▶️문제
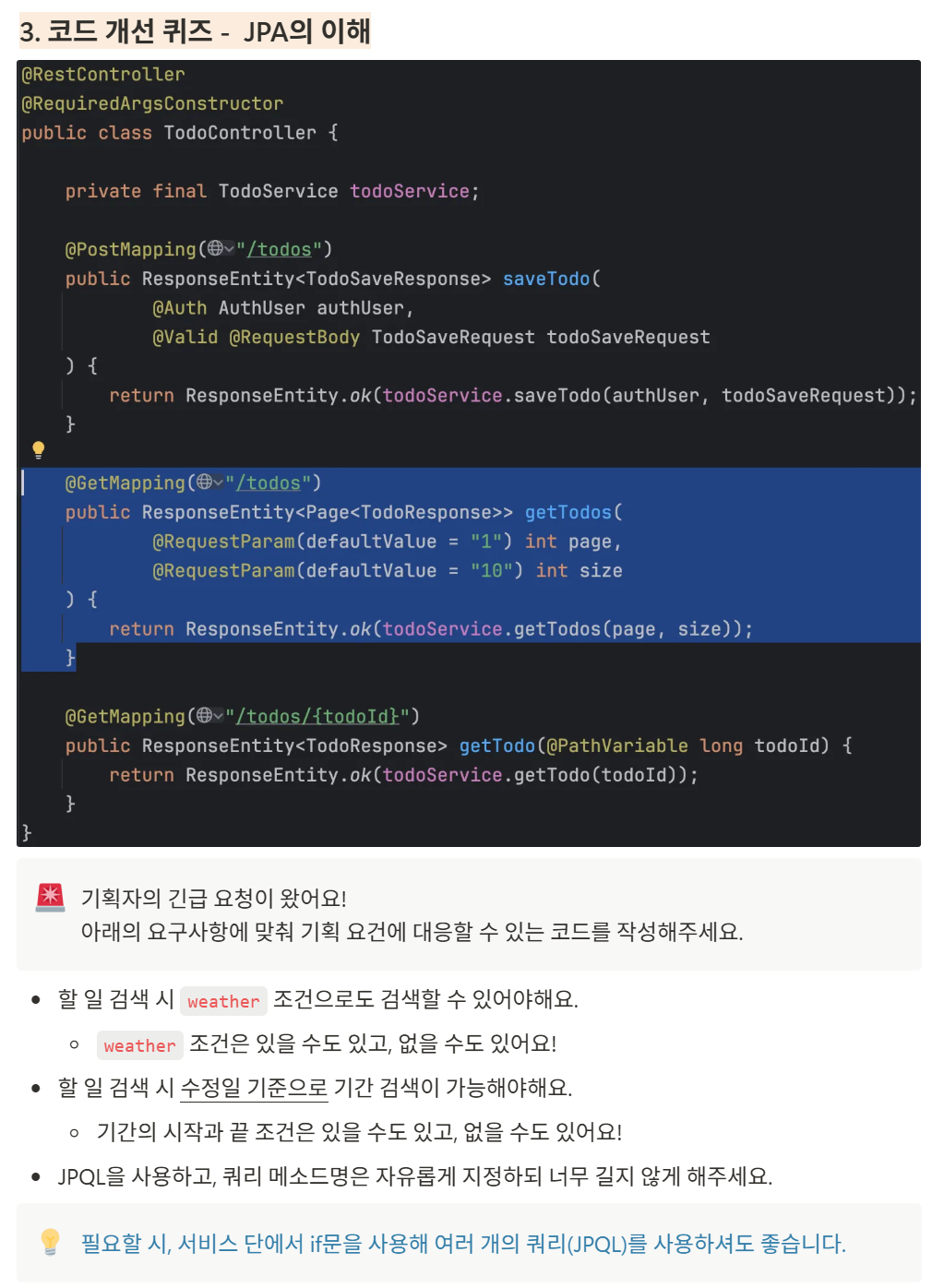
▶️요구사항 정리
날씨 조건: 있을 수도, 없을 수도 있다 → 선택적 파라미터를 사용
기간의 시작과 끝 날짜가 있을 수도, 없을 수도 있다. → 얘도 선택적 파라미터를 사용
→ @RequestParam(required = false)를 사용하면 선택적 파라미터를 받는다.
꼭
required = false를 사용해야 하는가?
