다른분(AWS 루트사용자)한테 access Key들을 받은 상태에서 시작!
1. 의존성 추가
/* build.gradle */
dependencies {
...
implementation "com.amazonaws:aws-java-sdk-s3:1.12.281" // 추가
}2. application.properties 작성
# S3
cloud.aws.region.static=ap-northeast-2
cloud.aws.stack.auto-=false
# 아래 세 항목은 git에 올라가지 않도록 조심!
cloud.aws.credentials.accessKey=ACCESS_KEY
cloud.aws.credentials.secretKey=SECRET_KEY
cloud.aws.s3.bucket=BUCKET_NAME3. AWS S3 Config 작성
/* AwsConfig.java */
@Configuration
public class AwsConfig {
@Value("${cloud.aws.credentials.accessKey}")
private String accessKey;
@Value("${cloud.aws.credentials.secretKey}")
private String secretKey;
@Value("${cloud.aws.region.static}")
private String region;
@Bean
public AmazonS3 amazonS3() {
AWSCredentials awsCredentials = new BasicAWSCredentials(accessKey, secretKey);
return AmazonS3ClientBuilder.standard()
.withRegion(region)
.withCredentials(new AWSStaticCredentialsProvider(awsCredentials))
.build();
}
}application.properties에 작성한 값들을 불러와서 AmazonS3Client인 객체 amazonS3를 만든 다음에 Bean으로 등록해준다.
4. S3Service 코드
작업상 편의를 위해 S3에 직접 접근하는 코드는 S3Service.java 안에 모아두고, 필요할때 꺼내쓰도록 하겠다.
/* S3Service.java */
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class S3Service {
@Value("${cloud.aws.s3.bucket}")
private String bucket;
private final AmazonS3 amazonS3;
/* 1. 파일 업로드 */
public String upload(MultipartFile multipartFile, String s3FileName) throws IOException {
// 메타데이터 생성
ObjectMetadata objMeta = new ObjectMetadata();
objMeta.setContentLength(multipartFile.getInputStream().available());
// putObject(버킷명, 파일명, 파일데이터, 메타데이터)로 S3에 객체 등록
amazonS3.putObject(bucket, s3FileName, multipartFile.getInputStream(), objMeta);
// 등록된 객체의 url 반환 (decoder: url 안의 한글or특수문자 깨짐 방지)
return URLDecoder.decode(amazonS3.getUrl(bucket, s3FileName).toString(), "utf-8");
}
/* 2. 파일 삭제 */
public void delete (String keyName) {
try {
// deleteObject(버킷명, 키값)으로 객체 삭제
amazonS3.deleteObject(bucket, keyName);
} catch (AmazonServiceException e) {
log.error(e.toString());
}
}
/* 3. 파일의 presigned URL 반환 */
public String getPresignedURL (String keyName) {
String preSignedURL = "";
// presigned URL이 유효하게 동작할 만료기한 설정 (2분)
Date expiration = new Date();
Long expTimeMillis = expiration.getTime();
expTimeMillis += 1000 * 60 * 2;
expiration.setTime(expTimeMillis);
try {
// presigned URL 발급
GeneratePresignedUrlRequest generatePresignedUrlRequest = new GeneratePresignedUrlRequest(bucket, keyName)
.withMethod(HttpMethod.GET)
.withExpiration(expiration);
URL url = amazonS3.generatePresignedUrl(generatePresignedUrlRequest);
preSignedURL = url.toString();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(e.toString());
}
return preSignedURL;
}
}🗝️ keyName은 객체를 고유하게 구별하는 키값, 즉 간단히 말해서 그냥 파일명이다. (폴더명까지 포함한 파일명)
(1) 파일 업로드
- 코드
/* Controller */
public ResponseEntity<?> submitFiles (@RequestParam("images") List<MultipartFile> multipartFileList) throws IOException {
return submitService.submitFiles(multipartFileList);
}/* Service */
public ResponseEntity<?> submitFiles (List<MultipartFile> multipartFileList) throws IOException {
...
