1. 데이터 분석 방향성
- 시계열 데이터 (datetime) 의 시간적 특성에 따른 대여량의 변화 및 차이를 확인. datetime 으로 타입을 변환한 뒤 파생변수를 생성. (day, month, dayofweek 등)
- 연속형 데이터 (temp, atemp, humidity, windspeed) 이상치 파악.
- 범주형 데이터 (season, holiday, workingday, weather) 를 시각화 하여 변수별 상관관계를 파악.
- Scaler 종류
2. 데이터 분석 과정
- 선제적으로 Baseline 코드를 GPT 사용하여 Pytorch로 변환후 제출
- 간단한 테이블 분석
- 범주형 데이터 시각화
- 시간대별 총 수요량 시각화
4번 weather 삭제
- 연속형 데이터 이상치 확인
- atemp 이상치 보완
- windspeed 이상치 보완
- 최종 결과 확인
2.1 GPT 코드 제출

0.61의 결과를 얻었고, Feature 엔지니어링을 통해 score를 낮추는 방향으로 가닥을 잡았다.
2.2 간단한 테이블 분석
2.2.1 레이블 확인
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Datetime | 시간 (YYYY-MM-DD 00:00:00) |
| Season | 봄(1) 여름(2) 가을(3) 겨울(4) |
| Holiday | 공휴일(1) 그외(0) |
| Workingday | 근무일(1) 그외(0) |
| Weather | 아주깨끗한날씨(1) 약간의 안개와 구름(2) 약간의 눈,비(3) 아주많은비와 우박(4) |
| Temp | 온도(섭씨로 주어짐) |
| Atemp | 체감온도(섭씨로 주어짐) |
| Humidity | 습도 |
| Windspeed | 풍속 |
