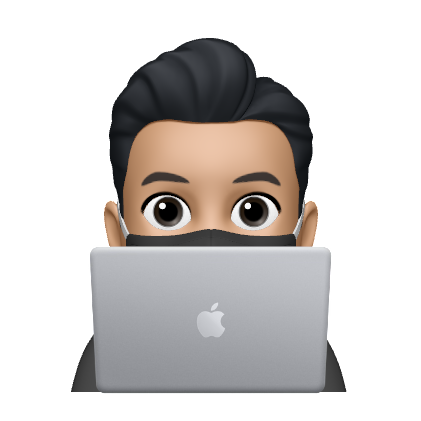
기능 분해
- 기능은 하위 기능으로 분해
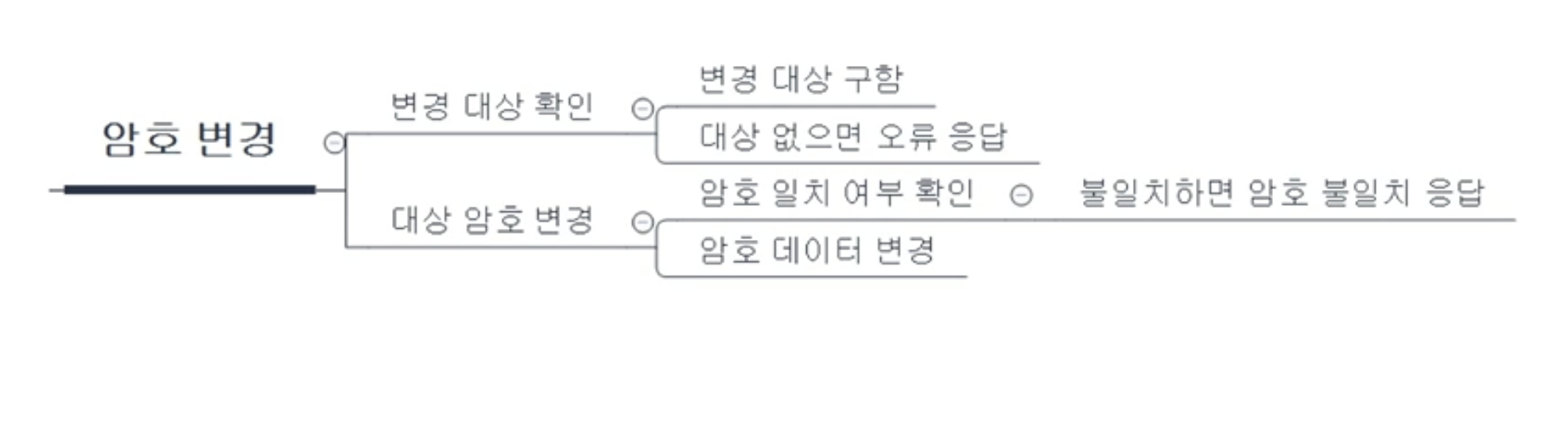
위와 같이 암호 변경이라는 기능은 여러 하위 기능으로 분해될 수 있다.
기능을 누가 제공할 것인가?