List<String> imageUrlList = new ArrayList<>();
for (MultipartFile multipartFile : multipartFileList) {
// 파일명 지정 (겹치면 안되고, 확장자 빼먹지 않도록 조심!)
String fileName = UUID.randomUUID() + multipartFile.getOriginalFilename();
// 파일데이터와 파일명 넘겨서 S3에 저장
s3Service.upload(multipartFile, fileName);
// DB에는 전체 url말고 파일명으로 저장할 것임
imageUrlList.add(fileName);
}
Submit submit = Submit.builder()
...
.imageUrl(imageUrlList)
.build();
...
return ResponseEntity.ok().build();
}- 테스트
form data로 이미지를 보내면
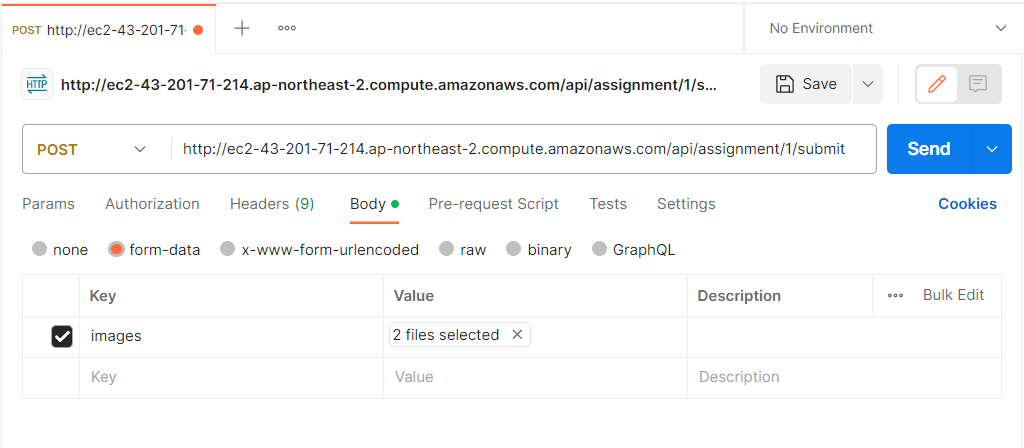
DB에는 keyName이 저장되고
🗂️ 전체 url을 저장하는것보다 keyName만 저장하는게 이후 삭제, presigned URL 발급 등 파일 관리하는데 편리해서 keyName만 저장했다.

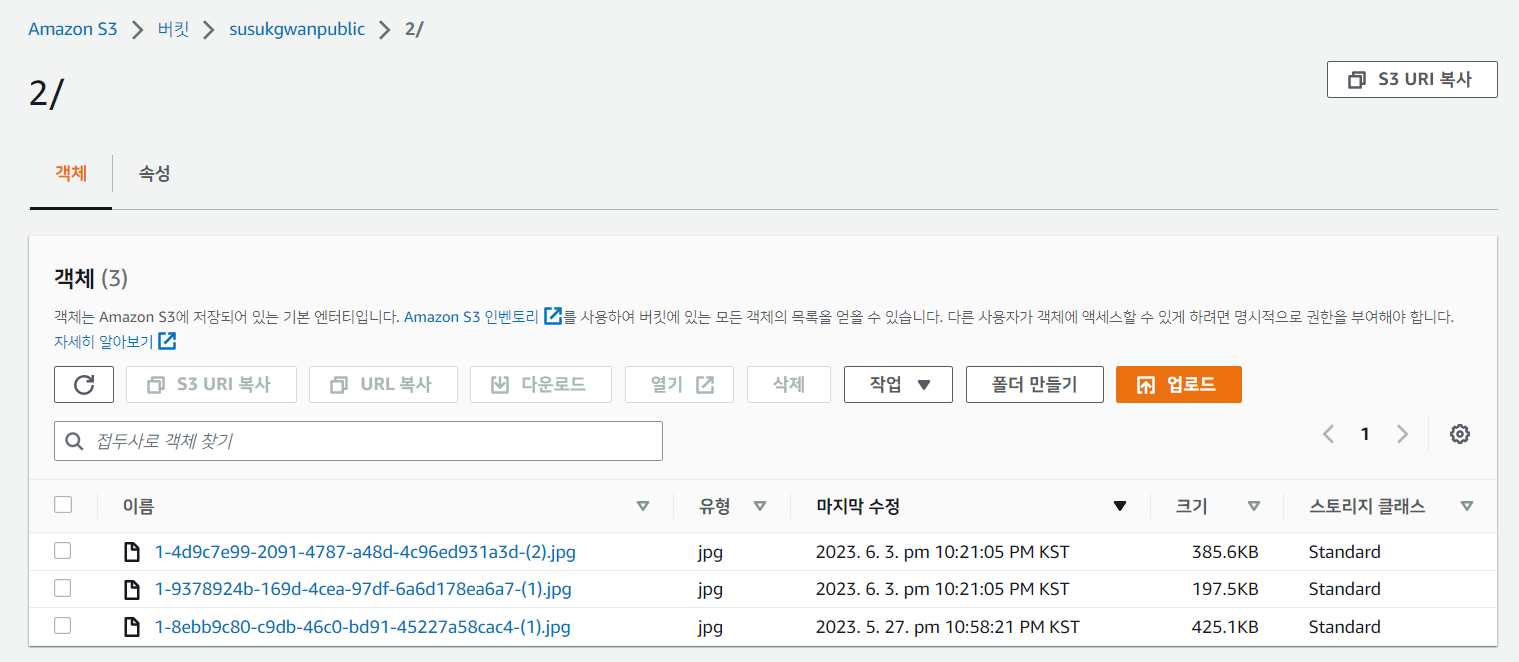
AWS S3에도 정상적으로 객체가 등록됐다.
(2) 파일 삭제
파일 삭제는 간단하다. 버킷이름과 키값만 알면 amazonS3.deleteObject(bucket, keyName); 이 코드 한줄로 삭제된다.
