쓰레드 상태
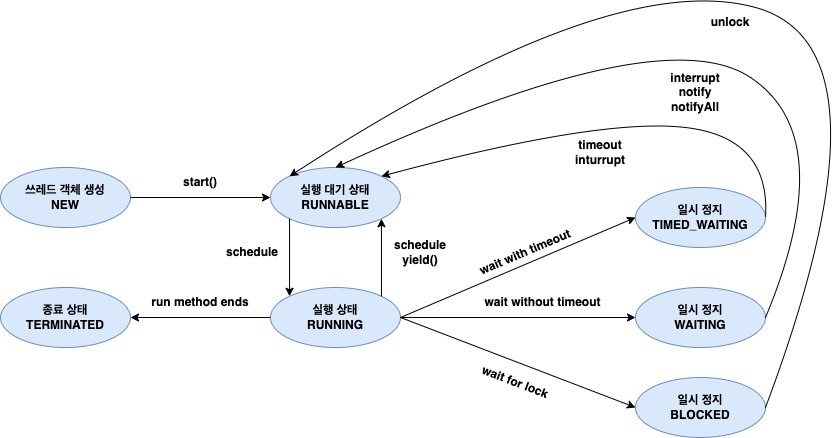
NEW
- 쓰레드 객체가 생성되고 start를 호출하지 않은 상태
RUNNABLE
- 쓰레드가 실행 중이거나 실행될 준비가 된 상태
- NEW 상태에서 start 메소드를 호출하면 이 상태가 된다.
WAITING
- 다른 쓰레드가 작업을 끝낼 때까지 기다리는 상태
- 시간을 지정하지 않은 wait, join 등을 호출하면 이 상태가 된다.
TIMED_WIATING
- 쓰레드가 지정된 대기 시간동안 대기하는 상태
- sleep이나 타임아웃이 설정된 wait, join 등을 호출하면 이 상태가 된다.
BLOCKED
- 사용하고자 하는 객체의 락이 풀릴 때까지 기다리는 상태이다.
TERMINATED
- 쓰레드의 실행이 완료된 상태이다.
- 정상적으로 종료하면 이 상태가 된다.
- 예외가 발생하여 종료되도 이 상태가 된다.
쓰레드의 상태를 알기 위해서는 getState 메소드를 사용하면 된다.
public Thread.State getState()만약 Thread 클래스의 currentThread로 현재 쓰레드를 얻은 다음 get
Thread.currentThread().getState();예시
import static java.lang.Thread.*;
public class Main {
private static Thread myThread;
private static Thread stateThread;
public static void main(String[] args) {
stateThread = new Thread(() -> {
while(true) {
State state = myThread.getState();
System.out.println(state);
if (state == State.NEW)
myThread.start();
if (state == State.WAITING)
myThread.interrupt();
if (state == State.TERMINATED) {
break;
}
try {
sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
myThread = new TestThread(stateThread);
stateThread.start();
}
static class TestThread extends Thread {
private Thread target;
public TestThread(Thread target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0; i <= 2000000000; i++);
for(int i = 0; i <= 2000000000; i++);
try {
sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
target.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
for(int i = 0; i <= 2000000000; i++);
for(int i = 0; i <= 2000000000; i++);
}
}
}
}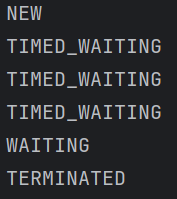
- 처음에 myThread가 생성됐을 때는 New 상태
- myThread의 run에서 sleep을 호출하여 TIMED_WAITING 상태가 된다.
- 2000ms가 지나고 myThread가 join을 통해 stateThread가 끝나길 기다리며 WAITING 상태가 된다.
- stateThread는 myThread가 WAITING 상태이니 interrupt로 종료 요청을 보낸다.
- myThread는 대기 상태에서 interrupt 요청이 들어오면서 InterruptException을 발생시키고 종료되며 TERMINATED가 된다.
쓰레드 제어 메소드
join
- 어떤 쓰레드의 실행이 완료될때까지 join을 호출한 쓰레드를 진행하지 않는다.
- 예를 들어 main 쓰레드에서 thread1.join을 하면 main 쓰레드는 thread1이 완료될 때까지 진행되지 않는다.
- InterruptedException을 발생시킬 수 있다.
- 멀티 쓰레딩 환경에서 OS는 실행 순서를 보장하지 않는다. join은 이런 환경에서 쓰레드의 실행 순서 보장을 위해 존재한다.
- 파라미터로 타임아웃 시간을 넣어줘 무한정 대기를 방지할 수도 있다.