- 기능은 곧 책임
- 분리한 각 기능을 알맞게 분배
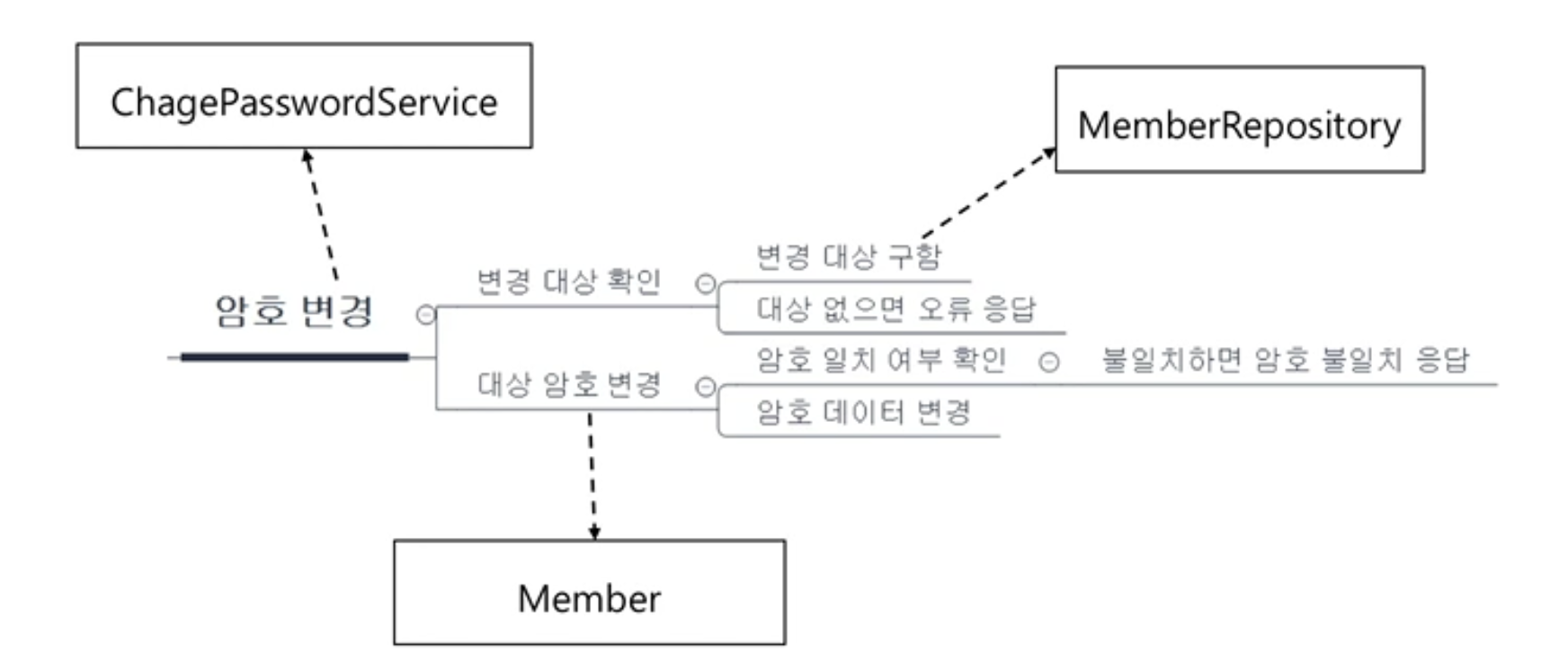
이처럼 각각의 하위 기능들을 책임을 가질 클래스에 알맞게 분배해야한다.
하위 기능 사용
public class ChangePasswordService {
public Result changePassword(String id, String oldPw, String newPw) {
Member mem = memeberRepository.findOne(id);
if(mem == null){
return Result.NO_MEMBER;
}
try {
mem.changePassword(oldPw, newPw);
return Result.SUCCESS;
} catch(BadPasswordException ex){
return Result.BAD_PASSWORD;
}
}
} 위 코드를 보면, MemebeRepository, Member가 각각의 기능을 제공하고 있음
큰 클래스, 큰 메소드
- 클래스나 메서드가 커지면 절차 지향의 문제가 발생
- 큰 클래스 → 많은 필드를 많은 메서드가 공유
- 큰 메서드 → 많은 변수를 많은 코드가 공유
- 여러 기능이 한 클래스/메서드에 섞여 있을 가능성이 높다
- 책임에 따라 알맞게 코드를 분리할 필요가 있음
몇가지 책임 분배/분리 방법
패턴 적용
- 전형적인 역할 분리
- 간단한 웹
- 컨트롤러, 서비스, DAO
- 복잡한 도메인
- 엔티티, 밸류, 리포지토리, 도메인 서비스
- AOP
- Aspect ( 공통 기능 )
- GoF
- 팩토리, 빌더, 전략, 템플릿 메서드, 프록시/데코레이터 등..
