Java Proxy Patten
프록시 패턴은 "원본 객체"를 대리하여 대신 처리하게 함으로써 로직의 흐름을 제어하는 행동 패턴입니다.
프록시의 사전적 의미는 "대리인"으로 어떠한 일을 대신 시키거나 대신 하는 것을 의미하며, OOP에서 클라이언트가 객체를 직접 사용하는 것이 아니라 프록시(대리인)을 거쳐서 쓰는 방법을 의미합니다.
따라서 객체(subject)의 메서드를 직접 실행하는 것이 아닌 대상 객체에 접근하기 전에 프록시 객체의 메서드를 접근 후 추가적인 로직을 처리한 뒤 접근하게 됩니다.
사용 목적
프록시처럼 중계대리인을 사용하는 이유는 민감한 정보, 무거운 데이터, 수정불가한 객체등을 극복하여 사용하기도 하며, 주로 접근제어 기능을 추가해야하는 상황에 특정객체 수정이 어려운경우 / 기존 코드의 수정없이 [지연 로딩, 로깅, 캐싱]등의 작업을 추가하는 경우에 사용됩니다.
- 보안
프록시는 클라이언트가 작업을 수행할 수 있는 권한이 있는 지 검증을 통해 요청을 대상으로 전달합니다.
- 캐싱
내부 캐시를 유지하여 데이터가 캐시에 존재하지 않는 경우에만 작업이 실행 됩니다.
- 유효성 검사
입력을 대상으로 전달하기전 유효성 검사를 통해 진행합니다.
- 지연 초기화
생성 비용이 비싸다면 해당 객체가 필요한 때에 생성하도록 지연시킵니다.
- 로깅
메서드 호출 및 파라미터를 인터셉트하여 기록합니다.
- 원격객체
원격 위치에 있는 객체를 가져와서 로컬처럼 보이게 할 수 있습니다.
사용 이점
-
OPC / SRP준수
- 기존 대상 객체 코드를 변경하지 않고 새로운 기능을 손쉽게 추가할 수 있습니다.
- 대상 객체는 본인의 책임에마 집중하여 동작하고 이외 부가 기능은 프록시에 위임하여 다중 책임에서 벗어날 수 있습니다.
