그래프의 특정 노드에서 출발하여 다른 노드까지의 최단 경로를 구하는 단일 경로 알고리즘
가중치 그래프에서 간선의 가중치 합이 최소가 되도록 하는 것이 목적
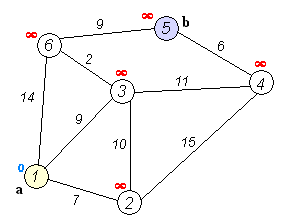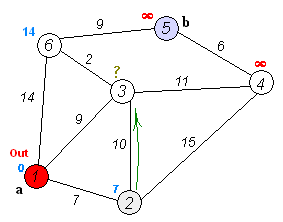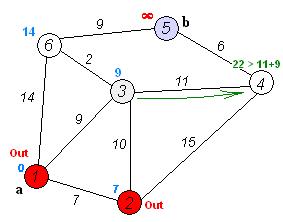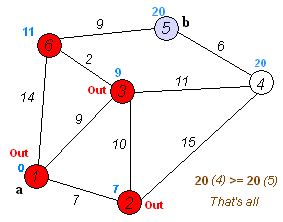
생각한 로직
- 우선순위 큐를 사용한다.
- 가장 짧은 거리를 가진 노드 정보를 꺼내게 된다.
- 거리 저장 배열을 사용한다. (최종 리턴이 될 정보를 저장)
- HashMap을 사용하여 하나의 노드(key)에서 갈 수 있는 Edge(노드와 가중치)(ArrayList)를 그래프로 저장한다.
- 우선순위 큐에서 맨 앞에 있는 값을 poll()하고 현재 값과 갈 수 있는 값들을 비교하여 현재 값보다 작으면 거리 저장 배열에 저장한다.
코드 구현 (Java)
package algorithms.search;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class DijkstraPath {
private static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
String vertex;
Integer distance;
public Edge(String vertex, Integer distance) {
this.vertex = vertex;
this.distance = distance;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Edge{" +
"vertex='" + vertex + '\'' +
", distance=" + distance +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge edge) {
return this.distance - edge.distance;
}
}
public HashMap<String, Integer> search(HashMap<String, ArrayList<Edge>> graph, String start) {
HashMap<String, Integer> distances = new HashMap<>();
Edge edgeNode;
Integer currentDistance;
String currentNode;
ArrayList<Edge> nodeList;
Edge adjacentNode;
String adjacent;
Integer weight;
Integer distance;
for (String key : graph.keySet()) {
distances.put(key, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
distances.put(start, 0);
PriorityQueue<Edge> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
priorityQueue.add(new Edge(start, 0));
while (priorityQueue.size() > 0) {
edgeNode = priorityQueue.poll();
currentDistance = edgeNode.distance;
currentNode = edgeNode.vertex;
if (distances.get(currentNode) < currentDistance) {
continue;
}
nodeList = graph.get(currentNode);
for (Edge node : nodeList) {
adjacent = node.vertex;
weight = node.distance;
distance = weight + currentDistance;
if (distance < distances.get(adjacent)) {
distances.put(adjacent, distance);
priorityQueue.add(new Edge(adjacent, distance));
}
}
}
return distances;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, ArrayList<Edge>> graph = new HashMap<>();
graph.put("A", new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(new Edge("B", 8), new Edge("C", 1), new Edge("D", 2))));
graph.put("B", new ArrayList<>());
graph.put("C", new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(new Edge("B", 5), new Edge("D", 2))));
graph.put("D", new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(new Edge("E", 3), new Edge("F", 5))));
graph.put("E", new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(new Edge("F", 1))));
graph.put("F", new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(new Edge("A", 5))));
System.out.println(graph);
DijkstraPath dijkstraPath = new DijkstraPath();
System.out.println(dijkstraPath.search(graph, "A"));
}
}고민한 부분
- 머리로 하나하나 생각하다가 터질 뻔 했기 때문에 그림을 그려가면서,
- 글로 써내려가면서 직접 반복되는 패턴을 파악해야 한다.
- 무조건 그림과 글로 파악하기
