백준에 신기한 시스템이 들어왔다.
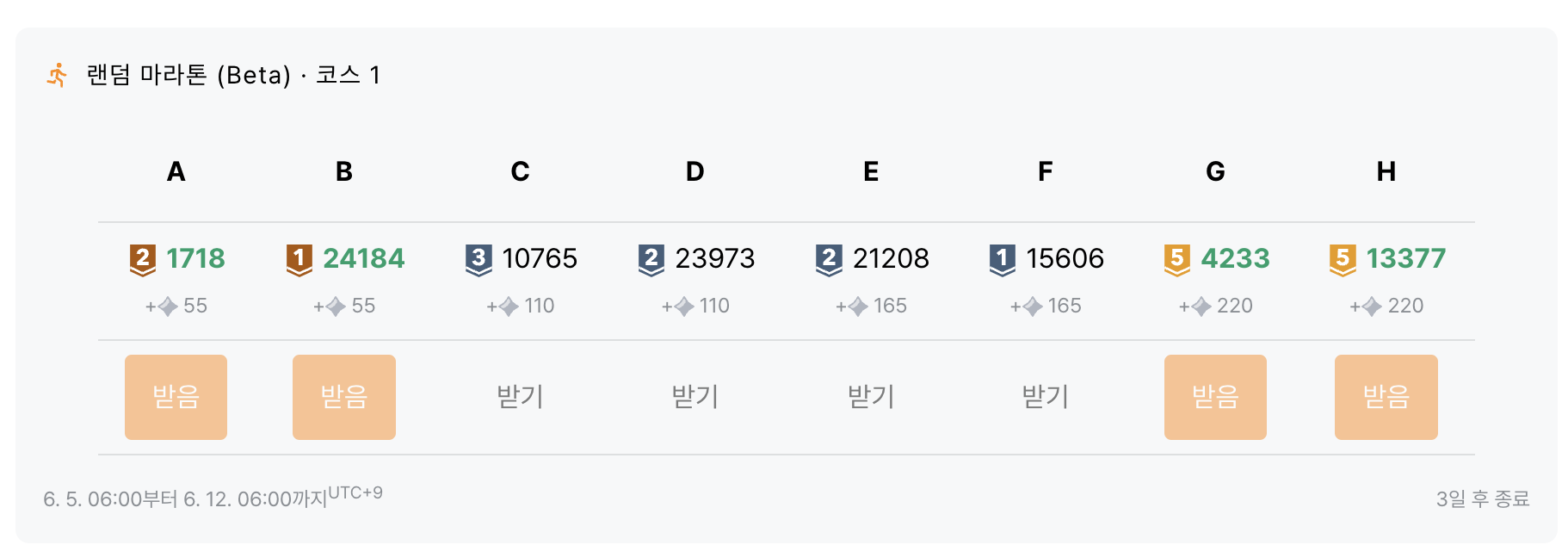
바로 마라톤이라는 시스템인데, 1주일마다 랜덤 8문제를 내주고 문제풀때마다 별가루/업적을 쌓는 시스템이다. 동기부여해주는거를 생각하면 정말 좋은시스템이다.
그래서 이번 글에 왜 이런 말을 하냐고 하면, 저 마라톤 시스템은 말 그대로 문제를 '랜덤'으로 뽑아주기 때문에 다양한 분야의 문제를 풀 수 있다는 것이다. 평소에 hash쪽은 생소해서 안풀었는데 해보니까 생각보다 간단하고 효과적인 방법이었다.
Dictionary
시간 제한 메모리 제한 제출 정답 맞힌 사람 정답 비율
2 초 512 MB 107 80 64 77.108%
문제
The isolated people of MacGuffin Island have a unique culture, and one of the most interesting things about them is their language. Their alphabet consists of the first 9 letters of the Roman alphabet (a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i). All of their words are exactly 9 letters long and use each of these 9 letters exactly once. They have a word for every possible permutation of these letters. In the library of their most sacred temple is a dictionary, and each word in their language has its own page. By coincidence they order their words exactly as they would be in ordered in English, so the word ‘abcdefghi’ is on the first page, and the word ‘ihgfedcba’ is on the last. The question is, given a list of random words from the MacGuffin language, can you say on which page of the MacGuffin dictionary each appears?
입력
The first line of the input file is a positive integer. This integer tells you how many words will follow. The upper limit for this number is 6000. Every subsequent line contains a single word from the MacGuffin language, so if the first number is 1000 there will be 1000 lines after it, each containing a single word.
출력
Each line of output will contain an integer. This integer should be the page number for the corresponding word.
오늘 적을 문제이다.
간단하게 문제를 요약하자면, abcdefghi 알파벳을 한번씩 써서 만든 모든 숫자들을(9!) 사전순으로 나열했을때, 특정 단어가 몇번째 단어인지 출력하라는 문제이다.
간단하다.
그냥 전체 리스트를 permutations를 활용해서 만들고, hash를 활용해서 찾아주면 된다.
from itertools import permutations
import sys
alphabet = ['a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i']
lst = list(permutations(alphabet,9))
for i in range(362880):
lst[i] = ''.join(lst[i])
check = {}
i = 1
for w in lst:
check[w] = i
i += 1
N = int(sys.stdin.readline())
for i in range(N):
string = sys.stdin.readline().strip()
print(check[string])코드도 정말 간단하지만 여기서 한가지 주의깊게 볼 부분이 있다.
check = {}
i = 1
for w in lst:
check[w] = i
i += 1
바로 이 코드인데, 이걸 넣고 안넣고의 차이는 상상이상으로 많이난다.
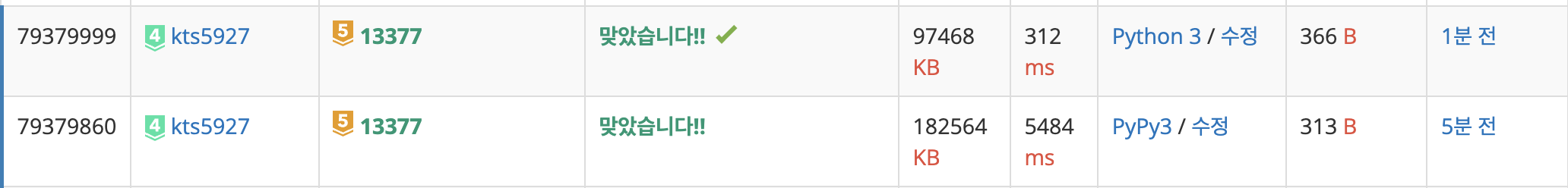
코드를 추가/제거 한 후에 실험해본 값인데
무려 공간복잡도는 2배, 시간복잡도는 거의 18배 차이가 난다.
그것은 index()를 활용해서 찾는 방식은 lst[0] ~ lst[len(lst)]를 한번씩 순회해서 찾는 방식이라 시간복잡도가 O(n)이 되기 때문이다.
하지만 hash를 활용해서 찾는 방식은 특정 key값의 value만 찾으면 되기 때문에 O(1)이 된다.
물론 hash도 충돌이 나면 안되겠지만 이번 문제에서는 key값을 지정해주기 때문에 그런 걱정은 안해도 된다.