다만 이 파일을 가지고 있는 스프링 객체를 삭제할때, S3 파일도 같이 삭제되는게 아니기 때문에 따로 삭제해줘야 하는 부분이 포인트인듯.
/* Service */
public ResponseEntity<?> deleteSubmit (Long submitId) {
...
if (submit.isPresent()) {
List<String> S3Urls = submit.get().getImageUrl();
for (String url : S3Urls) {
s3Service.delete(url); // S3에 업로드된 이미지들 삭제 먼저
}
submitRepository.deleteById(submitId); // 숙제 인증피드 삭제
return ResponseEntity.ok().build();
} else {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND).body(new ResponseMsg(ResponseMsgList.NOT_EXIST_SUBMIT.getMsg()));
}
}(3) presigned URL 발급
이제 이미지를 받아볼 차례. 그런데 S3에 등록된 객체 url에 접근하면
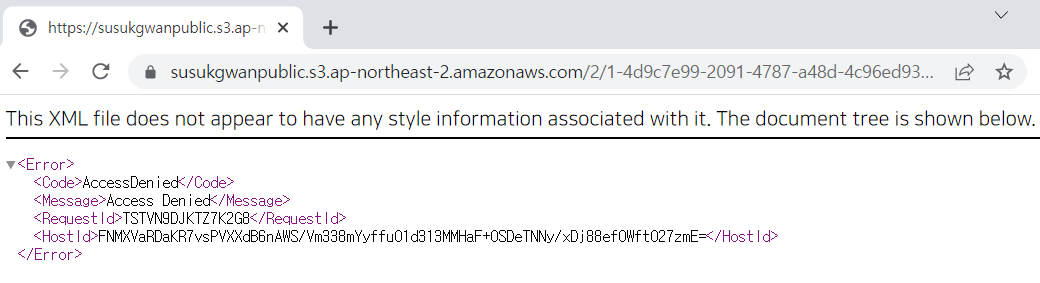
이렇게 뜨고 이미지를 받아볼 수 없다. 이미지에 접근할 권한이 없기 때문인데, 이를 해결하려면 접근 권한을 public으로 바꾸는 방법이 있다. 그러나 내가 원하는 것은 이미지를 누구나 볼 수 있도록 열어두는게 아니라, 접근권한이 있는 일부 사용자에게만 보이는 것이었다.