-
클라이언트는 객쳉 대한 신경이 적어지고 서비스 객체르 제어 또는 생명주기를 관리에 집중할 수 있습니다.
-
사용자 입장에서 프록시와 일반 객체는 유사하게 작성되기때문에 사용성에 문제가 없습니다.
단점
- 많은 프록시 클래스를 도입해야하므로 코드의 복잡성이 증가됩니다.
- 각각 클래스에 해당하는 프록시 객체를 만들어야하기 떄문에 코드량이 많아지고 중복이 발생합니다.
- 프로시 클래스 자체가 무거워지면 응답 속도가 저하됩니다.
Proxy 패턴 구조 및 생성
패턴 구조
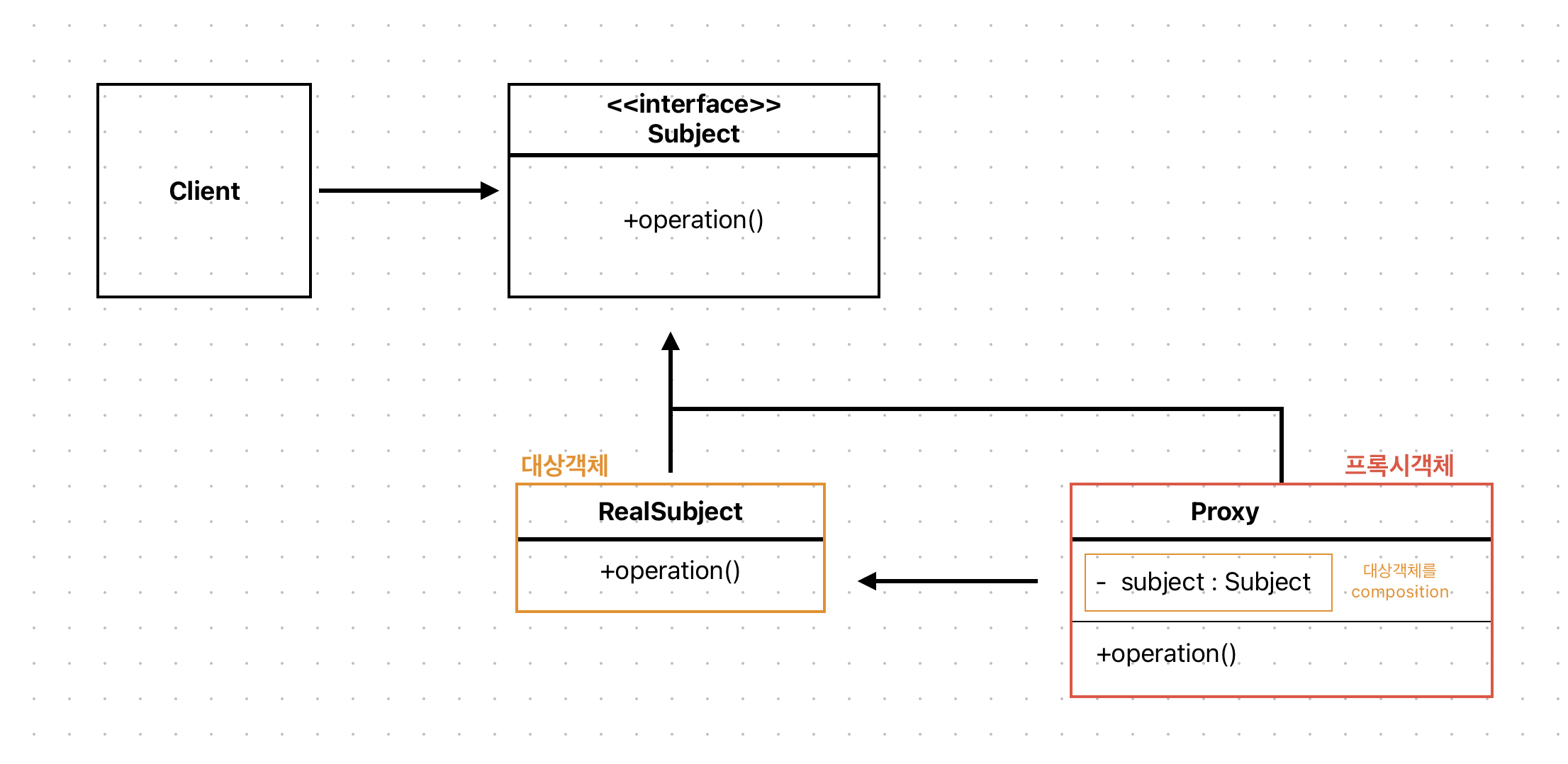
프록시는 다른 객체에 대한 접근을 제어하는 개체로 사용됩니다. 여기서 다른 객체는 Subject라고 합니다. 개체와 대상은 인터페이스를 구현하고 있으며, 다른 인터페이스와 호환되도록 변경도 가능합니다.
-
Subject : Proxydhk RealSubject를 하나로 묶는 인터페이스 (다형성)
- 대상 객체와 프록시 역할을 동일하게 하는 추상메서드를 정의
- 인터페이스가 있기 때문에 대상과 개체간 역할차이 의식하지 않아도 된다.
-
RealSubject : 원본 대상 객체
-
Proxy :
RealSubject를 중계하는 대리자- 프록시는 대상을 합성(composition)
- 대상 객체와 같은 이름의 메서르를 구현하며, 별도의 로직 수행가능.
- 프록시는 흐름에 대한 제어만 가능하다.
-
Client : Subject인터페이스를 사용하여 프록시 객체를 생성하여 이용한다.
패턴 생성
Proxy 패턴은 구성이 단순하여 자주 사용되며, 기본 구성 방식에서 다양한 로직 추가를 통해 종류가 분류됩니다.