- 간단한 웹
계산 기능 분리
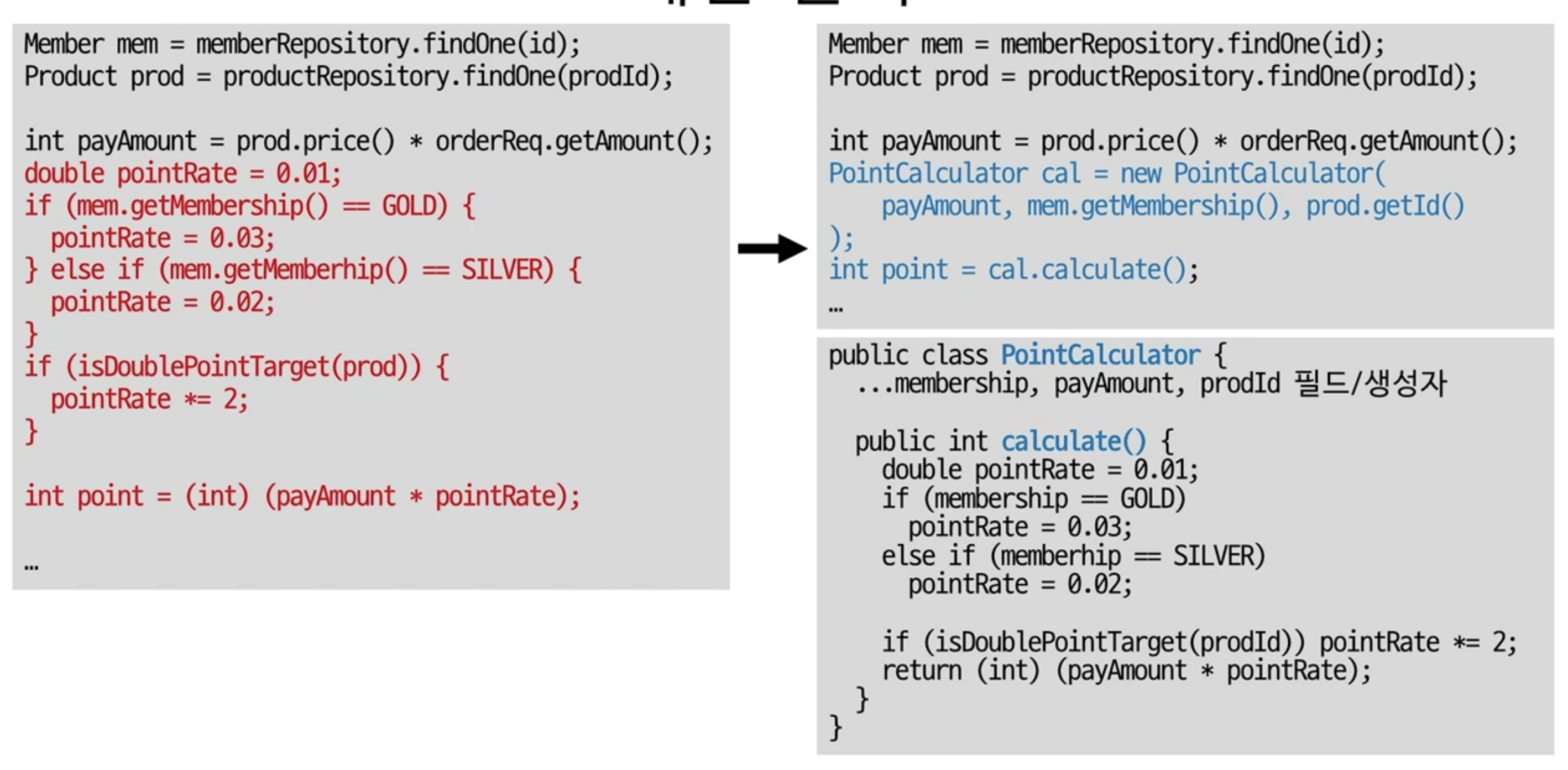
위와 같이 계산을 하는 부분을 새로운 클래스로 분리하여 구현하는 방법
연동 분리
- 네트워크, 메시징, 파일 등 연동 처리 코드를 분리

네트워크 처리와 같이 외부에 연동하는 부분을 별도의 클래스로 분리
조건 분기는 추상화
- 연속적인 if-else는 추상화 고민

추상화에 관련된 포스트에서 언급했던 것 처럼, 여러개의 조건 분기가 걸려있을 경우 추상화를 통해 해결
주의 : 의도가 잘 드러나는 이름을 사용
- 예 : HTTP로 추천 데이터를 읽어오는 기능을 분리시
- RecommendService > HttpService
- 위와 같이 의도를 잘 드러내는 이름을 사용
역할 분리와 테스트
- 역할 분리가 잘되면 테스트도 용이해짐

왼쪽의 코드처럼 작성하게 되면, repository들과 연동하여 테스트를 진행해야함.
