
이번엔 pandas에 대한 기본 툴을 배우는 시간을 가졌습니다. 우선 개략적으로 정리했던 .ipynb에서의 필기 내용을 기록해놓겠습니다.
TIL
I. pandas 시작하기
Table
- 행과 열을 이용해 데이터를 저장, 관리하는 자료구조(컨테이너))
- 주로, 행은 개체, 열은 속성을 나타냄
import pandas as pdII. pandas로 1차원 데이터 다루기 - Series
Series
- 1-D labeled array
- 인덱스를 지정할 수 있음.
s = pd.Series([1,4,9,16,25])
s
딕셔너리 형태로 index name을 구성할 수 있습니다.
t= pd.Series({'one':1, 'two':2, 'three':3, 'four':4})
t
bool index 이용하여 값을 도출할 수도 있습니다.
t[t>t.median()]
s[[3,1,2]] # 여러 index호출
Series를 함수에도 담을 수 있습니다.
import numpy as np
e = np.exp(s)
Series + dict
'one' in t # output : True
'seven' in t # output : False
t['seven']=t.get('seven',7) # 존재하지 않는 key -> 7을 return하여 저장합니다.
t['seven'] # output : 7series 이름 붙이기
- Series()내 name 속성을 가지고 있다.
s = pd.Series(np.random.normal(loc=1, scale=0.3,size=(10,)), name = 'Normalizatoin')
s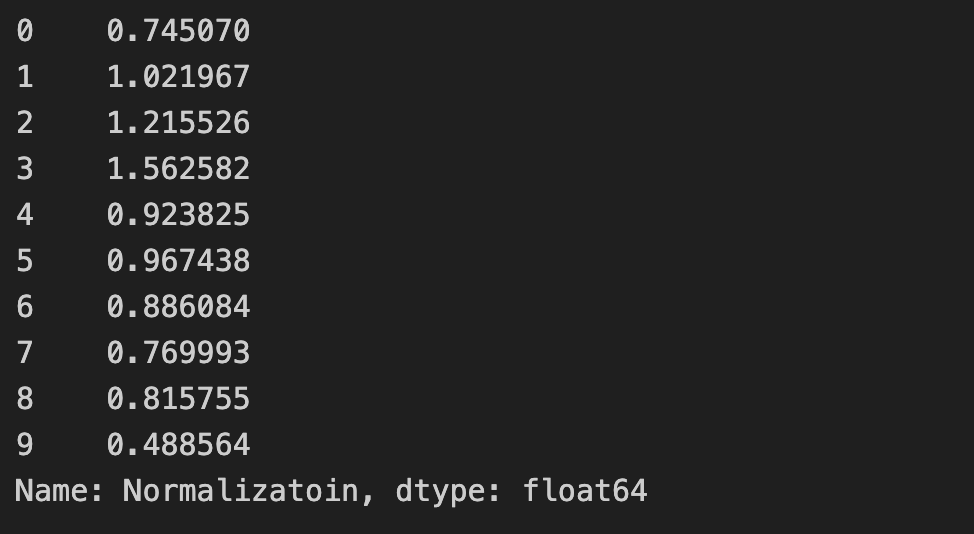
III. Pandas로 2차원 데이터 다루기 - dataframe
- 2-D labeled table
- 인덱스 지정 가능
- 시리즈의 병렬적인 모음
d = {"height":[1,2,3,4],"weight":[30,40,50,60]}
df = pd.DataFrame(d)
df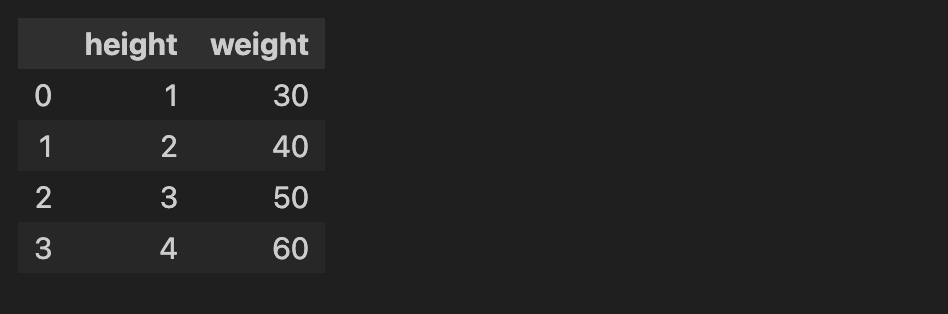
데이터 프레임의 data type을 확인합니다.
