첫번째 Team Proeject 기록.
Project 아이디어 및 선정
역할
나의 역활은 제품 설계및 3D프린팅, Raspberry Pi를 이용하여 28ybj-48와 NS-IRPSM 구동 및 서버에 값 올리고 받기 이다. (한명과 같이 협업을 하였다.)
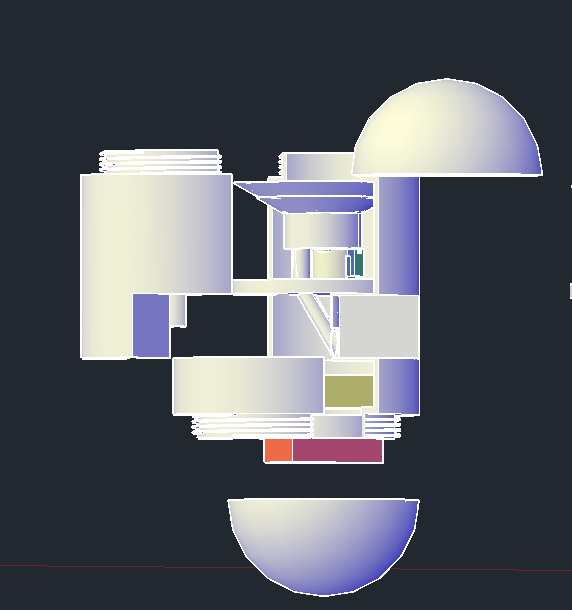
제품 설계 및 3D프린팅
AUTO CAD에서 사용한 단축키
| 단축키 | 의미 |
|---|---|
| L | 선 |
| HEXLIX | 나선 - t(회전 수), h(높이) |
| 3DROTATE | 3D 회전 |
| MOVE | 도형 움직이기 |
| PL | 연결된 선 작성 |
| J | 결합 |
| F8 | 직교모드 |
| REG | 평면작성 |
| REV | 3D 회전 돌출 |
| HEL | 나선 만들기 |
| SWEEP | 곡선을 따라 3D 혹은 표면 작성 |
| MIRROR | 대칭사본작성 |
| SL | 3D도형 자르기 -3(3군데 클릭으로 자르기) |
| TR | 부분 자르기 |
| EXT | 2D나 3D 곡선 돌출시켜 솔리드 또는 평면 만들기 |
| DLI | 일자 치수재기 |
| DAL | 사선 치수재기 |
| DAN | 각도 재기 |
| DDI | 지름 재기 |
| DRA | 반지름 재기 |
| UNI | 합집합 |
| SUB | 차집합 |
| SC | 배율로 크기설정 가능 |
| SHA | 뷰 |
완성본
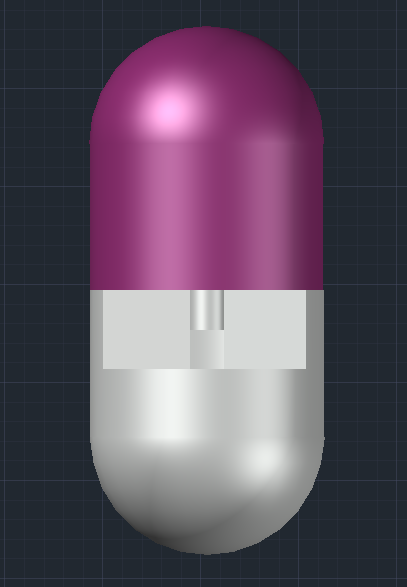

코드 및 설명
코드를 보기 전 GPIO모듈의 기본적인 함수들은 이 블로그를 참고하면 된다.
https://m.blog.naver.com/pk3152/221368513358
Raspberry Pi로 센서 구동
Raspberry Pi를 이용하여 28ybj-48와 NS-IRPSM 구동하는 코드이다.