그러다 찾은 방법이 presigned URL인데, 이 url을 가지고 있는 사람은 누구든지 만료기한까지 해당 이미지에 접근할 수 있다. 내가 따로 로직을 짜서(너무 길어서 포스팅에서는 제외) 파일에 접근할 수 있는 사람에게만 presigned URL을 발급해주면 이미지 보안 문제를 해결할 수 있지 않을까? 해서 프로젝트에 도입해보았다.
- 코드
/* SubmitResponseDTO */
@Getter
@Setter
public class SubmitResponseDTO { /* Submit 응답 DTO */
private Long id;
private LocalDateTime dateTime;
private Long rate;
private List<String> imageUrl = new ArrayList<>();
public SubmitResponseDTO(Submit submit, S3Service s3Service) {
this.id = submit.getId();
this.dateTime = submit.getDateTime();
this.rate = submit.getRate();
for (String keyName : submit.getImageUrl()) {
this.imageUrl.add(s3Service.getPresignedURL(keyName));
}
}
}/* Service */
public ResponseEntity<?> submitListOfAssignment (Long assignmentId) {
...
List<Submit> submitList = submitRepository.GetSubmitListByAssignmentId(assignmentId);
List<SubmitResponseDTO> responseList = submitList.stream().map(o->new SubmitResponseDTO(o, s3Service)).collect(Collectors.toList());
