Object클래스
- 모든 클래스의 최상위 클래스
- java.lang.Object 클래스
- 모든 클래스는 Object클래스에서 상속받음
- 모든 클래스는 Object클래스의 메서드를 사용할 수 있음
- 모든 클래스는 Object클래스의 일부 메서드를 재정의하여 사용할 수 있음
package object;
class Book{
String title;
String author;
public Book(String title, String author) {
this.title=title;
this.author=author;
}
//toString은 object의 메서드이며, 어떤 객체의 정보를 string형태로 표현해야할 때 호출되는 메서드
//String클래스 안에 가지고 있는 character의 배열을 출력
@Override
public String toString() {
return author + ","+title;
}
}
public class ToStringTest extends Object{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//오버라이딩안하면 객체의 주소만 출력하게 됨
//object.Book@6f539caf
Book book=new Book("토지","박경리");
System.out.println(book);
String str=new String("토지");
System.out.println(str.toString());
}
}toString()메서드
-
toString()메서드의 원형
getClass().getName() + '@' + Integer.toHexString(hashCode())
-
객체의 정보를 String으로 바꾸어 사용할 때 유용함
-
자바 클래스 중에는 이미 정의된 클래스가 많음 ex) String,Integer,Calendar 등
-
많은 클래스에서 재정의하여 사용
equals()메서드
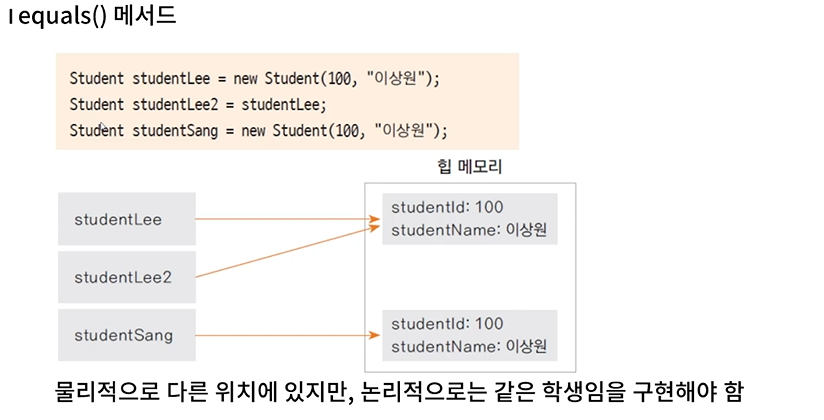
- 두 객체의 동일함을 논리적으로 재정의할 수 있음
- 물리적 동일함 : 같은 주소를 가지는 객체
- 논리적 동일함 : 같은 학번의 학생, 같은 주문 번호의 주문
- 물리적으로 다른 메모리에 위치한 객체라도 논리적으로 동일함을 구현하기 위해 사용하는 메서드
hashCode()메서드
- hashCode()메서드의 반환 값 : 인스턴스가 저장된 가상머신의 주소를 10진수로 반환
- 두 개의 서로 다른 메모리에 위치한 인스턴스가 동일하다는 것은?
- 논리적으로 동일 : equals()의 반환값이 true
- 동일할 hashCode값을 가짐 : hashCode()의 반환값이 동일
package object;
class Student{
int studentNum;
String studentName;
public Student(int studentNum,String studentName) {
this.studentName=studentName;
this.studentNum=studentNum;
}
//같은 객체의 논리적 동일함(다른 메모리에 위치하더라도 논리적으로 동일함)
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj instanceof Student) {
//Student클래스에 인스턴스화하여 obj를 다운캐스팅함
Student std=(Student)obj;
return(this.studentNum == std.studentNum);
}
return false;
}
//studentNum객체를 해시코드로 반환
//100
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return studentNum;
}
}
public class EqualsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
String str1=new String("abc");
String str2=new String("abc");
//str1과 str2의 메모리가 같은가? false
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
//str1과 str2의 문자열이 같은가? true
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));
Student Lee=new Student(100,"이순신");
Student Lee2=Lee;
Student Shin=new Student(100,"이순신");
//인스턴스 주소가 다르므로 false
System.out.println(Lee==Shin);
System.out.println(Lee.equals(Shin));
//인스턴스가 저장된 가상머신의 주소를 10진수로 반환
//1867750575