| Casual | 비회원의 자전거 대여량 |
| Registered | 회원의 자전거 대여량 |
| Count | 총 자전거 대여량 (비회원+회원) |
Column 확인.
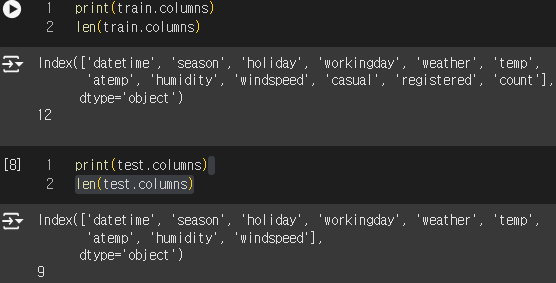
'casual' , 'registered', 'count' 유무를 통해 예측해야 할 값이 count임을 알게 되었다.
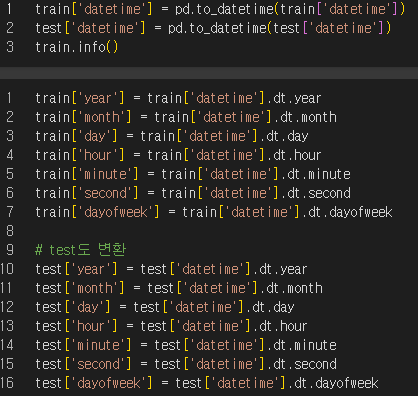
파생변수를 추출하기 위해 Datetime 컬럼을 datatime 형식으로 변환
(import datetime as dt 필요)
2.3 범주형 데이터 시각화
2.3.1 년도별 총 수요량
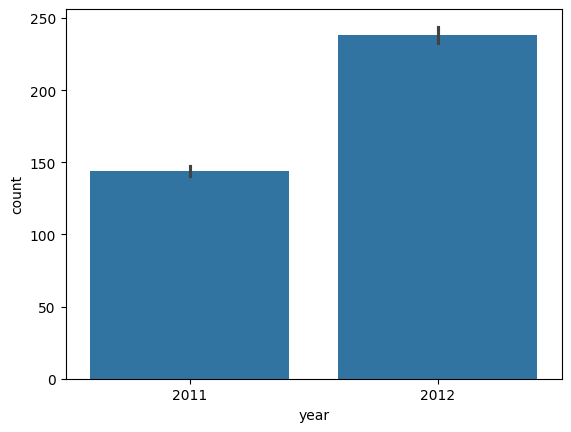
2011년에 비해서 2012년이 증가하긴 했지만 2개밖에 되지않으므로 year 변수는 사용할지 말지 고려
2.3.2 월별 총 수요량
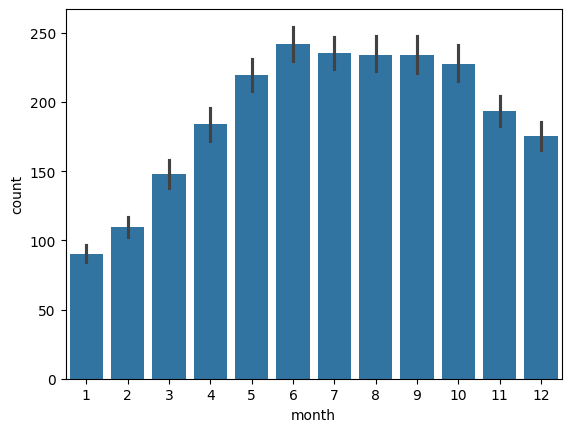
겨울(11, 12, 1, 2, ~3) 월에는 대여량이 많지 않음. month 변수는 사용가능
2.3.3 일별 총 수요량
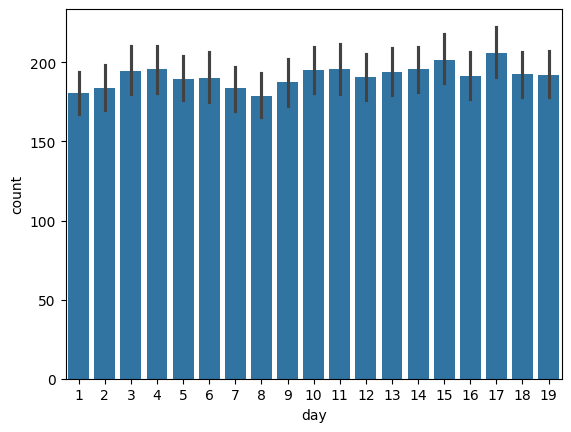
큰 차이는 없지만 변수량이 많이 않으므로 사용 고려
2.3.4 계절별 총 수요량
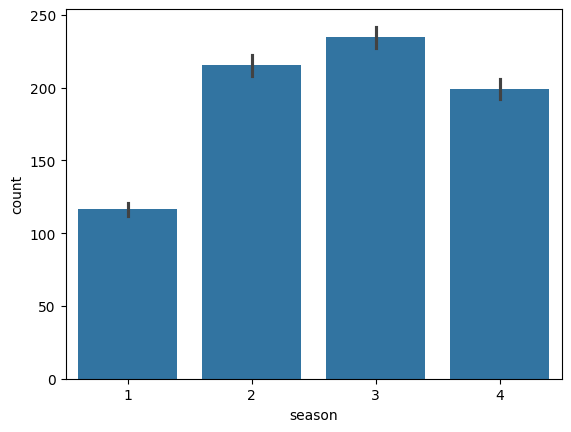
계절 별로 큰 차이가 있으므로 season은 사용
2.3.5 시간별 총 수요량
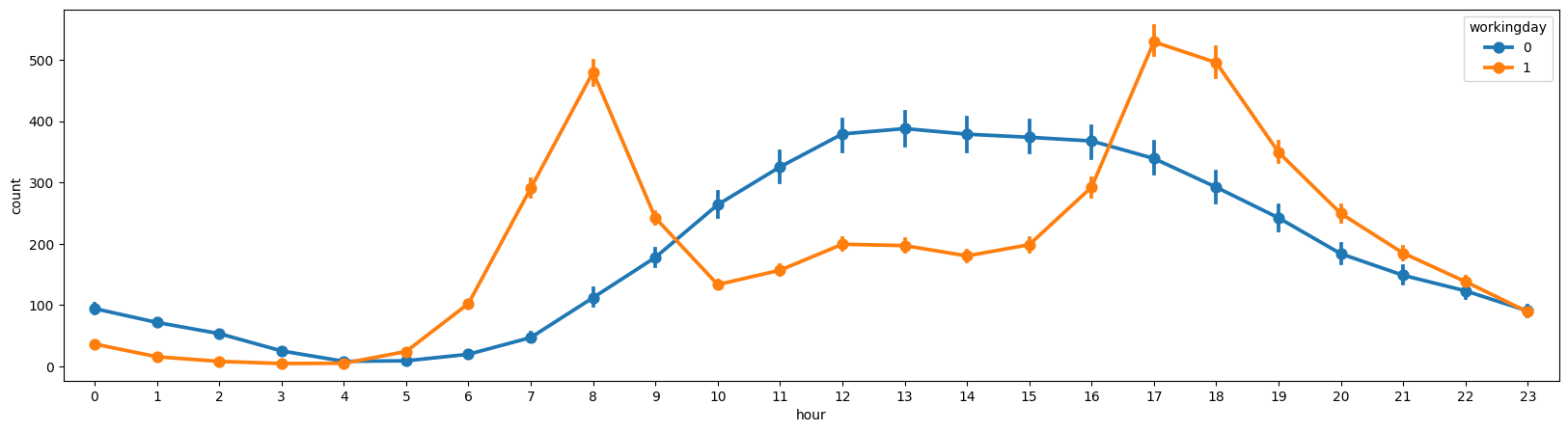
workingday=1 이면 출퇴근 시간대에 수요량이 높고, workingday=0 인 휴일에는 오후부터 수요량이 늘어나는 특징을 보임.