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(responseList);
}- 테스트
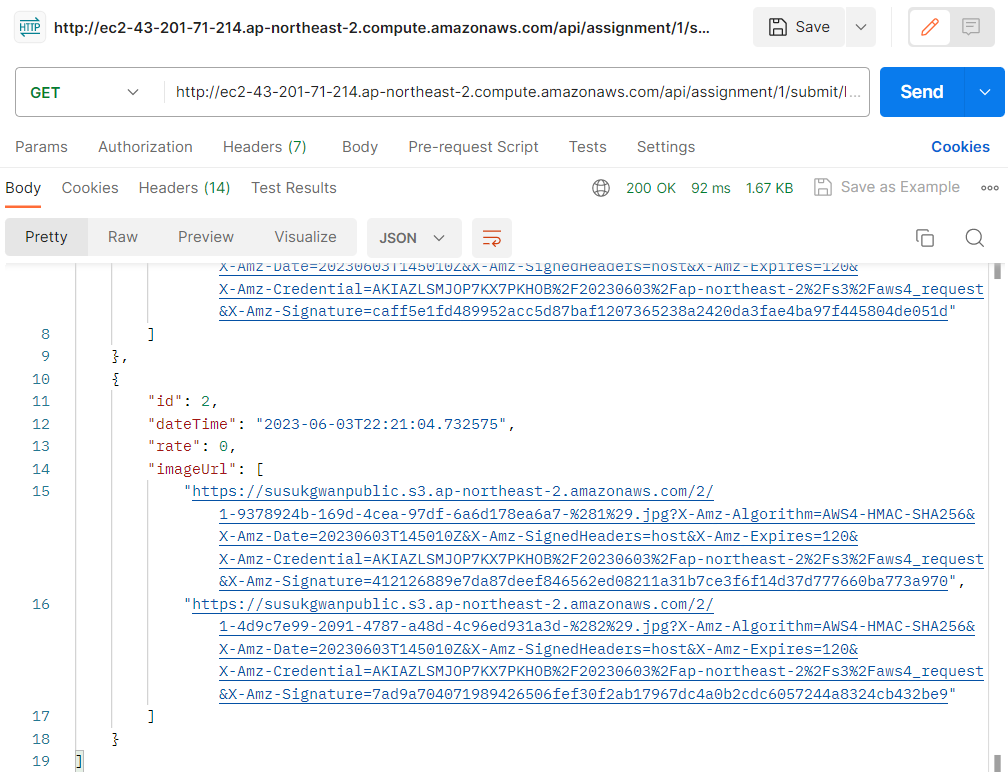
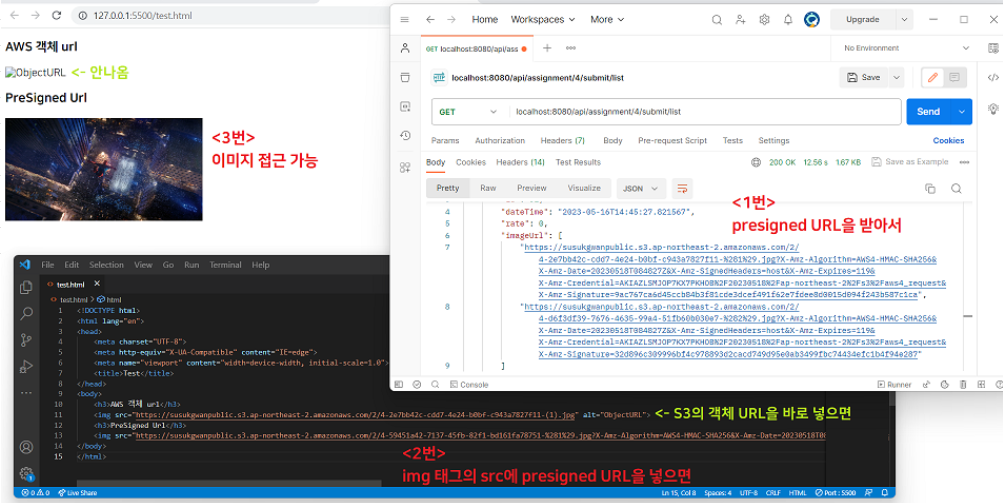
이 presigned URL에 접근하면
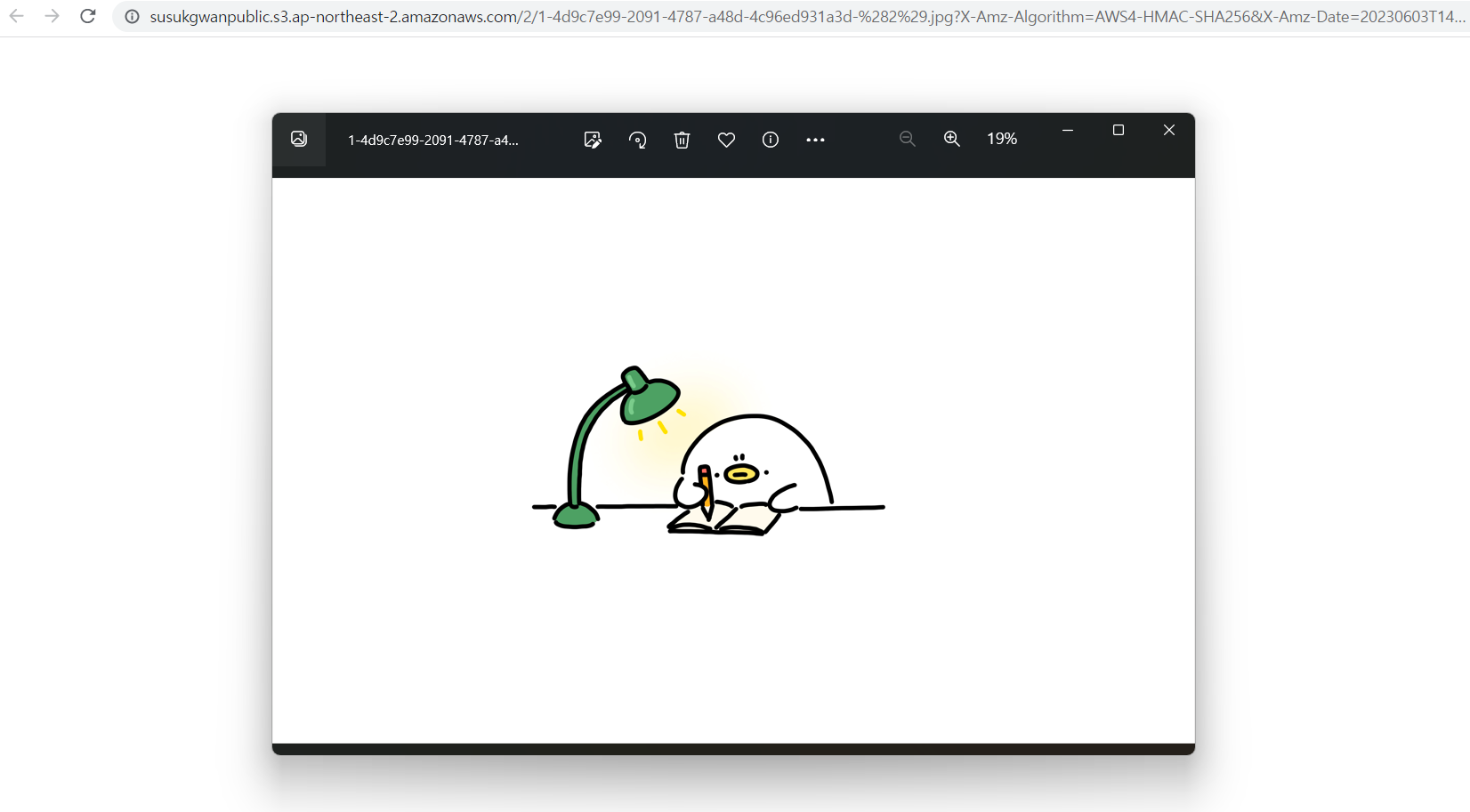
이렇게 이미지를 받아볼 수 있다.
하지만 만료기한(2분)이 지나면 이 url로도 접근할 수 없게 된다.
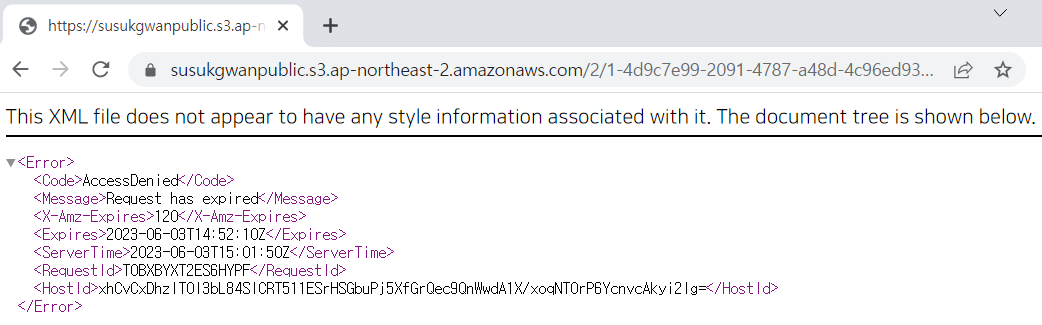
cf) 이미지태그 사용 예시
Reference
[Spring] Spring Boot AWS S3 사진 업로드 하는 법
Spring Boot | S3 Pre-Signed URL 생성