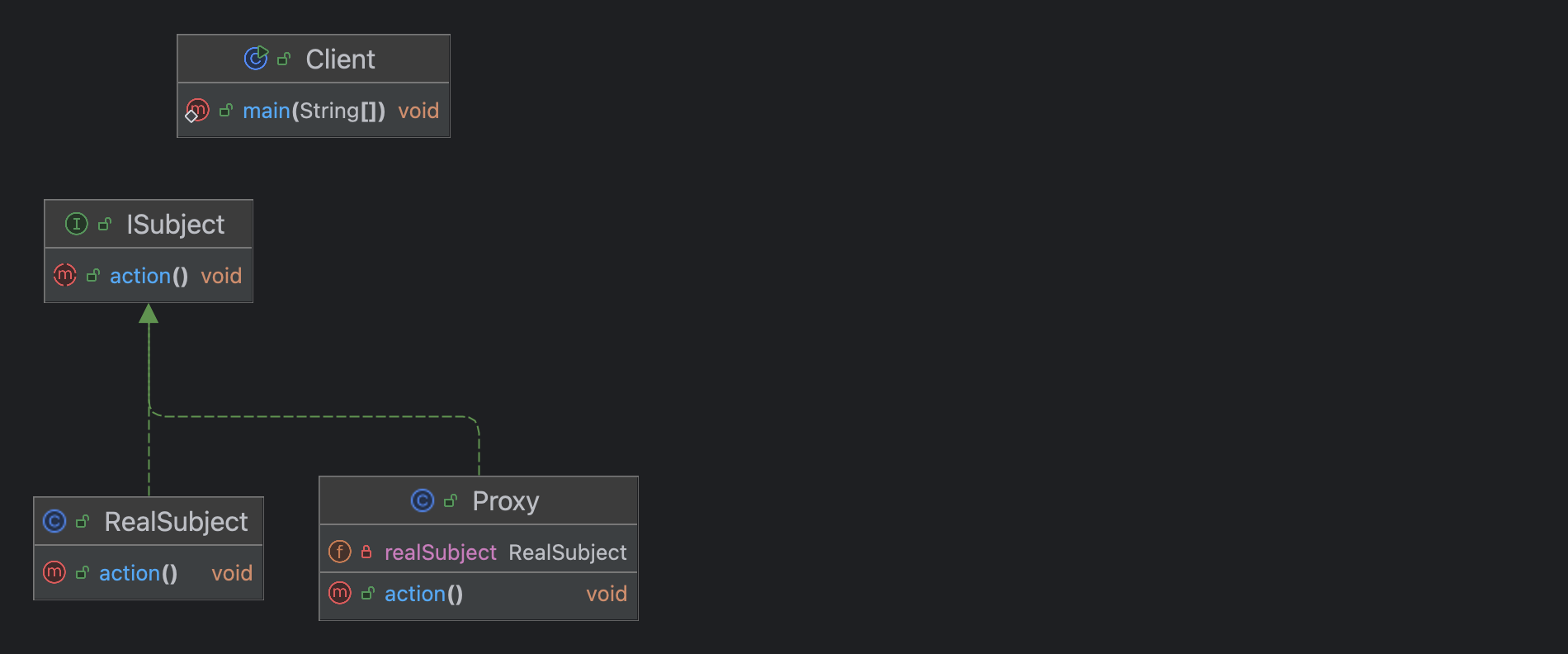
기본형
interface ISubject {
void action();
}
class RealSubject implements ISubjecy {
public vid action(){
System.out.println("원본 객체 액션");
}
}class Proxy implememts ISubject {
private RealSubject subject; //대상 객체 합성 composition
Proxy(RealSubject subject){
this.subject = subject;
}
@override
public void action() {
subject.action(); //위임
System.out.println("프록시 객체 액션");
}
}
class main
public static void main(String[] args){
ISubject sub = new Proxy(new RealSubject());
sub.action();
}
} 
가상 프록시
기본 프록시 형태에서 "지연초기화" 방식을 추가한 방법입니다.
주로 자주사용되지 않지만 실제 객체의 생성에 많은자원이 필요로 하고 필요시점에만 초기화를 진행하여 사용할 떄 사용됩니다. (이미지 로딩, pdf로딩 등등)
class Proxy implements ISubject{
private RealSubject subject;
Proxy() {}
@override
public void action() {
//프록시 객체는 실제 요청(action)이 호출되었을떄 생성을 진행한다.
if(subject == null){
subject = new RealSubject();
}
subject.action(); //위임
System.out.println("프록시 객체 액션");
}
}
class main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ISubject sub = new Proxy();
sub.action();
}
}(예제) PDF로더
interface Document {
void display();
}
class RealDocument implements Document {
private String fileName;
public RealDocument(String fileName) {
this.fileName = fileName;
loadDocument();
}
private void loadDocument() {
System.out.println("Loading document: " + fileName);
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.println("Displaying document: " + fileName);
}
}
class DocumentProxy implements Document {
private RealDocument realDocument;
private String fileName;
public DocumentProxy(String fileName) {
this.fileName = fileName;
}
@Override
public void display() {
if (realDocument == null) {
realDocument = new RealDocument(fileName); // 지연 초기화
}
realDocument.display();
}
}
public class VirtualProxyExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Document doc = new DocumentProxy("largeFile.pdf");
System.out.println("Document proxy created.");
// 실제로 display() 호출 시에만 PDF 로드
doc.display();
doc.display(); // 두 번째 호출에서는 이미 로드된 상태
}
}보호 프록시
프록시가 대상객체에 대한 접근권한을 지니고 있으며 특정 클라이언트만 서비스 객체를 이용하도록 하기 위해서 사용되는 방법입니다
프록시 객체를 통해 클라이언트의 자격조건을 통과해야 서비스객체를 통한 서비스 동작이 실행됩니다.