2.3.6 4번 weather 삭제
weather_out = train[train['weather'] != 4].copy() 
4번 날씨는 하루밖에 존재하지 않으므로 삭제를 했으나, 오히려 점수가 떨어짐.
그래서 4번 날씨는 추가하는 방식으로 접근.2.4 연속형 데이터 이상치 확인
2.4.1 atemp 이상치 보완
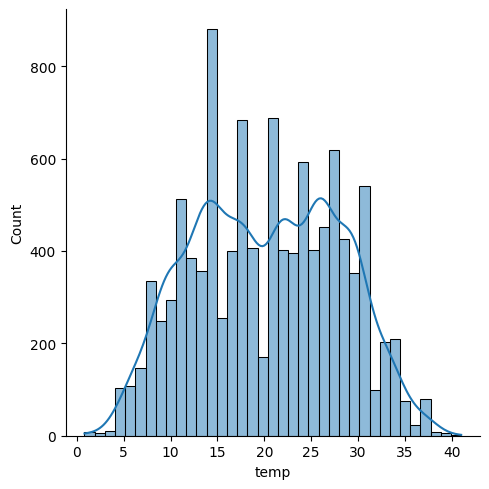
연속형 변수 [temp','atemp', 'humidity', 'windspeed']의 이상치를 확인해 보았다.
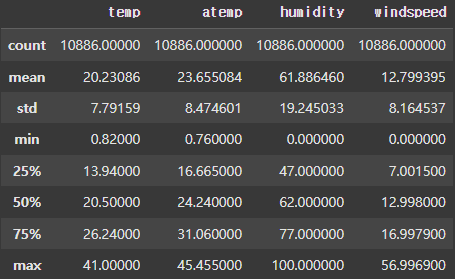 humudity(습도)와 windspeed(풍속)은 일반적으로 0일수 없기 때문에 이상치 or 결측치로 접근 고려.
humudity(습도)와 windspeed(풍속)은 일반적으로 0일수 없기 때문에 이상치 or 결측치로 접근 고려.
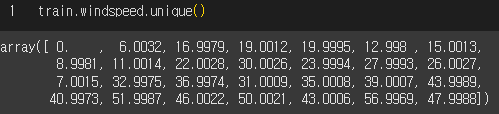
풍속이 6.0 이하이면 0으로 표기한다는 것 확인.
==================================================================
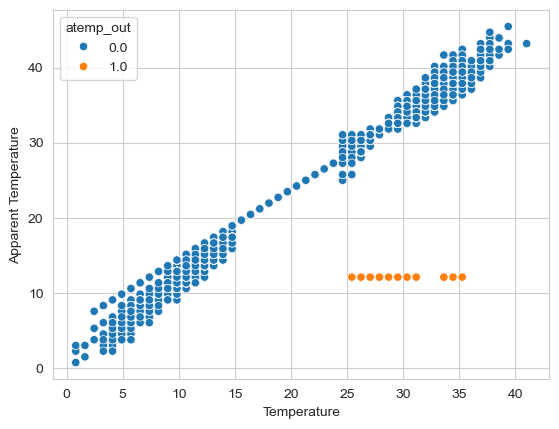
atemp 이상치 시각화(8월 12일에 모두 12.12로 기록되어있음)
def fill_atemp(train):
# atemp 이상치 기준 설정 (예: 1분위수 - 1.5*IQR 미만 또는 3분위수 + 1.5*IQR 초과)
Q1 = train['atemp'].quantile(0.25)
Q3 = train['atemp'].quantile(0.75)
IQR = Q3 - Q1
lower_bound = Q1 - 1.5 * IQR
upper_bound = Q3 + 1.5 * IQR
# 이상치에 해당하는 인덱스 저장
index_atemp = train[(train['atemp'] < lower_bound) | (train['atemp'] > upper_bound)].index
# Check if index_atemp is empty
if index_atemp.empty:
# If empty, return the original train DataFrame
return train
# 정상 범위의 데이터를 학습 데이터로 사용
X_train = train[(train['atemp'] >= lower_bound) & (train['atemp'] <= upper_bound)][['season', 'weather', 'temp', 'humidity', 'windspeed', 'month', 'hour']]
y_train = train[(train['atemp'] >= lower_bound) & (train['atemp'] <= upper_bound)]['atemp']
# 랜덤 포레스트 모델 생성 및 학습
model = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 이상치 데이터의 특성을 사용하여 체감온도 예측
y_pred = model.predict(train.loc[index_atemp, ['season', 'weather', 'temp', 'humidity', 'windspeed', 'month', 'hour']])
# 예측한 체감온도를 train 데이터에 업데이트
train.loc[index_atemp, 'atemp'] = y_pred
return train이상치를 randomforest 모델로 채워넣음. 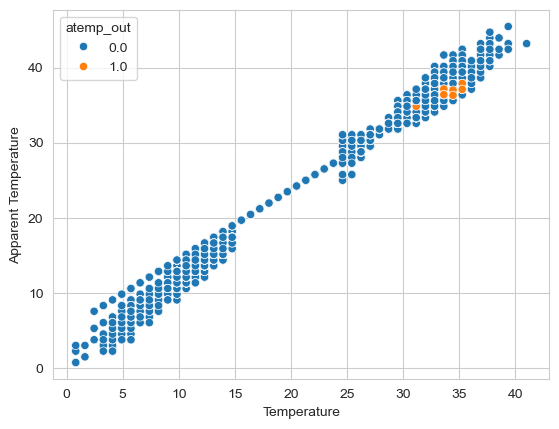
2.4.2 windspeed 이상치 보완
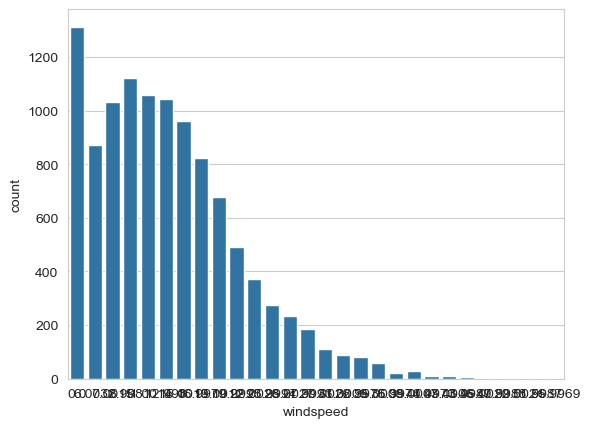
1300개 가량의 이상치가 있었음.
def fill_windspeed(train):
# 풍속이 0인/아닌 데이터 분리
df_wind_0 = train[train['windspeed'] == 0]
df_wind_not0 = train[train['windspeed'] != 0]
# 예측에 사용할 피처
features = ['season', 'weather', 'humidity', 'month', 'temp', 'day', 'hour']
# Random Forest 모델 학습
rf = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
rf.fit(df_wind_not0[features], df_wind_not0['windspeed'])
# 풍속 0인 데이터 예측
wind_pred = rf.predict(df_wind_0[features])
# 예측값으로 대체
train.loc[train['windspeed'] == 0, 'windspeed'] = wind_pred
return train똑같이 randomforest 모델 사용해서 이상치를 보완함.2.5 최종 결과

0.61 -> 0.57 성능 향상
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
# 사용자 정의 Dataset 클래스
class BikeDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, X, y=None):
self.X = torch.FloatTensor(X)
# Convert pandas Series to NumPy array before creating a tensor
self.y = torch.FloatTensor(y.values) if y is not None else None