Raspberry Pi로 28ybj-48 구동
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
# 해당 모델을 사용하기 위해 python code를 작성할 때 import 해줘야 한다.
import time
in1 = 17
in2 = 18
in3 = 27
in4 = 22
# careful lowering this, at some point you run into the mechanical limitation of how quick your motor can move
step_sleep = 0.002
step_count = 4096 # 5.625*(1/64) per step, 4096 steps is 360°
direction = False # 시계방향일 때 True 시계반대방향일 때 False
# defining stepper motor sequence (found in documentation http://www.4tronix.co.uk/arduino/Stepper-Motors.php)
step_sequence = [[1,0,0,1],
[1,0,0,0],
[1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0],
[0,1,1,0],
[0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1],
[0,0,0,1]]
# setting up
GPIO.setmode( GPIO.BCM )
GPIO.setup( in1, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( in2, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( in3, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( in4, GPIO.OUT )
# initializing
GPIO.output( in1, GPIO.LOW )
GPIO.output( in2, GPIO.LOW )
GPIO.output( in3, GPIO.LOW )
GPIO.output( in4, GPIO.LOW )
motor_pins = [in1,in2,in3,in4]
motor_step_counter = 0
def cleanup():
GPIO.output( in1, GPIO.LOW )
GPIO.output( in2, GPIO.LOW )
GPIO.output( in3, GPIO.LOW )
GPIO.output( in4, GPIO.LOW )
GPIO.cleanup()
# the meat
try:
i = 0
for i in range(step_count):
for pin in range(0, len(motor_pins)):
GPIO.output( motor_pins[pin], step_sequence[motor_step_counter][pin] )
if direction==True:
motor_step_counter = (motor_step_counter - 1) % 8
elif direction==False:
motor_step_counter = (motor_step_counter + 1) % 8
else: # defensive programming
print( "uh oh... direction should *always* be either True or False" )
cleanup()
exit( 1 )
time.sleep( step_sleep )
except KeyboardInterrupt:
cleanup()
exit( 1 )
cleanup()
exit( 0 )Raspberry Pi로 NS-IRPSM 구동
#importing the library of RPi.GPIO
#importing the library of time
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
sensor = 16
#시작과 동시에 Object detected를 하므로 default 값을 -1로 선언
count =-1
#declaring BCM pin 16 which is GPIO 23 of Raspberry Pi
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD)
#declaring the BCM mode of pins
GPIO.setup(sensor,GPIO.IN)
#set the behaviour of sensor as input
try:
while True:
#initiated a infinite while loop
if GPIO.input(sensor):
#checking input on sensor
count+=1
print("count : {}, Object detected".format(count))
while GPIO.input(sensor):
#checking input on sensor again
time.sleep(0.01)
#generate time delay of 0.2 seconds
except KeyboardInterrupt:
#if any key is pressed on keyboard terminate the program
GPIO.cleanup()
#cleanup the GPIO pins for any other program useRaspberry Pi로 서버에서 값 Get
#onem2m 가장 최신 리소스 가져오기(get la)
import requests
url = 'http://203.253.128.177:7579/Mobius/phone/data/la'
headers = {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'X-M2M-RI': '12345',
'X-M2M-Origin': 'SluN3OkDey-',
'Content-Type': 'application/vnd.onem2m-res+json; ty=4'
}
r = requests.get(url, headers = headers)
try:
r.raise_for_status()
jr = r.json()
print(jr["m2m:cin"]["con"])
except Exception as exc:
print("There was a problem : %s".format(exc))28ybj-48가 DATA 마지막 서버 값 Get
#final
#휴대폰에서 서버에 값을 올리면 기기가 값을 실시간으로 받아온 다음 모터를 구동하는 로직
import requests
import time
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
in1 = 17
in2 = 18
in3 = 27
in4 = 22
# careful lowering this, at some point you run into the mechanical limitation of how quick your motor can move
step_sleep = 0.002
step_count = 4096 # 5.625*(1/64) per step, 4096 steps is 360°
direction = False # 시계방향일 때 True 시계반대방향일 때 False
# defining stepper motor sequence (found in documentation http://www.4tronix.co.uk/arduino/Stepper-Motors.php)
step_sequence = [[1,0,0,1],
[1,0,0,0],
[1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0],
[0,1,1,0],
[0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1],
[0,0,0,1]]
# setting up
GPIO.setmode( GPIO.BCM )
GPIO.setup( in1, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( in2, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( in3, GPIO.OUT )
