컨버터, 포맷터 - ConversionService
Spring
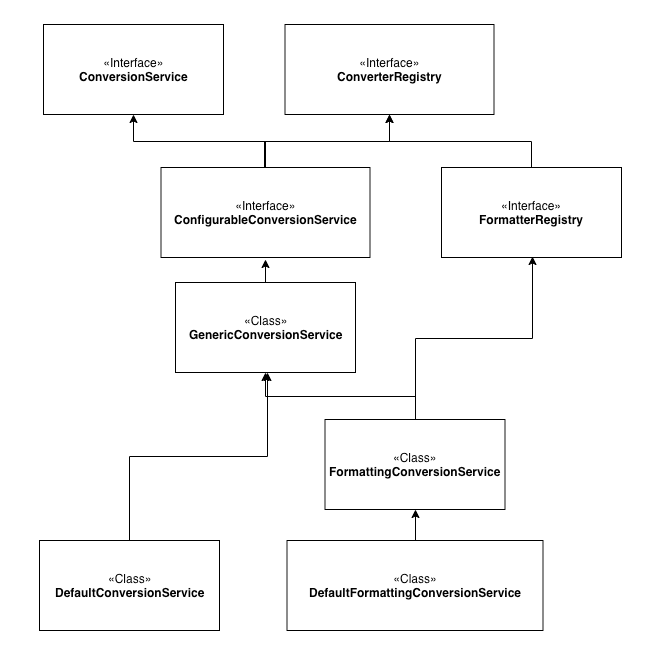
ConversionService
package org.springframework.core.convert;
public interface ConversionService {
// 컨버팅 가능한지 여부
boolean canConvert(@Nullable Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType);
boolean canConvert(@Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
// 컨버팅 기능
@Nullable
<T> T convert(@Nullable Object source, Class<T> targetType);
@Nullable
Object convert(@Nullable Object source, @Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
}/////////////////////////////
// Converter 구현체 직접 사용
MyCustomConverter converter = new MyCustomConverter();
converter.convert(10);
/////////////////////////////
// ConversionService 사용
DefaultConversionService conversionService = new DefaultConversionService();
// ConversionService에 등록
conversionService.addConverter(new MyCustomConverter());
// ConversionService를 통해 사용
conversionService.convert(10, Integer.class);컨버터을 상속하여 구현하더라도 컨트롤러에서 new Converter로 선언하여 사용하면 메서드로 빼서 구현한 것과 차이가 없다. ConversionService는 컨버터의 구현체를 등록하고 사용하는 것을 분리하여 클래스간의 의존성을 낮출 수 있게 도와준다.
FormattingConversionService
package org.springframework.format.support;
public class FormattingConversionService extends GenericConversionService
implements FormatterRegistry, EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
// ...
@Override
public void addPrinter(
Printer<?> printer
) { ... }
@Override
public void addParser(
Parser<?> parser
) { ... }
@Override
public void addFormatter(
Formatter<?> formatter
) { ... }
@Override
public void addFormatterForFieldType(
Class<?> fieldType,
Formatter<?> formatter
) { ... }
@Override
public void addFormatterForFieldType(
Class<?> fieldType,
Printer<?> printer,
Parser<?> parser
) { ... }
// ...
}/////////////////////////////
// Converter 구현체 직접 사용
MyCustomConverter converter = new MyCustomConverter();
converter.convert(10);
// Formatter 구현체 직접 사용
MyCustomFormatter formatter = new MyCustomFormatter();
formatter.print(10, Locale.KOREA);
/////////////////////////////
// FormattingConversionService 사용
DefaultFormattingConversionService service = new DefaultFormattingConversionService();
// FormattingConversionService에 등록
service.addConverter(new MyCustomConverter());
service.addFormatter(new MyCustomFormatter());
// FormattingConversionService를 통해 사용
service.convert(10, Integer.class);ConversionService는 포맷터를 등록할 수 없다. 그래서 스프링은 ConversionService와 FormatterRegistry를 상속하여 확장한 FormattingConversionService를 제공한다. 이 클래스를 통해 컨버터를 등록하면 어댑터 패턴을 통해 포맷터가 컨버터처럼 동작하도록 지원한다.
WebMvcConfigurer.addFormatters
@Configuration
public class ConverterConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addFormatters(
FormatterRegistry registry
) {
// 컨버터 등록
registry.addConverter(new MyCustomConverter());
// 포맷터 등록
registry.addFormatter(new MyCustomFormatter());
}
}스프링에서 자신이 만든 컨버터와 포맷터를 등록하기 위해선 WebMvcConfigurer 인터페이스의 addFormatters 메서드를 이용해 등록하면 된다. 이렇게 하면 자신이 만든 컨버터와 포맷터를 전역적으로 사용할 수 있게 된다.
스프링에서는 DefaultFormattingConversionService를 상속한 WebConversionService를 기본으로 사용하며, 이는 @RequestParam, @ModelAttribute가 붙은 Argument에 대해서 변환하는 작업을 진행한다.
Thymeleaf
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>${ipPort}: <span th:text="${ipPort}"></span></li>
<li>${{ipPort}}: <span th:text="${{ipPort}}"></span></li>
</ul>
<form th:method="post" th:object="${form}">
th:field <input th:field="*{ipPort}" type="text">
</form>
</body>
</html>또한, Thymeleaf에서도 해당 컨버터를 직접 사용할 수 있도록 지원하는데, ${{...}} 을 사용하여 model.attribute의 변수를 불러오면 그에 맞는 컨버터(Object → String)를 찾아 자동으로 실행하게 된다.
${...}- toString 호출
${{...}}- ConversionService 호출
th:field="${...}"th:field로 생성되는th:value의 경우 ConversionService 호출
HttpMessageConverter, ConversionService
둘 다 클라이언트에서 오는 요청을 객체로 변환해주는 역할을 가지고 있어서 오해하기 쉬운데, 엄연히 둘은 분리되어있다. 사용처가 다르고 처리되는 구현체도 다르다.
ConversionService
- @PathVariable, @RequestParam, @ModelAttribute, 뷰 템플릿을 통해 전달되는 데이터를 변환
- Converter의 구현체를 통해 처리된다.
HttpMessageConverter
- @RequestBody를 통해 전달되는 데이터를 변환
- 기본 설정으로 JSON 데이터를 처리할 때는 Jackson 라이브러리를 통해 처리된다.
- JSON 결과로 만들어지는 숫자나 날짜의 포맷을 변경하고 싶다면 해당 라이브러리가 제공하는 설정을 통해서 포맷을 지정해야 한다.
- 즉, HttpMessageConverter에는 ConversionService가 적용되지 않는다.