예시
- 전처리 작업을 하는 쓰레드 3개 후처리 작업을 하는 쓰레드 2개가 있을 때
- 후처리 작업은 반드시 전처리 작업이 끝난 후 시작되어야 한다.
- 이를 위해서 아래와 같이 join을 이용해서 전처리 작업들이 모두 끝날 때까지 기다려야 한다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new CustomThread(1, 4000));
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new CustomThread(2, 4000));
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new CustomThread(3, 2000));
Thread thread4 = new Thread(new CustomThread(4, 3000));
Thread thread5 = new Thread(new CustomThread(5, 10000));
thread5.start();
thread3.start();
thread1.start();
thread5.join();
thread3.join();
thread1.join();
thread2.start();
thread4.start();
}
public static class CustomThread implements Runnable {
private int number;
private int millis;
public CustomThread(int number, int millis) {
this.number = number;
this.millis = millis;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(millis);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(number);
}
}
}
- 실행 결과를 보면 전처리 작업인 1, 3, 5가 모두 끝난 후 2, 4가 실행되는 것을 볼 수 있다.
- main에는 2, 4에 대한 조인이 없어 2, 4가 완료되기 전에 끝난다. 하지만 2, 4가 출력되는 것을 볼 수 있다
- 이는 쓰레드들이 데몬 쓰레드가 아닌 사용자 쓰레드이기 때문에 그렇다.
- 메인 쓰레드는 2, 4가 끝나기 전에 끝나지만 프로그램 종료 즉 JVM이 종료되는 시점은 모든 사용자 쓰레드가 종료되 때이므로 쓰레드 2, 4는 계속 돌아간다.
interrupt
- 작업을 멈추라고 요청한다.
- 쓰레드를 강제로 종료하지는 못한다.
- 즉 쓰레드를 바로 종료시키지 않고 쓰레드 인터럽트 플래그를 true로 만든다.
interrupt 호출 시점 또는 이후 쓰레드가 일시정지 상태(= 플래그가 true)가 되면 InterruptedException을 발생시켜 쓰레드를 종료시킨다.
- 쓰레드가 일시정지가 되지 않으면 interrupt의 호출은 의미가 없다.
- 따라서 쓰레드가 runnable 상태일 때 interrupt를 호출해도 예외가 발생하지 않고 쓰레드가 멈추지 않는다.
InterruptedException
InterruptedException은 다음과 같은 상황에서 발생한다.
- 대기 상태(WAITING 또는 TIMED_WAITING)에서 어떤 쓰레드가 interrupt를 호출해 플래그가 true가 되는 경우
- 어떤 쓰레드가 interrupt를 호출해 쓰레드의 플래그 true인 상태에서 작업 스레드에 제어권이 넘어오고 sleep 등의 메서드가 호출되며 대기상태로 변할 때
InterruptedException이 발생하면
쓰레드 인터럽트 플래그가 자동으로 false가 된다.
- 이 예외는 sleep, wait, join 등의 메소드가 발생시킬 수 있다.
- 이런 메소드를 사용하지 않았는데 InterruptedException을 잡으려고 하면 catch 문에 도달할 수 없으므로 컴파일 에러가 뜬다.
인터럽트 상태 확인 메소드
isInterrupted: 쓰레드 인터럽트 플래그를 변화시키지 않고 확인만 한다.interrupted: 인터럽트 상태를 반환한 뒤 false로 만든다.
예시 1
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TestThread thread = new TestThread();
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(3000);
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("isInterrupted() : "+ thread.isInterrupted());
}
static class TestThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
int count = 10;
while (count != 0){
System.out.println(count--);
for (long i = 0 ; i < 2500000000L; i++);
}
System.out.println("종료");
}
}
}출력 결과를 보면
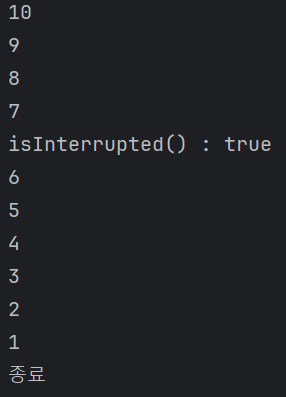
인터럽트가 호출됐어도 계속 쓰레드가 진행되는 것을 볼 수 있다. 이는 플래그는 interrupt를 호출하며 true로 변하였지만 쓰레드가 대기상태에 들어가지 않아서 그렇다.