GPIO.setup( in4, GPIO.OUT )
# initializing
GPIO.output( in1, GPIO.LOW )
GPIO.output( in2, GPIO.LOW )
GPIO.output( in3, GPIO.LOW )
GPIO.output( in4, GPIO.LOW )
motor_pins = [in1,in2,in3,in4]
motor_step_counter = 0
def cleanup():
GPIO.output( in1, GPIO.LOW )
GPIO.output( in2, GPIO.LOW )
GPIO.output( in3, GPIO.LOW )
GPIO.output( in4, GPIO.LOW )
GPIO.cleanup()
print("실시간으로 값 읽어오기")
print("----------------------------------")
while(True):
url = 'http://203.253.128.177:7579/Mobius/phone/data/la'
headers = {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'X-M2M-RI': '12345',
'X-M2M-Origin': 'SluN3OkDey-',
'Content-Type': 'application/vnd.onem2m-res+json; ty=4'
}
r = requests.get(url, headers = headers)
r.raise_for_status()
jr = r.json()
if(jr["m2m:cin"]["con"][-1]=="1"):
print("motor_working")
i = 0
for i in range(step_count):
for pin in range(0, len(motor_pins)):
GPIO.output( motor_pins[pin], step_sequence[motor_step_counter][pin] )
if direction==True:
motor_step_counter = (motor_step_counter - 1) % 8
elif direction==False:
motor_step_counter = (motor_step_counter + 1) % 8
else: # defensive programming
print( "uh oh... direction should *always* be either True or False" )
cleanup()
exit( 1 )
time.sleep( step_sleep )
else:
print(jr["m2m:cin"]["con"])Raspberry Pi로 서버에서 값 Post
#onem2m 리소스 생성하기 (cin)
import requests
url = "http://203.253.128.177:7579/Mobius/phone/data"
headers = {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'X-M2M-RI': '12345',
'X-M2M-Origin': 'SluN3OkDey-',
'Content-Type': 'application/vnd.onem2m-res+json; ty=4'
}
data = {
"m2m:cin": {
"con" : "test on raspberry"
}
}
r = requests.post(url, headers = headers, json = data)
try:
r.raise_for_status()
jr = r.json()
#가장 최근에 생긴 con 값 받아오기
print(jr['m2m:cin']['con'])
except Exception as exc:
print('There was a problem %s' %(exc))Get Post 활용
Get Post가 일어나야하는 IR센서 코드이다.
NS-IRPSM Post Get
#final
#모터가 구동되는 상태에서 IR이 Phone/count 값 만큼 약을 카운트했을 때 서버에 0을 올리는 코드
#서버에 0을 올림으로 써 추후게 모터를 중지시킬
#importing the library of RPi.GPIO
#importing the library of time
from http import server
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
import requests
sensor = 16
#시작과 동시에 Object detected를 하므로 default 값을 -1로 선언
count =-1
#declaring BCM pin 16 which is GPIO 23 of Raspberry Pi
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD)
#declaring the BCM mode of pins
GPIO.setup(sensor,GPIO.IN)
#set the behaviour of sensor as input
while True:
#서버에서 count 값을 Get
url_count_get = 'http://203.253.128.177:7579/Mobius/phone/count/la'
headers_count_get = {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'X-M2M-RI': '12345',
'X-M2M-Origin': 'SluN3OkDey-',
'Content-Type': 'application/vnd.onem2m-res+json; ty=4'
}
r_count_get = requests.get(url_count_get, headers = headers_count_get)
r_count_get.raise_for_status()
jr_count_get=r_count_get.json()
server_count = (int)(jr_count_get["m2m:cin"]["con"])
print("서버에서 읽어온 count의 값 : {}".format(server_count))
#initiated a infinite while loop
if GPIO.input(sensor):
#checking input on sensor
count+=1 #어플에서 보낸 알약투여 갯수랑 비교하기 위한 변수
if(server_count == count ): # 만약 알약 투여 갯수가 같다면
print("잘 들어왔습니다, 서버카운트 값 : {}, 알약이 나온 개수 : {}".format(server_count, count))
#*****************Post cin****************************
url = "http://203.253.128.177:7579/Mobius/phone/data"
#데이터에
headers = {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'X-M2M-RI': '12345',
'X-M2M-Origin': 'SluN3OkDey-',
'Content-Type': 'application/vnd.onem2m-res+json; ty=4'
}
#0의 값을 서버에 올려준다.
data = {
"m2m:cin": {
"con" : "0"
}
}
r = requests.post(url, headers = headers, json = data)
#*****************Post cin******************************
break
print("count : {}, Object detected".format(count))
while GPIO.input(sensor): #센서에 아무런 일이 없으면 이 루프에 빠진다.
#checking input on sensor again
time.sleep(0.01)구동
final라고 써있는 두 개의 코드를 동시에 실행시킨다.
이렇게 Post Get를 동시에 하여 어플에서 보내는 값하고 센서에서 보내는 값을
서버에서 처리하여 제품이 구동하게 된다.
구동 영상
추가적인 기능들(IOS어플 만들기 및 QR코드 인식으로 사용자 등록, 스피커로 알약 배출 완료시 알림 기능)은 SW파트에서 해결했다.