class Proxy implements ISubject {
private RealSubject subject; // 대상 객체를 composition
boolean access; // 접근 권한
Proxy(RealSubject subject, boolean access) {
this.subject = subject;
this.access = access;
}
@override
public void action() {
if(access) {
subject.action(); // 위임
/* do something */
System.out.println("프록시 객체 액션 !!");
}
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ISubject sub = new Proxy(new RealSubject(), false);
sub.action();
}
}(예제)관리자 접근 제어
interface DataService {
void updateData(String data);
}
class RealDataService implements DataService {
@Override
public void updateData(String data) {
System.out.println("Data updated: " + data);
}
}
class AdminProxy implements DataService {
private RealDataService realService;
private boolean isAdmin;
public AdminProxy(boolean isAdmin) {
this.realService = new RealDataService();
this.isAdmin = isAdmin;
}
@Override
public void updateData(String data) {
if (isAdmin) {
realService.updateData(data);
} else {
System.out.println("Access Denied: Admin rights required.");
}
}
}
public class ProtectionProxyExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataService adminProxy = new AdminProxy(true); // 관리자 권한
adminProxy.updateData("Important Data");
DataService userProxy = new AdminProxy(false); // 일반 사용자
userProxy.updateData("Sensitive Data");
}
}로깅 프록시
대상 객체에 로깅을 추가해야하는 경우에 사용됩니다.
class Proxy implements ISubject {
private RealSubject subject;
Proxy(RealSubject subject) {
this.subject = subject
}
@override
public void action(){
System.out.priintln("loading");
subject.action();//위임
/
System.out.println("프록시 객체 액션");
System.out.priintln("loading");
}
}
class main {
public static void main(String[] args){
ISubject sub = new Proxy(new RealSubjet());
sub.action();
}
} (예제) API호출 로깅 추가
interface ApiService {
void fetchData();
}
class RealApiService implements ApiService {
@Override
public void fetchData() {
System.out.println("Fetching data from API...");
}
}
class LoggingProxy implements ApiService {
private RealApiService realService;
public LoggingProxy(RealApiService realService) {
this.realService = realService;
}
@Override
public void fetchData() {
System.out.println("Logging: API call started.");
realService.fetchData();
System.out.println("Logging: API call completed.");
}
}
public class LoggingProxyExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApiService service = new LoggingProxy(new RealApiService());
service.fetchData();
}
}Dynamic Proxy
java.lang.reflect.Proxy를 사용해 실행 시점에 프록시를 생성하는 방법입니다.
인터페이스 기반으로 동작하며 런타임에 메서드 호출을 가로채 추가 로직 삽입이 가능합니다.
package proxy.dynamic;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
public class DynamicMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// newProxyInstance() 메서드로 동적으로 프록시 객체를 생성할 수 있다.
Animal rabbitProxy = (Animal) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
Animal.class.getClassLoader(), //대상 객체의 인터페이스의 클래스 로더
new Class[]{Animal.class}, // 대상 객체의 인터페이스
new InvocationHandler() { //프록시 핸들러
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object target = new rabbit();
System.out.println("---eat 호출 전 ---");
Object result = method.invoke(target, args); //타겟 메서드 호출
System.out.println("---eat 호출 후---");
return result;
}
}
);
rabbitProxy.eat();
}
}Spring AOP
스프링 프레임워크에서는 내부적으로 프록시 기술을 많이 사용하고 있습니다. - JPA / AOP
Bean등록을 할떄 Singleton을 유지하기 위해 Dynamic Proxy를 사용하여 프록시 객체를 Bean으로 등록하여 사용하고, Bean으로 등록하려는 기본적인 객체가 Interface가 하나라도 구현되어 잇으면 JDK를 사용하고 없으면 내장 CGLIB를 사용합니다.
@Service
public class userService{
public void login(){
System.out.println("로그인에 성공하였씁니다.");
}
}@Aspect
@Comonent
public class PerfAspect {
@Around("bean(userService)")
public void timestamp(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("프록시 실행 1");
point.proceed(); // 대상 객체의 원본 메서드를 실행
System.out.println("프록시 실행 2");
}
}요약
| 유형 | 목적 | 활용 시점 | 예시 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 가상 프록시 | 지연 초기화 | 객체 생성 비용이 클 때 | 대용량 이미지 로더 |
| 보호 프록시 | 접근 제어 | 사용자 권한을 검증할 때 | 관리자 페이지 접근 제어 |
| 로깅 프록시 | 메서드 호출 기록 | 디버깅 또는 요청 로깅 시 | API 호출 로깅 |
| Dynamic Proxy | 런타임 동적 처리 | 런타임에 추가 로직 삽입 필요 | Java Reflection 기반 |

