3) At the end of the linked list.
"""
curn = self.head
prevn = None
cur_i = 0
# (1) Add 0 index
if idx == 0:
if self.head:
nextn = self.head
self.head = node
self.head.next = nextn
else:
self.head = node
else:
# (2) Add at given index &
# (3) At the end of the linked list
while cur_i < idx:
if curn:
prevn = curn
curn = curn.next
else:
break
cur_i += 1
if cur_i == idx:
node.next = curn
prevn.next = node
else:
return -1
# Add new node before the given data
def insertNodeAtData(self, data, node):
index = self.getdataIndex(data
if 0 <= index:
self.insertNodeIndex(index, node)
else:
return -1
# Delete data at given index.
def deleteAtIndex(self, idx):
curn_i = 0
curn = self.head
prevn = None
nextn = self.head.next
if idx == 0:
self.head = nextn
else:
while curn_i < idx:
if curn.next:
prevn = curn
curn = nextn
nextn = nextn.next
else:
break
if curn_i == idx:
prevn.next = nextn
else:
return -1
# Empty linked list
def clear(self):
self.head = None
# 출력
def print(self):
curn = self.head
string = ""
while curn:
string += str(curn.data)
if curn.next:
string += "->"
curn = curn.next
print(string)
if __name__ == "__main__":
s1 = SinglyLinkedList()
s1.append(Node(1))
s1.append(Node(2))
s1.append(Node(3))
s1.append(Node(5))
s1.insertNodeAtIndex(3, Node(4))
s1.print()
print(s1.getdataIndex(1))
print(s1.getdataIndex(2))
print(s1.getdataIndex(3))
print(s1.getdataIndex(4))
print(s1.getdataIndex(5))
s1.insertNodeAtData(1, Node(0))
s1.print()