System.out.println(Lee.hashCode());
System.out.println(Shin.hashCode());
*/
Integer i1=new Integer(100);
Integer i2=new Integer(100);
//두 객체가 같을 때 두 객체가 반환하는 해시코드값도 동일하게끔 오버라이딩함
System.out.println(i1.equals(i2));
System.out.println(i1.hashCode());
System.out.println(i2.hashCode());
//실제 가지고 있는 해시코드값이 얼마인지 비교 ->동일하지않음 ->메모리값이 다르다
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(i1));
System.out.println(System.identityHashCode(i2));
}
}clone()메서드
- 객체의 복사본을 만듦
- 기본 틀(prototype)으로부터 같은 속성 값을 가진 객체의 복사본을 생성할 수 있음
- 객체지향 프로그래밍의 정보은닉에 위배되는 가능성이 있으므로 복제할 객체는 cloneable 인터페이스를 명시해야함
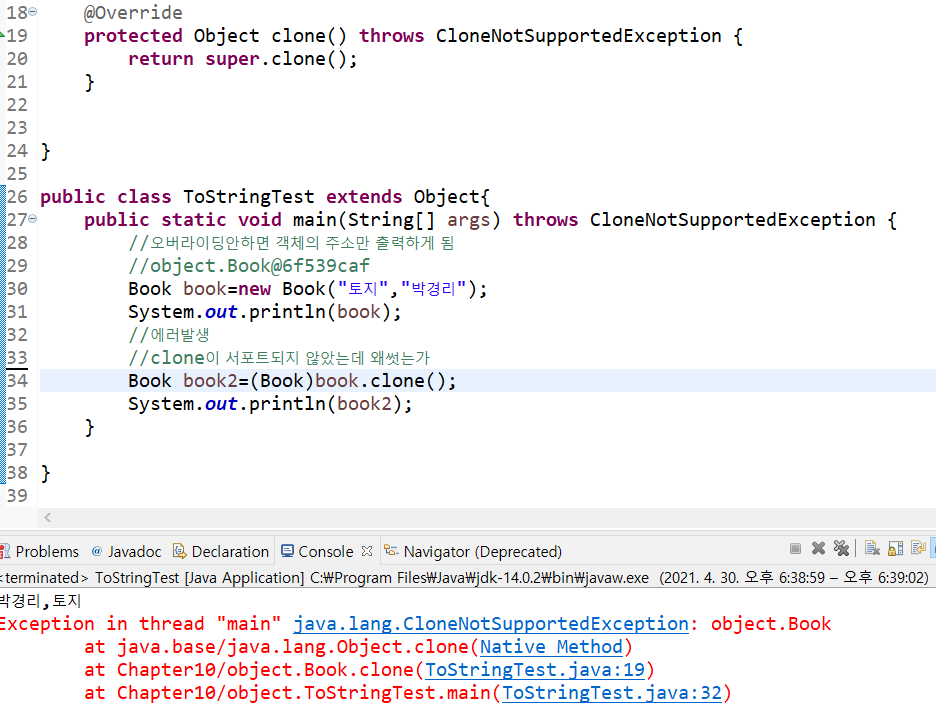
clone이 서포트되지 않았는데 썼다고 에러발생함
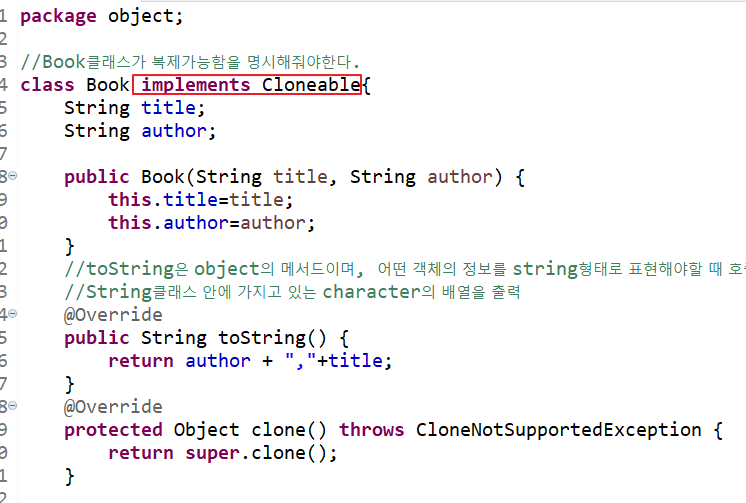
Cloneable을 인터페이스화하여 book클래스가 복제가능하다는 것을 명시해야함
package object;
//Book클래스가 복제가능함을 명시해줘야한다.
class Book implements Cloneable{
String title;
String author;
public Book(String title, String author) {
this.title=title;
this.author=author;
}
//toString은 object의 메서드이며, 어떤 객체의 정보를 string형태로 표현해야할 때 호출되는 메서드
//String클래스 안에 가지고 있는 character의 배열을 출력
@Override
public String toString() {
return author + ","+title;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
//Object의 finalize메서드는 이 객체가 팀 메모리에서 해제될 때 가비지콜렉터에서 호출되는 메서드
//toString,hashcode,clone과 다르게 직접불리는 메서드가 아님
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
super.finalize();
}
}
public class ToStringTest extends Object{
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//오버라이딩안하면 객체의 주소만 출력하게 됨
//object.Book@6f539caf
Book book=new Book("토지","박경리");
System.out.println(book);
Book book2=(Book)book.clone();
System.out.println(book2);
}
}코딩해보세요
날짜를 구현한 클래스 Mydate가 있습니다.
날짜가 같으면 equals()메서드의 결과가 true가 되도록 구현해보세요.
hashCode()메서드도 구현해보세요.
package object;
class MyDate {
int day;
int month;
int year;
public MyDate(int day, int month, int year) {
this.day = day;
this.month = month;
this.year = year;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof MyDate) {
MyDate date=(MyDate)obj;
return (this.day == date.day && this.year==date.year && this.month==date.month);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return day*11+month*101+year*1001;
}
}
public class MyDateTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyDate date1=new MyDate(10, 12, 2020);
MyDate date2=new MyDate(10,12,2020);
System.out.println(date1.equals(date2));
System.out.println(date1.hashCode());
System.out.println(date2.hashCode());
}
}