→ 반드시 필요한 것은 아니다. 하지만 선택적(optional) 파라미터를 받고 싶을 때는 사용해야 한다.
- @RequestParam의 기본값은
required = true이다.- 해당 파라미터가 없다면 400 에러가 발생한다.
- weather, start, end(검색 조건)가 필수가 아니기 때문에
required = false로 선언해야 파라미터가 없어도 에러가 발생하지 않는다.
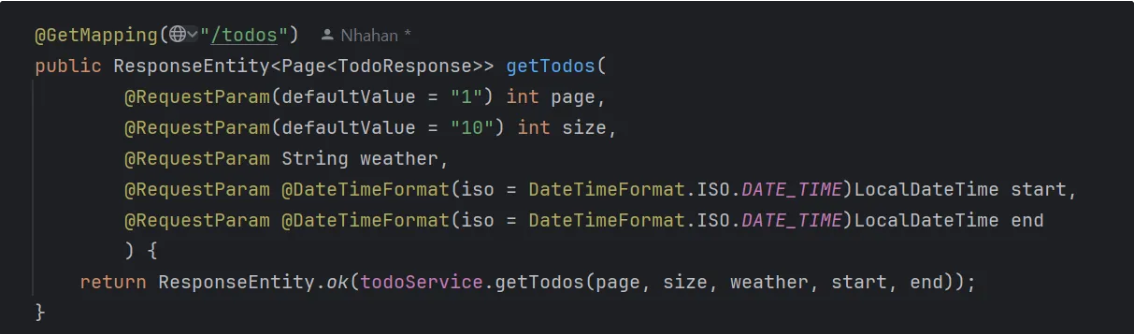
▶️@DateTimeFormat 어노테이션
Spring에서 날짜/시간 문자열을 자바의 날짜/시간 객체로 변환할 때 사용하는 어노테이션으로
Url에서 2025-05-08T12:00:00 같이 문자열 값을 자동으로 변환해준다.
- POST/PUT 등에서 JSON으로 날짜를 받을 때는
@JsonFormat을 사용 - GET 쿼리 파라미터(문자열) → 자바 날짜 타입 변환에는
@DateTimeFormat을 사용
▶️해결
아는 지인은
EntityManager와StringBuilder로 동적으로JPQL을 생성하는 방식을 채용하였다.
확실히 깔끔하게 보였다.
그래서 다른 방법이 있을까 찾던 도중에Spring JPA의Specification이랑Query By Example(QBE)를 사용하면
깔끔하게 코드가 작성이 되길래, 전자의 방법인 Specification을 사용해 보았다.
▶️사용 방법
우선 Specification을 사용하려면 Repository 인터페이스를 수정해 주어야 한다.
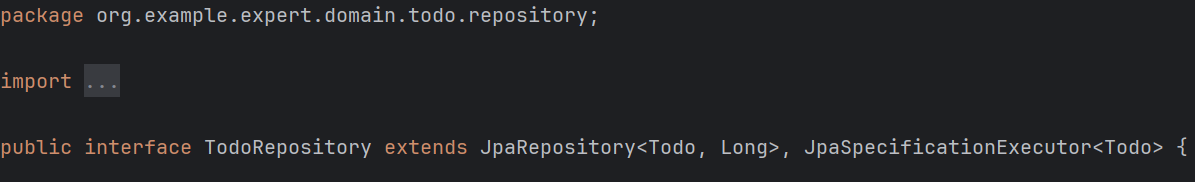
extends JpaRepository<Todo, Long>뒤에 , 을 넣고
JpaSpecificationExecutor<Todo> 를 추가해준다.
public interface TodoRepository extends JpaRepository<Todo, Long>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<Todo> {}그 후 공식문서와 타 블로그글을 활용했다.