예시 2
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TestThread thread = new TestThread();
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(400);
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("isInterrupted() : "+ thread.isInterrupted());
}
static class TestThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
int count = 10;
try{
while (count != 0){
System.out.println(count--);
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}catch (InterruptedException e){
System.out.println("종료");
}
}
}
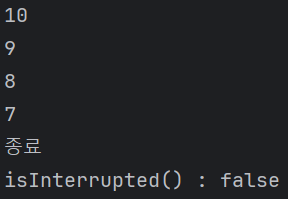
}이번에는 대기를 for문을 통해서 하지 않고 sleep을 이용해서 했다. 따라서 쓰레드가 대기 상태로 들어가고 아래와 같이 작업을 모두 끝내기 전에 InterruptedException이 발생해 숫자를 모두 출력하지 못한다.
yield
- 다른 쓰레드에게 실행을 양보하고 자신은 실행 대기 상태로 간다.
- 쓰레드의 작업은 반복 실행을 위해 반복문을 실행하는 경우가 많다.
- 의미 없는 반복을 하는 경우 자원이 낭비될 수 있다. 이런 경우 yield로 다른 쓰레드가 실행되게 할 수 있다.
- yield를 호출한다고 쓰레드가 항상 양보한다는 것은 아니다. 스케쥴러에 의해 언제드 다시 선택되어 돌아갈 수 있다.
예시
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadA threadA = new ThreadA();
ThreadB threadB = new ThreadB();
threadA.start();
threadB.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
threadA.work = false;
System.out.println("--------------------양보 시작 ----------------------");
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("--------------------양보 끝 ----------------------");
threadA.work = true;
Thread.sleep(2000);
threadA.stop = true;
threadB.stop = true;
}
public static class ThreadA extends Thread {
public boolean stop = false;
public boolean work = true;
public void run() {
while (!stop) {
if (work) {
System.out.println("ThreadA 작업");
for (long i = 0; i < 1500000000L; i++);
} else {
Thread.yield();
}
}
System.out.println("ThreadA 종료");
}
}
public static class ThreadB extends Thread {
public boolean stop = false;
public boolean work = true;
public void run() {
while (!stop) {
if (work) {
System.out.println("ThreadB 작업");
for (long i = 0; i < 1500000000L; i++);
} else {
Thread.yield();
}
}
System.out.println("ThreadB 종료");
}
}
}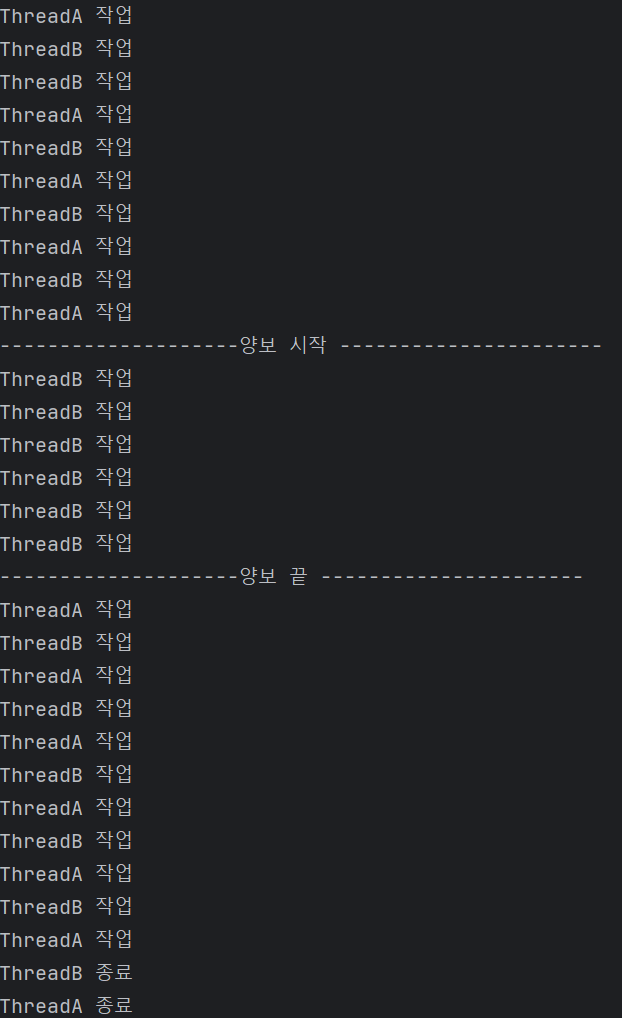
- stop은 작업 종료 플래그 work는 작업 플래그이다.
- threadA의 작업 플래그가 false가 되면서 자신이 실행되기 보다는 yield를 통해 threadB에게 양보하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
- 실행 결과를 봐도 양보를 시작한 후 threadB만 작업하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