하지만, 오른쪽처럼 분리하게 된다면 PointCalculator만 따로 테스트를 할 수 있음.
분리 연습
분리 연습 1
public class CashClient {
private SecretKeySpec keySpec;
private IvParamterSpec ivSpec;
private Res post(Req req){
String reqBody = toJson(req);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(DEFAULT_TRANSFORM);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, keySpec, ivSpec);
String encReqBody = new String(Base64.getEncoder().encode(chipher.doFinal(reqBody)));
ResponseEntity<String> responseEntity = restTemplate.postForEntity(api, encReqBody, String.class);
String encRespBody = responseEntity.getBody();
Cipher cipher2 = Cipher.getInstance(DEFAULT_TRANSFORM);
cipher2.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, keySpec, ivSpec);
String respBody = new String(chipher2.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(encRespBody)));
return jsonToObj(respBody);
}
}위 코드에서는 Cipher를 통한 암호화 및 복호화 ( 계산 기능 ) 을 분리할 수 있다.
분리하면 아래와 같다.
public class CashClient {
private Cryptor cryptor;
private Res post(Req req){
String reqBody = toJson(req);
String encReqBody = cryptor.encrypt(reqBody);
ResponseEntity<String> responseEntity = restTemplate.postForEntity(api, encReqBody, String.class);
String encRespBody = responseEntity.getBody();
String respBody = cryptor.decrypt(encRespBody);
return jsonToObj(respBody);
}
}
public class Cryptor {
private SecretKeySpec keySpec;
private IvParamterSpec ivSpec;
public String encrypt(String plain){
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(DEFAULT_TRANSFORM);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, keySpec, ivSpec);
return new String(Base64.getEncoder().encode(chipher.doFinal(reqBody)));
}
public String decrypt(String encrypted){
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(DEFAULT_TRANSFORM);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, keySpec, ivSpec);
return new String(chipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(encRespBody)));
}
}분리 연습 2
public class Rental {
private Movie movie;
private int daysRented;
public int getFrequentRenterPoints(){
if(movie.getPriceCode() == Movie.NEW_RELEASE && daysRented > 1 ){
return 2;
}
return 1;
}
}
public class Movie {
public static int REGULAR = 0;
public static int NEW_RELEASE = 1;
private int priceCode;
public int getPriceCode(){
return priceCode;
}
}위 코드의 조건 분기를 추상화를 통해 분리하면 아래와 같다.
public class Rental {
private Movie movie;
private int daysRented;
public int getFrequentRenterPoints(){
return movie.getFrequentRenterPoints(daysRented);
}
}
public abstract class Movie {
public abstract int FrequentRenterPoints(int daysRented);
}
public class NewRelaseMovie extends Movie {
public int FrequentRenterPoints(int daysRented){
return daysRented > 1 ? 2 : 1;
}
}
public class RegularMovie extends Movie {
public int FrequentRenterPoints(int daysRented){
return 1;
}
}위와 같이 Movie를 추상화하여 하위 클래스를 만들어 분리를 하였다.