- Specification 공식문서
https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/jpa/reference/jpa/specifications.html
- 참고 블로그 글
https://dev-setung.tistory.com/20
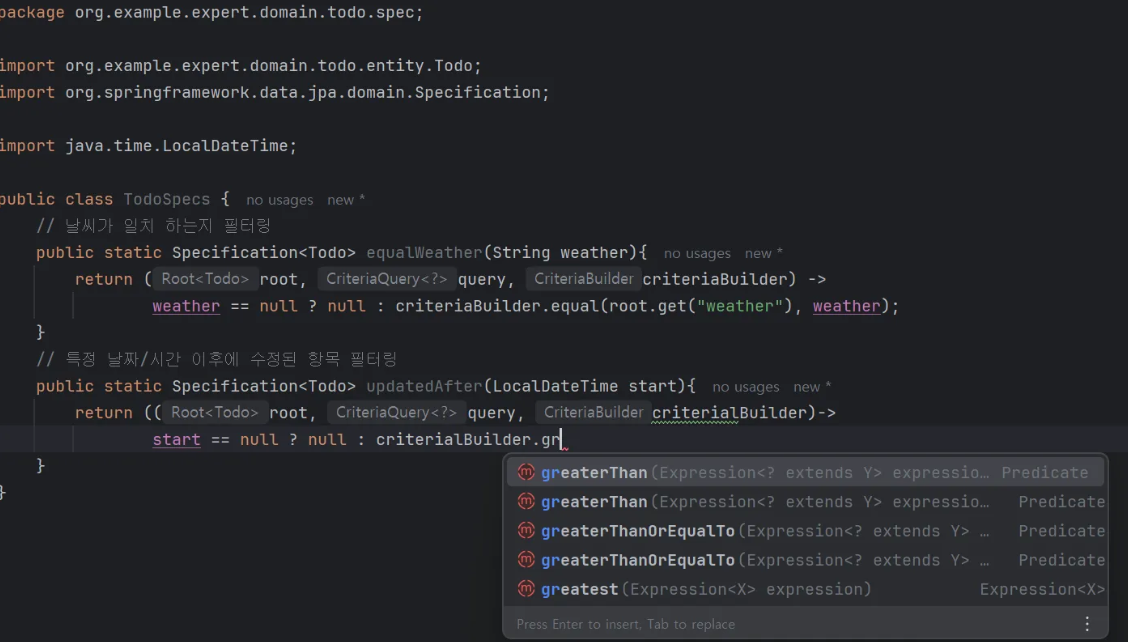
첫번째는 날씨가 같을 때(.equal)
두 번째는 수정된 날짜/시간이 같거나 이후일 때(greaterThanOrEqualTo) 위 사진과 같이 선택할 수 있다.
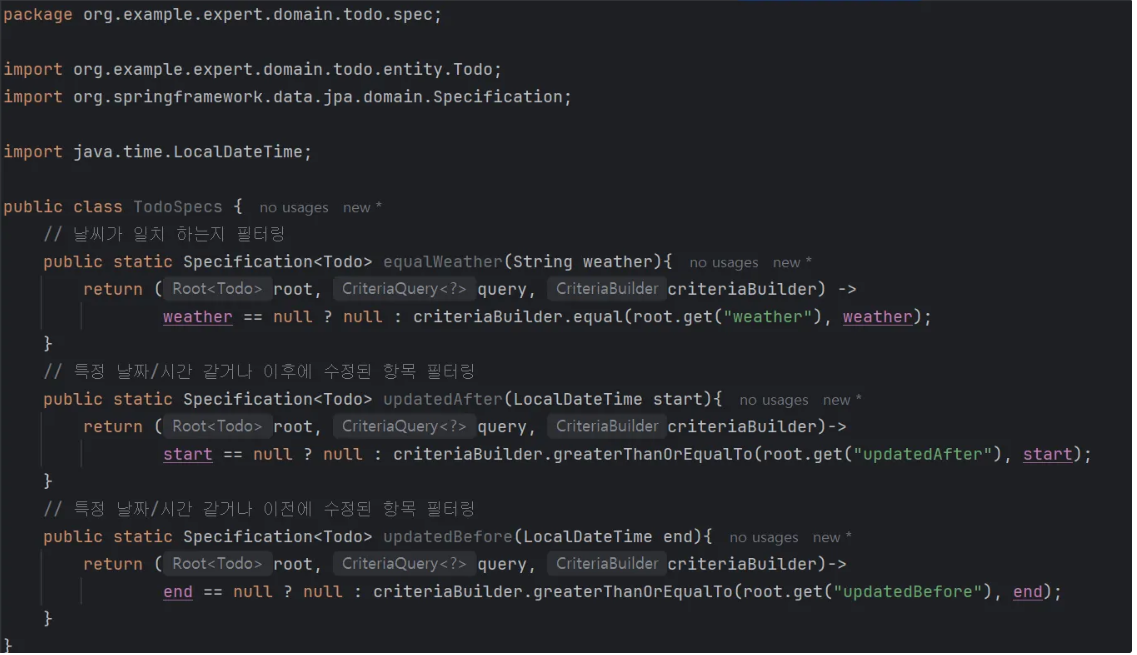
- 완성본
▶️Service에 적용하기
- 본래 코드
public Page<TodoResponse> getTodos(int page, int size, String weather, LocalDateTime start, LocalDateTime end) {
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(page - 1, size);
Page<Todo> todos = todoRepository.findAllByOrderByModifiedAtDesc(pageable);
return todos.map(todo -> new TodoResponse(
todo.getId(),
todo.getTitle(),
todo.getContents(),
todo.getWeather(),
new UserResponse(todo.getUser().getId(), todo.getUser().getEmail()),
todo.getCreatedAt(),
todo.getModifiedAt()
));
}- 수정 후 코드
public Page<TodoResponse> getTodos(int page, int size, String weather, LocalDateTime start, LocalDateTime end) {
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(page - 1, size,
Sort.by(Sort.Direction.DESC, "updatedAt"));
// Specification 사용.