def __len__(self):
return len(self.X)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
if self.y is not None:
return self.X[idx], self.y[idx]
return self.X[idx]
# 신경망 모델 정의
class BikeNeuralNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim):
super(BikeNeuralNetwork, self).__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Linear(input_dim, 128)
self.layer2 = nn.Linear(128, 64)
self.layer3 = nn.Linear(64, 32)
self.layer4 = nn.Linear(32, 1)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.dropout(self.relu(self.layer1(x)))
x = self.dropout(self.relu(self.layer2(x)))
x = self.dropout(self.relu(self.layer3(x)))
x = self.layer4(x)
return x.squeeze()
def fill_windspeed(train):
# 풍속이 0인/아닌 데이터 분리
df_wind_0 = train[train['windspeed'] == 0]
df_wind_not0 = train[train['windspeed'] != 0]
# 예측에 사용할 피처
features = ['season', 'weather', 'humidity', 'month', 'temp', 'day', 'hour']
# Random Forest 모델 학습
rf = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
rf.fit(df_wind_not0[features], df_wind_not0['windspeed'])
# 풍속 0인 데이터 예측
wind_pred = rf.predict(df_wind_0[features])
# 예측값으로 대체
train.loc[train['windspeed'] == 0, 'windspeed'] = wind_pred
return train
def fill_atemp(train):
# atemp 이상치 기준 설정 (예: 1분위수 - 1.5*IQR 미만 또는 3분위수 + 1.5*IQR 초과)
Q1 = train['atemp'].quantile(0.25)
Q3 = train['atemp'].quantile(0.75)
IQR = Q3 - Q1
lower_bound = Q1 - 1.5 * IQR
upper_bound = Q3 + 1.5 * IQR
# 이상치에 해당하는 인덱스 저장
index_atemp = train[(train['atemp'] < lower_bound) | (train['atemp'] > upper_bound)].index
# Check if index_atemp is empty
if index_atemp.empty:
# If empty, return the original train DataFrame
return train
# 정상 범위의 데이터를 학습 데이터로 사용
X_train = train[(train['atemp'] >= lower_bound) & (train['atemp'] <= upper_bound)][['season', 'weather', 'temp', 'humidity', 'windspeed', 'month', 'hour']]
y_train = train[(train['atemp'] >= lower_bound) & (train['atemp'] <= upper_bound)]['atemp']
# 랜덤 포레스트 모델 생성 및 학습
model = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 이상치 데이터의 특성을 사용하여 체감온도 예측
y_pred = model.predict(train.loc[index_atemp, ['season', 'weather', 'temp', 'humidity', 'windspeed', 'month', 'hour']])
# 예측한 체감온도를 train 데이터에 업데이트
train.loc[index_atemp, 'atemp'] = y_pred
return train
# 사용 예시
atemp_out = fill_atemp(train.copy())
# 데이터 전처리 함수
def preprocess_data():
train = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
test = pd.read_csv('test.csv')
# datetime 처리
for df in [train, test]:
df['datetime'] = pd.to_datetime(df['datetime'])
df['year'] = df['datetime'].dt.year
df['month'] = df['datetime'].dt.month
df['day'] = df['datetime'].dt.day
df['hour'] = df['datetime'].dt.hour
df['dayofweek'] = df['datetime'].dt.dayofweek
features = ['season', 'holiday', 'workingday', 'weather', 'temp',
