Software Construction
Software Construction
- Detailed Design
• Internal design of individual components
• Design of logic and data structures - Coding
• Map component design to code
구성 요소 설계를 코드로 매핑 - Unit Testing
• Test individual components
개별 구성 요소가 올바르게 동작하는지 확인하는 단계
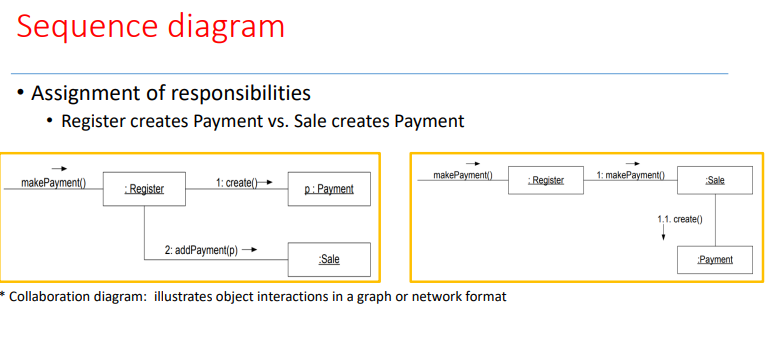
OO Design Model(Object-Oriented Design)
• sequence diagram
• design class diagram
Domain model vs. Design Model classes
- Design Class Diagram
- Software class
- Attributes
- Attribute type
- Methods
- Relationships
- Software class
Centralized vs. Decentralized control
-
Decentralized control structure is appropriate when:
- The operations have a strong connection
- The operations will always be performed in the same order
- You want to abstract or encapsulate behavior.
-
Centralized control is appropriate when:
- The operations can change order,
- New operations could be inserted
Design Principals
- How to achieve
• Easy to understand
• Low change impact
• Increased Reuse (decreased redundancy)
Modularity: High cohesion & Low coupling
시스템이나 컴퓨터 프로그램이 독립적으로 개발, 유지 관리 및 교체될 수 있는 개별 구성 요소로 구성되는 정도를 나타냅니다.
- degree to which a system or computer program is composed of discrete components such that a change to one component has minimal impact on other components [ISO/IEC 25010]
시스템이나 컴퓨터 프로그램이 이산적인 구성 요소들로 구성되어 있어, 한 구성 요소에 대한 변경이 다른 구성 요소들에 미치는 영향이 최소화된 정도 - property of a system that has been decomposed into a set of cohesive and loosely coupled modules [Booch1994]
시스템이 일련의 응집력 있고 느슨하게 결합된 모듈들의 집합으로 분해된 성질
Design Principles- Modularity
-
Modularity is the principle of keeping separate the various unrelated aspects of a system, so that each aspect can be studied in isolation (also called separation of concerns)
시스템의 여러 관련 없는 측면들을 분리하여 각 측면이 독립적으로 분석될 수 있도록 유지하는 설계 원칙입니다 -
If the principle is applied well, each resulting module will have a single purpose and will be relatively independent of the others
이 원칙이 잘 적용된다면, 각 모듈은 하나의 명확한 목적을 가지며 다른 모듈들과 비교적 독립적일 것입니다
• each module will be easy to understand and develop
각 모듈은 개발자가 쉽게 이해하고 개발할 수 있어야 합니다.
• easier to locate faults (because there are fewer suspect modules per fault)
모듈화된 시스템에서는 결함이 발생했을 때 적용 범위가 제한되어 있어, 문제가 발생한 모듈들을 신속하게 식별할 수 있습니다.