# dtype 확인
df.dtypes
From CSV to dataframe
.csv파일을 읽어온다.- Comma Saperated Value -> DataFrame
.read_csv()
ex1= pd.read_csv('../3w/archive/country_wise_latest.csv')
ex1.head(5) # 처음 5개 행 보여주기ex1.tail(5) # 마지막 5개행 보여주기ex1.describe()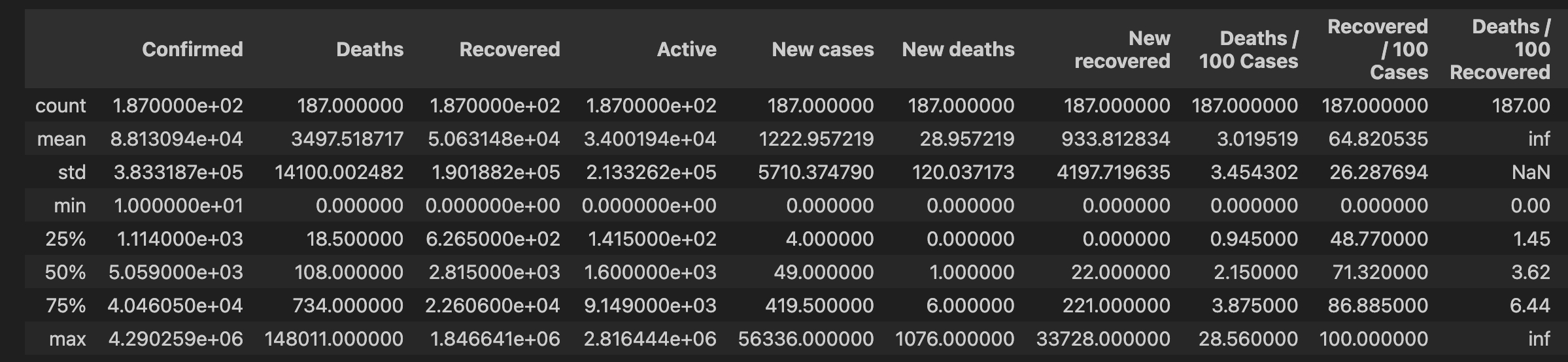
data 접근하기
df['Deaths / 100 Cases'`#해당 열을 추출행에 bool index를 부여하여 해당 조건을 만족하는 True인 행들의 해당 열만 뽑아올 수 있습니다.
# 신규 확진자 100명이 넘는 나라 찾기
ex1[ex1['New cases']>=100]['Country/Region']행기준 데이터 접근
- 인덱스 이름 이용 :
.loc[row,col]
books = pd.read_csv('../path')
# 이때는 index name이 번호라 번호를 활용한것
# 이름이 있다면 row자리에 index name을 적으면 됨.
books.loc[9064,'Lat'] 23.885942- 인덱스 번호 이용
.iloc[row_idx, col_idx]
books.iloc[9064,2]23.885942groupby
- split : 특정 '기준'을 바탕으로 dataFrame 분할
- Apply : 통계 함수 -
sum(),mean(),median()을 적용하여 각 데이터 압축 - Combine : Apply된 결과를 바탕으로 새로운 Series 생성
avo.head() # 이 데이터 프레임에 groupby를 적용한 예문이 mission3에 있습니다.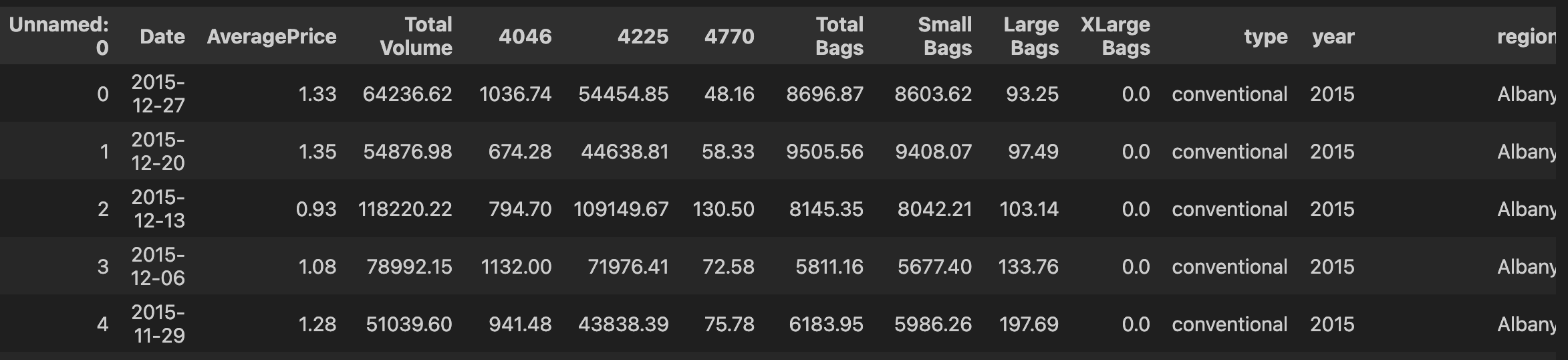
Mission:
1. covid 데이터에서 100 case 대비 사망률(Deaths / 100 Cases)이 가장 높은 국가는?
df = pd.read_csv('../3w/archive/country_wise_latest.csv')
df[df['Deaths / 100 Cases']== df['Deaths / 100 Cases'].max()]['Country/Region']
2. covid 데이터에서 신규 확진자가 없는 나라 중 WHO Region이 'Europe'를 모두 출력하면?
Hint : 한 줄에 동시에 두가지 조건을 Apply하는 경우 Warning이 발생할 수 있습니다.
no_case= df[df['New cases']==0]
no_case[no_case['WHO Region']=='Europe']['Country/Region']
3. 다음 데이터를 이용해 각 Region별로 아보카도가 가장 비싼 평균가격(AveragePrice)을 출력하면?
# 1. 'AveragePrice'열 중에서
# 2. 'region' 별 max치를 뽑아옴.
avo = pd.read_csv('../3w/archive/avocado.csv')
g = avo[['AveragePrice']].groupby(avo['region']).max()
g.head()
g