분리 연습 3
- 기능 : 회원 가입
- 사용자는 이메일, 이름, 암호 입력
- 모두 필수
- 암호가 다음 규칙을 통과하지 않았다면 다시 입력
- 규칙1, 규칙2, 규칙3 ...
- 같은 이메일로 가입한 회원이 있으면 다시 입력
- 이메일 인증을 위한 메일 발송
- 유효성 검증을 위해 암호화된 토큰을 사용
- 회원 가입 완료
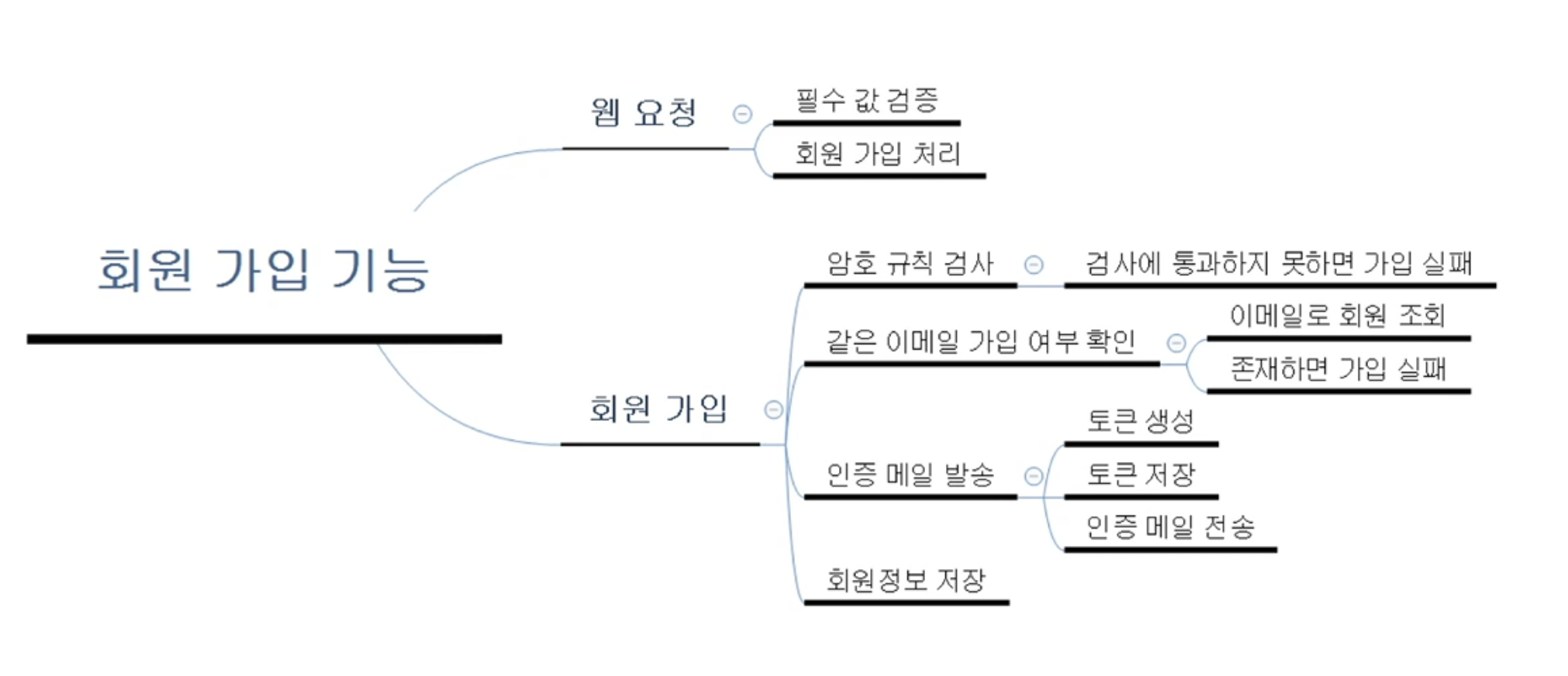
전체 회원 가입기능을 웹 요청과 회원 가입으로 분리하고, 각각의 기능들을 더 작은 하위 기능들로 분리하였음.