• Easier to change the system (because a change to one module affects relatively few other modules
모듈의 변경이 다른 모듈에 미치는 영향이 적기 때문에 시스템을 변경하거나 업데이트하기가 훨씬 용이합니다. -
To determine how well a design separates concerns, we use two concepts that measure module
independence: coupling and cohesion
Design Principles - Coupling
두 모듈 간의 상호 의존 정도를 나타내는 개념
• Two modules are tightly coupled when they depend a great deal on each other
• Loosely coupled modules have some dependence, but their interconnections are weak
• Uncoupled modules have no interconnections at all; they are completely unrelated
Design Principles - Cohesion
한 모듈 내의 요소들 간의 관련성 또는 의존도를 나타내는 개념입니다
• Cohesion refers to the dependence within and among a module’s internal elements
(e.g., data, functions, internal modules)
Design Pattern
-
A design pattern codifies design decisions and best practices for solving a particular design problem according to design principles
-
Façade pattern
복잡한 시스템의 서브시스템을 감싸고 이를 더 쉽게 사용할 수 있는 단순화된 인터페이스를 제공하는 패턴- Provide a unified interface to a set of interfaces in a subsystem.
스템의 복잡한 부분을 단일화된 인터페이스로 감싸고, 클라이언트에게 이를 제공합니다. - Facade defines a higher-level interface that makes the subsystem easier to use.
서브시스템의 내부 복잡성을 숨기고, 오직 필요한 기능만 노출시킴으로써 단순화된 접근을 제공
- Provide a unified interface to a set of interfaces in a subsystem.
-
Motivation: Structuring a system into subsystems helps reduce complexity.
복잡한 시스템을 여러 서브시스템으로 구분하고 각각을 독립적으로 관리할 수 있게 합니다.
A common design goal is to minimize the communication and dependencies between subsystems
직접 여러 서브시스템과 상호작용하는 것보다 퍼사드를 통해 간접적으로 상호작용함으로써 서브시스템 간의 의존성을 줄입니다.
Control Flow Testing
프로그램을 통해 가능한 모든 경로가 적어도 한 번 실행되는지 확인하기 위해 소프트웨어 테스트에 사용되는 기술
• 프로그램 코드상의 수행경로(execution path)를 정의하고, 그 경로를 cover하는 테스트케이스 개발/수행.
• Flow Graph상에서 Node는 프로그램 문장(statement), Edge는 제어의 흐름을 의미함.
노드의 예로는 할당문, 조건문(if-else 등), 루프, 메서드 호출, return 문 등이 있습니다.
에지의 예로는 함수 시작에서 첫 번째 문으로, 블록 내 한 문에서 다음 문으로, 조건 분기(예: if 문)에서 다른 분기(true 또는 false)로의 전환이 포함됩니다.
Statement Coverage
모든 실행 가능한 문장이 적어도 한 번 실행되었는지를 보장하는 기본적인 메트릭
• 프로그램 내 모든 executable statement가 최소한 한번 수행됨
• 코드 커버리지 중 가장 약한 커버리지 기준임
Decision Coverage
프로그램 내의 모든 결정문(Decision statement)이 모든 가능한 결과(예를 들어, true와 false)를 적어도 한 번씩 실행하도록 보장하는 것을 목표
• 프로그램내 모든 Decision statement가 모든 가능한 결과 (true 와 false)를 수행하도록 테스팅
• Decision : if – else, switch, case, loop (for, while, until)
• 여러 개의 condition으로 구성된 복잡한 Decision은 고려되지 않음.
Condition Coverage
프로그램 내의 각 조건(condition)이 모든 가능한 결과(예를 들어, true와 false)를 적어도 한 번씩 실행하도록 보장하는 것을 목표로 합니다.
• Decision내의 각 condition이 모든 가능한 결과 (true와 false)를 수행하도록 테스팅
• Statement coverage도 만족 못할 수 있음.
Condition/Decision Coverage (C/DC)
• Condition 및 Decision 별로 가능한 결과 (true 또는 false)를 최소한 한번 수행하도록 테스팅
Multiple Condition Coverage (MCC)
• Decision 내에서 Condition 결과의 모든 가능한 조합을 최소 한번 테스트
Modified Condition/Decision Coverage (MC/DC)
• Condition/Decision Coverage를 보완한 것
• Condition 및 Decision이 모든 가능한 결과 (true와 false)를 수행하면서, 각 condition이 decision의 결과에 독립적으로 영향 주는 경우를 테스팅 함