Specification<Todo> spec = Specification.where(TodoSpecs.equalWeather(weather))
.and(TodoSpecs.updatedAfter(start))
.and(TodoSpecs.updatedBefore(end));
// 모든 조건이 null이면 기존 메서드를 사용 아니면 Specification을 사용.
Page<Todo> todos;
if (weather == null && start == null && end == null){
todos = todoRepository.findAllByOrderByModifiedAtDesc(pageable);
} else {
todos = todoRepository.findAll(spec, pageable);
}
return todos.map(todo -> new TodoResponse(
todo.getId(),
todo.getTitle(),
todo.getContents(),
todo.getWeather(),
new UserResponse(todo.getUser().getId(), todo.getUser().getEmail()),
todo.getCreatedAt(),
todo.getModifiedAt()
));
}▶️정리
조건별로 Specification을 static 메서드로 분리하면 재사용과 조합이 쉽고 코드가 깔끔해진다.
🤔return에 들어가는 root, query, cb는 어디서 나오는 것인가?
weatherEq 메서드는 람다 표현식에서
세 개의 파라미터(root, query, cb)를 받는데, 이들은 JPA Criteria API의 핵심 객체들이다.
- 여기서 cb는 CriteriaBuilder의 약자이다.
return (root, query, cb) -> weather == null ? null : cb.equal(root.get("weather"), weather);이 파라미터들은 Spring Data JPA가 내부적으로 제공한다.
1. root:
Root<Todo> 타입으로, 쿼리의 루트 엔티티(FROM 절의 대상)를 나타낸다. root.get("weather")와 같이 사용하여 엔티티의 필드에 접근한다.
2. query:
CriteriaQuery<?> 타입으로, 전체 쿼리 객체이다. 주로 ORDER BY, GROUP BY 등을 추가할 때 사용한다.
3. cb:
CriteriaBuilder 타입으로, 조건문(WHERE 절)을 생성하는 팩토리다.
equal, greaterThan, like 등의 메서드를 제공한다.
실제로는 이 파라미터들이 어디서 생성되는지 직접 볼 수 없다.
repository.findAll(spec, pageable) 호출 시
Spring Data JPA가 내부적으로 JPA Criteria API를 사용하여 쿼리를 만들 때
이 객체들을 생성하고 람다 표현식에 전달한다.
전체 사용 예시
// 1. Specification 클래스 정의 public class TodoSpecs { // weather가 일치하는지 확인하는 명세 public static Specification<Todo> weatherEq(String weather) { return (root, query, cb) -> weather == null ? null : cb.equal(root.get("weather"), weather); } } // 2. Repository 인터페이스 public interface TodoRepository extends JpaRepository<Todo, Long>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<Todo> { // JpaSpecificationExecutor를 상속하면 추가 메서드 없이도 Specification 사용 가능 } // 3. Service에서 사용 public Page<TodoResponse> searchTodos(String weather, Pageable pageable) { // Specification 객체 생성 및 실행 Specification<Todo> spec = TodoSpecs.weatherEq(weather); return todoRepository.findAll(spec, pageable).map(TodoResponse::from); }
이러한 방식으로 Specification을 활용하면 여러 조건을 동적으로 조합할 수 있어
복잡한 검색 쿼리도 깔끔하게 처리할 수 있다.

ㅎㅇ