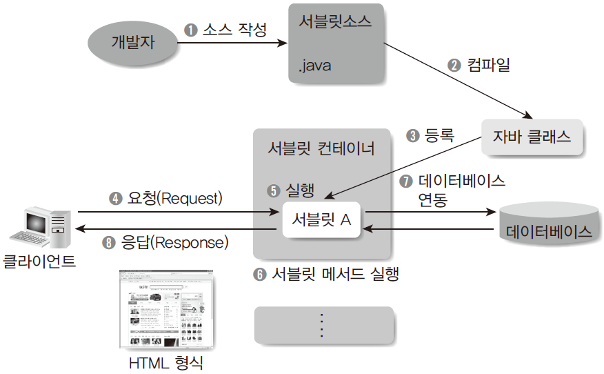
POST 방식 요청 및 응답
✔️ POST 방식 : GET 방식과는 다르게 주소 뒤에 전달하는 값이 붙는게 아니다
HTTP Protocol의 body 부분에 숨겨져서 전달되는 방식
✔️ 장점 : 길이 제한 X, 보안성 향상(데이터가 직접적으로 보이지 않음)
✔️ 단점 : 캐싱 불가능, 추가적인 문자 인코딩 처리가 필요
회원가입 만들기
1) index.html 만들기
<form action="/ServletProject1/signUp" method="POST">
아이디 : <input type="text" name="inputId"> <br>
비밀번호 : <input type="password" name="inputPw"> <br>
비밀번호 확인 : <input type="password" name="inputPw"> <br>
이메일 : <input type="email" name="inputEmail"> <br>
이메일 수신 동의(선택) <input type="checkbox" name="agree"> <br>
<button>가입하기</button>
</form>
2) Servlet 만들기
@WebServlet("/signUp")
public class ServletEx3 extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
String inputId = req.getParameter("inputId");
String[] inputPw = req.getParameterValues("inputPw");
String email = req.getParameter("inputEmail");
String agree = req.getParameter("agree");
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
out.println("<!DOCTYPE html>");
out.println("<html>");
out.println("<head> <title>회원 가입 결과</title></head>");
out.println("<body>");
if(inputPw[0].equals(inputPw[1])){
out.printf("<h3>%s님 환영합니다</h3>", inputId);
if(agree != null) {
out.println("<h3>이메일 동의 수신 여부 : O</h3>");
out.printf("<h3>수신할 이메일 : %s</h3>", email);
} else {
out.println("<h3>이메일 동의 수신 여부 : X</h3>");
}
} else {
out.println("<h1 style='color:red'>비밀번호가 일치하지 않습니다.</h1>");
}
out.println("</body>");
out.println("</html>");