'atemp','humidity', 'windspeed', 'year', 'month',
'day', 'hour', 'dayofweek']
# 제외 :
return train[features], train['count'], test[features]
# 학습 함수
def train_model(model, train_loader, criterion, optimizer, device):
model.train()
total_loss = 0
for X_batch, y_batch in train_loader:
X_batch, y_batch = X_batch.to(device), y_batch.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
y_pred = model(X_batch)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_batch)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
return total_loss / len(train_loader)
# 검증 함수
def validate_model(model, val_loader, criterion, device):
model.eval()
total_loss = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for X_batch, y_batch in val_loader:
X_batch, y_batch = X_batch.to(device), y_batch.to(device)
y_pred = model(X_batch)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_batch)
total_loss += loss.item()
return total_loss / len(val_loader)
def main():
# 데이터 전처리
X, y, X_test = preprocess_data()
# 데이터 스케일링
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X)
X_test_scaled = scaler.transform(X_test)
# 학습/검증 데이터 분리
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(
X_scaled, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42
)
# 데이터셋 및 데이터로더 생성
train_dataset = BikeDataset(X_train, y_train)
val_dataset = BikeDataset(X_val, y_val)
test_dataset = BikeDataset(X_test_scaled)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=32)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=32)
# 디바이스 설정
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# 모델 초기화
model = BikeNeuralNetwork(input_dim=X.shape[1]).to(device)
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
# 모델 학습
num_epochs = 1000
best_val_loss = float('inf')
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_loss = train_model(model, train_loader, criterion, optimizer, device)
val_loss = validate_model(model, val_loader, criterion, device)
if val_loss < best_val_loss:
best_val_loss = val_loss
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'best_model.pth')
if (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0:
print(f'Epoch [{epoch+1}/{num_epochs}], Train Loss: {train_loss:.4f}, Val Loss: {val_loss:.4f}')
# 테스트 데이터 예측
model.eval()
predictions = []
with torch.no_grad():
for X_batch in test_loader:
X_batch = X_batch.to(device)
y_pred = model(X_batch)
predictions.extend(y_pred.cpu().numpy())
# 제출 파일 생성
submission = pd.DataFrame({
'datetime': pd.to_datetime(pd.read_csv('test.csv')['datetime']).dt.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'),
'count': predictions
})
submission.to_csv('submission_08.csv', index=False)
print('제출 파일이 생성되었습니다.')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()