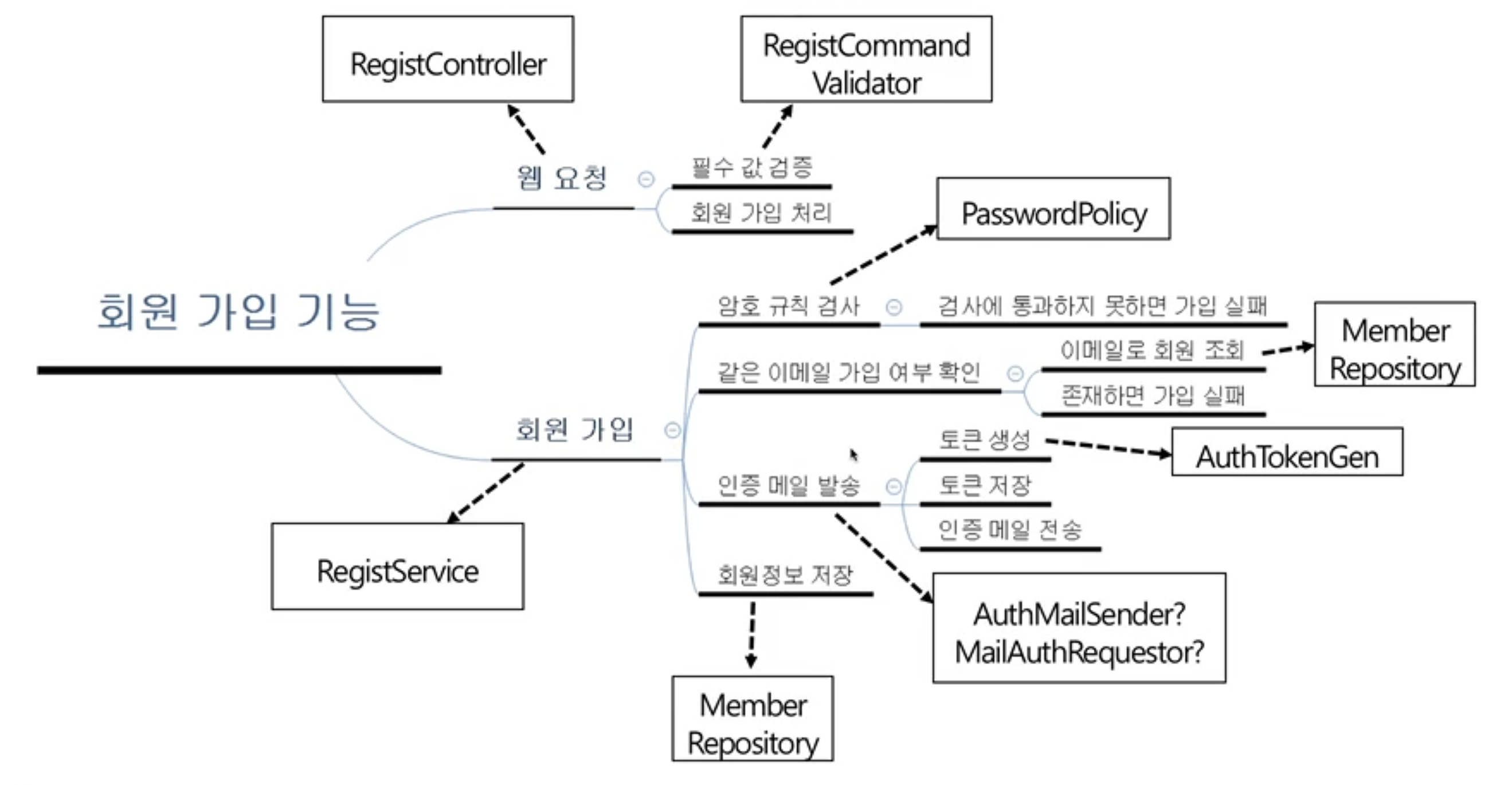
실제로 기능을 분리하여 설계를 하면 위와 같다.
